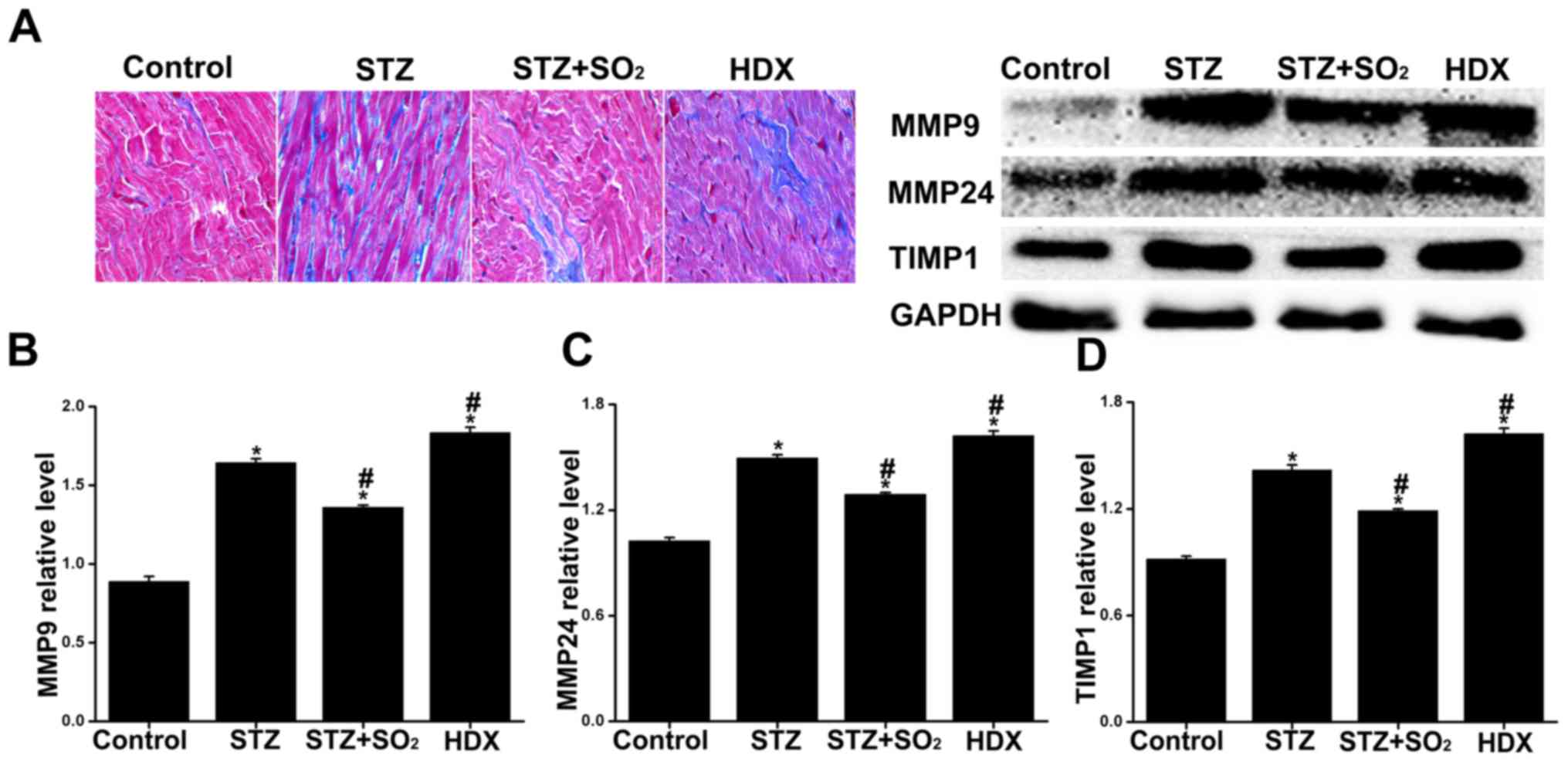
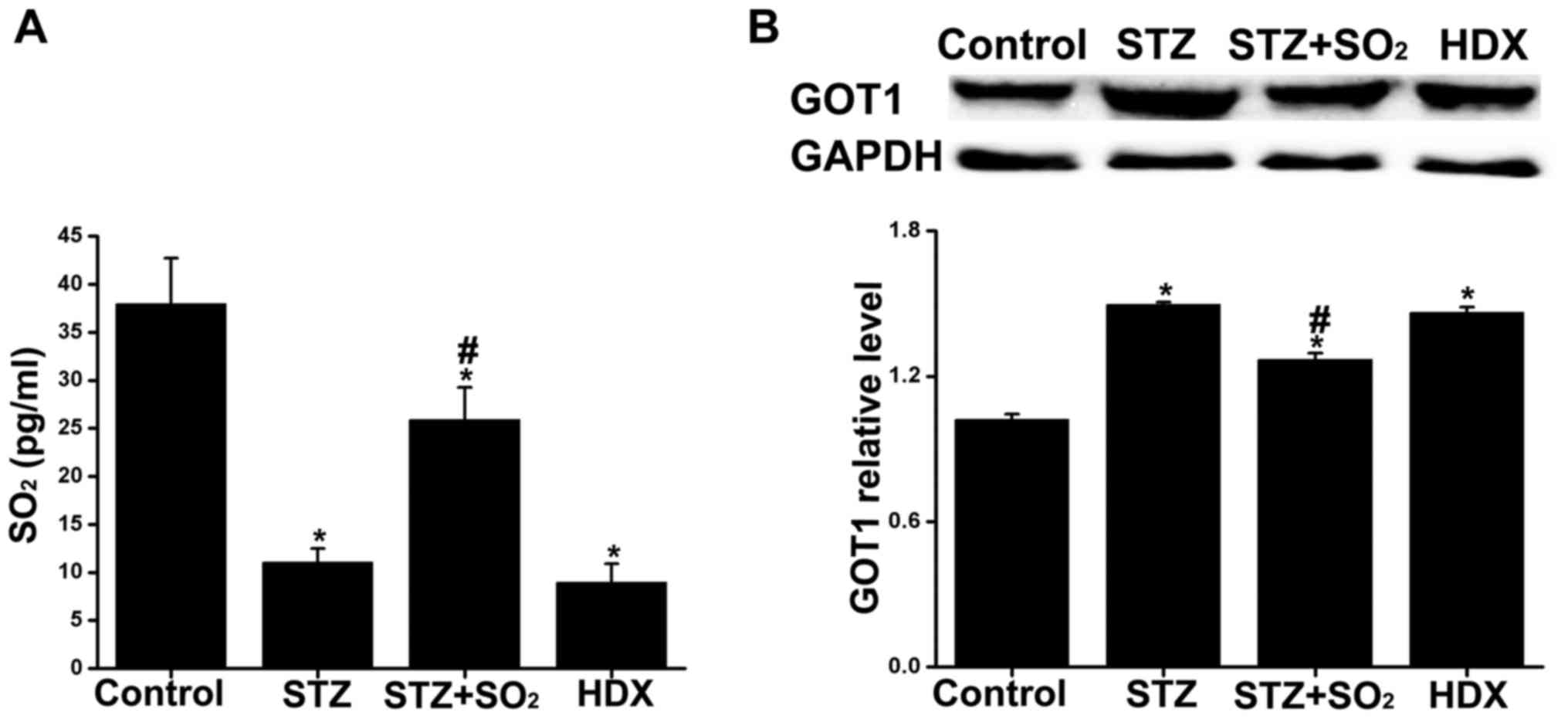
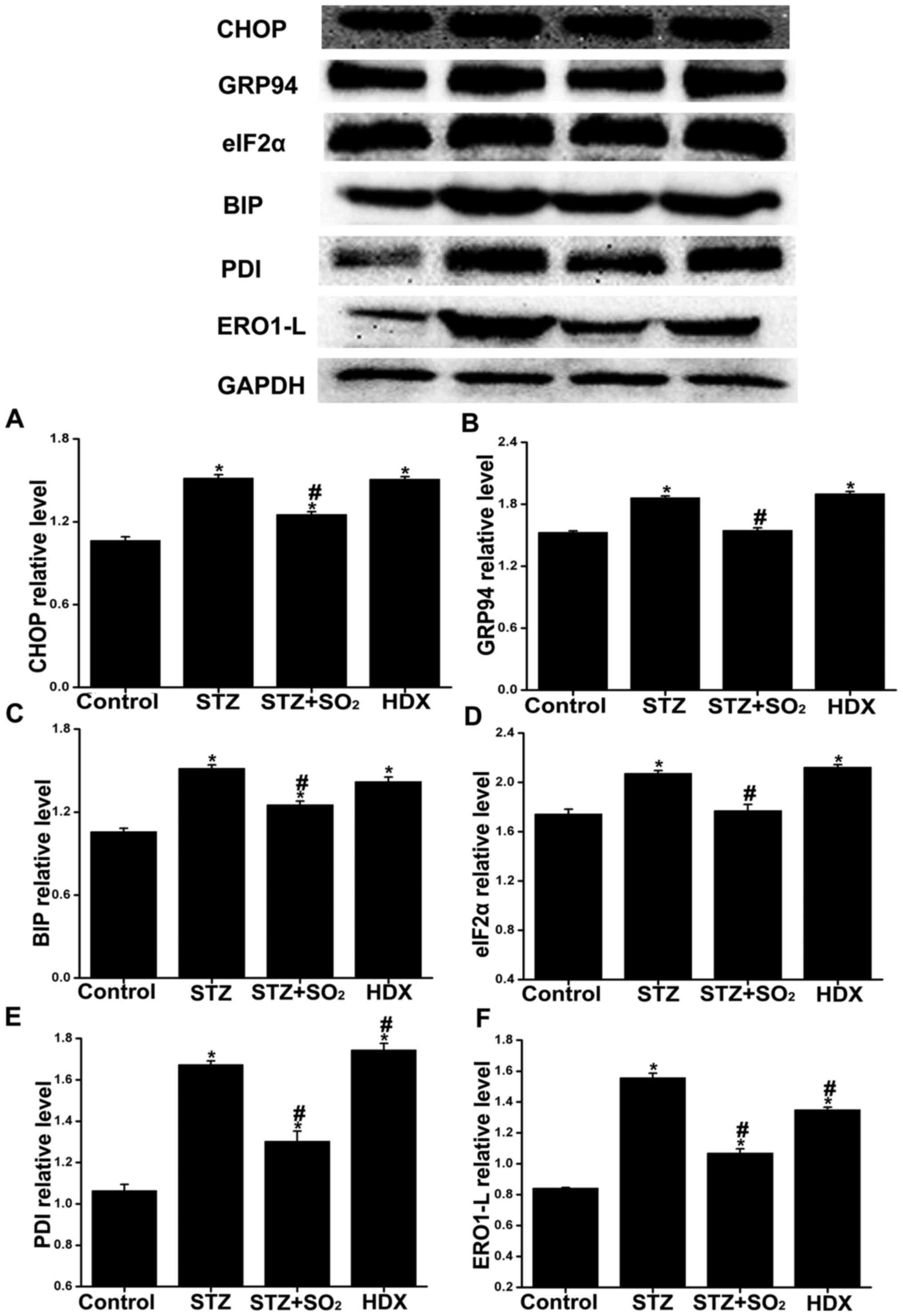
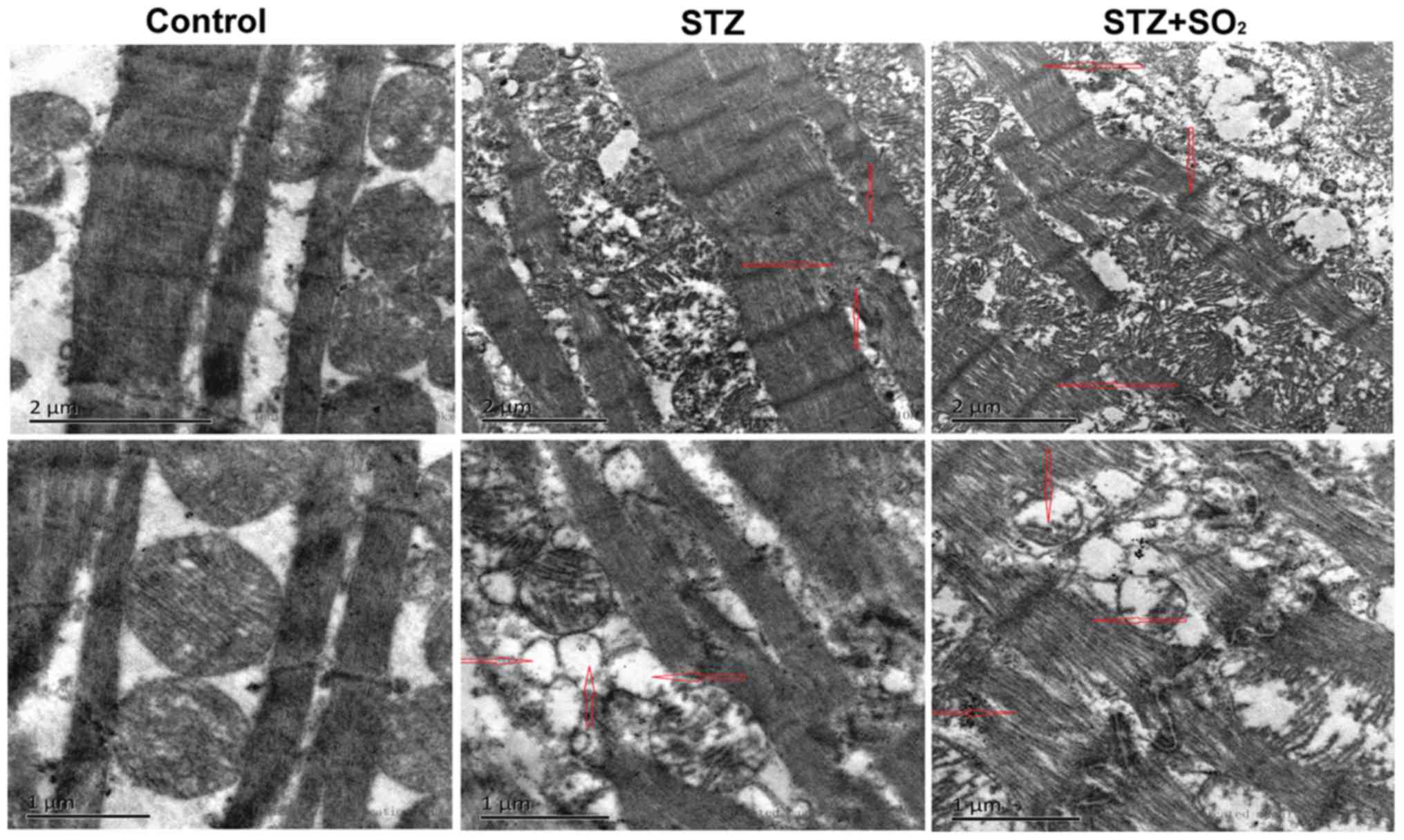
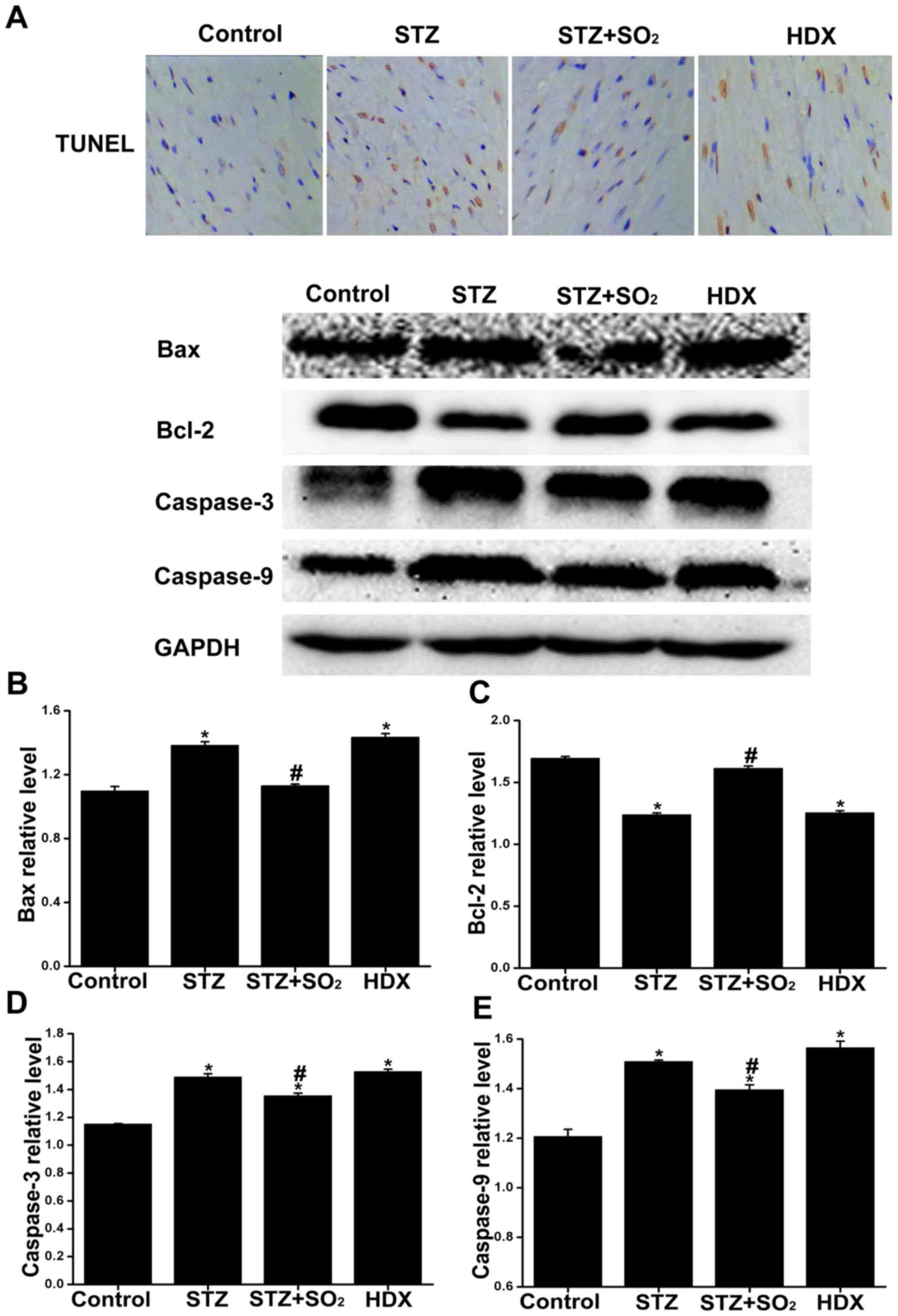
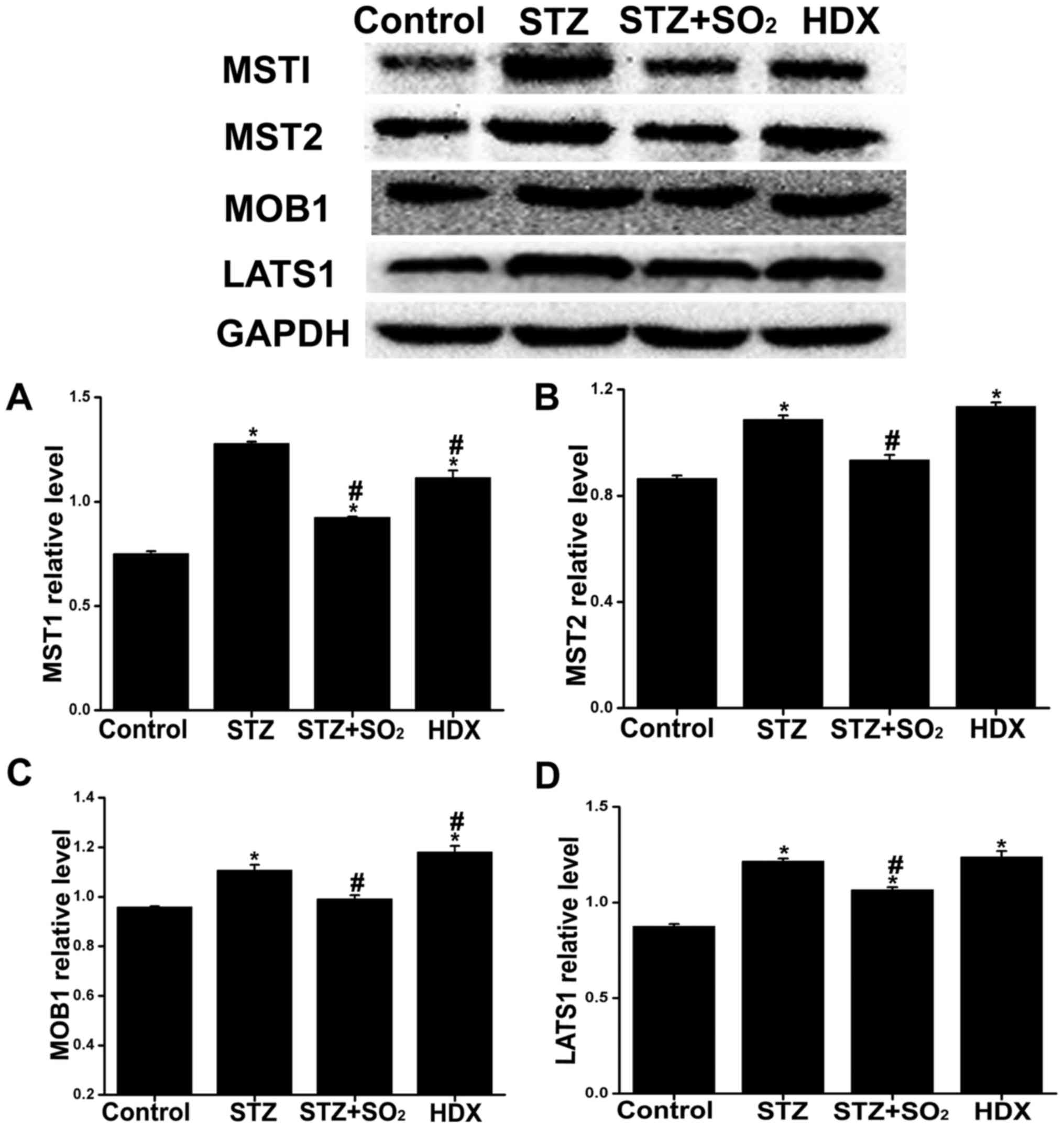
|
1
|
Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J,
Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, Ji Q, et al: Prevalence of diabetes among
men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 362:1090–1101. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jia G, DeMarco VG and Sowers JR: Insulin
resistance and hyperinsulinaemia in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Nat
Rev Endocrinol. 12:144–153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mizushige K, Yao L, Noma T, Kiyomoto H, Yu
Y, Hosomi N, Ohmori K and Matsuo H: Alteration in left ventricular
diastolic filling and accumulation of myocardial collagen at
insulin-resistant prediabetic stage of a type II diabetic rat
model. Circulation. 101:899–907. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Varga ZV, Giricz Z, Liaudet L, Haskó G,
Ferdinandy P and Pacher P: Interplay of oxidative,
nitrosative/nitrative stress, inflammation, cell death and
autophagy in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1852:232–242. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang JS, Hou YL, Lu WW, Ni XQ, Lin F, Yu
YR, Tang CS and Qi YF: Intermedin1-53 protects against myocardial
fibrosis by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and
inflammation induced by homocysteine in apolipoprotein E-deficient
mice. J AtherosclerThromb. 23:1294–1306. 2016.
