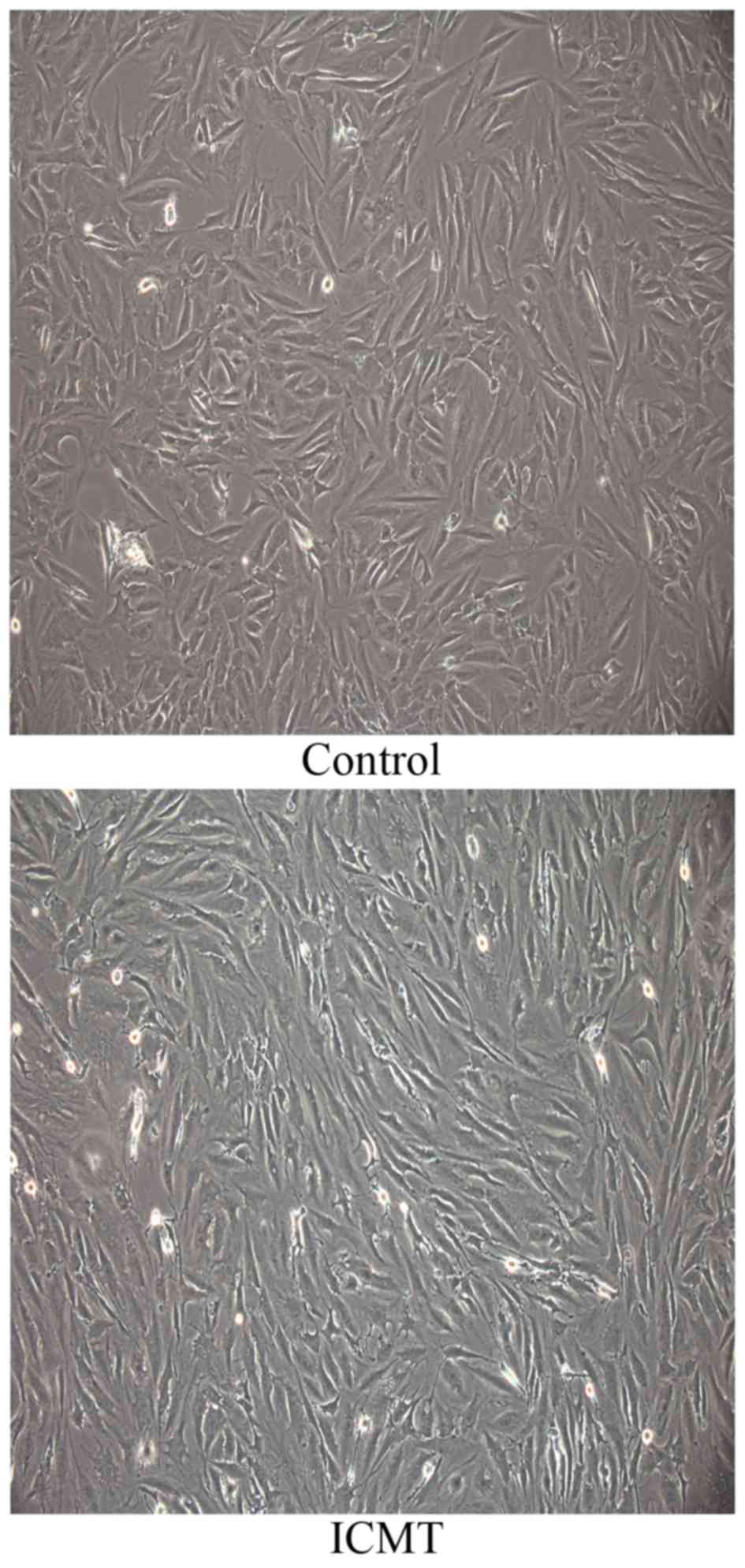
