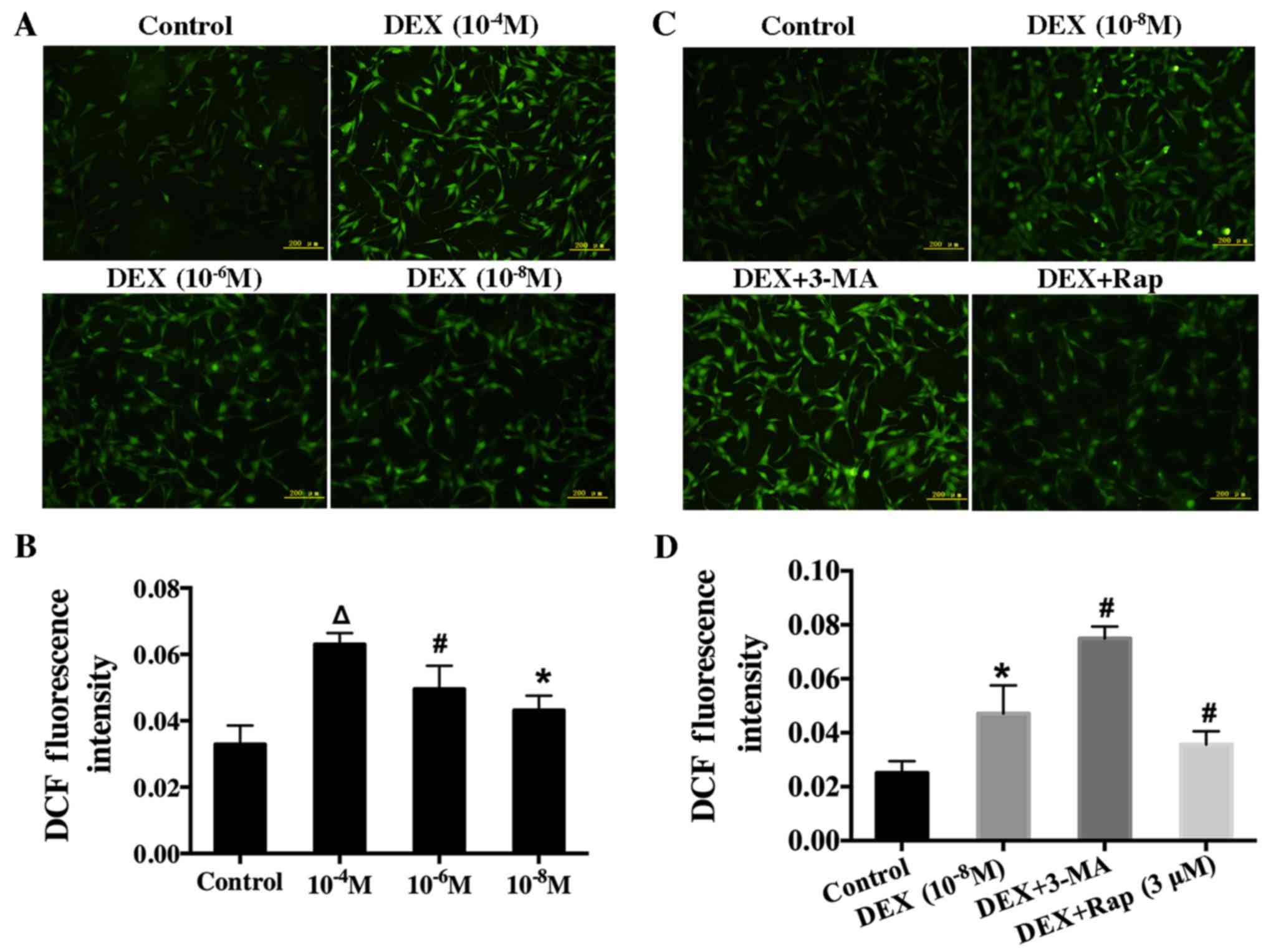
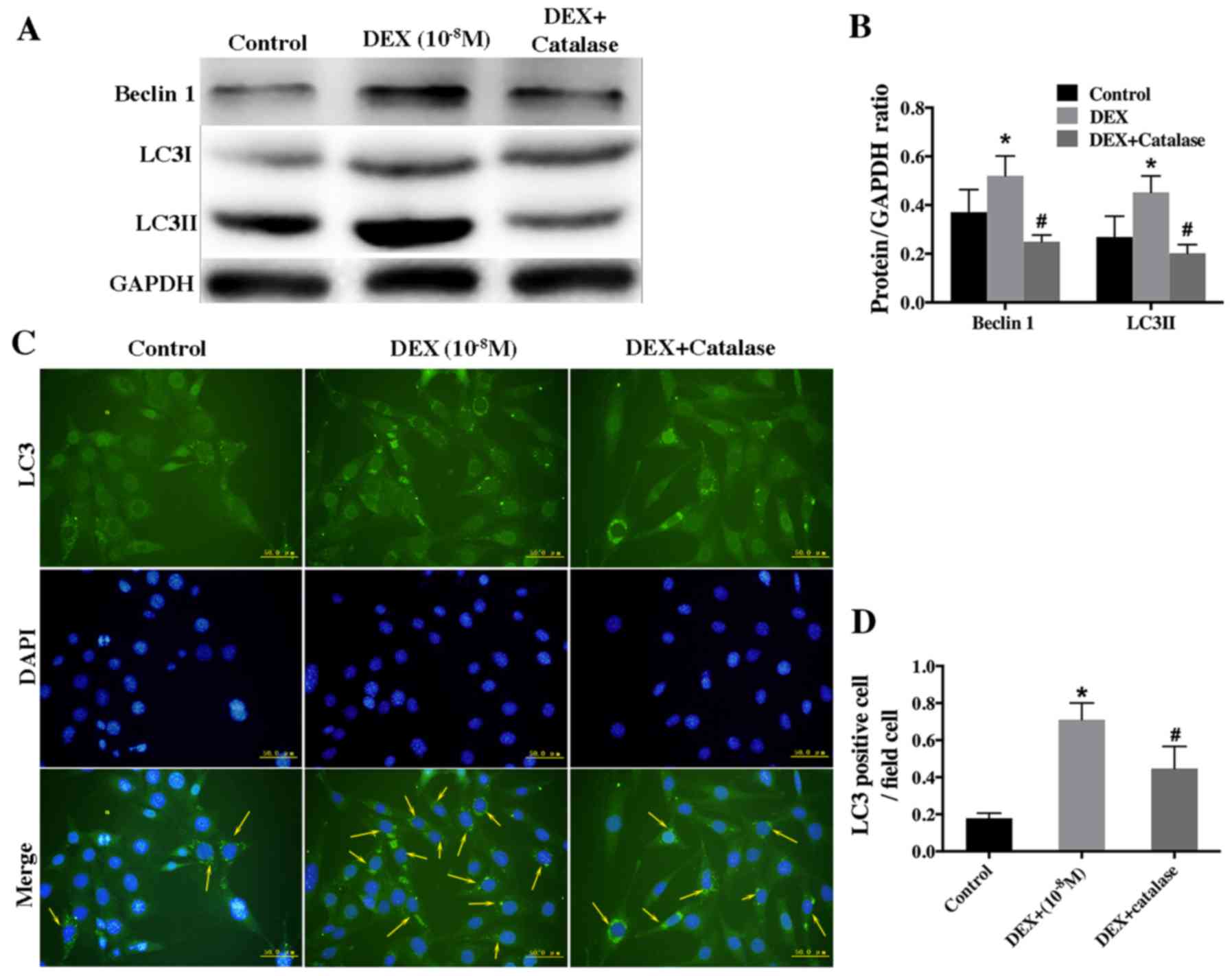
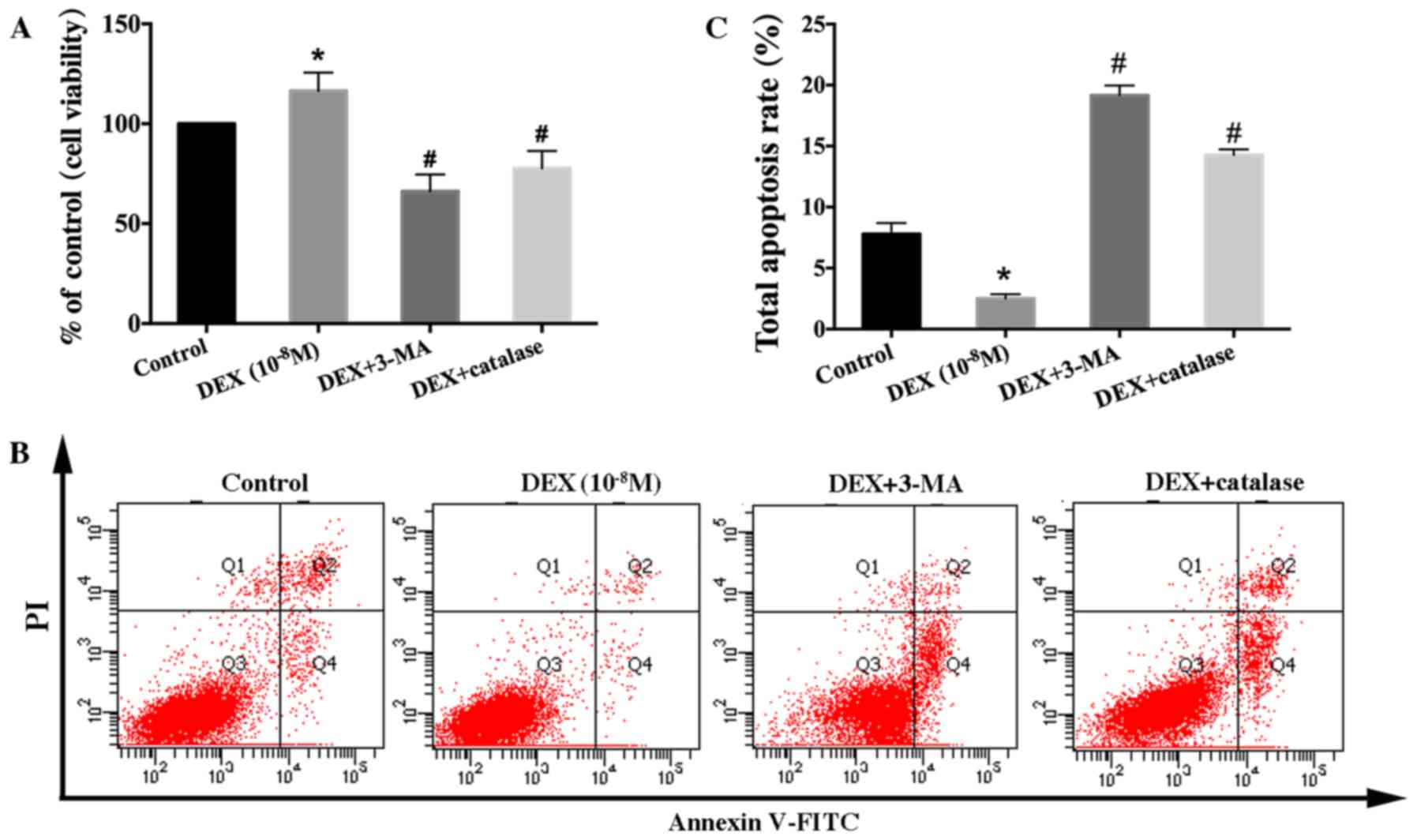
|
1
|
Kenanidis E, Potoupnis ME, Kakoulidis P,
Leonidou A, Sakellariou GT, Sayegh FE and Tsiridis E: Management of
glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: Clinical data in relation to
disease demographics, bone mineral density and fracture risk.
Expert Opin Drug Saf. 14:1035–1053. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Frenkel B, White W and Tuckermann J:
Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 872:179–215.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dalle Carbonare L, Arlot ME, Chavassieux
PM, Roux JP, Portero NR and Meunier PJ: Comparison of trabecular
bone microarchitecture and remodeling in glucocorticoid-induced and
postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 16:97–103. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Van Staa TP, Laan RF, Barton IP, Cohen S,
Reid DM and Cooper C: Bone density threshold and other predictors
of vertebral fracture in patients receiving oral glucocorticoid
therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 48:3224–3229. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Capulli M, Paone R and Rucci N: Osteoblast
and osteocyte: Games without frontiers. Arch Biochem Biophys.
