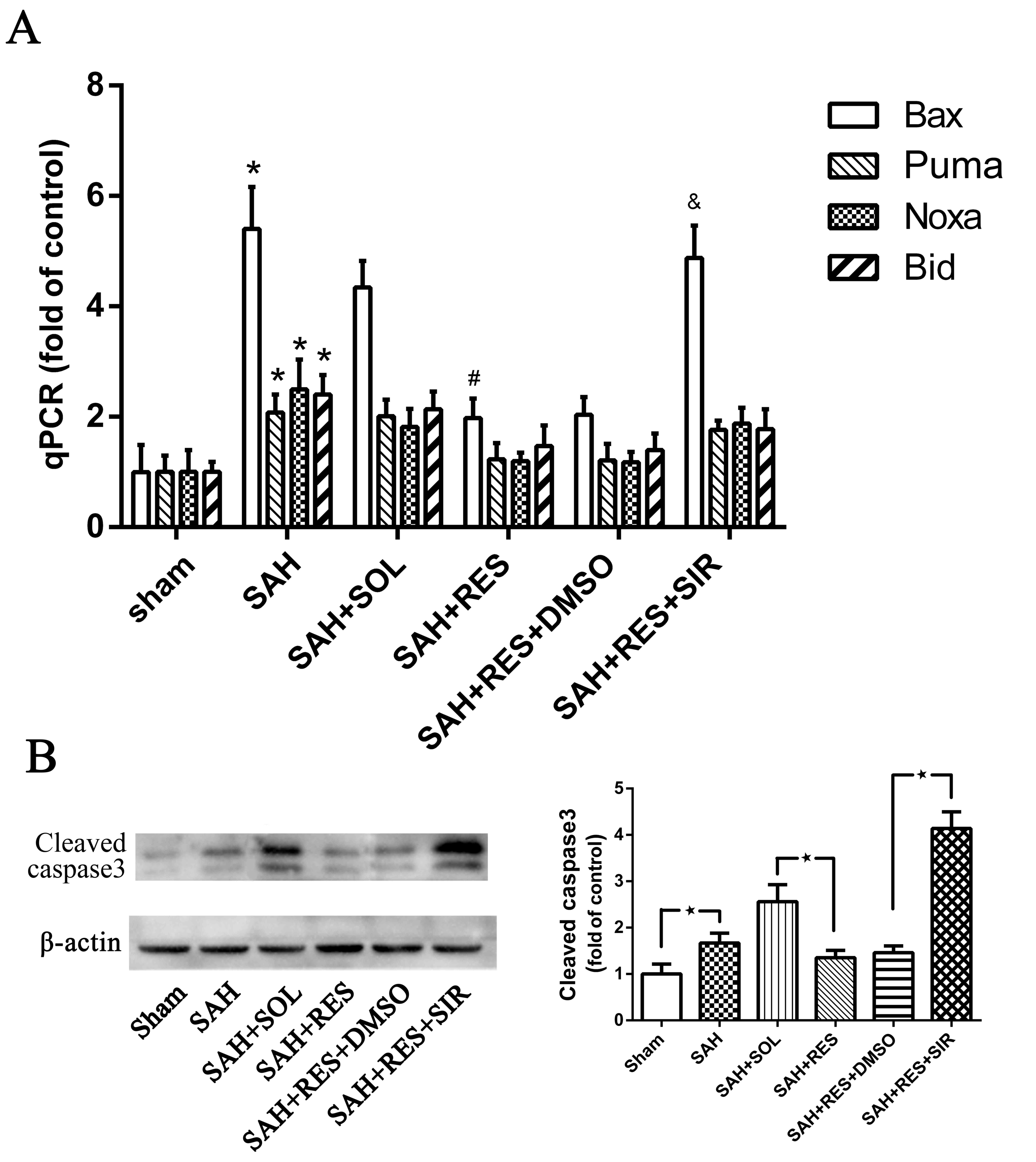
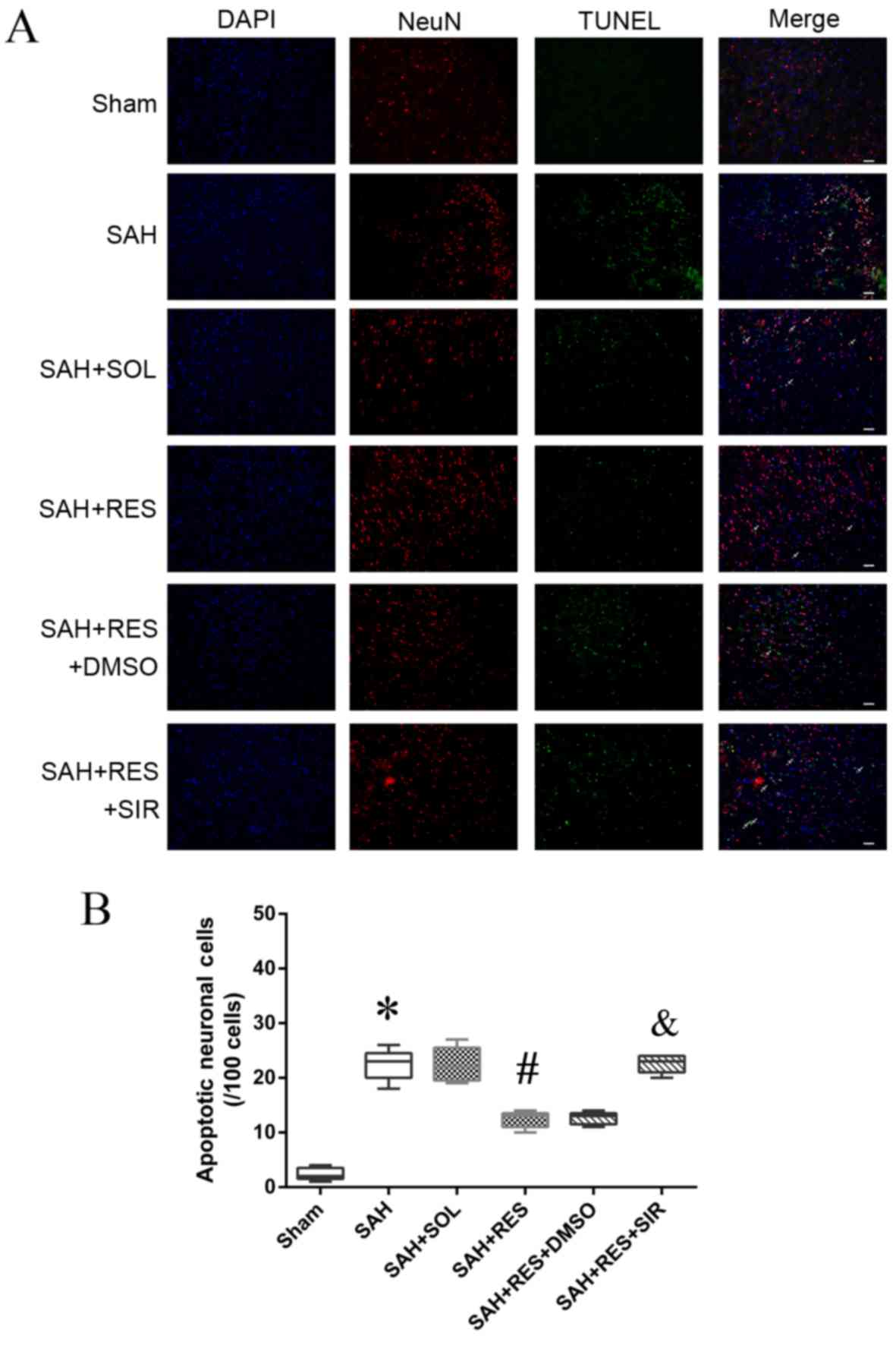
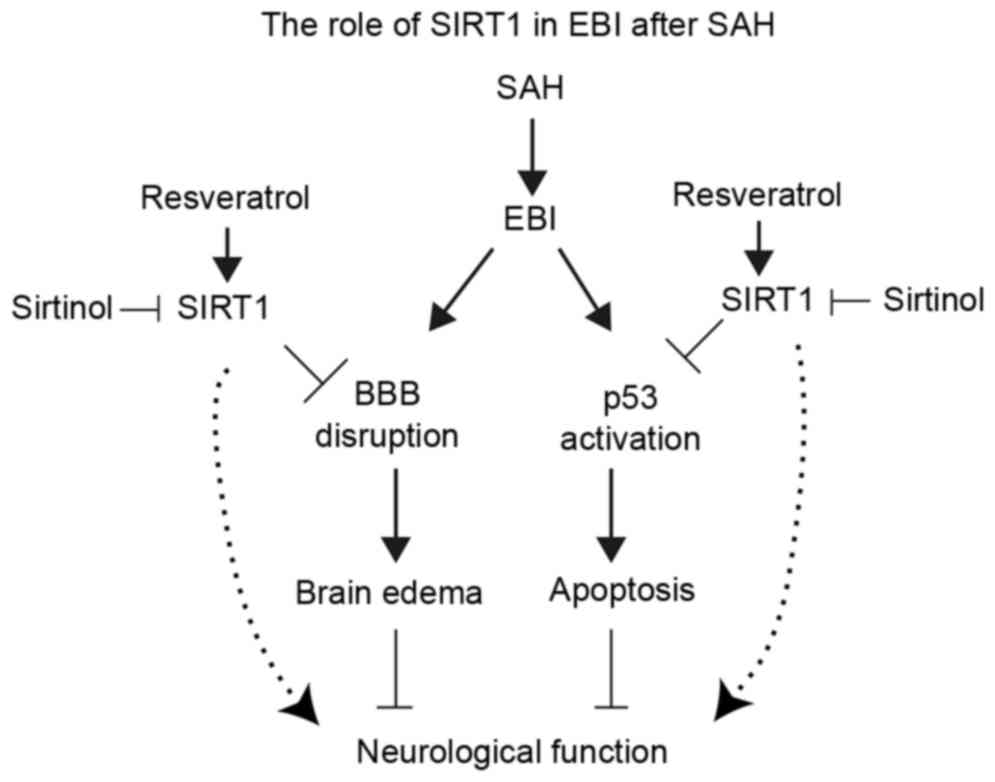
|
1
|
Bederson JB, Connolly ES Jr, Batjer HH,
Dacey RG, Dion JE, Diringer MN, Duldner JE Jr, Harbaugh RE, Patel
AB and Rosenwasser RH; American Heart Association, : Guidelines for
the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A statement
for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the
Stroke Council, American Heart Association. Stroke. 40:994–1025.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kaptain GJ, Lanzino G and Kassell NF:
Subarachnoid haemorrhage: Epidemiology, risk factors, and treatment
options. Drugs Aging. 17:183–199. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Weir B, Macdonald RL and Stoodley M:
Etiology of cerebral vasospasm. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 72:27–46.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
King JT Jr: Epidemiology of aneurysmal
subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 7:659–668.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Becker KJ: Epidemiology and clinical
