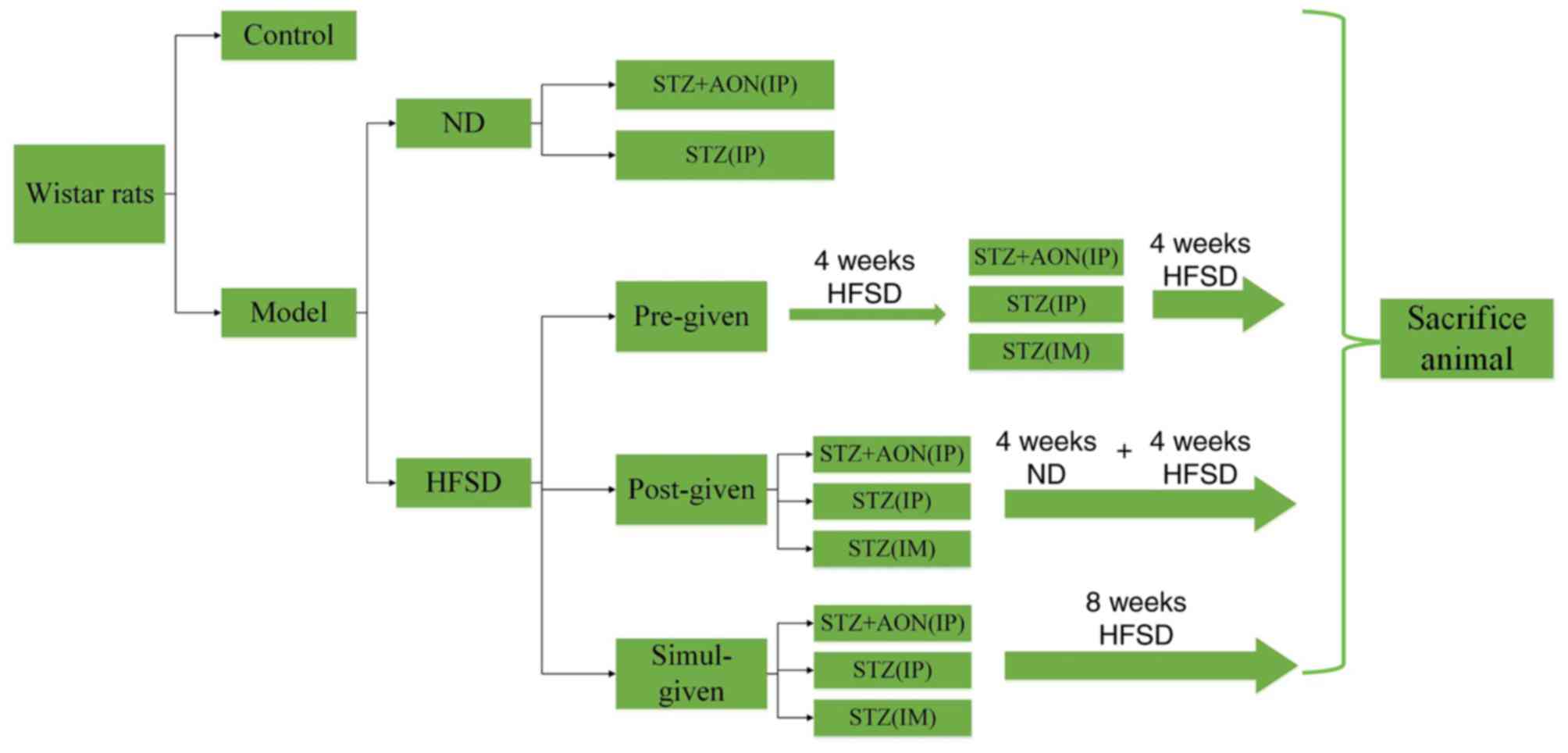
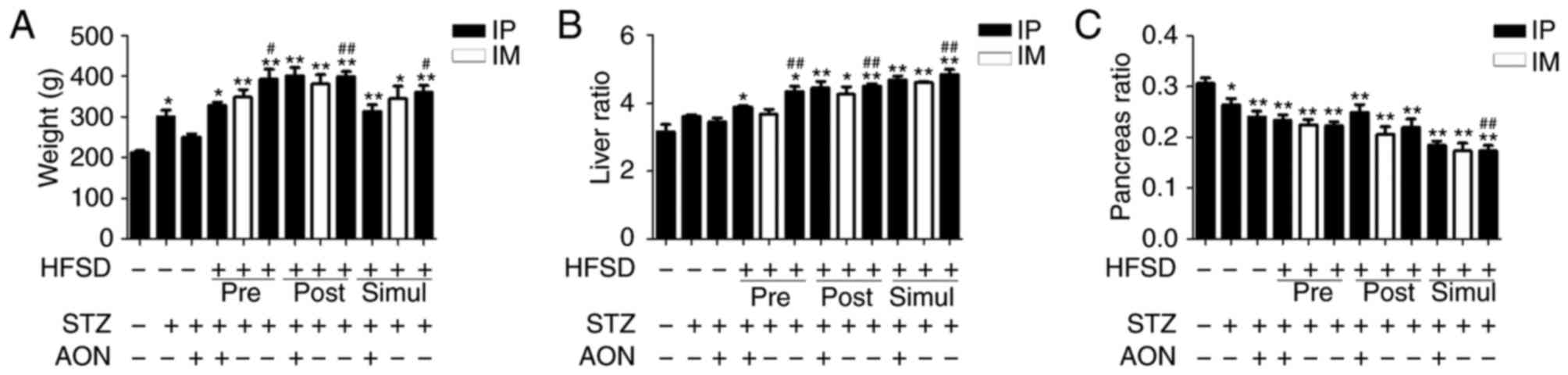
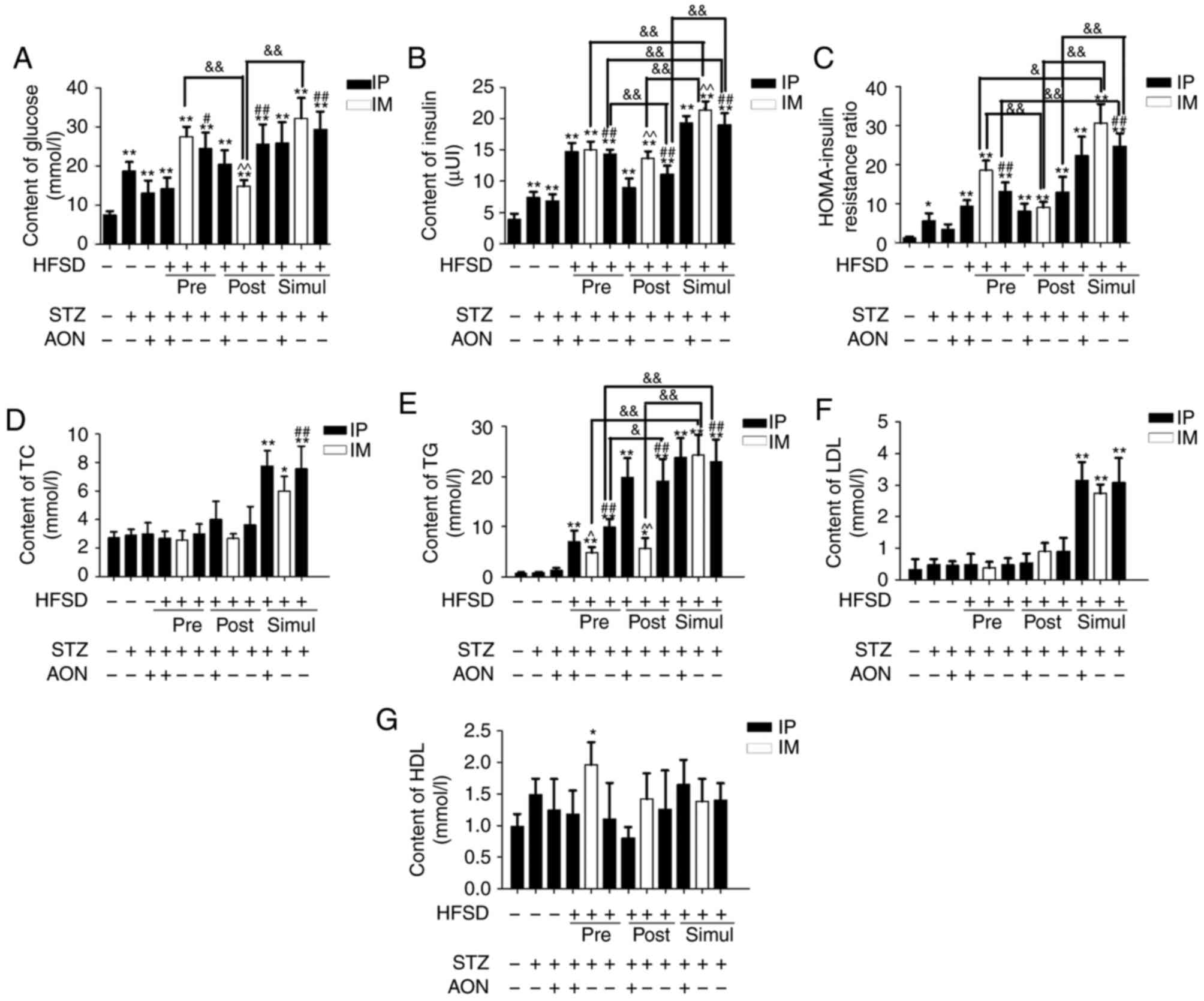
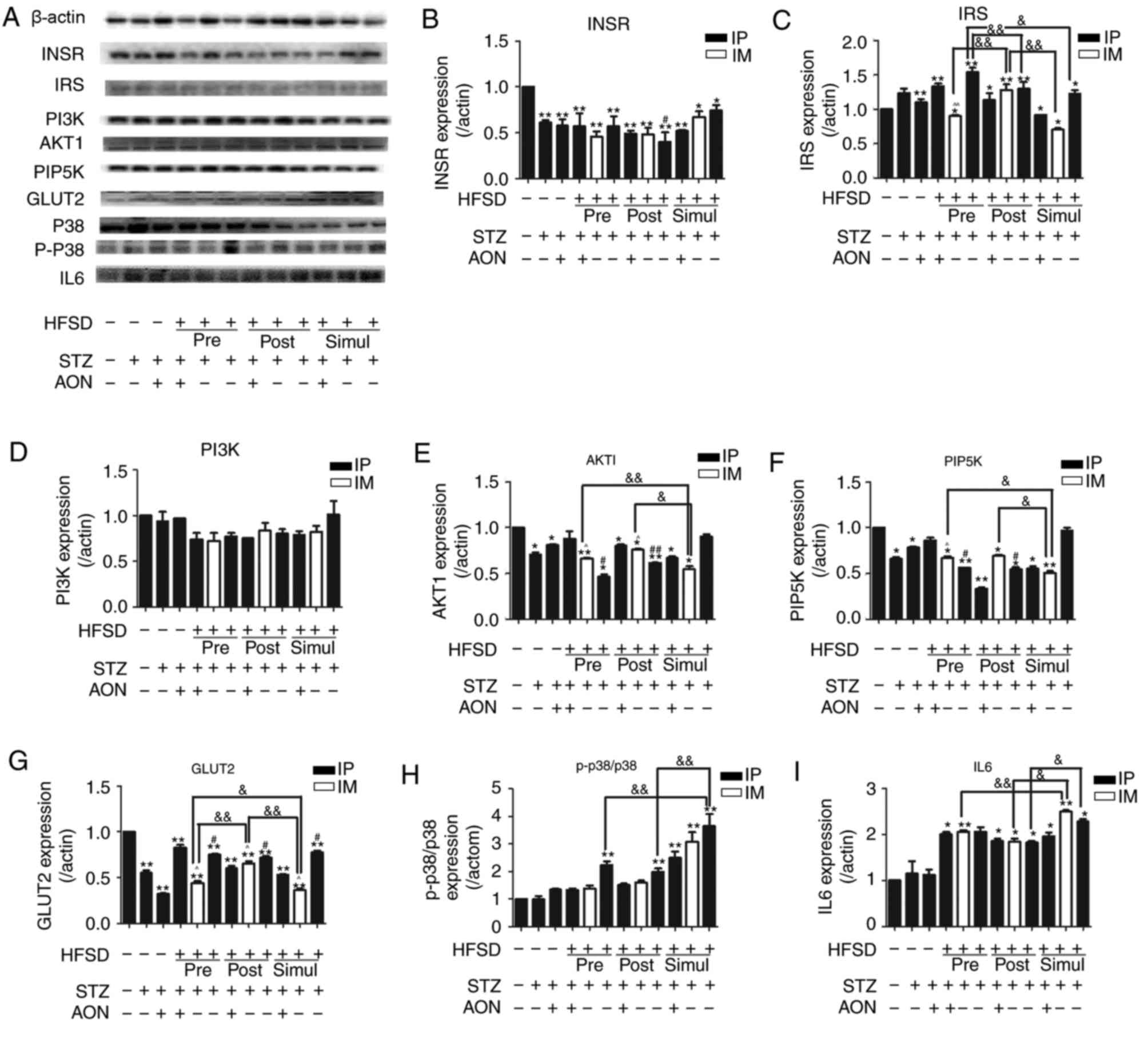
|
1
|
Chang WC, Wu JS, Chen CW, Kuo PL, Chien
HM, Wang YT and Shen SC: Protective effect of vanillic acid against
hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia via alleviating
hepatic insulin resistance and inflammation in high-fat diet
(HFD)-Fed rats. Nutrients. 7:9946–9959. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Global Burden of Disease Study 2013
Collaborators: Global, regional, and national incidence,
prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and
chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: A
systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.