561:3–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moriishi T and Komori T: Glucocorticoid
and bone. The inhibition of osteoblast differentiation and
induction of osteocyte apoptosis through the regulation of Bcl-2 by
glucocorticoids. Clin Calcium. 24:1329–1336. 2014.(In
Japanese).
|
|
7
|
Komori T: Glucocorticoid signaling and
bone biology. Horm Metab Res. 48:755–763. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jia J, Yao W, Guan M, Dai W, Shahnazari M,
Kar R, Bonewald L, Jiang JX and Lane NE: Glucocorticoid dose
determines osteocyte cell fate. FASEB J. 25:3366–3376. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shi J, Wang L, Zhang H, Jie Q, Li X, Shi
Q, Huang Q, Gao B, Han Y, Guo K, et al: Glucocorticoids:
Dose-related effects on osteoclast formation and function via
reactive oxygen species and autophagy. Bone. 79:222–232. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Martinez-Lopez N, Athonvarangkul D and
Singh R: Autophagy and aging. Adv Exp Med Biol. 847:73–87. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang JY, Yao WX, Wang Y, Fan YL and Wu JB:
Network analysis reveals crosstalk between autophagy genes and
disease genes. Sci Rep. 7:443912017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee JY, Koga H, Kawaguchi Y, Tang W, Wong
E, Gao YS, Pandey UB, Kaushik S, Tresse E, Lu J, et al: HDAC6
controls autophagosome maturation essential for ubiquitin-selective
quality-control autophagy. EMBO J. 29:969–980. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Degenhardt K, Mathew R, Beaudoin B, Bray
K, Anderson D, Chen G, Mukherjee C, Shi Y, Gélinas C, Fan Y, et al:
Autophagy promotes tumor cell survival and restricts necrosis,
inflammation, and tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 10:51–64. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sid B, Verrax J and Calderon PB: Role of
AMPK activation in oxidative cell damage: Implications for
alcohol-induced liver disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 86:200–209. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kouroku Y, Fujita E, Tanida I, Ueno T,
Isoai A, Kumagai H, Ogawa S, Kaufman RJ, Kominami E and Momoi T: ER
stress (PERK/eIF2alpha phosphorylation) mediates the
polyglutamine-induced LC3 conversion, an essential step for
autophagy formation. Cell Death Differ. 14:230–239. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gu X, Han D, Chen W, Zhang L, Lin Q, Gao
J, Fanning S and Han B: SIRT1-mediated FoxOs pathways protect
against apoptosis by promoting autophagy in osteoblast-like
MC3T3-E1 cells exposed to sodium fluoride. Oncotarget.
7:65218–65230. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang L, Meng H and Yang M: Autophagy
protects osteoblasts from advanced glycation end products-induced
apoptosis through intracellular reactive oxygen species. J Mol
Endocrinol. 56:291–300. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin
MJ, Abeliovich H, Acevedo Arozena A, Adachi H, Adams CM, Adams PD,
Adeli K, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays
for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 12:1–222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tanida I, Ueno T and Kominami E: LC3 and
autophagy. Methods Mol Biol. 445:77–88. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fu LL, Cheng Y and Liu B: Beclin-1:
Autophagic regulator and therapeutic target in cancer. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 45:921–924. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Grishko V, Xu M, Ho R, Mates A, Watson S,
Kim JT, Wilson GL and Pearsall AW IV: Effects of hyaluronic acid on
mitochondrial function and mitochondria-driven apoptosis following
oxidative stress in human chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 284:9132–9139.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ong SL, Zhang Y and Whitworth JA: Reactive
oxygen species and glucocorticoid-induced hypertension. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 35:477–482. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Henrotin Y, Kurz B and Aigner T: Oxygen
and reactive oxygen species in cartilage degradation: Friends or
foes? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 13:643–654. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ghavami S, Shojaei S, Yeganeh B, Ande SR,
Jangamreddy JR, Mehrpour M, Christoffersson J, Chaabane W, Moghadam
AR, Kashani HH, et al: Autophagy and apoptosis dysfunction in
neurodegenerative disorders. Prog Neurobiol. 112:24–49. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Almeida M, Han L, Martin-Millan M, Plotkin
LI, Stewart SA, Roberson PK, Kousteni S, O'Brien CA, Bellido T,
Parfitt AM, et al: Skeletal involution by age-associated oxidative
stress and its acceleration by loss of sex steroids. J Biol Chem.
282:27285–27297. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wauquier F, Leotoing L, Coxam V, Guicheux
J and Wittrant Y: Oxidative stress in bone remodelling and disease.
Trends Mol Med. 15:468–477. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Harris SA, Enger RJ, Riggs BL and
Spelsberg TC: Development and characterization of a conditionally
immortalized human fetal osteoblastic cell line. J Bone Miner Res.
