|
1
|
Losina E, Weinstein AM, Reichmann WM,
Burbine SA, Solomon DH, Daigle ME, Rome BN, Chen SP, Hunter DJ,
Suter LG, et al: Lifetime risk and age at diagnosis of symptomatic
knee osteoarthritis in the US. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken).
65:703–711. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Musumeci G, Aiello F, Szychlinska M, Di
Rosa M, Castrogiovanni P and Mobasheri A: Osteoarthritis in the
XXIst century: Risk factors and behaviours that influence disease
onset and progression. Int J Mol Sci. 16:6093–6112. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
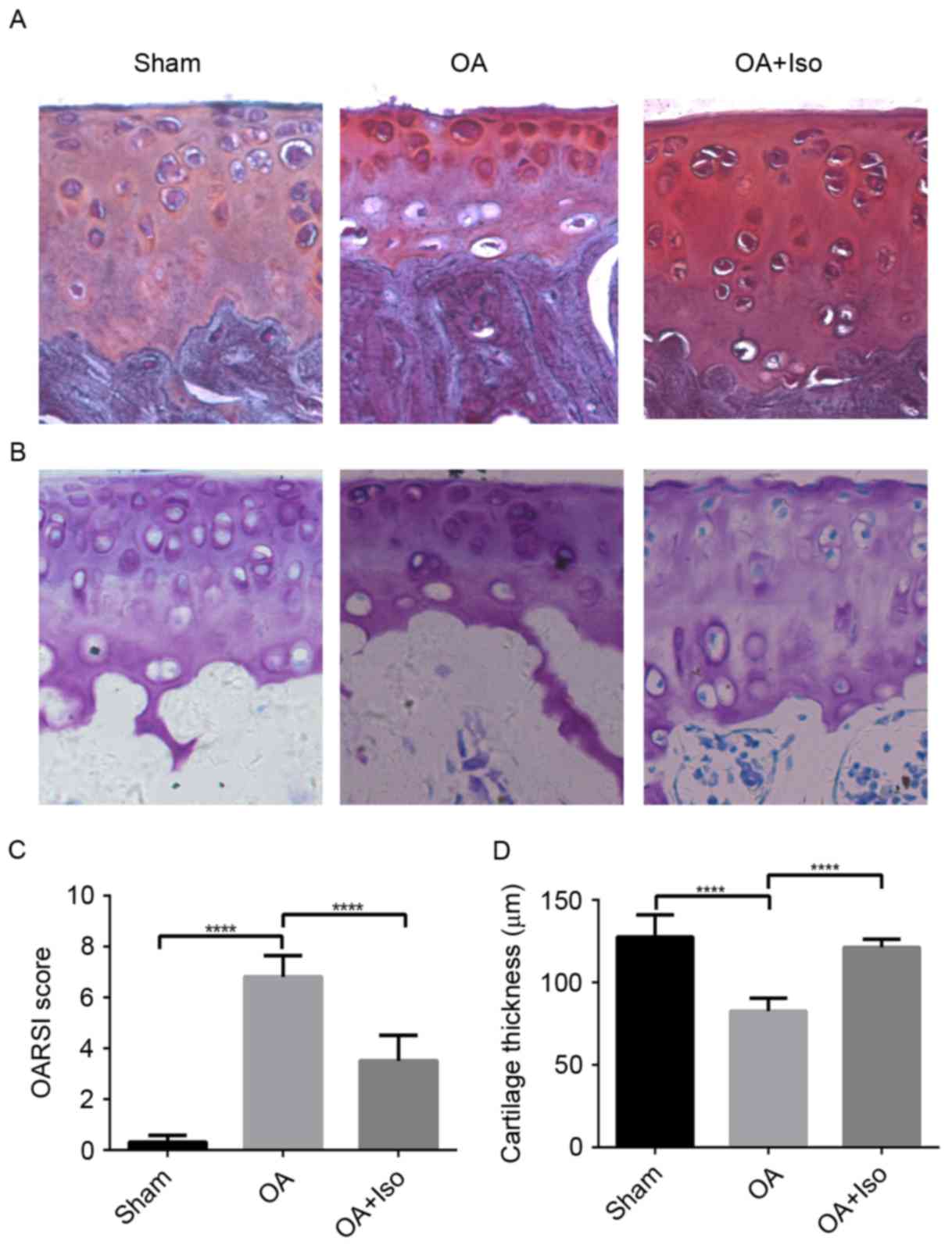
Musumeci G, Szychlinska MA and Mobasheri
A: Age-related degeneration of articular cartilage in the
pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Molecular markers of senescent
chondrocytes. Histol Histopathol. 30:1–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Aigner T, Sachse A, Gebhard PM and Roach
HI: Osteoarthritis: Pathobiology-targets and ways for therapeutic
intervention. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 58:128–149. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jacques C, Gosset M, Berenbaum F and Gabay
C: The role of IL-1 and IL-1Ra in joint inflammation and cartilage
degradation. Vitam Horm. 74:371–403. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Loeser RF, Goldring SR, Scanzello CR and
Goldring MB: Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ.
