|
1
|
Hayashida K, Sano M, Kamimura N, Yokota T,
Suzuki M, Maekawa Y, Kawamura A, Abe T, Ohta S, Fukuda K and Hori
S: H(2) gas improves functional outcome after cardiac arrest to an
extent comparable to therapeutic hypothermia in a rat model. J Am
Heart Assoc. 1:e0034592012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hayashi T, Yoshioka T, Hasegawa K,
Miyamura M, Mori T, Ukimura A, Matsumura Y and Ishizaka N:
Inhalation of hydrogen gas attenuates left ventricular remodeling
induced by intermittent hypoxia in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 301:H1062–H1069. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kato R, Nomura A, Sakamoto A, Yasuda Y,
Amatani K, Nagai S, Sen Y, Ijiri Y, Okada Y, Yamaguchi T, et al:
Hydrogen gas attenuates embryonic gene expression and prevents left
ventricular remodeling induced by intermittent hypoxia in
cardiomyopathic hamsters. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
307:H1626–H1633. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hayashida K, Sano M, Ohsawa I, Shinmura K,
Tamaki K, Kimura K, Endo J, Katayama T, Kawamura A, Kohsaka S, et
al: Inhalation of hydrogen gas reduces infarct size in the rat
model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 373:30–35. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lekic T, Manaenko A, Rolland W, Fathali N,
Peterson M, Tang J and Zhang JH: Protective effect of hydrogen gas
therapy after germinal matrix hemorrhage in neonatal rats. Acta
Neurochir Suppl. 111:237–241. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun Q, Kang Z, Cai J, Liu W, Liu Y, Zhang
JH, Denoble PJ, Tao H and Sun X: Hydrogen-rich saline protects
myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Exp Biol
Med (Maywood). 234:1212–1219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang Y, Sun Q, He B, Xiao J, Wang Z and
Sun X: Anti-inflammatory effect of hydrogen-rich saline in a rat
model of regional myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Int J
Cardiol. 148:91–95. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu YS and Zheng H: Chronic hydrogen-rich
saline treatment reduces oxidative stress and attenuates left
ventricular hypertrophy in spontaneous hypertensive rats. Mol Cell
Biochem. 365:233–242. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Xu J, Long Z, Wang C, Wang L, Sun
P, Li P and Wang T: Hydrogen (H2) Inhibits Isoproterenol-Induced
Cardiac Hypertrophy via Antioxidative pathways. Front Pharmacol.
7:3922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang YX, Xu JT, You XC, Wang C, Zhou KW,
Li P, Sun P, Wang L and Wang TH: Inhibitory effects of hydrogen on
proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via
Down-Regulation of mitogen/activated protein kinase and
Ezrin-Radixin-Moesin signaling pathways. Chin J Physiol. 59:46–55.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dai DF, Johnson SC, Villarin JJ, Chin MT,
Nieves-Cintrón M, Chen T, Marcinek DJ, Dorn GW II, Kang YJ, Prolla
TA, et al: Mitochondrial oxidative stress mediates angiotensin
II-induced cardiac hypertrophy and Galphaq overexpression-induced
heart failure. Circ Res. 108:837–846. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Porrello ER, D'Amore A, Curl CL, Allen AM,
Harrap SB, Thomas WG and Delbridge LM: Angiotensin II type 2
receptor antagonizes angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated
cardiomyocyte autophagy. Hypertension. 53:1032–1040. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu H, Tannous P, Johnstone JL, Kong Y,
Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Le V, Levine B, Rothermel BA and Hill
JA: Cardiac autophagy is a maladaptive response to hemodynamic
stress. J Clin Invest. 117:1782–1793. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nakai A, Yamaguchi O, Takeda T, Higuchi Y,
Hikoso S, Taniike M, Omiya S, Mizote I, Matsumura Y, Asahi M, et
al: The role of autophagy in cardiomyocytes in the basal state and
in response to hemodynamic stress. Nat Med. 13:619–624. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ohsumi Y: Historical landmarks of
autophagy research. Cell Res. 24:9–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Ohsumi Y: The
role of Atg proteins in autophagosome formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev
Biol. 27:107–132. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Levine B and Yuan J: Autophagy in cell
death: An innocent convict? J Clin Invest. 115:2679–2688. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: Molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev Cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lavandero S, Chiong M, Rothermel BA and
Hill JA: Autophagy in cardiovascular biology. J Clin Invest.
125:55–64. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jeong K, Kwon H, Min C and Pak Y:
Modulation of the caveolin-3 localization to caveolae and STAT3 to
mitochondria by catecholamine-induced cardiac hypertrophy in H9c2
cardiomyoblasts. Exp Mol Med. 41:226–235. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tshori S, Gilon D, Beeri R, Nechushtan H,
Kaluzhny D, Pikarsky E and Razin E: Transcription factor MITF
regulates cardiac growth and hypertrophy. J Clin Invest.