Lancet. 386:743–800. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Levey AS and Coresh J: Chronic kidney
disease. Lancet. 379:165–180. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sabanayagam C, Yip W, Ting DS, Tan G and
Wong TY: Ten emerging trends in the epidemiology of diabetic
retinopathy. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 23:209–222. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Qian J, Thomas AP, Schroeder AM, Rakshit
K, Colwell CS and Matveyenko AV: Development of diabetes does not
alter behavioral and molecular circadian rhythms in a transgenic
rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 313:E213–E221. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li N, Liu Q, Li XJ, Bai XH, Liu YY, Jin
ZY, Jing YX, Yan ZY and Chen JX: Establishment and evaluation of a
rat model of type 2 diabetes associated with depression. Zhongguo
Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 31:23–26. 2015.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fatih A, Ydın A, Küçükgergin C, Bingül İ,
Doğan-Ekici I, Doğru-Abbasoğlu S and Uysal M: Effect of Carnosine
on renal function, oxidation and glycation products in the kidneys
of high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Exp Clin
Endocrinol Diabetes. 125:282–289. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu XY, Liu FC, Deng CY, Zhang MZ, Yang M,
Xiao DZ, Lin QX, Cai ST, Kuang SJ, et al: Left ventricular
deformation associated with cardiomyocyte Ca(2+) transients delay
in early stage of low-dose of STZ and high-fat diet induced type 2
diabetic rats. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 16:412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma YG, Zhang YB, Bai YG, Dai ZJ, Liang L,
Liu M, Xie MJ and Guan HT: Berberine alleviates the cerebrovascular
contractility in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats through
modulation of intracellular Ca2+ handling in smooth
muscle cells. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 15:632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Andrade EF, Lima AR, Nunes IE, Orlando DR,
Gondim PN, Zangeronimo MG, Alves FH and Pereira LJ: Exercise and
Beta-Glucan consumption (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) improve the
metabolic profile and reduce the atherogenic index in Type 2
diabetic rats (HFD/STZ). Nutrients. 8:E7922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Y, Zhang T, Zhang X, Zou W, Gong X and
Fu J: Cinepazide maleate improves cognitive function and protects
hippocampal neurons in diabetic rats with chronic cerebral
hypoperfusion. Biol Pharm Bull. 40:249–255. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bolzán AD and Bianchi MS: Genotoxicity of
streptozotocin. Mutat Res. 512:121–134. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiao X, Xu L, Zhu L and Ding Q: Study on
the model of diabetic mice and rat induced by Alloxan. Science
Mosaic. 7:112–114. 2010.
|
|
14
|
Hu C, Zhang G, Sun D, Han H and Hu S:
Duodenal-jejunal bypass improves glucose metabolism and adipokine
expression independently of weight loss in a diabetic rat model.