10:178–186. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brand MD, Affourtit C, Esteves TC, Green
K, Lambert AJ, Miwa S, Pakay JL and Parker N: Mitochondrial
superoxide: Production, biological effects, and activation of
uncoupling proteins. Free Radic Biol Med. 37:755–767. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wohlgemuth SE, Calvani R and Marzetti E:
The interplay between autophagy and mitochondrial dysfunction in
oxidative stress-induced cardiac aging and pathology. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 71:62–70. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kalak R, Zhou H, Street J, Day RE,
Modzelewski JR, Spies CM, Liu PY, Li G, Dunstan CR and Seibel MJ:
Endogenous glucocorticoid signalling in osteoblasts is necessary to
maintain normal bone structure in mice. Bone. 45:61–67. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou H, Mak W, Kalak R, Street J, Fong-Yee
C, Zheng Y, Dunstan CR and Seibel MJ: Glucocorticoid-dependent Wnt
signaling by mature osteoblasts is a key regulator of cranial
skeletal development in mice. Development. 136:427–436. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ishida Y, Tertinegg I and Heersche JN:
Progesterone and dexamethasone stimulate proliferation and
differentiation of osteoprogenitors and progenitors for adipocytes
and macrophages in cell populations derived from adult rat
vertebrae. J Bone Miner Res. 11:921–930. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Atmani H, Chappard D and Basle MF:
Proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts and adipocytes in
rat bone marrow stromal cell cultures: Effects of dexamethasone and
calcitriol. J Cell Biochem. 89:364–372. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang F, Jia J and Rodrigues B: Autophagy,
metabolic disease, and pathogenesis of heart dysfunction. Can J
Cardiol. 33:850–859. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Booth LA, Tavallai S, Hamed HA,
Cruickshanks N and Dent P: The role of cell signalling in the
crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Signal. 26:549–555.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bhutia SK, Kegelman TP, Das SK, Azab B, Su
ZZ, Lee SG, Sarkar D and Fisher PB: Astrocyte elevated gene-1
induces protective autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:pp.
22243–22248. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT,
Liu B and Bao JK: Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A
review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell
Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bhutia SK, Mukhopadhyay S, Sinha N, Das
DN, Panda PK, Patra SK, Maiti TK, Mandal M, Dent P, Wang XY, et al:
Autophagy: Cancer's friend or foe? Adv Cancer Res. 118:61–95. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Manolagas SC and Parfitt AM: What old
means to bone. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 21:369–374. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lv XH, Zhao DH, Cai SZ, Luo SY, You T, Xu
BL and Chen K: Autophagy plays a protective role in cell death of
osteoblasts exposure to lead chloride. Toxicol Lett. 239:131–140.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang L, Fan J, Lin YS, Guo YS, Gao B, Shi
QY, Wei BY, Chen L, Yang L, Liu J and Luo ZJ: Glucocorticoids
induce autophagy in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med
Rep. 11:2711–2716. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao Y, Zuo Y, Huo HJ, Xiao YL, Yang XJ
and Xin DQ: Glucocorticoid induced autophagy in N1511 chondrocyte
cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:3573–3579. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Grander D, Kharaziha P, Laane E,
Pokrovskaja K and Panaretakis T: Autophagy as the main means of
cytotoxicity by glucocorticoids in hematological malignancies.
Autophagy. 5:1198–1200. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Almeida M, Han L, Ambrogini E, Weinstein
RS and Manolagas SC: Glucocorticoids and tumor necrosis factor
alpha increase oxidative stress and suppress Wnt protein signaling
in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem. 286:44326–44335. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kiffin R, Bandyopadhyay U and Cuervo AM:
Oxidative stress and autophagy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 8:152–162.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhen YF, Wang GD, Zhu LQ, Tan SP, Zhang
FY, Zhou XZ and Wang XD: P53 dependent mitochondrial permeability
transition pore opening is required for dexamethasone-induced death
of osteoblasts. J Cell Physiol. 229:1475–1483. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Manolagas SC: From estrogen-centric to
aging and oxidative stress: A revised perspective of the
pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 31:266–300. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Schroder K: NADPH oxidases in bone
homeostasis and osteoporosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 72:25–38. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Suzuki M, Bandoski C and Bartlett JD:
Fluoride induces oxidative damage and SIRT1/autophagy through
ROS-mediated JNK signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 89:369–378. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Scherz-Shouval R and Elazar Z: ROS,
mitochondria and the regulation of autophagy. Trends Cell Biol.
17:422–427. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|