Arthritis Rheum. 64:1697–1707. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yuan Q, Sun L, Li JJ and An CH: Elevated
VEGF levels contribute to the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. BMC
Musculoskelet Disord. 15:4372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Musumeci G, Carnazza ML and Loreto C,
Leonardi R and Loreto C: β-Defensin-4 (HBD-4) is expressed in
chondrocytes derived from normal and osteoarthritic cartilage
encapsulated in PEGDA scaffold. Acta Histochem. 114:805–812. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Musumeci G, Carnazza ML, Leonardi R and
Loreto C: Expression of β-defensin-4 in ‘an in vivo and ex vivo
model’ of human osteoarthritic knee meniscus. Knee Surg Sports
Traumatol Arthrosc. 20:216–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Philp AM, Davis ET and Jones SW:
Developing anti-inflammatory therapeutics for patients with
osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 56:869–881. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Goldring MB and Goldring SR:
Osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. 213:626–634. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang S, Chen Q and He L: Development and
validation of a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method for the
determination of isoimperatorin in rat plasma and tissue:
Application to the pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution study. J
Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 852:473–478. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wei Y and Ito Y: Preparative isolation of
imperatorin, oxypeucedanin and isoimperatorin from traditional
Chinese herb ‘bai zhi’ Angelica dahurica (Fisch. ex Hoffm) Benth.
et Hook using multidimensional high-speed counter-current
chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 1115:112–117. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kang OH, Chae HS, Oh YC, Choi JG, Lee YS,
Jang HJ, Kim JH, Kim YC, Sohn DH, Park H and Kwon DY:
Anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of Angelicae
dahuricae radix through inhibition of the expression of inducible
nitric oxide synthase and NO production. Am J Chin Med. 36:913–928.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zheng YM, Shen JZ, Wang Y, Lu AX and Ho
WS: Anti-oxidant and anti-cancer activities of Angelica dahurica
extract via induction of apoptosis in colon cancer cells.
Phytomedicine. 23:1267–1274. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nie H, Meng LZ, Zhou JY, Fan XF, Luo- Y
and Zhang GW: Imperatorin is responsible for the vasodilatation
activity of Angelica Dahurica var. Formosana regulated by nitric
oxide in an endothelium-dependent manner. Chin J Integr Med.
