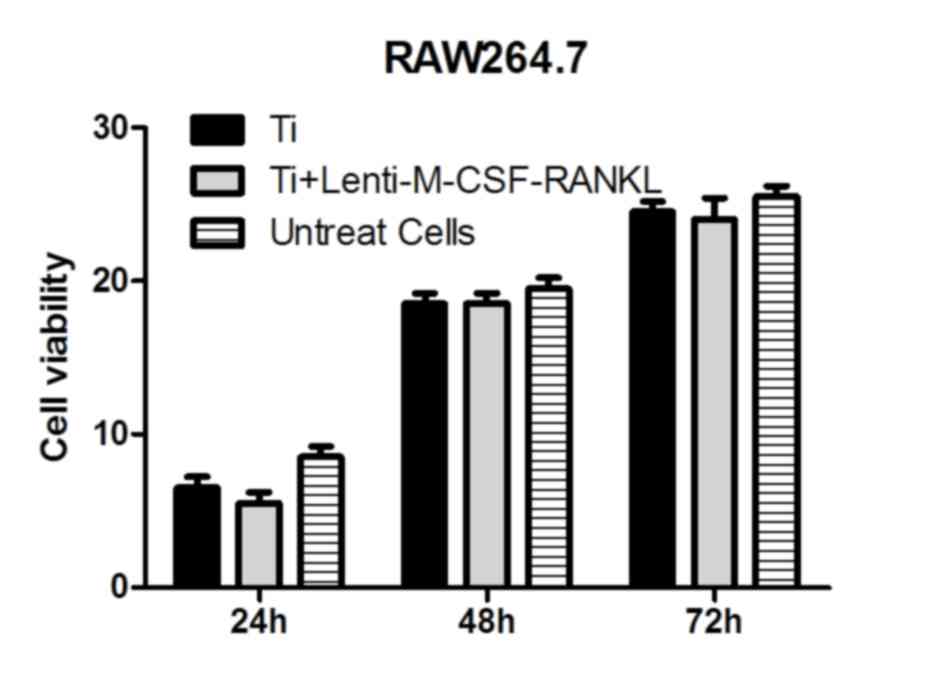
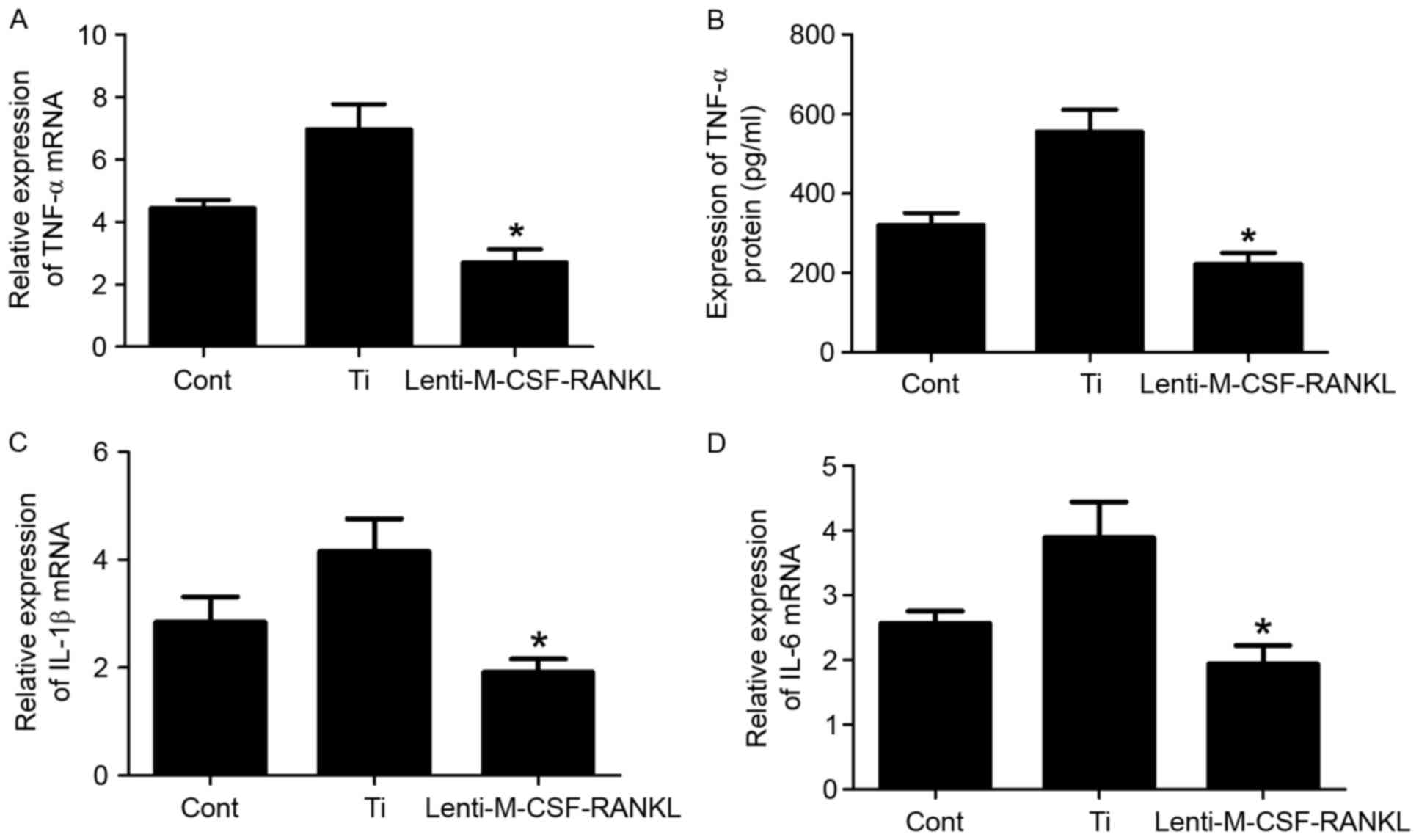
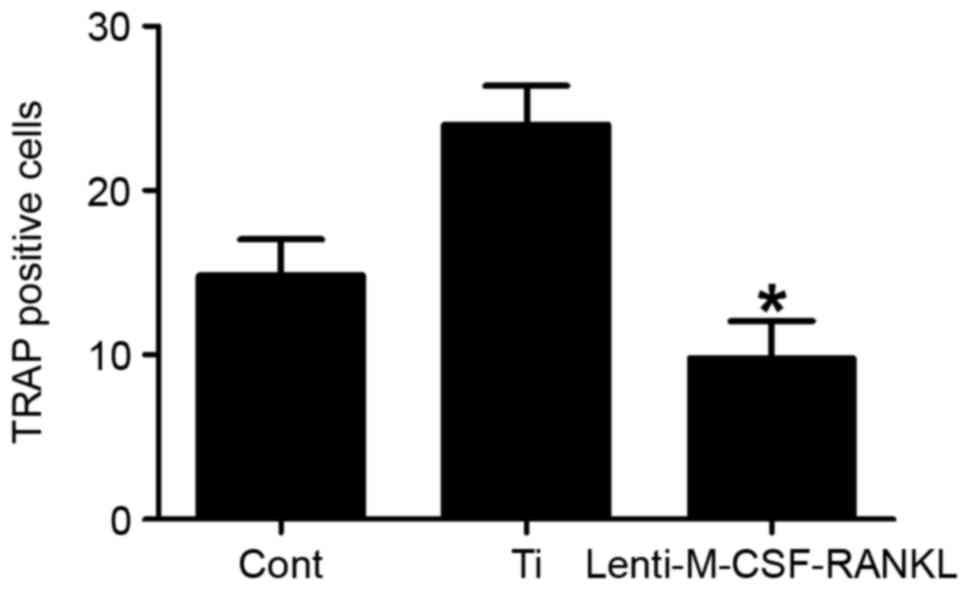
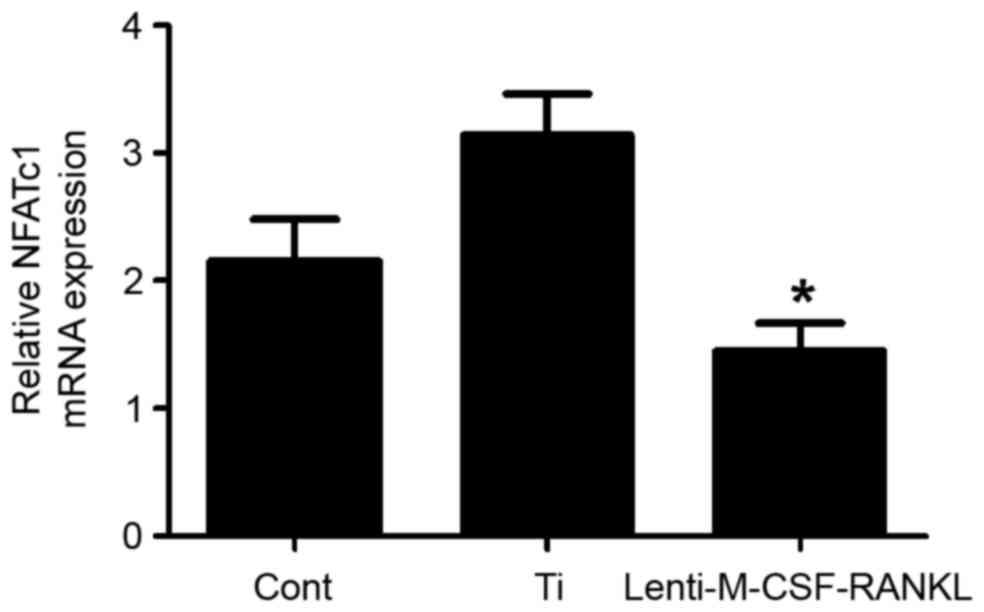
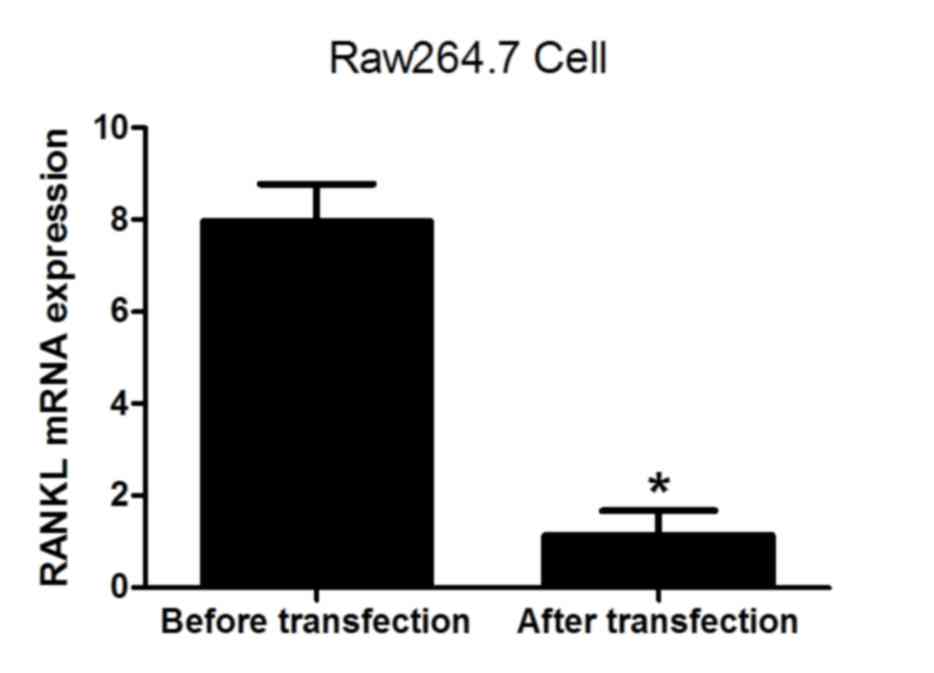
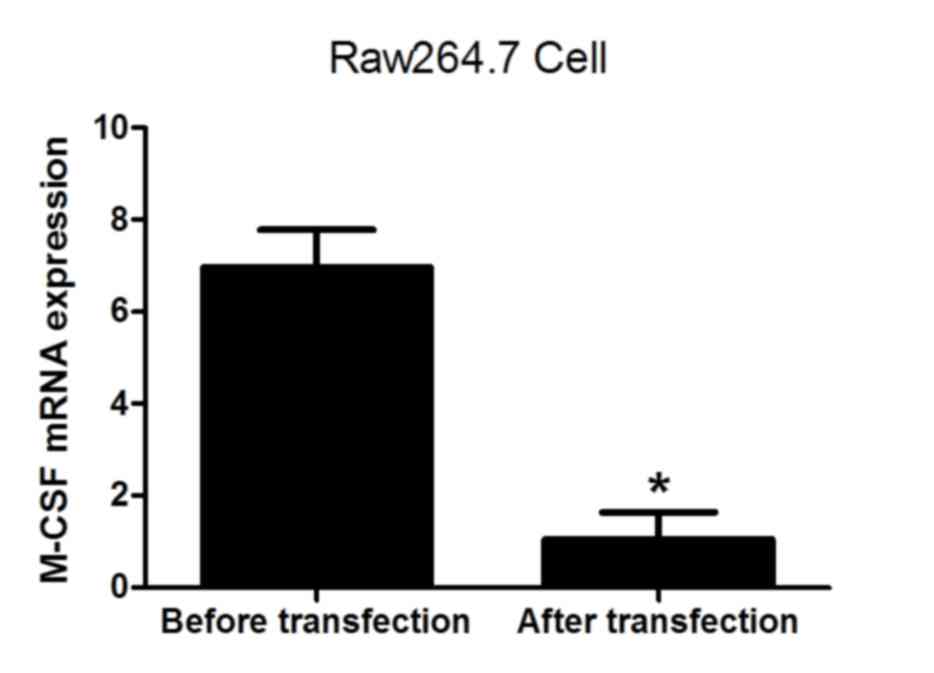
|
1
|
Gallo J, Goodman SB, Konttinen YT and
Raska M: Particle disease: Biologic mechanisms of periprosthetic
osteolysis in total hip arthroplasty. Innate Immun. 19:213–224.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mellon SJ, Liddle AD and Pandit H: Hip
replacement: Landmark surgery in modern medical history. Maturitas.
75:221–226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abu-Amer Y, Darwech I and Clohisy JC:
Aseptic loosening of total joint replacements: Mechanisms
underlying osteolysis and potential therapies. Arthritis Res Ther.
9 Suppl 1:S62007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jacobs JJ, Hallab NJ, Urban RM and Wimmer
MA: Wear particles. J Bone Joint Surg. 88 Supple 2:S99–S102. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ollivere B, Wimhurst JA, Clark IM and