|
|
6
|
Li F, Luo J, Wu Z, Xiao T, Zeng O, Li L,
Li Y and Yang J: Hydrogen sulfide exhibits cardioprotective effects
by decreasing endoplasmic reticulum stressin a diabetic
cardiomyopathy rat model. Mol Med Rep. 14:865–873. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bugger H and Abel ED: Molecular mechanisms
of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetologia. 57:660–671. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nerheim P, Krishnan SC and Olshansky B:
Apoptosis in the genesis of cardiac rhythm disorders. Cardiology
clinics. 19:155–163. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang Y, Tang C, Du J and Jin H:
Endogenous sulfur dioxide: A new member of gasotransmitter family
in the cardiovascular system. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:89619512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pan D: The hippo signaling pathway in
development and cancer. Dev Cell. 19:491–505. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Radu M and Chernoff J: The DeMSTification
of mammalian Ste20 kinases. Curr Bio. 19:R421–R425. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lin J, Zhang L, Zhang M, Hu J, Wang T,
Duan Y, Man W, Wu B, Feng J, Sun L, et al: Mst1 inhibits CMECs
autophagy and participates in the development of diabetic coronary
microvascular dysfunction. Sci Rep. 6:341992016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen Y, Du J, Zhao YT, Zhang L, Lv G,
Zhuang S, Qin G and Zhao TC: Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition
improves myocardial function and prevents cardiac remodeling in
diabetic mice. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 14:992015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang L, Ding WY, Wang ZH, Tang MX, Wang
F, Li Y, Zhong M, Zhang Y and Zhang W: Erratum to: Early
administration of trimetazidine attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy
in rats by alleviating fibrosis, reducing apoptosis and enhancing
autophagy. J Transl Med. 14:3092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang B, Shen Q, Chen Y, Pan R, Kuang S,
Liu G, Sun G and Sun X: Myricitrin alleviates oxidative
stress-induced inflammation and apoptosis and protects mice against
diabetic cardiomyopathy. Sci Rep. 7:442392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu W, Zha W, Guo S, Cheng H, Wu J and Liu
C: Flos puerariae extract prevents myocardial apoptosis via
attenuation oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic
mice. PLoS One. 9:e980442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou W, Yang J, Zhang DI, Li F, Li G, Gu Y
and Luo M: Role of Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa-interacting protein
3 in myocardial cells in diabetes. Exp Ther Med. 10:67–73. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Biden TJ, Boslem E, Chu KY and Sue N:
Lipotoxic endoplasmic reticulum stress, β cell failure and type 2
diabetes mellitus. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 25:389–398. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tang C, Koulajian K, Schuiki I, Zhang L,
Desai T, Ivovic A, Wang P, Robson-Doucette C, Wheeler MB, Minassian
B, et al: Glucose-induced beta cell dysfunction in vivo in rats:
Link between oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Diabetologia. 55:1366–1379. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Avruch J, Zhou D, Fitamant J, Bardeesy N,
Mou F and Barrufet LR: Protein kinases of the Hippo pathway:
Regulation and substrates. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 23:770–784. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Meng Z, Moroishi T and Guan KL: Mechanisms
of Hippo pathway regulation. Genes Dev. 30:1–17. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Praskova M, Xia F and Avruch J:
MOBKL1A/MOBKL1B phosphorylation by MST1 and MST2 inhibits cell
proliferation. Curr Biol. 18:311–321. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nakamura M, Zhai P, Del Re DP, Maejima Y
and Sadoshima J: Mst1-mediated phosphorylation of Bcl-xL is
required for myocardial reperfusion injury. JCI Insight.
