|
1
|
Zumla A, George A, Sharma V, Herbert RH;
Baroness Masham of Ilton, ; Oxley A and Oliver M: The WHO 2014
global tuberculosis report-further to go. Lancet Glob Health.
3:e10–e12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferreira LM: Gammadelta T cells: Innately
adaptive immune cells? Int Rev Immunol. 32:223–248. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
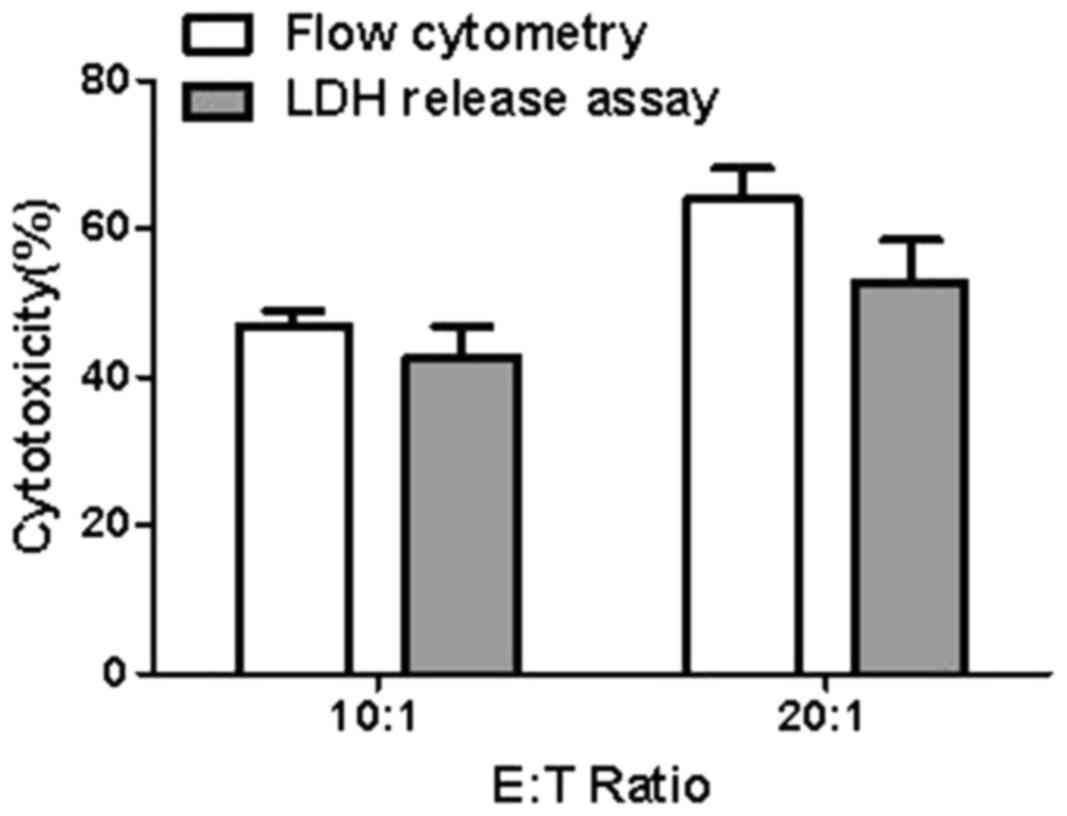
Born WK, Kemal Aydintug M and O'Brien RL:
Diversity of γδ T-cell antigens. Cell Mol Immunol. 10:13–20. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
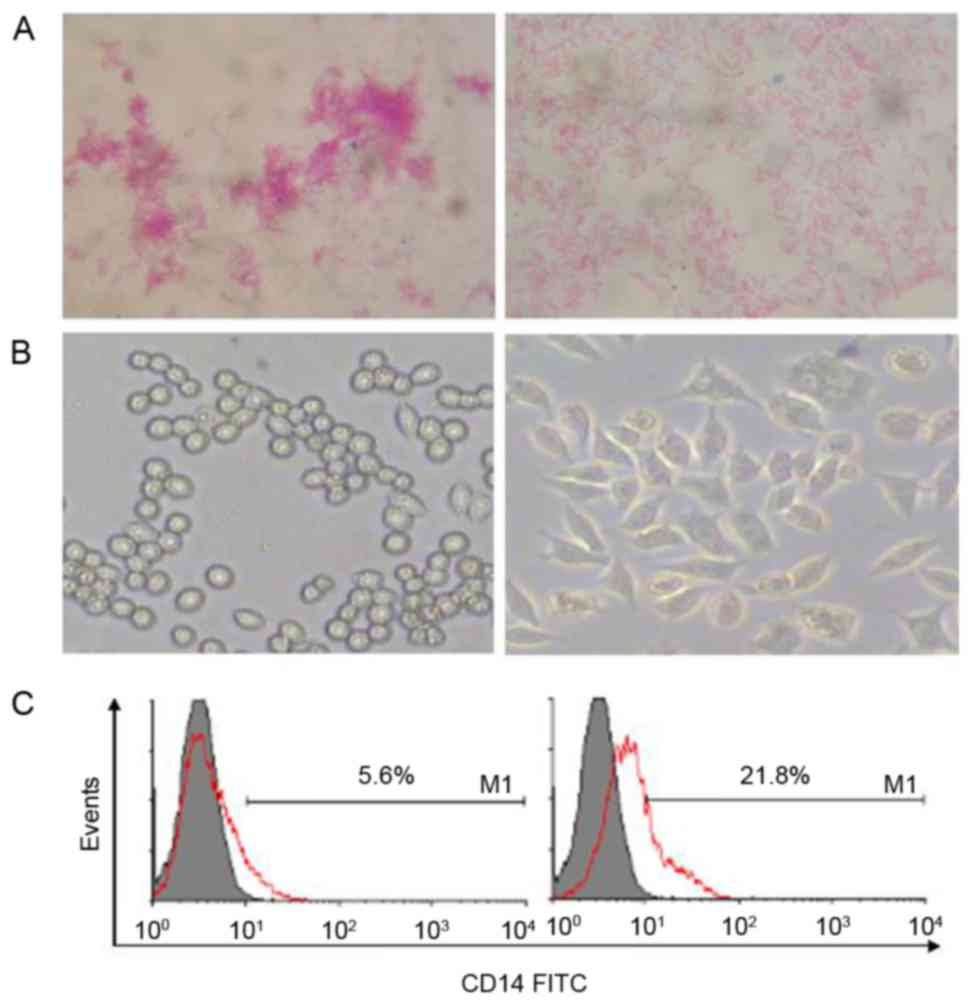
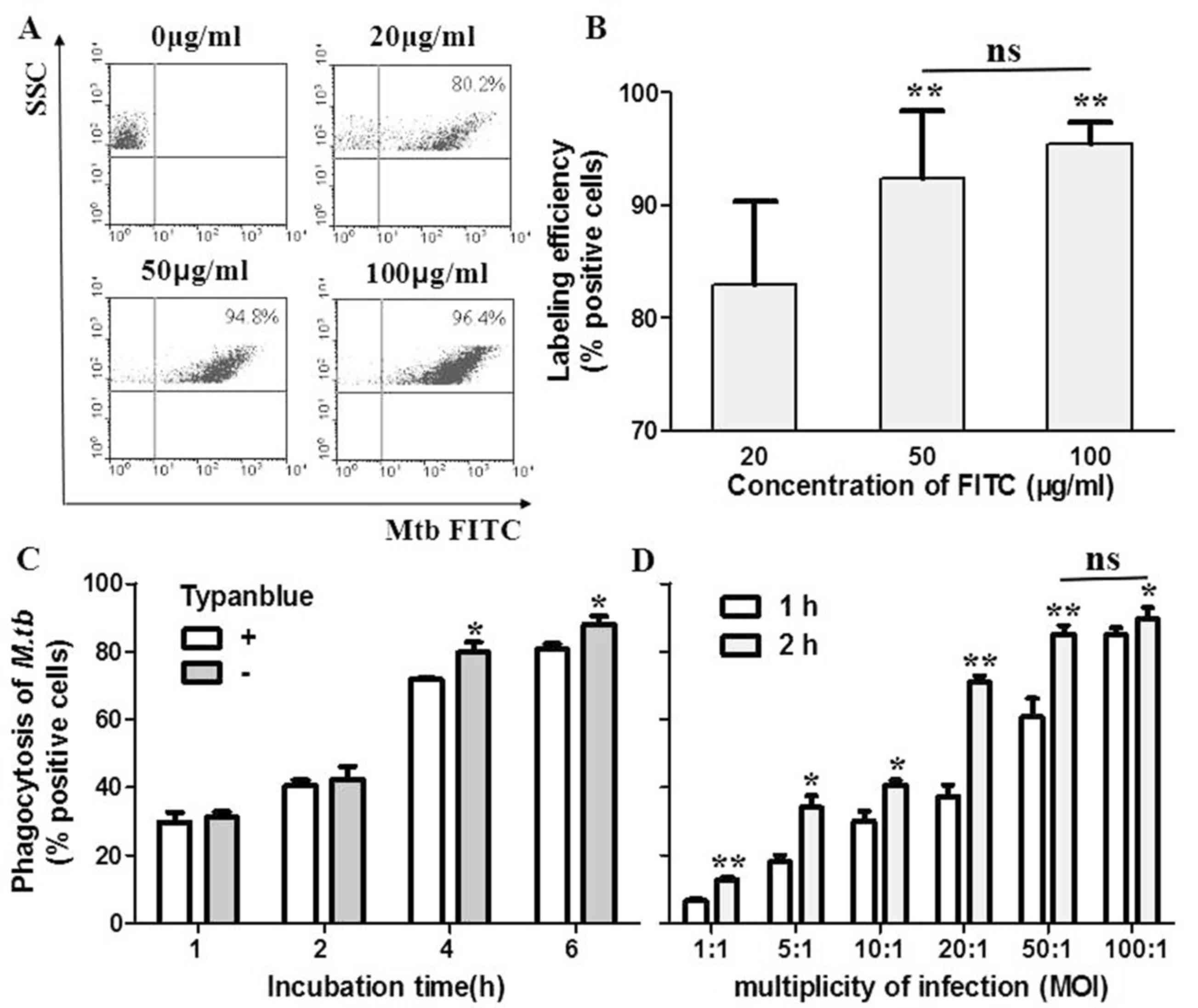
|
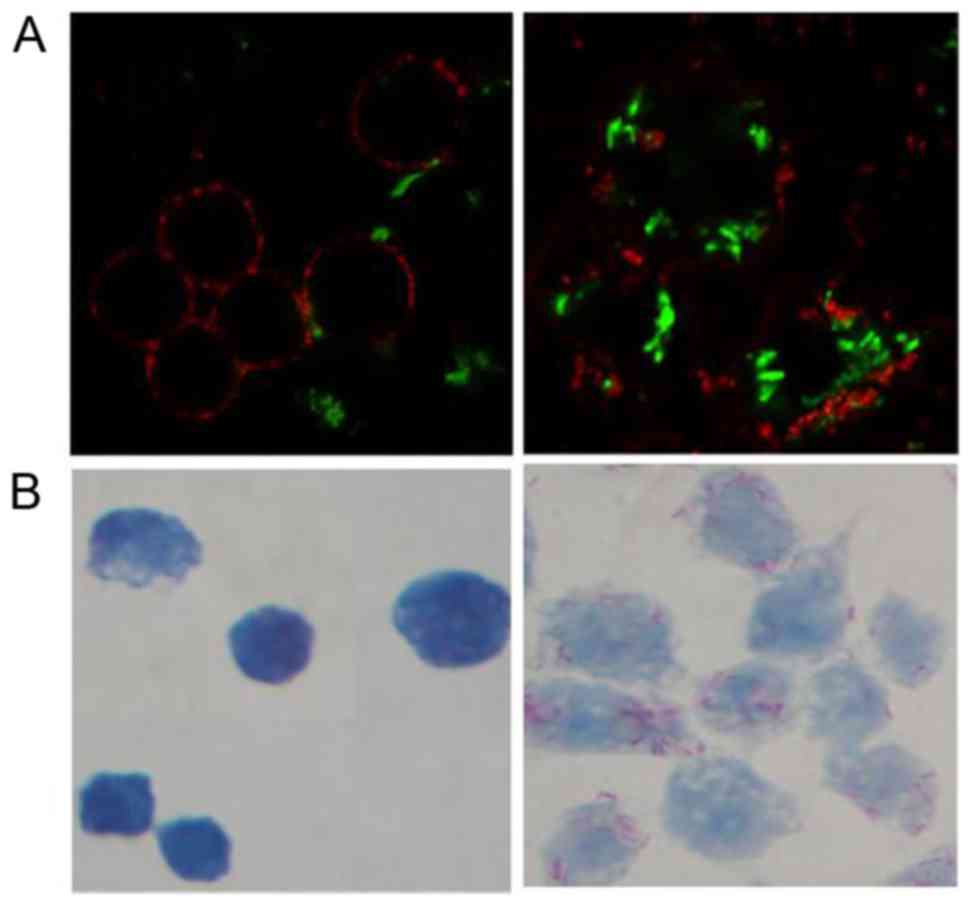
|
4
|
Baldwin CL and Telfer JC: The bovine model
for elucidating the role of γδ T cells in controlling infectious