Donell ST: Current concepts in osteolysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br.
94:10–15. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yamanaka Y, Clohisy JC, Ito H, Matsuno T
and Abu-Amer Y: Blockade of JNK and NFAT pathways attenuates
orthopedic particle-stimulated osteoclastogenesis of human
osteoclast precursors and murine calvarial osteolysis. J Orthop
Res. 31:67–72. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jones LC, Frondoza C and Hungerford DS:
Immunohistochemical evaluation of interface membranes from failed
cemented and uncemented acetabular components. J Biomed Mater Res.
48:889–898. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rao AJ, Gibon E, Ma T, Yao Z, Smith RL and
Goodman SB: Revision joint replacement, wear particles, and
macrophage polarization. Acta Biomater. 8:2815–2823. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Teitelbaum SL and Ross FP: Genetic
regulation of osteoclast development and function. Nat Rev Genet.
4:638–649. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ikeda K and Takeshita S: The role of
osteoclast differentiation and function in skeletal homeostasis. J
Biochem. 159:1–8. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Jimi E,
Gillespie MT and Martin TJ: Modulation of osteoclast
differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor
necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev.
20:345–357. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ,
Dunstan CR, Burgess T, Elliott R, Colombero A, Elliott G, Scully S,
et al: Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates
osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell. 93:165–176. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim JH and Kim N: Signaling pathways in
osteoclast differentiation. Chonnam Med J. 52:12–17. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tanaka H, Mine T, Ogasa H, Taguchi T and
Liang CT: Expression of RANKL/OPG during bone remodeling in vivo.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 411:690–694. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakashima T and Takayanagi H: New
regulation mechanisms of osteoclast differentiation. Ann N Y Acad
Sci. 1240:E13–E18. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tsurukai T, Udagawa N, Matsuzaki K,
Takahashi N and Suda T: Roles of macrophage-colony stimulating
factor and osteoclast differentiation factor in osteoclastogenesis.
J Bone Miner Metab. 18:177–184. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jiang Y, Jia T, Gong W, Wooley PH and Yang
SY: Titanium particle-challenged osteoblasts promote
osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis in a murine model of
periprosthestic osteolysis. Acta Biomater. 9:7564–7572. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Takayanagi H: Osteoclast differentiation
and activation. Clin Calcium. 17:484–492. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamashita T, Takahashi N and Udagawa N:
New roles of osteoblasts involved in osteoclast differentiation.
