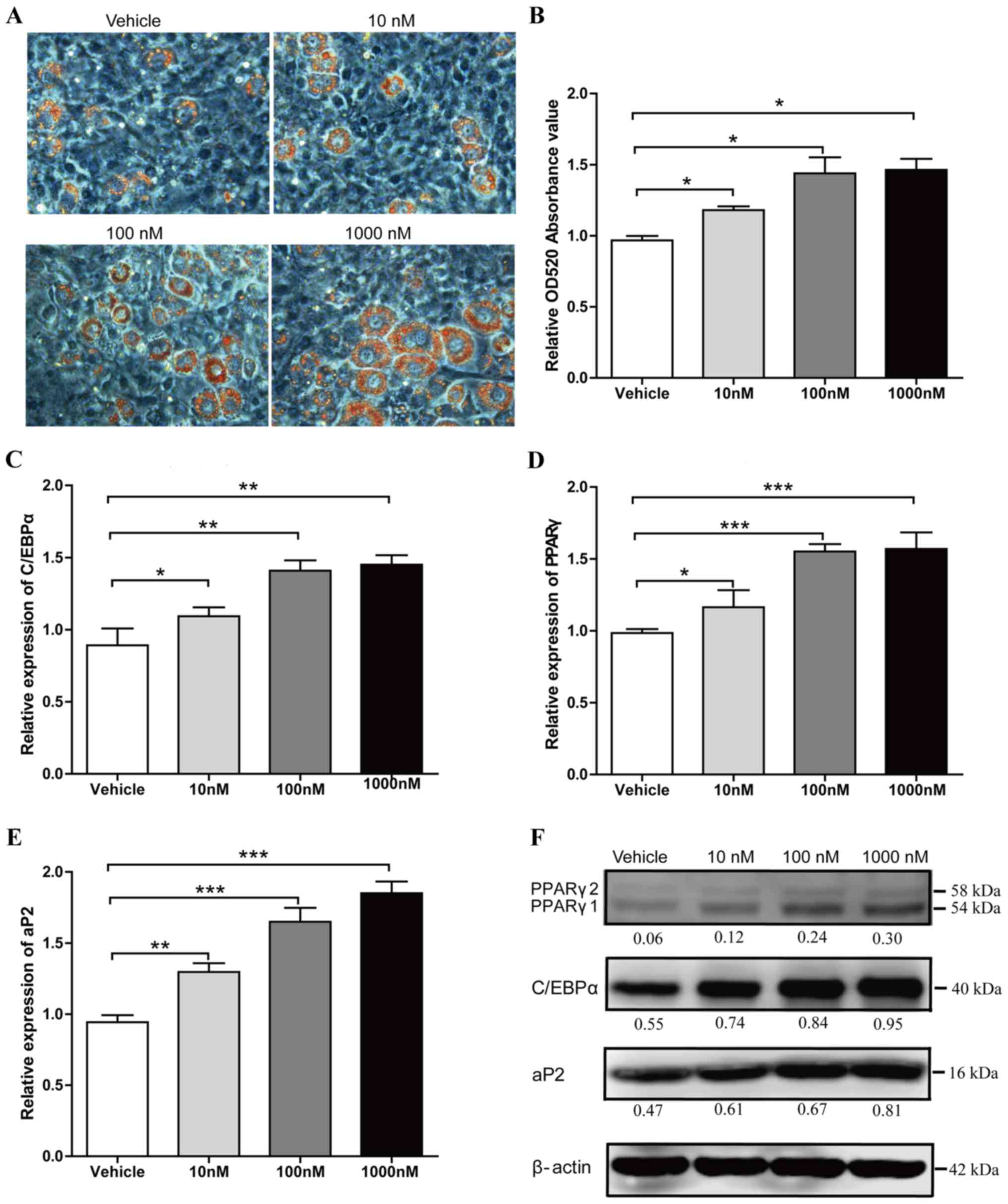
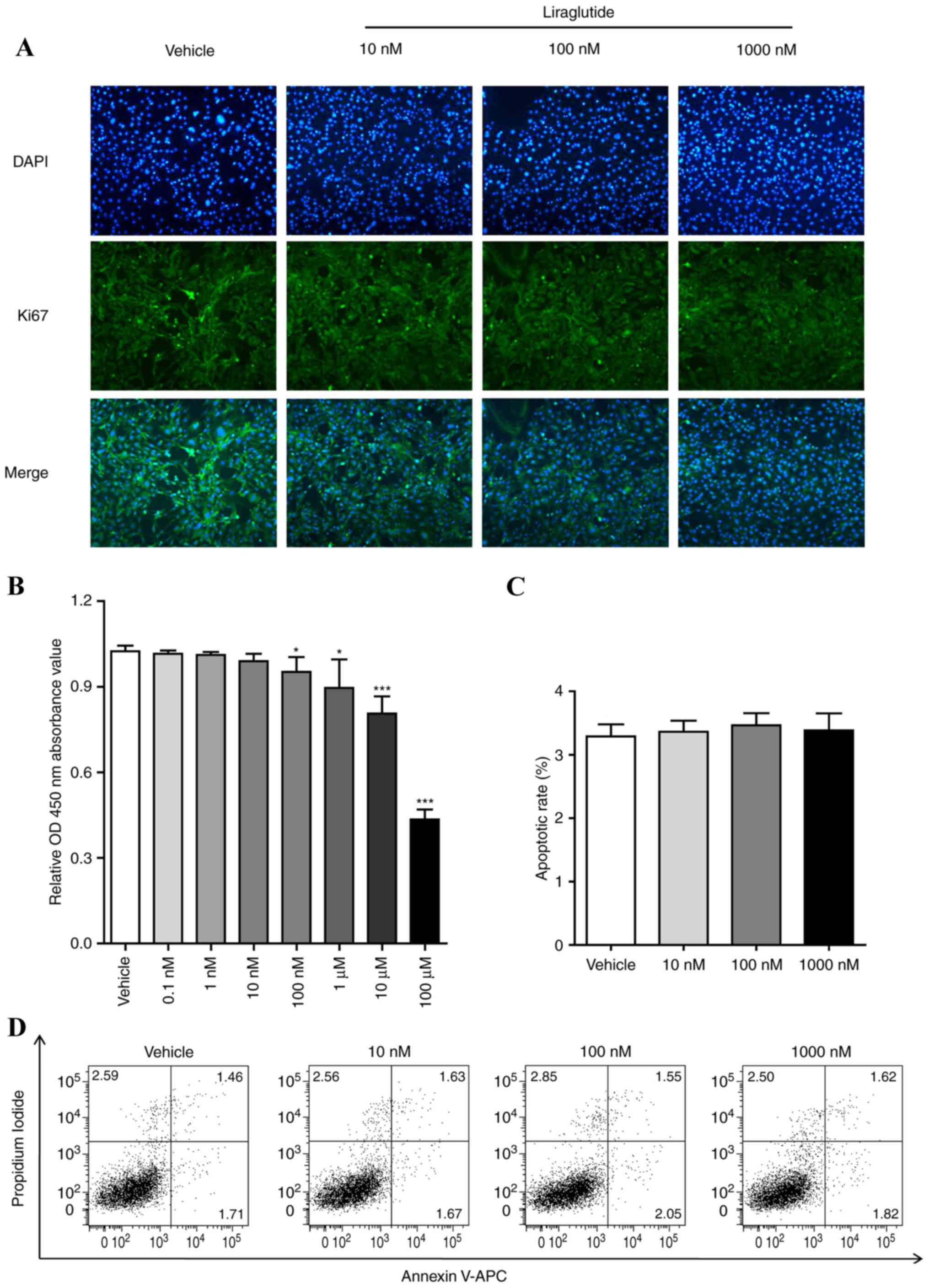
