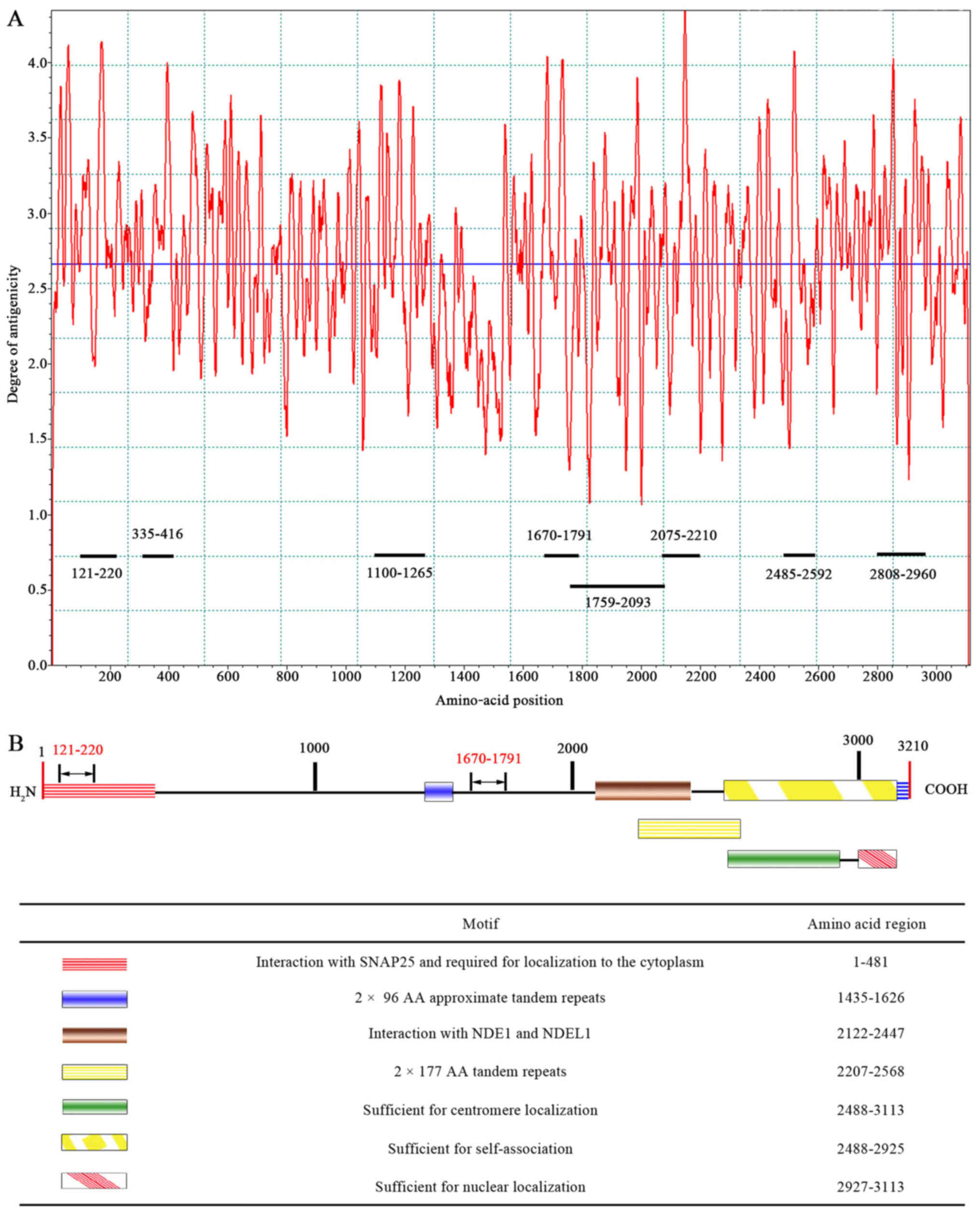
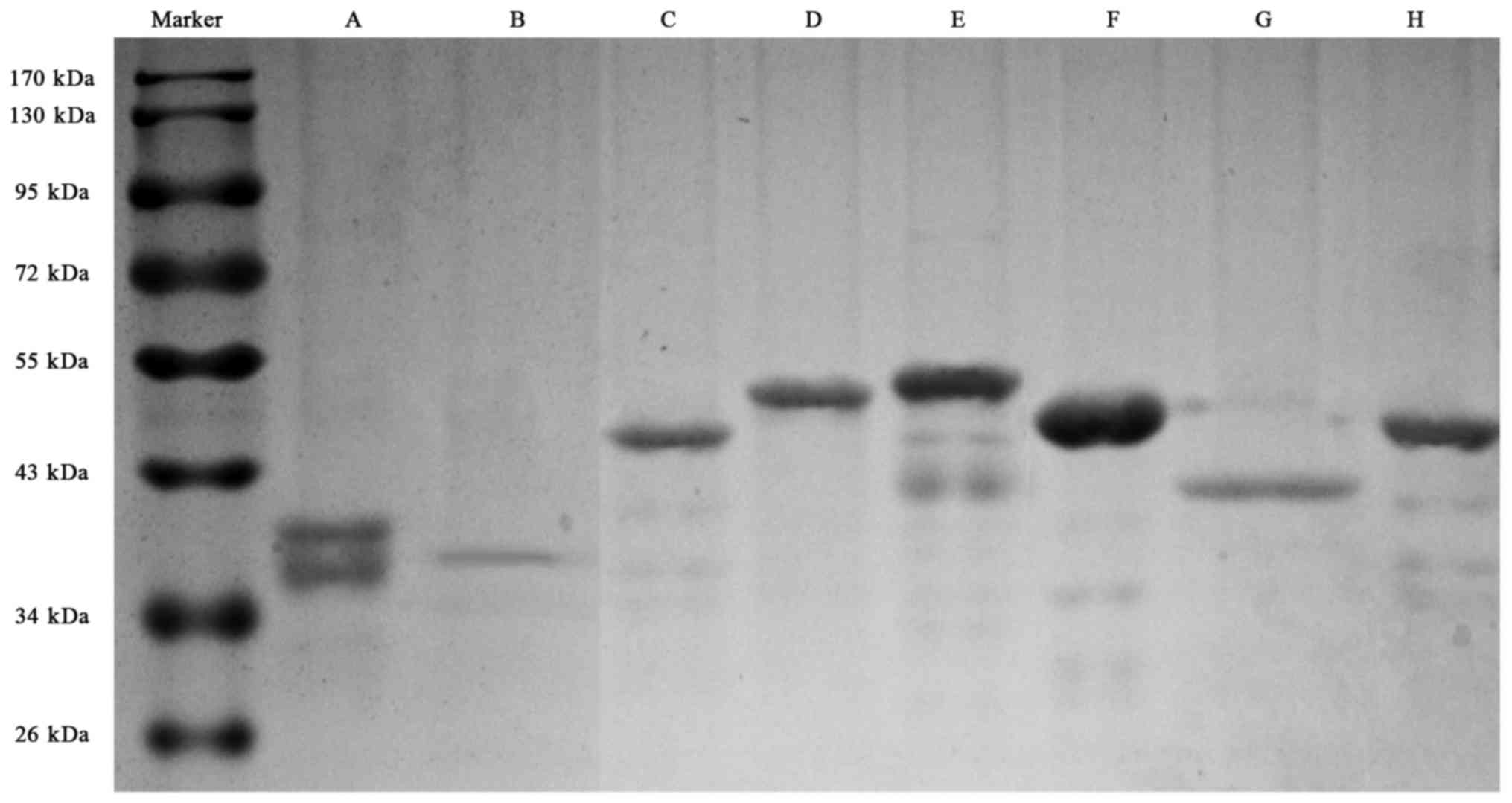
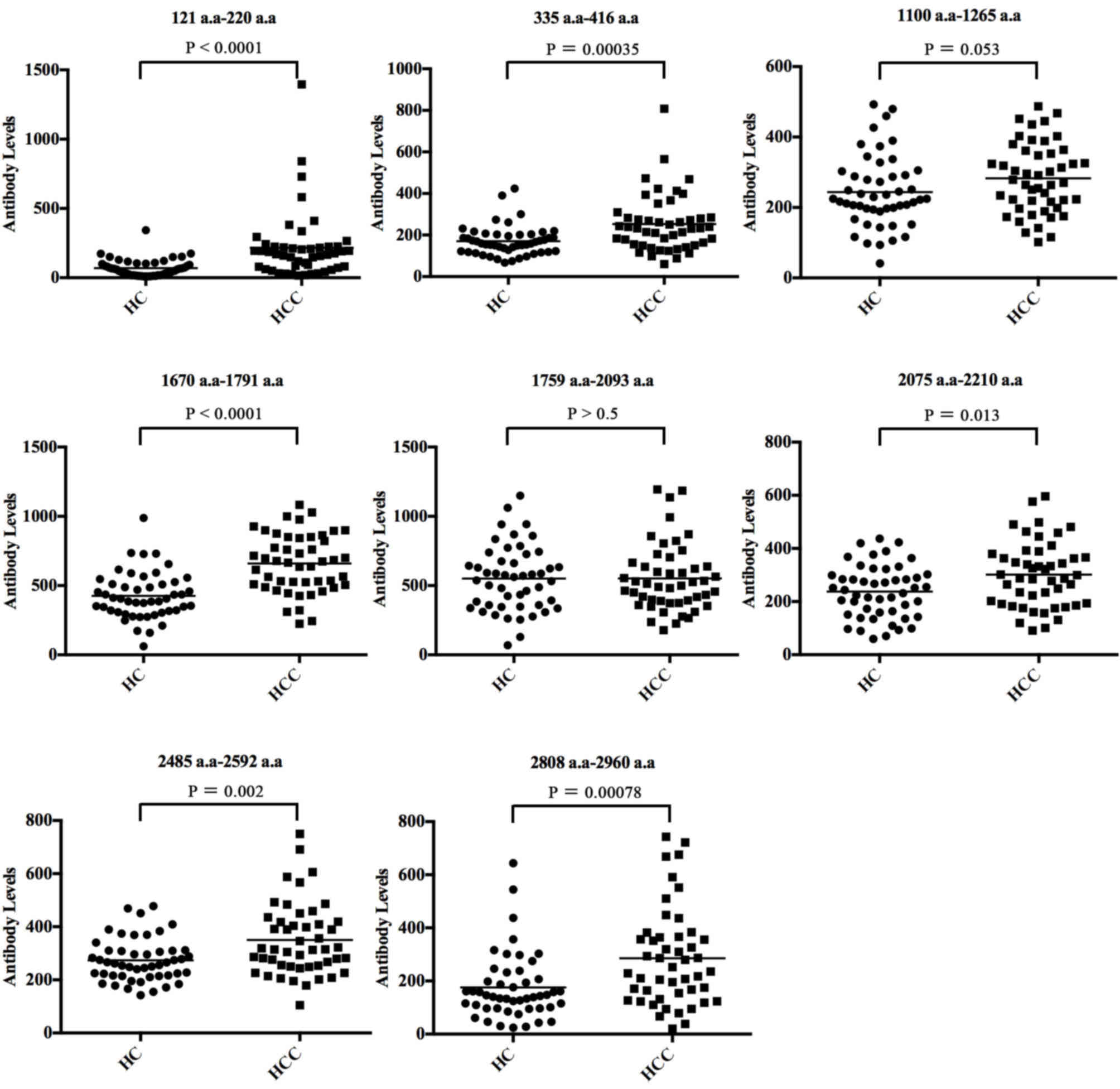
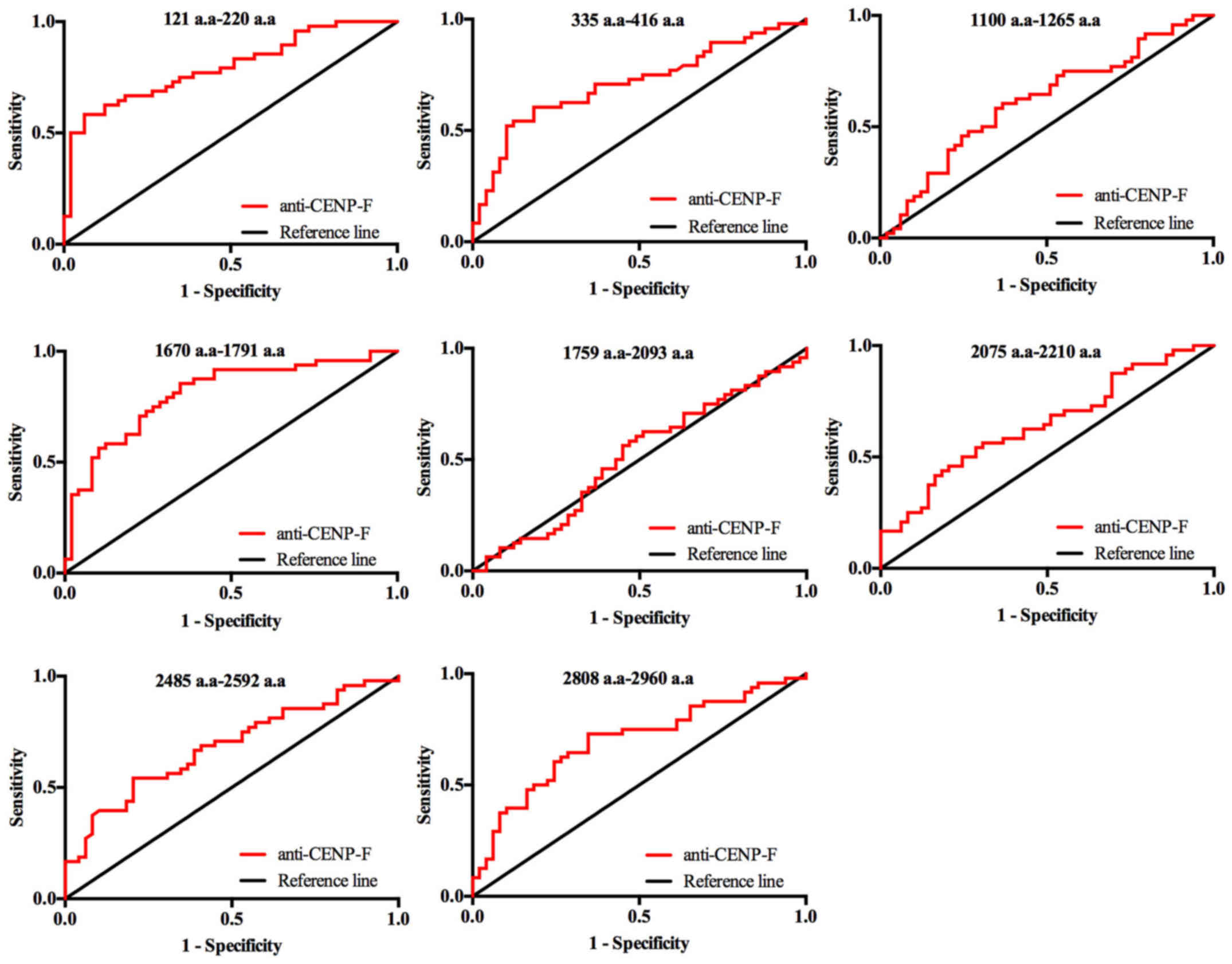
|
1
|
Venook AP, Papandreou C, Furuse J and de
Guevara LL: The incidence and epidemiology of hepatocellular
carcinoma: A global and regional perspective. Oncologist. 15 Suppl
4:S5–S13. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Colli A, Fraquelli M, Casazza G, Massironi
S, Colucci A, Conte D and Duca P: Accuracy of ultrasonography,
spiral CT, magnetic resonance and alpha-fetoprotein in diagnosing
hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol.