presentation of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurg Clin
N Am. 9:435–444. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fujii M, Yan J, Rolland WB, Soejima Y,
Caner B and Zhang JH: Early brain injury, an evolving frontier in
subarachnoid hemorrhage research. Transl Stroke Res. 4:432–446.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sehba FA, Hou J, Pluta RM and Zhang JH:
The importance of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Prog Neurobiol. 97:14–37. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matz PG, Fujimura M and Chan PH:
Subarachnoid hemolysate produces DNA fragmentation in a pattern
similar to apoptosis in mouse brain. Brain Res. 858:312–319. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Matz PG, Fujimura M, Lewen A,
Morita-Fujimura Y and Chan PH: Increased cytochrome c-mediated DNA
fragmentation and cell death in manganese-superoxide
dismutase-deficient mice after exposure to subarachnoid hemolysate.
Stroke. 32:506–515. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nau R, Haase S, Bunkowski S and Brück W:
Neuronal apoptosis in the dentate gyrus in humans with subarachnoid
hemorrhage and cerebral hypoxia. Brain Pathol. 12:329–336.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Endo H, Nito C, Kamada H, Yu F and Chan
PH: Akt/GSK3beta survival signaling is involved in acute brain
injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke. 37:2140–2146.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kusaka G, Ishikawa M, Nanda A, Granger DN
and Zhang JH: Signaling pathways for early brain injury after
subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 24:916–925.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yan J, Chen C, Hu Q, Yang X, Lei J, Yang
L, Wang K, Qin L, Huang H and Zhou C: The role of p53 in brain
edema after 24 h of experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in a rat
model. Exp Neurol. 214:37–46. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen X, Ghribi O and Geiger JD: Caffeine
protects against disruptions of the blood-brain barrier in animal
models of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. J Alzheimers Dis.