Obes Surg. 23:1436–1444. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu X, Shen N, Zhang ML, Pan FY, Wang C,
Jia WP, Liu C, Gao Q, Gao X, Xue B and Li CJ: Egr-1 decreases
adipocyte insulin sensitivity by tilting PI3K/Akt and MAPK signal
balance in mice. EMBO J. 30:3754–3765. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dai B, Wu Q, Zeng C, Zhang J, Cao L, Xiao
Z and Yang M: The effect of Liuwei Dihuang decoction on PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway in liver of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) rats
with insulin resistance. J Ethnopharmacol. 192:382–389. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Antony PJ, Gandhi GR, Stalin A,
Balakrishna K, Toppo E, Sivasankaran K, Ignacimuthu S and Al-Dhabi
NA: Myoinositol ameliorates high-fat diet and
streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats through promoting insulin
receptor signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 88:1098–1113. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zouari R, Hamden K, Feki AE, Chaabouni K,
Makni-Ayadi F, Kallel C, Sallemi F, Ellouze-Chaabouni S and
Ghribi-Aydi D: Protective and curative effects of Bacillus subtilis
SPB1 biosurfactant on high-fat-high-fructose diet induced
hyperlipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia and deterioration of liver
function in rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:323–329. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
International Guiding Principles for
Biomedical Research Involving Animals issued by CIOMS. Vet Q.
8:350–352. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Feng W, Zhao T, Mao G, Wang W, Feng Y, Li
F, Zheng D, Wu H, Jin D, Yang L and Wu X: Type 2 diabetic rats on
diet supplemented with chromium malate show improved
glycometabolism, glycometabolism-related enzyme levels and lipid
metabolism. PLoS One. 10:e1259522015.
|
|
21
|
Smith U and Kahn BB: Adipose tissue
regulates insulin sensitivity: Role of adipogenesis, de novo
lipogenesis and novel lipids. J Intern Med. 280:465–475. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu Y, Wu T, Wu J, Zhao L, Li Q, Varghese
Z, Moorhead JF, Powis SH, Chen Y and Ruan XZ: Chronic inflammation
exacerbates glucose metabolism disorders in C57BL/6J mice fed with
high-fat diet. J Endocrinol. 219:195–204. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Savary S, Trompier D, Andréoletti P, Le
Borgne F, Demarquoy J and Lizard G: Fatty acids - induced
lipotoxicity and inflammation. Curr Drug Metab. 13:1358–1370. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao Y, Zhang M, Wu T, Xu M, Cai H and
Zhang Z: Effects of D-Pinitol on insulin resistance through the
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in Type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. J
Agric Food Chem. 63:6019–6026. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang M, Ren Y, Lin Z, Tang C, Jia Y, Lai
Y, Zhou T, Wu S, Liu H, Yang G and Li L: Krüppel-like factor 14
increases insulin sensitivity through activation of PI3K/Akt signal
pathway. Cell Signal. 27:2201–2208. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gao TT, Qin ZL, Ren H, Zhao P and Qi ZT:
Inhibition of IRS-1 by hepatitis C virus infection leads to insulin
resistance in a PTEN-dependent manner. Virol J. 12:122015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu T, Yu B, Kakino M, Fujimoto H, Ando Y,
Hakuno F and Takahashi SI: A novel IRS-1-associated protein,
DGKzeta regulates GLUT4 translocation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Sci
Rep. 6:354382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bae JS, Kim TH, Kim MY, Park JM and Ahn
YH: Transcriptional regulation of glucose sensors in pancreatic
beta-cells and liver: An update. Sensors (Basel). 10:5031–5053.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Garvey WT, Maianu L, Hancock JA,
Golichowski AM and Baron A: Gene expression of GLUT4 in skeletal
muscle from insulin-resistant patients with obesity, IGT, GDM, and
NIDDM. Diabetes. 41:465–475. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zorzano A, Palacin M and Gumà A:
Mechanisms regulating GLUT4 glucose transporter expression and
glucose transport in skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand.
183:43–58. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Narasimhan A, Chinnaiyan M and Karundevi
B: Ferulic acid regulates hepatic GLUT2 gene expression in high fat
and fructose-induced type-2 diabetic adult male rat. Eur J
Pharmacol. 761:391–397. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bloch KO, Zemel R, Bloch OV, Grief H and
Vardi P: Streptozotocin and alloxan-based selection improves toxin
resistance of insulin-producing RINm cells. Int J Exp Diabetes Res.
1:211–219. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Erion DM, Park HJ and Lee HY: The role of
lipids in the pathogenesis and treatment of type 2 diabetes and
associated co-morbidities. BMB Rep. 49:139–148. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|