101:513–523. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Poon D, Anderson BO, Chen LT, Tanaka K,
Lau WY, Van Cutsem E, Singh H, Chow WC, Ooi LL, Chow P, et al:
Management of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia: Consensus statement
from the Asian oncology summit 2009. Lancet Oncol. 10:1111–1118.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marrero JA, Feng Z, Wang Y, Nguyen MH,
Befeler AS, Roberts LR, Reddy KR, Harnois D, Llovet JM, Normolle D,
et al: Alpha-fetoprotein, des-gamma carboxyprothrombin, and
lectin-bound alpha-fetoprotein in early hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 137:110–118. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Xu L and Xu W:
Alpha-fetoprotein-L3 and Golgi protein 73 may serve as candidate
biomarkers for diagnosing alpha-fetoprotein-negative hepatocellular
carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 9:123–129. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ji J, Wang H, Li Y, Zheng L, Yin Y, Zou Z,
Zhou F, Zhou W, Shen F and Gao C: Diagnostic evaluation of
Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin versus α-fetoprotein for hepatitis B
virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma in China: A large-scale,
multicentre study. PLoS One. 11:e01532272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang J, Shao C, Zhou Q, Zhu Y, Zhu J and
Tu C: Diagnostic accuracy of serum squamous cell carcinoma antigen
and squamous cell carcinoma antigen-immunoglobulin M for
hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Mol Clin Oncol.
3:1165–1171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shen Q, Fan J, Yang XR, Tan Y, Zhao W, Xu
Y, Wang N, Niu Y, Wu Z, Zhou J, et al: Serum DKK1 as a protein
biomarker for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A
large-scale, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 13:817–826. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lim TS, Kim DY, Han KH, Kim HS, Shin SH,
Jung KS, Kim BK, Kim SU, Park JY and Ahn SH: Combined use of AFP,
PIVKA-II and AFP-L3 as tumor markers enhances diagnostic accuracy
for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients. Scand J
Gastroenterol. 51:344–353. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu J, Wang ZJ, Chen LH and Dong WZ:
Diagnostic value of serum squamous cell carcinoma antigen for
hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 77:8–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Giannelli G, Fransvea E, Trerotoli P,
Beaugrand M, Marinosci F, Lupo L, Nkontchou G, Dentico P and
Antonaci S: Clinical validation of combined serological biomarkers
for improved hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis in 961 patients.
Clin Chim Acta. 383:147–152. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Marrero JA, Romano PR, Nikolaeva O, Steel
L, Mehta A, Fimmel CJ, Comunale MA, D'Amelio A, Lok AS and Block
TM: GP73, a resident Golgi glycoprotein, is a novel serum marker
for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 43:1007–1012. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hong Y: Autoantibodies against
tumor-associated antigens for detection of hepatocellular
carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 7:1581–1585. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang JY, Zhu W, Imai H, Kiyosawa K, Chan
EK and Tan EM: De-novo humoral immune responses to
cancer-associated autoantigens during transition from chronic liver
disease to hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Exp Immunol. 125:3–9.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dai Y, Liu L, Zeng T, Zhu YH, Li J, Chen
L, Li Y, Yuan YF, Ma S and Guan XY: Characterization of the
oncogenic function of centromere protein F in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 436:711–718. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu X, Mancini MA, Chang KH, Liu CY, Chen
CF, Shan B, Jones D, Yang-Feng TL and Lee WH: Characterization of a
novel 350-kilodalton nuclear phosphoprotein that is specifically
involved in mitotic-phase progression. Mol Cell Biol. 15:5017–5029.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ma L, Zhao X and Zhu X: Mitosin/CENP-F in
mitosis, transcriptional control and differentiation. J Biomed Sci.
13:205–213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Varis A, Salmela AL and Kallio MJ: Cenp-F
(mitosin) is more than a mitotic marker. Chromosoma. 115:288–295.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu X, Ding L and Pei G: Carboxyl terminus
of mitosin is sufficient to confer spindle pole localization. J
Cell Biochem. 66:441–449. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
The national center for biotechnology
information database. http://www/uniprot.org/uniprot/P49454
|
|
22
|
Hong Y, Long J, Li H, Chen S, Liu Q, Zhang
B, He X, Wang Y, Li H, Li Y, et al: An analysis of immunoreactive
signatures in early stage hepatocellular carcinoma. EBioMedicine.
2:438–446. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rattner JB, Rees J, Whitehead CM, Casiano
CA, Tan EM, Humbel RL, Conrad K and Fritzler MJ: High frequency of
neoplasia in patients with autoantibodies to centromere protein
CENP-F. Clin Invest Med. 20:308–319. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Welner S, Trier NH, Houen G and Hansen PR:
Identification and mapping of a linear epitope of centromere
protein F using monoclonal antibodies. J Pept Sci. 19:95–101. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|