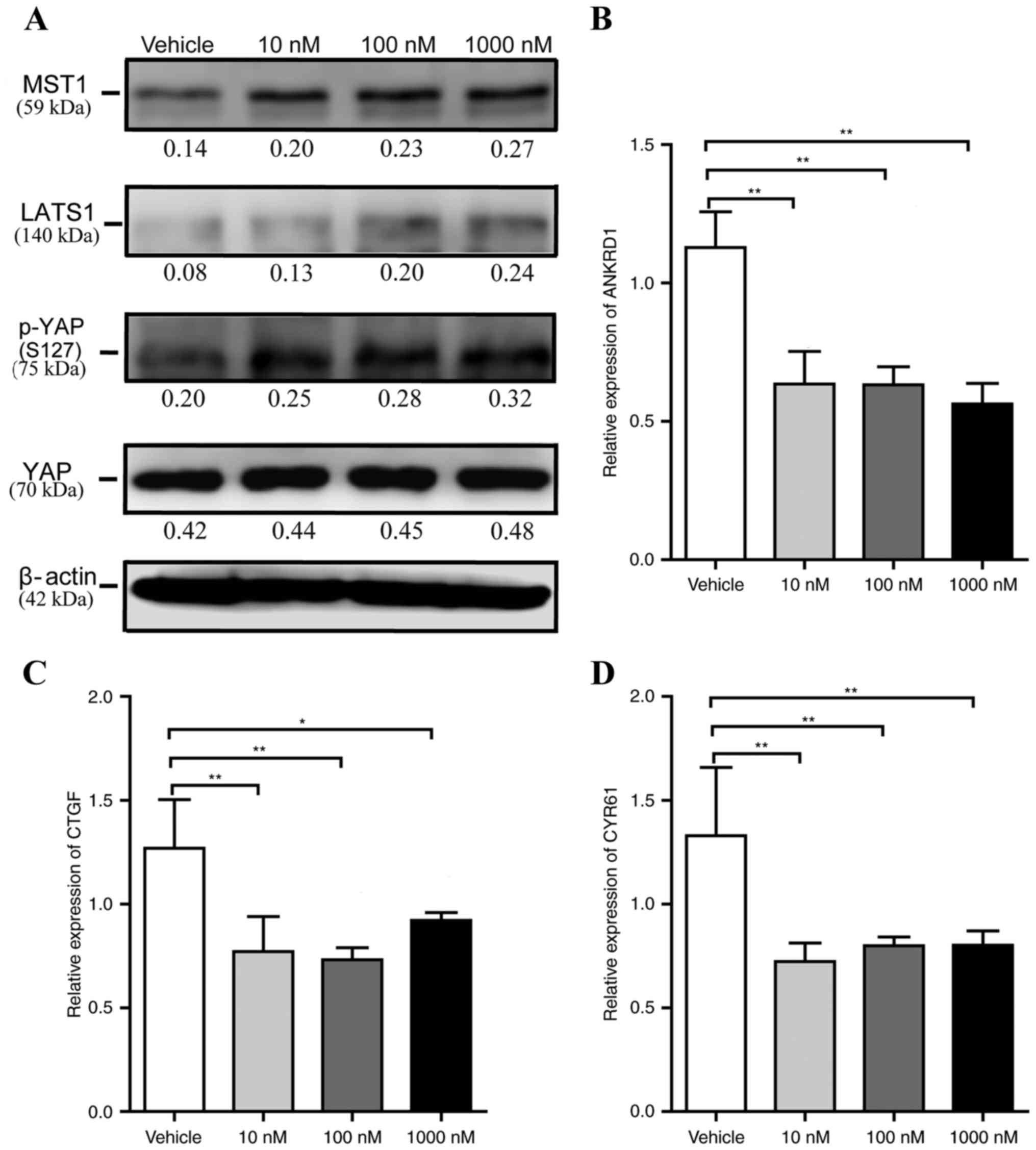
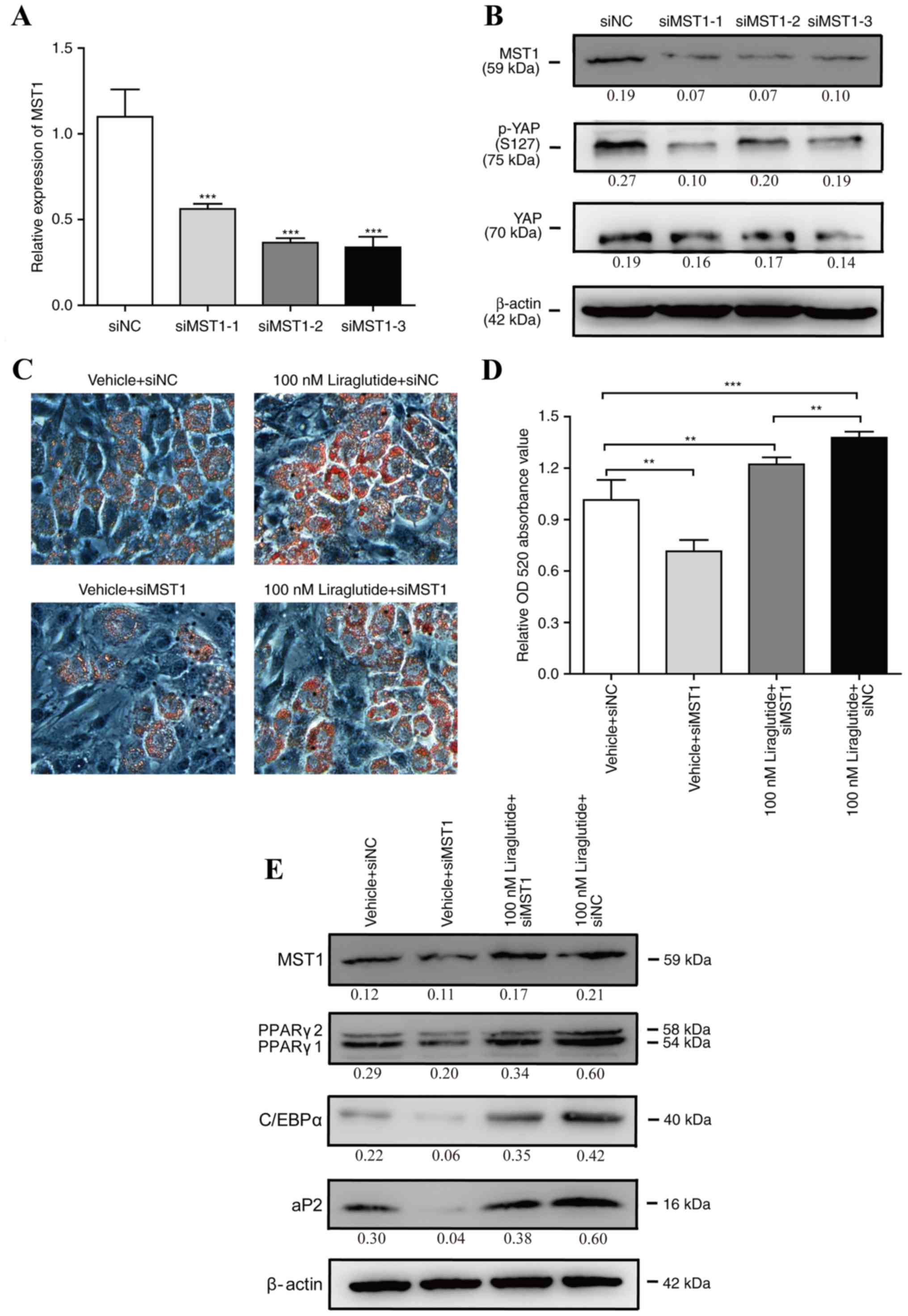
|
1
|
Yu D, He Y, Guo Q, Fang H, Xu X, Fang Y,
Li J and Zhao L: Trends of energy and nutrients intake among
Chinese population in 2002–2012. J Hygiene Res. 45:527–533.