diseases of importance to cattle and humans. Mol Immunol. 66:35–47.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Latha TS, Reddy MC, Durbaka PV, Rachamallu
A, Pallu R and Lomada D: γδ T cell-mediated immune responses in
disease and therapy. Front Immunol. 5:5712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Augustin A, Kubo RT and Sim GK: Resident
pulmonary lymphocytes expressing the gamma/delta T-cell receptor.
Nature. 340:239–241. 1989. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pechhold K, Wesch D, Schondelmaier S and
Kabelitz D: Primary activation of V gamma 9-expressing gamma delta
T cells by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Requirement for Th1-type CD4
T cell help and inhibition by IL-10. J Immunol. 152:4984–4992.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
El Daker S, Sacchi A, Montesano C, Altieri
AM, Galluccio G, Colizzi V, Martini F and Martino A: An abnormal
phenotype of lung Vγ9Vδ2 T cells impairs their responsiveness in
tuberculosis patients. Cell Immunol. 282:106–112. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zheng J, Liu Y, Lau YL and Tu W: γδ-T
cells: An unpolished sword in human anti-infection immunity. Cell
Mol Immunol. 10:50–57. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qin G, Liu Y, Zheng J, Xiang Z, Ng IH,
Malik Peiris JS, Lau YL and Tu W: Phenotypic and functional
characterization of human γδ T-cell subsets in response to
influenza A viruses. J Infect Dis. 205:1646–1653. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li H, Xiang Z, Feng T, Li J, Liu Y, Fan Y,
Lu Q, Yin Z, Yu M, Shen C and Tu W: Human Vγ9Vδ2-T cells
efficiently kill influenza virus-infected lung alveolar epithelial
cells. Cell Mol Immunol. 10:159–164. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qin G, Liu Y, Zheng J, Ng IH, Xiang Z, Lam
KT, Mao H, Li H, Peiris JS, Lau YL and Tu W: Type 1 responses of
human Vγ9Vδ2 T cells to influenza A viruses. J Virol.
85:10109–10116. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wallace M, Bartz SR, Chang WL, Mackenzie
DA, Pauza CD and Malkovsky M: Gamma delta T lymphocyte responses to
HIV. Clin Exp Immunol. 103:177–184. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mattarollo SR, Kenna T, Nieda M and Nicol
AJ: Chemotherapy and zoledronate sensitize solid tumour cells to
Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cell cytotoxicity. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
56:1285–1297. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bonneville M, Chen ZW, Déchanet-Merville
J, Eberl M, Fournié JJ, Jameson JM, Lopez RD, Massaia M and
Silva-Santos B: Chicago 2014–30 years of γδ T cells. Cell Immunol.