20 Suppl 1:S127–S141. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Engelhardt B and Sorokin L: The
blood-brain and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers: Function
and dysfunction. Semin Immunopathol. 31:497–511. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sugawara T, Jadhav V, Ayer R, Chen W,
Suzuki H and Zhang JH: Thrombin inhibition by argatroban
ameliorates early brain injury and improves neurological outcomes
after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke.
40:1530–1532. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim WJ, Rivera MN, Coffman EJ and Haber
DA: The WTX tumor suppressor enhances p53 acetylation by CBP/p300.
Mol Cell. 45:587–597. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sykes SM, Mellert HS, Holbert MA, Li K,
Marmorstein R, Lane WS and McMahon SB: Acetylation of the p53
DNA-binding domain regulates apoptosis induction. Mol Cell.
24:841–851. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tang Y, Luo J, Zhang W and Gu W:
Tip60-dependent acetylation of p53 modulates the decision between
cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. Mol Cell. 24:827–839. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gu W and Roeder RG: Activation of p53
sequence-specific DNA binding by acetylation of the p53 C-terminal
domain. Cell. 90:595–606. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cahill J, Calvert JW, Marcantonio S and
Zhang JH: p53 may play an orchestrating role in apoptotic cell
death after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery.
60:531–545. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miyashita T, Krajewski S, Krajewska M,
Wang HG, Lin HK, Liebermann DA, Hoffman B and Reed JC: Tumor
suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene expression in
vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 9:1799–1805. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nakano K and Vousden KH: A novel
proapoptotic gene, is induced by p53. Mol Cell. 7:683–694. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oda E, Ohki R, Murasawa H, Nemoto J,
Shibue T, Yamashita T, Tokino T, Taniguchi T and Tanaka N: Noxa, a
BH3-only member of the Bcl-2 family and candidate mediator of
p53-induced apoptosis. Science. 288:1053–1058. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Becatti M, Taddei N, Cecchi C, Nassi N,
Nassi PA and Fiorillo C: SIRT1 modulates MAPK pathways in
ischemic-reperfused cardiomyocytes. Cell Mol Life Sci.
69:2245–2260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang P, Xu TY, Guan YF, Tian WW, Viollet
B, Rui YC, Zhai QW, Su DF and Miao CY: Nicotinamide
phosphoribosyltransferase protects against ischemic stroke through
SIRT1-dependent adenosine monophosphate-activated kinase pathway.
Ann Neurol. 69:360–374. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yan W, Fang Z, Yang Q, Dong H, Lu Y, Lei C
and Xiong L: SirT1 mediates hyperbaric oxygen
preconditioning-induced ischemic tolerance in rat brain. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 33:396–406. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou XM, Zhang X, Zhang XS, Zhuang Z, Li
W, Sun Q, Li T, Wang CX, Zhu L, Shi JX and Zhou ML: SIRT1
inhibition by sirtinol aggravates brain edema after experimental
subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosci Res. 92:714–722. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Della-Morte D, Dave KR, DeFazio RA, Bao
YC, Raval AP and Perez-Pinzon MA: Resveratrol pretreatment protects
rat brain from cerebral ischemic damage via a sirtuin 1-uncoupling
protein 2 pathway. Neuroscience. 159:993–1002. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sugawara T, Ayer R, Jadhav V and Zhang JH:
A new grading system evaluating bleeding scale in filament
perforation subarachnoid hemorrhage rat model. J Neurosci Methods.
167:327–334. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen S, Ma Q, Krafft PR, Chen Y, Tang J,
Zhang J and Zhang JH: P2X7 receptor antagonism inhibits p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and ameliorates
neuronal apoptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Crit Care
Med. 41:e466–e474. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Garcia JH, Wagner S, Liu KF and Hu XJ:
Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable
to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Statistical
validation. 26:627–635. 1995.