1:e862172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee GJ, Yan L, Vatner DE and Vatner SF:
Mst1 inhibition rescues β1-adrenergic cardiomyopathy by reducing
myocyte necrosis and non-myocyte apoptosis ratherthan myocyte
apoptosis. Basic Res Cardiol. 110:72015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu J, Man W, Shen M, Zhang M, Lin J, Wang
T, Duan Y, Li C, Zhang R, Gao E, et al: Luteolin alleviates
post-infarction cardiac dysfunction by up-regulating autophagy
through Mst1 inhibition. J Cell Mol Med. 20:147–156. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yamamoto S, Yang G, Zablocki D, Liu J,
Hong C, Kim SJ, Soler S, Odashima M, Thaisz J, Yehia G, et al:
Activation of Mst1 causes dilated cardiomyopathy by stimulating
apoptosis without compensatory ventricular myocyte hypertrophy. J
Clin Invest. 111:1463–1474. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang M, Zhang L, Hu J, Lin J, Wang T,
Duan Y, Man W, Feng J, Sun L, Jia H, et al: MST1 coordinately
regulates autophagy and apoptosis in in mice. Diabetologia.
59:2435–2447. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ardestani A and Maedler K: MST1: A
promising therapeutic target to restore functional beta cell mass
in diabetes. Diabetologia. 59:1843–1849. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shen Y, Shen Z, Luo S, Guo W and Zhu YZ:
The cardioprotective effects of hydrogen sulfide in heart diseases:
From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic potential. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2015:9251672015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stipanuk MH: Sulfur amino acid metabolism:
Pathways for production and removal of homocysteine and cysteine.
Annu Rev Nutr. 24:539–577. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Singer TP and Kearney EB: Intermediary
metabolism of L-cysteinesulfinic acid in animal tissues. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 61:397–409. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jin H, Liu AD, Holmberg L, Zhao M, Chen S,
Yang J, Sun Y, Chen S, Tang C and Du J: The role of sulfur dioxide
in the regulation of mitochondrion-related cardiomyocyte apoptosis
in ratswith isopropylarterenol-induced myocardial injury. Int J Mol
Sci. 14:10465–10482. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang Y, Shen Z, Chen Q, Huang P, Zhang H,
Du S, Geng B, Zhang C, Li K, Tang C, et al: Endogenous sulfur
dioxide alleviates collagen remodeling via inhibiting TGF-β/Smad
pathway invascular smooth muscle cells. Sci Rep. 6:195032016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang H, Huang Y, Bu D, Chen S, Tang C,
Wang G, Du J and Jin H: Endogenous sulfur dioxide isa novel
adipocyte-derived inflammatory inhibitor. Sci Rep. 6:270262016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu D, Huang Y, Bu D, Liu AD, Holmberg L,
Jia Y, Tang C, Du J and Jin H: Sulfur dioxide inhibits vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferation via suppressing the Erk/MAP
kinasepathway mediated by cAMP/PKA signaling. Cell Death Dis.
5:e12512014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang XB, Jin HF, Tang CS and Du JB: The
biological effect of endogenous sulfur dioxide in the
cardiovascular system. Eur J Pharmacol. 670:1–6. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Huang P, Sun Y, Yang J, Chen S, Liu AD,
Holmberg L, Huang X, Tang C, Du J and Jin H: The ERK1/2 signaling
pathway is involved in sulfur dioxide preconditioning-induced
protection against cardiac dysfunction in isolated perfused rat
heart subjected tomyocardial ischemia/reperfusion. Int J Mol Sci.
14:22190–22201. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yu W, Liu D, Liang C, Ochs T, Chen S, Chen
S, Du S, Tang C, Huang Y, Du J and Jin H: Sulfur dioxide protects
against collagen accumulation in pulmonary artery in association
with downregulation of the transforming growth factor β1/smad
pathway in pulmonary hypertensive rats. J Am Heart Assoc.
5:e0039102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen Q, Zhang L, Chen S, Huang Y, Li K, Yu
X, Wu H, Tian X, Zhang C, Tang C, et al: Downregulated endogenous
sulfur dioxide/aspartate aminotransferase pathway is involved
inangiotensin II-stimulated cardiomyocyte autophagy and myocardial
hypertrophy in mice. Int J Cardiol. 225:392–401. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu J, Huang Y, Chen S, Tang C, Jin H and
Du J: Role of endogenous sulfur dioxide in regulating vascular
structural remodeling in hypertension. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:45290602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|