116:2673–2681. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang G, Zhou J, Zhan W, Xiong Y, Hu C, Li
X, Li X, Li Y and Liao X: The neuroprotective effects of
intraperitoneal injection of hydrogen in rabbits with cardiac
arrest. Resuscitation. 84:690–695. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
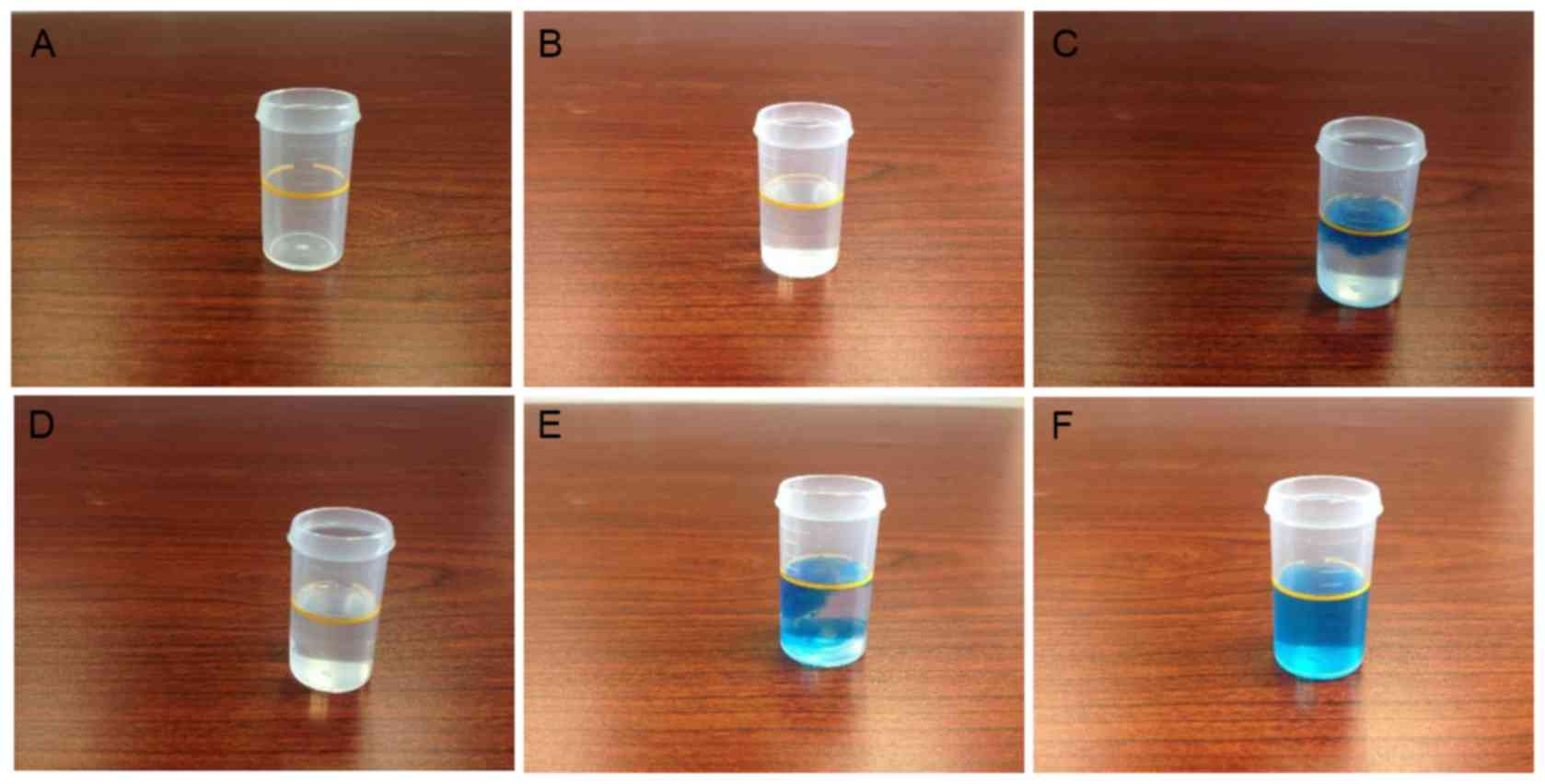
Seo T, Kurokawa R and Sato B: A convenient
method for determining the concentration of hydrogen in water: Use
of methylene blue with colloidal platinum. Med Gas Res. 2:12012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakatogawa H, Suzuki K, Kamada Y and
Ohsumi Y: Dynamics and diversity in autophagy mechanisms: Lessons
from yeast. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:458–467. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang W, Tian L, Li Y, Wang X, Xia F, Li L,
Li J and Zhang Z: Effects of hydrogen-rich saline on rats with
acute carbon monoxide poisoning. J Emerg Med. 44:107–115. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nagatani K, Wada K, Takeuchi S, Kobayashi
H, Uozumi Y, Otani N, Fujita M, Tachibana S and Nawashiro H: Effect
of hydrogen gas on the survival rate of mice following global
cerebral ischemia. Shock. 37:645–652. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|