15:442–447. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen YF, Tsai HY and Wu TS:
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities from roots of Angelica
pubescens. Planta Med. 61:2–8. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moon TC, Jin M, Son JK and Chang HW: The
effects of isoimperatorin isolated from Angelicae dahuricae on
cyclooxygenase-2 and 5-lipoxygenase in mouse bone marrow-derived
mast cells. Arch Pharm Res. 31:210–215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ban HS, Lim SS, Suzuki K, Jung SH, Lee S,
Lee YS, Shin KH and Ohuchi K: Inhibitory effects of furanocoumarins
isolated from the roots of Angelica dahurica on prostaglandin E2
production. Planta Med. 69:408–412. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Moon L, Ha YM, Jang HJ, Kim HS, Jun MS,
Kim YM, Lee YS, Lee DH, Son KH, Kim HJ, et al: Isoimperatorin,
cimiside E and 23-O-acetylshengmanol-3-xyloside from Cimicifugae
rhizome inhibit TNF-α-induced VCAM-1 expression in human
endothelial cells: Involvement of PPAR-γ upregulation and PI3K,
ERK1/2 and, PKC signal pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 133:336–344.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Glasson SS, Chambers MG, Van Den Berg WB
and Little CB: The OARSI histopathology initiative -
recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in
the mouse. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 18 Suppl 3:S17–S23. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lotz M and Caramés B: Autophagy: A new
therapeutic target in cartilage injury and osteoarthritis. J Am
Acad Orthop Surg. 20:261–262. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vasheghani F, Zhang Y, Li YH, Blati M,
Fahmi H, Lussier B, Roughley P, Lagares D, Endisha H, Saffar B, et
al: PPARγ deficiency results in severe, accelerated osteoarthritis
associated with aberrant mTOR signalling in the articular
cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 74:569–578. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guba M, von Breitenbuch P, Steinbauer M,
Koehl G, Flegel S, Hornung M, Bruns CJ, Zuelke C, Farkas S,
Anthuber M, et al: Rapamycin inhibits primary and metastatic tumor
growth by antiangiogenesis: Involvement of vascular endothelial
growth factor. Nat Med. 8:128–135. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: Regulation of
mTORC1 and its impact on gene expression at a glance. J Cell Sci.
126:1713–1719. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Berenbaum F, Griffin TM and Liu-Bryan R:
Review: Metabolic regulation of inflammation in osteoarthritis.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 69:9–21. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
van der Kraan PM and van den Berg WB:
Chondrocyte hypertrophy and osteoarthritis: Role in initiation and
progression of cartilage degeneration? Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