2016.
|
|
2
|
Zhang N, Du SM and Ma GS: Current
lifestyle factors that increase risk of T2DM in China. Eur J Clin
Nutr. 71:832–838. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Flier JS: Obesity wars: Molecular progress
confronts an expanding epidemic. Cell. 116:337–350. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V and
Czech MP: Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin
resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:367–377.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
de Ferranti S and Mozaffarian D: The
perfect storm: Obesity, adipocyte dysfunction, and metabolic
consequences. Clin Chem. 54:945–955. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao B, Li L, Lei Q and Guan KL: The
Hippo-YAP pathway in organ size control and tumorigenesis: An
updated version. Genes Dev. 24:862–874. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu FX and Guan KL: The Hippo pathway:
Regulators and regulations. Genes Dev. 27:355–371. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y, Park HW, Jewell JL, Chen Q, Deng
Y, Pan D, Taylor SS, Lai ZC and Guan KL: Protein kinase A activates
the Hippo pathway to modulate cell proliferation and
differentiation. Genes Dev. 27:1223–1232. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao B, Panupinthu N, Jewell JL, Lian I,
Wang LH, Zhao J, Yuan H, Tumaneng K, Li H, Fu XD, et al: Regulation
of the Hippo-YAP pathway by G-protein-coupled receptor signaling.
Cell. 150:780–791. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
An Y, Kang Q, Zhao Y, Hu X and Li N: Lats2
modulates adipocyte proliferation and differentiation via hippo
signaling. PLoS One. 8:e720422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Seo E, Basu-Roy U, Gunaratne PH, Coarfa C,
Lim DS, Basilico C and Mansukhani A: SOX2 regulates YAP1 to
maintain stemness and determine cell fate in the osteo-adipo
lineage. Cell Rep. 3:2075–2087. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen SN, Gurha P, Lombardi R, Ruggiero A,
Willerson JT and Marian AJ: The hippo pathway is activated and is a
causal mechanism for adipogenesis in arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy.
Circ Res. 114:454–468. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ali AT, Hochfeld WE, Myburgh R and Pepper
MS: Adipocyte and adipogenesis. Eur J Cell Biol. 92:229–236. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Russell-Jones D: Molecular,
pharmacological and clinical aspects of liraglutide, a once-daily
human GLP-1 analogue. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 297:137–140. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Challa TD, Beaton N, Arnold M, Rudofsky G,
Langhans W and Wolfrum C: Regulation of adipocyte formation by
GLP-1/GLP-1R signaling. J Biol Chem. 287:6421–6430. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang J, Ren J, Song J, Liu F, Wu C, Wang
X, Gong L, Li W, Xiao F, Yan F, et al: Glucagon-like peptide 1
regulates adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Int J Mol Med.
31:1429–1435. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu R, Li N, Lin Y, Wang M, Peng Y, Lewi K
and Wang Q: Glucagon like peptide-1 promotes adipocyte
differentiation via the Wnt4 mediated sequestering of beta-catenin.
PLoS One. 11:e01602122016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu E, Yang Y, Zhang J, Li Y, Li C, Chen L
and Sun B: Liraglutide suppresses obesity and induces brown
fat-like phenotype via Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase mediated pathway in
vivo and in vitro. Oncotarget. 7:81077–81089. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Arsenijevic T, Grégoire F, Delforge V,
Delporte C and Perret J: Murine 3T3-L1 adipocyte cell
differentiation model: Validated reference genes for qPCR gene
expression analysis. PLoS One. 7:e375172012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu E, Wang X, Zheng B, Wang Q, Hao J,
Chen S, Zhao Q, Zhao L, Wu Z and Yin Z: miR-20b suppresses Th17
differentiation and the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis by targeting RORγt and STAT3. J Immunol.
192:5599–5609. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Astrup A, Rössner S, Van Gaal L, Rissanen
A, Niskanen L, Al Hakim M, Madsen J, Rasmussen MF and Lean ME;
NN8022-1807 Study Group, : Effects of liraglutide in the treatment
of obesity: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Lancet. 374:1606–1616. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ng SY and Wilding JP: Liraglutide in the
treatment of obesity. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 14:1215–1224. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lefterova MI and Lazar MA: New
developments in adipogenesis. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 20:107–114.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gumbiner BM and Kim NG: The Hippo-YAP
signaling pathway and contact inhibition of growth. J Cell Sci.
127:709–717. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Park BH, Kim DS, Won GW, Jeon HJ, Oh BC,
Lee Y, Kim EG and Lee YH: Mammalian ste20-like kinase and SAV1
promote 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation by activation of PPARγ.
PLoS One. 7:e309832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|