296:3–9. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Poccia F, Battistini L, Cipriani B,
Mancino G, Martini F, Gougeon ML and Colizzi V:
Phosphoantigen-reactive Vgamma9Vdelta2 T lymphocytes suppress in
vitro human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by
cell-released antiviral factors including CC chemokines. J Infect
Dis. 180:858–861. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Watanabe N, Narita M, Yokoyama A,
Sekiguchi A, Saito A, Tochiki N, Furukawa T, Toba K, Aizawa Y and
Takahashi M: Type I IFN-mediated enhancement of anti-leukemic
cytotoxicity of gammadelta T cells expanded from peripheral blood
cells by stimulation with zoledronate. Cytotherapy. 8:118–129.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Somanchi SS, McCulley KJ, Somanchi A, Chan
LL and Lee DA: A novel method for assessment of natural killer cell
cytotoxicity using image cytometry. PLoS One. 10:e01410742015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jang YY, Cho D, Kim SK, Shin DJ, Park MH,
Lee JJ, Shin MG, Shin JH, Suh SP and Ryang DW: An improved flow
cytometry-based natural killer cytotoxicity assay involving calcein
AM staining of effector cells. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 42:42–49.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peng MY, Wang ZH, Yao CY, Jiang LN, Jin
QL, Wang J and Li BQ: Interleukin 17-producing gamma delta T cells
increased in patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis. Cell Mol
Immunol. 5:203–208. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fuss IJ, Kanof ME, Smith PD and Zola H:
Isolation of whole mononuclear cells from peripheral blood and cord
blood. Curr Protoc Immunol. 7:Unit7.12009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hingley-Wilson SM, Sly LM, Reiner NE and
McMaster WR: The immunobiology of the mycobacterial infected
macrophage. Mod Aspects Immunobiol. 1:96–101. 2000.
|
|
23
|
Chanput W, Mes JJ and Wichers HJ: THP-1
cell line: An in vitro cell model for immune modulation approach.
Int Immunopharmacol. 23:37–45. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Daigneault M, Preston JA, Marriott HM,
Whyte MK and Dockrell DH: The identification of markers of
macrophage differentiation in PMA-stimulated THP-1 cells and
monocyte-derived macrophages. PLoS One. 5:e86682010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chanput W, Mes JJ, Savelkoul HF and
Wichers HJ: Characterization of polarized THP-1 macrophages and
polarizing ability of LPS and food compounds. Food Funct.
4:266–276. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chanput W, Reitsma M, Kleinjans L, Mes JJ,
Savelkoul HF and Wichers HJ: β-Glucans are involved in
immune-modulation of THP-1 macrophages. Mol Nutr Food Res.
56:822–833. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dong C, Zhao G, Zhong M, Yue Y, Wu L and
Xiong S: RNA sequencing and transcriptomal analysis of human
monocyte to macrophage differentiation. Gene. 519:279–287. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Thakur A, Zaman A, Hummel J, Jones K and
Hortelano G: Single-colour flow cytometric assay to determine NK
cell-mediated cytotoxicity and viability against non-adherent human
tumor cells. Biotechnol Lett. 34:447–453. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Richard J, Veillette M, Batraville LA,
Coutu M, Chapleau JP, Bonsignori M, Bernard N, Tremblay C, Roger M,
Kaufmann DE and Finzi A: Flow cytometry-based assay to study HIV-1
gp120 specific antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity responses.
J Virol Methods. 208:107–114. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wabnitz GH, Kirchgessner H and Samstag Y:
Imaging flow cytometry for multiparametric analysis of molecular
mechanism involved in the cytotoxicity of human CD8+
T-cells. J Cell Biochem. 118:2528–253. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|