World J Orthop. 3:175–181. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Negishi-Koga T and Takayanagi H:
Ca2+-NFATc1 signaling is an essential axis of osteoclast
differentiation. Immunol Rev. 231:241–256. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Aliprantis AO, Ueki Y, Sulyanto R, Park A,
Sigrist KS, Sharma SM, Ostrowski MC, Olsen BR and Glimcher LH:
NFATc1 in mice represses osteoprotegerin during osteoclastogenesis
and dissociates systemic osteopenia from inflammation in cherubism.
J Clin Invest. 118:3775–3789. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H,
Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T, Inoue J, et al:
Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2)
integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of
osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 3:889–901. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Asagiri M, Sato K, Usami T, Ochi S,
Nishina H, Yoshida H, Morita I, Wagner EF, Mak TW, Serfling E and
Takayanagi H: Autoamplification of NFATc1 expression determines its
essential role in bone homeostasis. J Exp Med. 202:1261–1269. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim JH, Youn BU, Kim K, Moon JB, Lee J,
Nam KI, Park YW, O'Leary DD, Kim KK and Kim N: Lhx2 regulates bone
remodeling in mice by modulating RANKL signaling in osteoclasts.
Cell Death Differ. 21:1613–1621. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao B, Takami M, Yamada A, Wang X, Koga
T, Hu X, Tamura T, Ozato K, Choi Y, Ivashkiv LB, et al: Interferon
regulatory factor-8 regulates bone metabolism by suppressing
osteoclastogenesis. Nat Med. 15:1066–1071. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu F, Zhu Z, Mao Y, Liu M, Tang T and Qiu
S: Inhibition of titanium particle-induced osteoclastogenesis
through inactivation of NFATc1 by VIVIT peptide. Biomaterials.
30:1756–1762. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maoqiang L, Zhenan Z, Fengxiang L, Gang W,
Yuanqing M, Ming L, Xin Z and Tingting T: Enhancement of osteoblast
differentiation that is inhibited by titanium particles through
inactivation of NFATc1 by VIVIT peptide. J Biomed Mater Res A.
95:727–734. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Howie DW, Neale SD, Haynes DR, Holubowycz
OT, McGee MA, Solomon LB, Callary SA, Atkins GJ and Findlay DM:
Periprosthetic osteolysis after total hip replacement: Molecular
pathology and clinical management. Inflammopharmacology.
21:389–396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lehil MS and Bozic KJ: Trends in total hip
arthroplasty implant utilization in the United States. J
Arthroplasty. 29:1915–1918. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Peng L, Wang H, Song K, Wang H and Liu P:
Lentivirus-mediated TNF-α gene silencing and overexpression of
osteoprotegerin inhibit titanium particle-induced inflammatory
response and osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Mol Med Rep.
13:1010–1018. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Clohisy JC, Hirayama T, Frazier E, Han SK
and Abu-Amer Y: NF-kB signaling blockade abolishes implant
particle-induced osteoclastogenesis. J Orthop Res. 22:13–20. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zheng H, Yu X, Collin-Osdoby P and Osdoby
P: RANKL stimulates inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression and
nitric oxide production in developing osteoclasts. An autocrine
negative feedback mechanism triggered by RANKL-induced
interferon-beta via NF-kappaB that restrains osteoclastogenesis and
bone resorption. J Biol Chem. 281:15809–15820. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Del Buono A, Denaro V and Maffulli N:
Genetic susceptibility to aseptic loosening following total hip
arthroplasty: A systematic review. Br Med Bull. 101:39–55. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Singh JA and Sloan JA: Health-related
quality of life in veterans with prevalent total knee arthroplasty
and total hip arthroplasty. Rheumatology (Oxford). 47:1826–1831.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim JH and Kim N: Regulation of NFATc1 in
Osteoclast Differentiation. J Bone Metab. 21:233–241. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zaidi M, Blair HC, Moonga BS, Abe E and
Huang CL: Osteoclastogenesis, bone resorption, and osteoclast-based
therapeutics. J Bone Miner Res. 18:599–609. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang K and Kaufman RJ: From
endoplasmic-reticulum stress to the inflammatory response. Nature.
454:455–462. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hotamisligil GS: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell.
140:900–917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sabokbar A, Itonaga I, Sun SG, Kudo O and
Athanasou NA: Arthroplasty membrane-derived fibroblasts directly
induce osteoclast formation and osteolysis in aseptic loosening. J
Orthop Res. 23:511–519. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|