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Broderick JP, Brott TG, Duldner JE,
Tomsick T and Leach A: Initial and recurrent bleeding are the major
causes of death following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke.
25:1342–1347. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shao AW, Wu HJ, Chen S, Ammar AB, Zhang JM
and Hong Y: Resveratrol attenuates early brain injury after
subarachnoid hemorrhage through inhibition of NF-κB-dependent
inflammatory/MMP-9 pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. 20:182–185. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang XS, Li W, Wu Q, Wu LY, Ye ZN, Liu
JP, Zhuang Z, Zhou ML, Zhang X and Hang CH: Resveratrol attenuates
acute inflammatory injury in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage
in rats via inhibition of TLR4 pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 17:pii:
E13312016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Claassen J, Carhuapoma JR, Kreiter KT, Du
EY, Connolly ES and Mayer SA: Global cerebral edema after
subarachnoid hemorrhage: Frequency, predictors, and impact on
outcome. Stroke. 33:1225–1232. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Unterberg AW, Stover J, Kress B and
Kiening KL: Edema and brain trauma. Neuroscience. 129:1021–1029.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Suzuki H, Hasegawa Y, Kanamaru K and Zhang
JH: Mechanisms of osteopontin-induced stabilization of blood-brain
barrier disruption after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke.
41:1783–1790. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kniesel U and Wolburg H: Tight junctions
of the blood-brain barrier. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 20:57–76. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fang S, Jensen JP, Ludwig RL, Vousden KH
and Weissman AM: Mdm2 is a RING finger-dependent ubiquitin protein
ligase for itself and p53. J Biol Chem. 275:8945–8951. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liebner S, Kniesel U, Kalbacher H and
Wolburg H: Correlation of tight junction morphology with the
expression of tight junction proteins in blood-brain barrier
endothelial cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 79:707–717. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao L, Liu H, Yue L, Zhang J, Li X, Wang
B, Lin Y and Qu Y: Melatonin attenuates early brain injury via the
melatonin receptor/Sirt1/NF-κB signaling pathway following
subarachnoid hemorrhage in mice. Mol Neurobiol. 54:1612–1621. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Asahi M, Wang X, Mori T, Sumii T, Jung JC,
Moskowitz MA, Fini ME and Lo EH: Effects of matrix
metalloproteinase-9 gene knock-out on the proteolysis of
blood-brain barrier and white matter components after cerebral
ischemia. J Neurosci. 21:7724–7732. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bauer AT, Bürgers HF, Rabie T and Marti
HH: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 mediates hypoxia-induced vascular
leakage in the brain via tight junction rearrangement. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 30:837–848. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cunnea P, McMahon J, O'Connell E,
Mashayekhi K, Fitzgerald U and McQuaid S: Gene expression analysis
of the microvascular compartment in multiple sclerosis using laser
microdissected blood vessels. Acta Neuropathol. 119:601–615. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yang Y, Estrada EY, Thompson JF, Liu W and
Rosenberg GA: Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated disruption of tight
junction proteins in cerebral vessels is reversed by synthetic
matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor in focal ischemia in rat. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 27:697–709. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wei H, Wang S, Zhen L, Yang Q, Wu Z, Lei
X, Lv J, Xiong L and Xue R: Resveratrol attenuates the blood-brain
barrier dysfunction by regulation of the MMP-9/TIMP-1 balance after
cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats. J Mol Neurosci. 55:872–879.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cohen M, Wuillemin C, Irion O and Bischof
P: Regulation of MMP-9 by p53 in first trimester cytotrophoblastic
cells. Hum Reprod. 23:2273–2281. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Vaziri H, Dessain SK, Ng Eaton E, Imai SI,
Frye RA, Pandita TK, Guarente L and Weinberg RA: hSIR2(SIRT1)
functions as an NAD-dependent p53 deacetylase. Cell. 107:149–159.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li M, Luo J, Brooks CL and Gu W:
Acetylation of p53 inhibits its ubiquitination by Mdm2. J Biol
Chem. 277:50607–50611. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|