20:223–232. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
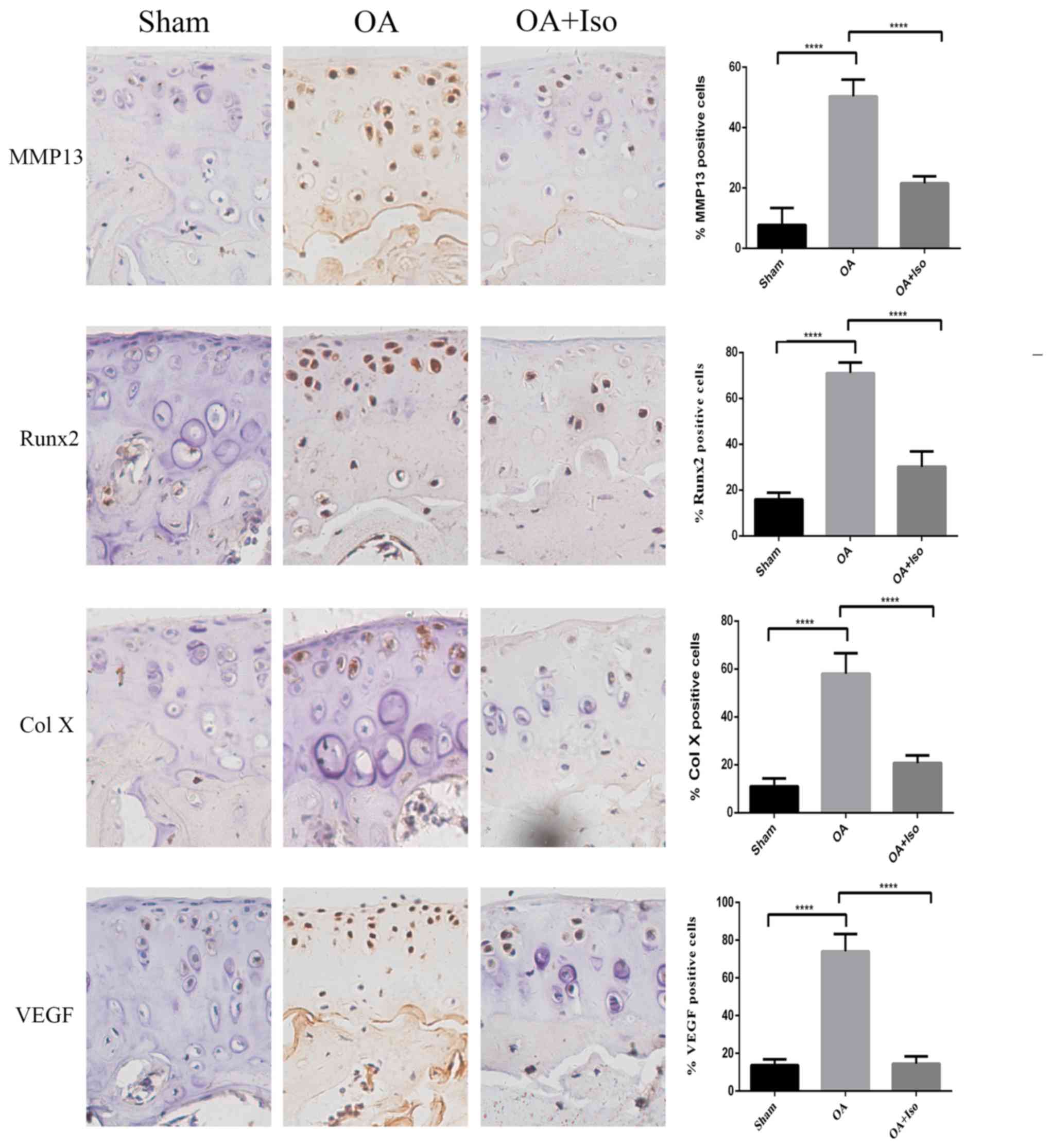
Higashikawa A, Saito T, Ikeda T, Kamekura
S, Kawamura N, Kan A, Oshima Y, Ohba S, Ogata N, Takeshita K, et
al: Identification of the core element responsive to runt-related
transcription factor 2 in the promoter of human type X collagen
gene. Arthritis Rheum. 60:166–178. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kamekura S, Kawasaki Y, Hoshi K, Shimoaka
T, Chikuda H, Maruyama Z, Komori T, Sato S, Takeda S, Karsenty G,
et al: Contribution of runt-related transcription factor 2 to the
pathogenesis of osteoarthritis in mice after induction of knee
joint instability. Arthritis Rheum. 54:2462–2470. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yi JW, Lee WS, Kim SB, Heo YM and Chae DS:
Effect of zoledronate on the expression of vascular endothelial
growth factor-A by articular chondrocytes and synovial cells: An in
vitro study. J Bone Metab. 21:249–255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Neve A, Cantatore FP, Corrado A, Gaudio A,
Ruggieri S and Ribatti D: In vitro and in vivo angiogenic activity
of osteoarthritic and osteoporotic osteoblasts is modulated by VEGF
and vitamin D3 treatment. Regul Pept. 184:81–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Takimoto A, Nishizaki Y, Hiraki Y and
Shukunami C: Differential actions of VEGF-A isoforms on
perichondrial angiogenesis during endochondral bone formation. Dev
Biol. 332:196–211. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Saetan N, Honsawek S, Tanavalee A,
Yuktanandana P, Meknavin S, Ngarmukos S, Tanpowpong T and Parkpian
V: Relationship of plasma and synovial fluid vascular endothelial
growth factor with radiographic severity in primary knee
osteoarthritis. Int Orthop. 38:1099–1104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim HR, Lee JH, Kim KW, Kim BM and Lee SH:
The relationship between synovial fluid VEGF and serum leptin with
ultrasonographic findings in knee osteoarthritis. Int J Rheum Dis.
19:233–240. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nagai T, Sato M, Kobayashi M, Yokoyama M,
Tani Y and Mochida J: Bevacizumab, an anti-vascular endothelial
growth factor antibody, inhibits osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res
Ther. 16:4272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nagai T, Sato M, Kutsuna T, Kokubo M,
Ebihara G, Ohta N and Mochida J: Intravenous administration of
anti-vascular endothelial growth factor humanized monoclonal
antibody bevacizumab improves articular cartilage repair. Arthritis
Res Ther. 12:R1782010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bouderlique T, Vuppalapati KK, Newton PT,
Li L, Barenius B and Chagin AS: Targeted deletion of Atg5 in
chondrocytes promotes age-related osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis.
