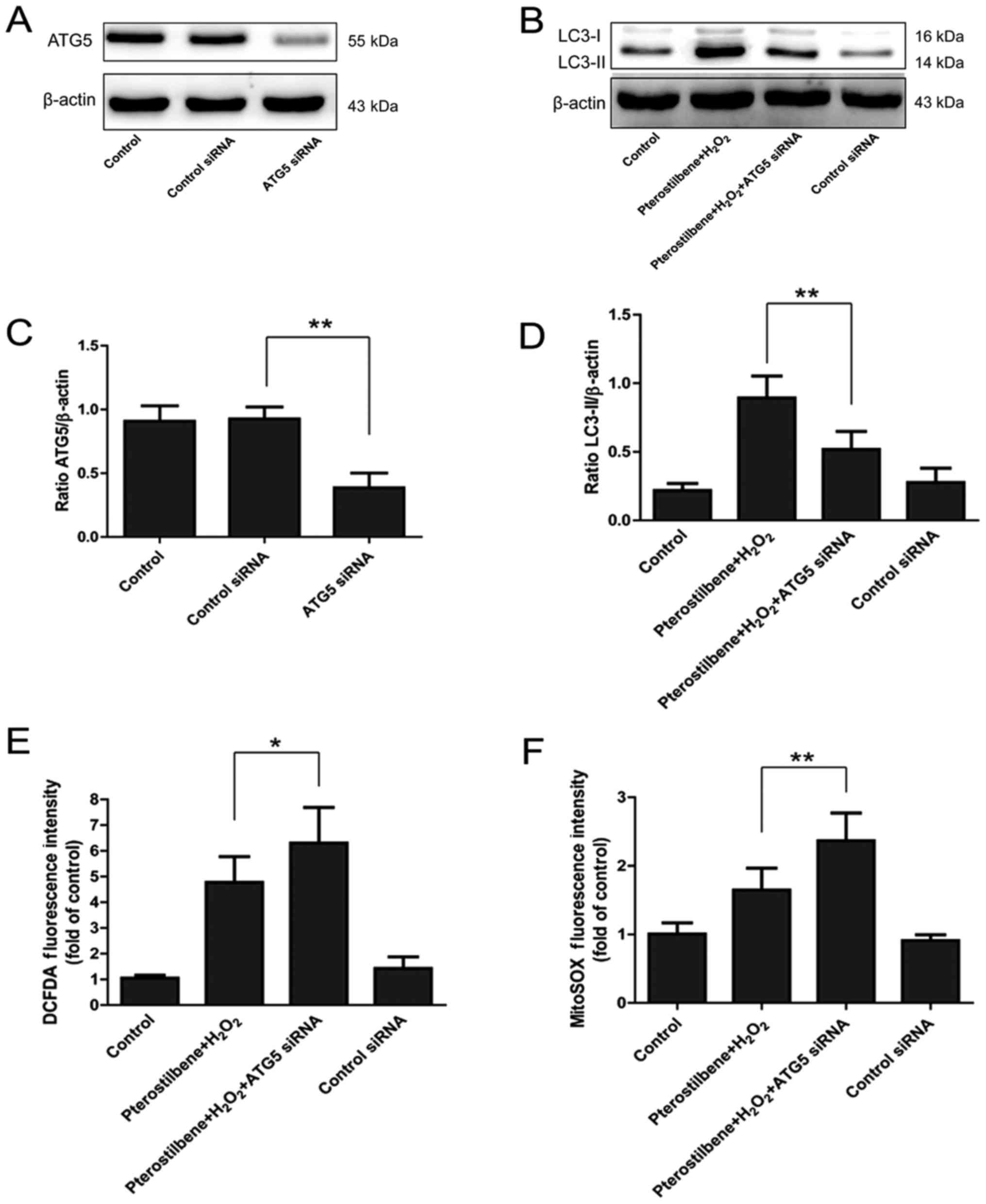
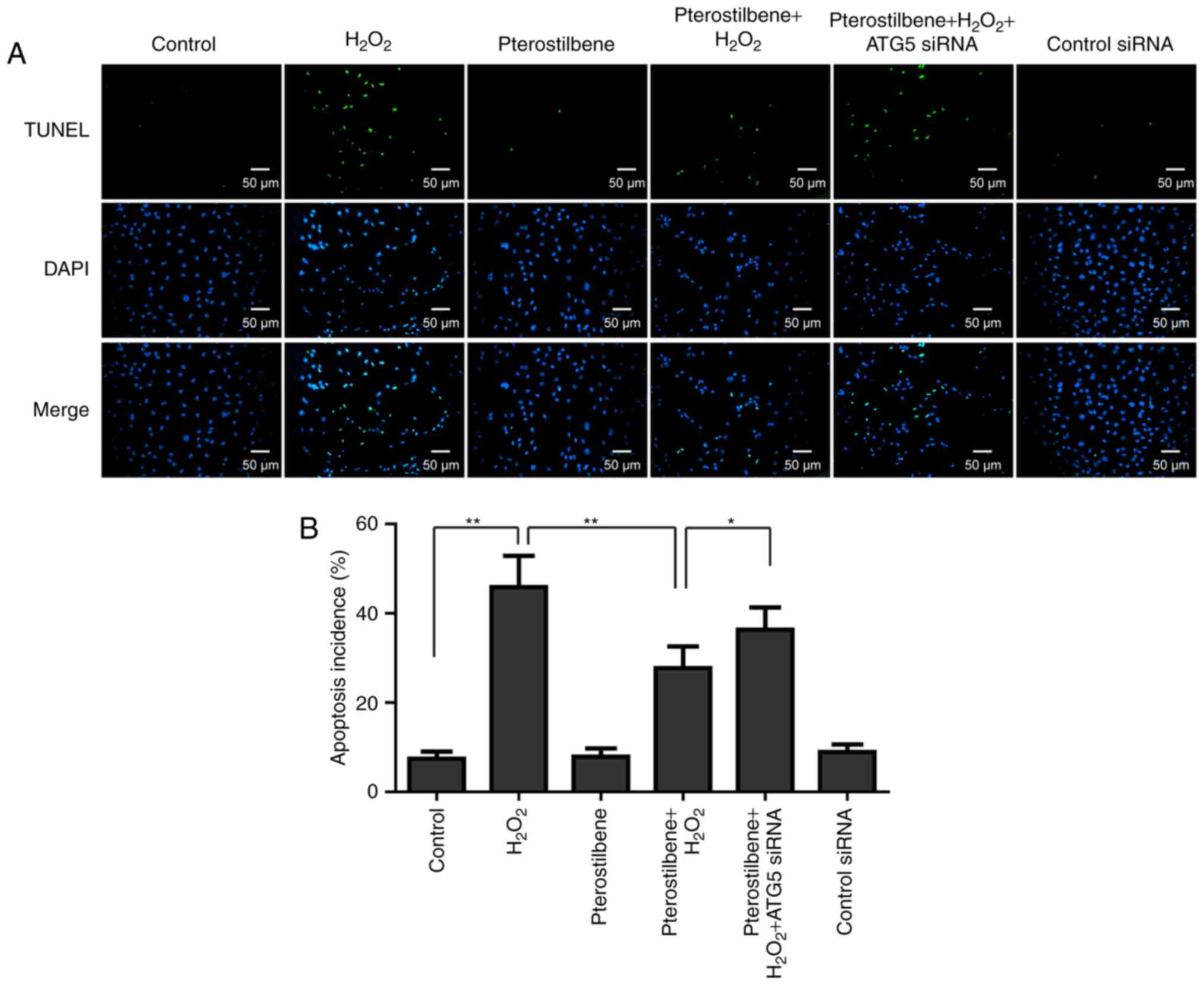
|
1
|
Chen HC, Fong TH, Lee AW and Chiu WT:
Autophagy is activated in injured neurons and inhibited by
methylprednisolone after experimental spinal cord injury. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 37:470–475. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang JF, Li Y, Song JN and Pang HG: Role
of hydrogen sulfide in secondary neuronal injury. Neurochem Int.
64:37–47. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jia Z, Zhu H, Li J, Wang X, Misra H and Li
Y: Oxidative stress in spinal cord injury and antioxidant-based
intervention. Spinal Cord. 50:264–274. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu D, Liu J, Sun D and Wen J: The time
course of hydroxyl radical formation following spinal cord injury:
The possible role of the iron-catalyzed Haber-Weiss reaction. J
Neurotrauma. 21:805–816. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Remsberg CM, Yáñez JA, Ohgami Y,
Vega-Villa KR, Rimando AM and Davies NM: Pharmacometrics of
pterostilbene: Preclinical pharmacokinetics and metabolism,
anticancer, antiinflammatory, antioxidant and analgesic activity.