75:627–631. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li YS, Zhang FJ, Zeng C, Luo W, Xiao WF,
Gao SG and Lei GH: Autophagy in osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine.
83:143–148. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Caramés B, Taniguchi N, Otsuki S, Blanco
FJ and Lotz M: Autophagy is a protective mechanism in normal
cartilage, and its aging-related loss is linked with cell death and
osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 62:791–801. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Borzì RM, Guidotti S, Minguzzi M, Facchini
A, Platano D, Trisolino G, Filardo G, Cetrullo S, D'Adamo S,
Stefanelli C, et al: Polyamine delivery as a tool to modulate stem
cell differentiation in skeletal tissue engineering. Amino Acids.
46:717–728. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang RT, Zhang C, Liu Y, Zhou HH and Li
ZB: Autophagy prior to chondrocyte cell death during the
degeneration of Meckel's cartilage. Anat Rec (Hoboken).
295:734–741. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Alvarez-García O, García-López E, Loredo
V, Gil-Peña H, Rodríguez-Suárez J, Ordóñez FA, Carbajo-Pérez E and
Santos F: Rapamycin induces growth retardation by disrupting
angiogenesis in the growth plate. Kidney Int. 78:561–568. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: Regulation of
mTORC1and its impact on gene expression at a glance. J Cell Sci.
126:1713–1719. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Howell JJ, Ricoult SJ, Ben-Sahra I and
Manning BD: A growing role for mTOR in promoting anabolic
metabolism. Biochem Soc Trans. 41:906–912. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Caramés B, Hasegawa A, Taniguchi N, Miyaki
S, Blanco FJ and Lotz M: Autophagy activation by rapamycin reduces
severity of experimental osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 71:575–581.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bohensky J, Leshinsky S, Srinivas V and
Shapiro IM: Chondrocyte autophagy is stimulated by HIF-1 dependent
AMPK activation and mTOR suppression. Pediatr Nephrol. 25:633–642.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Matsuzaki T, Matsushita T, Tabata Y, Saito
T, Matsumoto T, Nagai K, Kuroda R and Kurosaka M: Intra-articular
administration of gelatin hydrogels incorporating
rapamycin-micelles reduces the development of experimental
osteoarthritis in a murine model. Biomaterials. 35:9904–9911. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Takayama K, Kawakami Y, Kobayashi M, Greco
N, Cummins JH, Matsushita T, Kuroda R, Kurosaka M, Fu FH and Huard
J: Local intra-articular injection of rapamycin delays articular
cartilage degeneration in a murine model of osteoarthritis.
Arthritis Res Ther. 16:4822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huang MJ, Wang L, Jin DD, Zhang ZM, Chen
TY, Jia CH, Wang Y, Zhen XC, Huang B, Yan B, et al: Enhancement of
the synthesis of n-3 PUFAs infat-1 transgenic mice inhibits mTORC1
signalling and delays surgically induced osteoarthritis in
comparison with wild-type mice. Ann Rheum Dis. 73:1719–1727. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang Y, Vasheghani F, Li YH, Blati M,
Simeone K, Fahmi H, Lussier B, Roughley P, Lagares D, Pelletier JP,
et al: Cartilage-specific deletion of mTOR upregulates autophagy
and protects mice from osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 74:1432–1440.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Alvarez-Garcia O, Olmer M, Akagi R,
Akasaki Y, Fisch KM, Shen T, Su AI and Lotz MK: Suppression of
REDD1 in osteoarthritis cartilage, a novel mechanism for
dysregulated mTOR signaling and defective autophagy. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 24:1639–1647. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Dell'Accio F and Sherwood J: PPARγ/mTOR
signalling: Striking the right balance in cartilage homeostasis.
Ann Rheum Dis. 74:477–479. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chagin AS: Effectors of mTOR-autophagy
pathway: Targeting cancer, affecting the skeleton. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 28:1–7. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Shi J, Zhang C, Yi Z and Lan C: Explore
the variation of MMP3, JNK, p38 MAPKs, and autophagy at the early
stage of osteoarthritis. IUBMB Life. 68:293–302. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|