Phytother Res. 22:169–179. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li D, Song T, Yang L, Wang X, Yang C and
Jiang Y: Neuroprotective actions of pterostilbene on
hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats through upregulation
of heme oxygenase-1. Int J Dev Neurosci. 54:22–31. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou Y, Zhang XM, Ma A, Zhang YL, Chen YY,
Zhou H, Li WJ and Jin X: Orally administrated pterostilbene
attenuates acute cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in a dose-
and time-dependent manner in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav.
135:199–209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang LB, Lee S, Wang Y, Xu QT, Meng DH
and Zhang J: Adipose-derived stem cells induce autophagic
activation and inhibit catabolic response to pro-inflammatory
cytokines in rat chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
24:1071–1081. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiang L, Yuan F, Yin X and Dong J:
Responses and adaptations of intervertebral disc cells to
microenvironmental stress: A possible central role of autophagy in
the adaptive mechanism. Connect Tissue Res. 55:311–321. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Su M, Guan H, Zhang F, Gao Y, Teng X and
Yang W: HDAC6 regulates the chaperone-mediated autophagy to prevent
oxidative damage in injured neurons after experimental spinal cord
injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:72637362016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang L, Cui L, Zhou G, Jing H, Guo Y and
Sun W: Pterostilbene, a natural small-molecular compound, promotes
cytoprotective macroautophagy in vascular endothelial cells. J Nutr
Biochem. 24:903–911. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ko CP, Lin CW, Chen MK, Yang SF, Chiou HL
and Hsieh MJ: Pterostilbene induce autophagy on human oral cancer
cells through modulation of Akt and mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathway. Oral Oncol. 51:593–601. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Anderson KN, Potter AC, Piccenna LG, Quah
AK, Davies KE and Cheema SS: Isolation and culture of motor neurons
from the newborn mouse spinal cord. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc.
12:132–136. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fatima G, Sharma VP, Das SK and Mahdi AA:
Oxidative stress and antioxidative parameters in patients with
spinal cord injury: Implications in the pathogenesis of disease.
Spinal Cord. 53:3–6. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
McEwen ML, Sullivan PG and Springer JE:
Pretreatment with the cyclosporin derivative, NIM811, improves the
function of synaptic mitochondria following spinal cord contusion
in rats. J Neurotrauma. 24:613–624. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Subramanian L, Youssef S, Bhattacharya S,
Kenealey J, Polans AS and van Ginkel PR: Resveratrol: Challenges in
translation to the clinic-a critical discussion. Clin Cancer Res.
16:5942–5948. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang L, Zhou G, Song W, Tan X, Guo Y,
Zhou B, Jing H, Zhao S and Chen L: Pterostilbene protects vascular
endothelial cells against oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced
apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Apoptosis. 17:25–36. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hall ED: Lipid peroxidation. Adv Neurol.
71:247–258. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fariss MW, Chan CB, Patel M, Van Houten B
and Orrenius S: Role of mitochondria in toxic oxidative stress. Mol
Interv. 5:94–111. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang B, Liu H, Yue L, Li X, Zhao L, Yang
X, Wang X, Yang Y and Qu Y: Neuroprotective effects of
pterostilbene against oxidative stress injury: Involvement of
nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 pathway. Brain Res.
1643:70–79. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang Y, Fan C, Wang B, Ma Z, Wang D, Gong
B, Di S, Jiang S, Li Y, Li T, et al: Pterostilbene attenuates high
glucose-induced oxidative injury in hippocampal neuronal cells by
activating nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1863:827–837. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang C, Liang CC, Bian ZC, Zhu Y and Guan
JL: FIP200 is required for maintenance and differentiation of
postnatal neural stem cells. Nature Neurosci. 16:532–542. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Taguchi K, Fujikawa N, Komatsu M, Ishii T,
Unno M, Akaike T, Motohashi H and Yamamoto M: Keap1 degradation by
autophagy for the maintenance of redox homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 109:pp. 13561–13566. 2012; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao H, Chen S, Gao K, Zhou Z, Wang C,
Shen Z, Guo Y, Li Z, Wan Z, Liu C and Mei X: Resveratrol protects
against spinal cord injury by activating autophagy and inhibiting
apoptosis mediated by the SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway.
Neuroscience. 348:241–251. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fang B, Qin M, Li Y, Li X, Tan W, Zhang Y
and Ma H: Electroacupuncture preconditioning and postconditioning
inhibit apoptosis and neuroinflammation induced by spinal cord
ischemia reperfusion injury through enhancing autophagy in rats.
Neurosci Lett. 642:136–141. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|