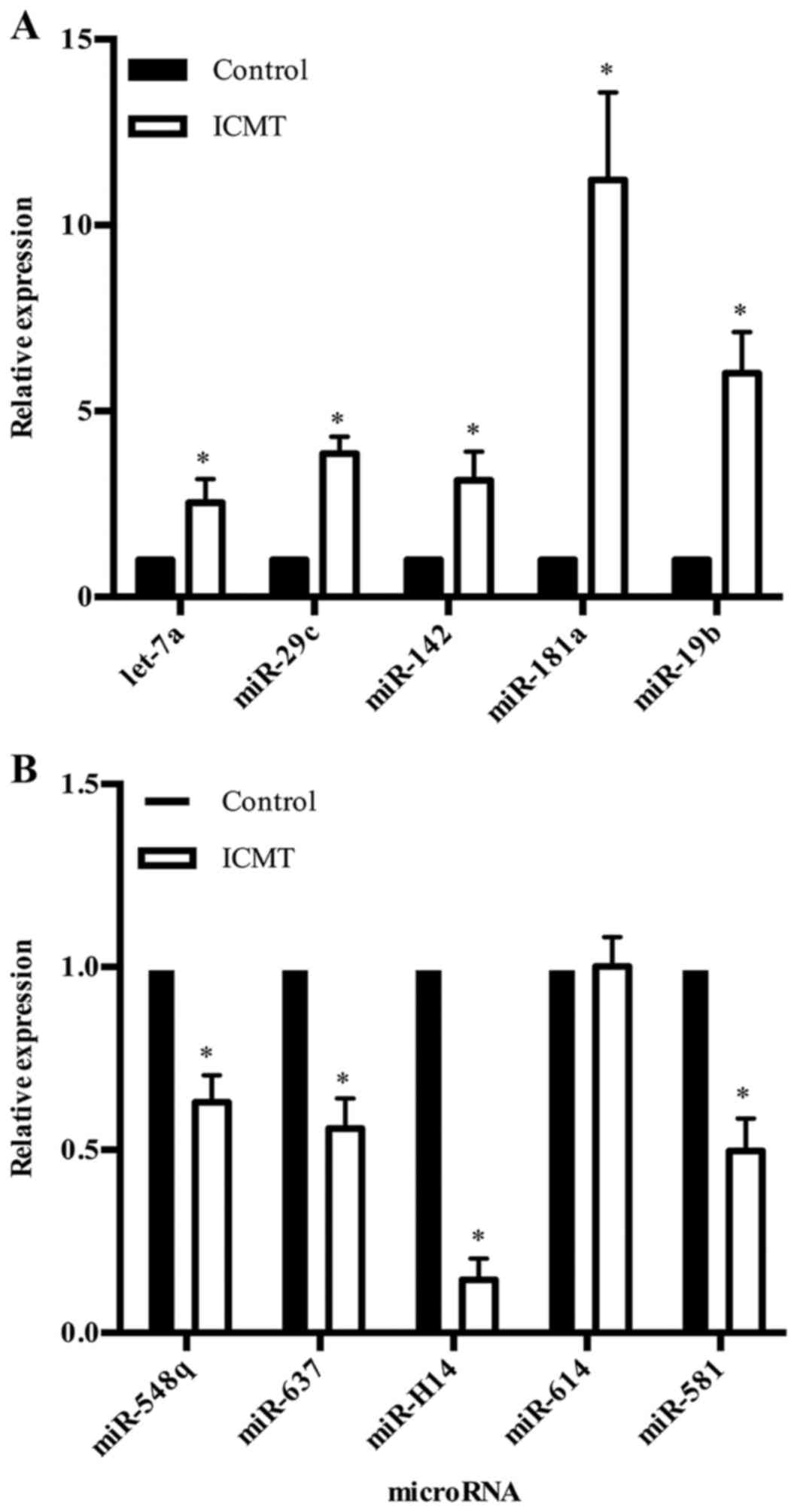
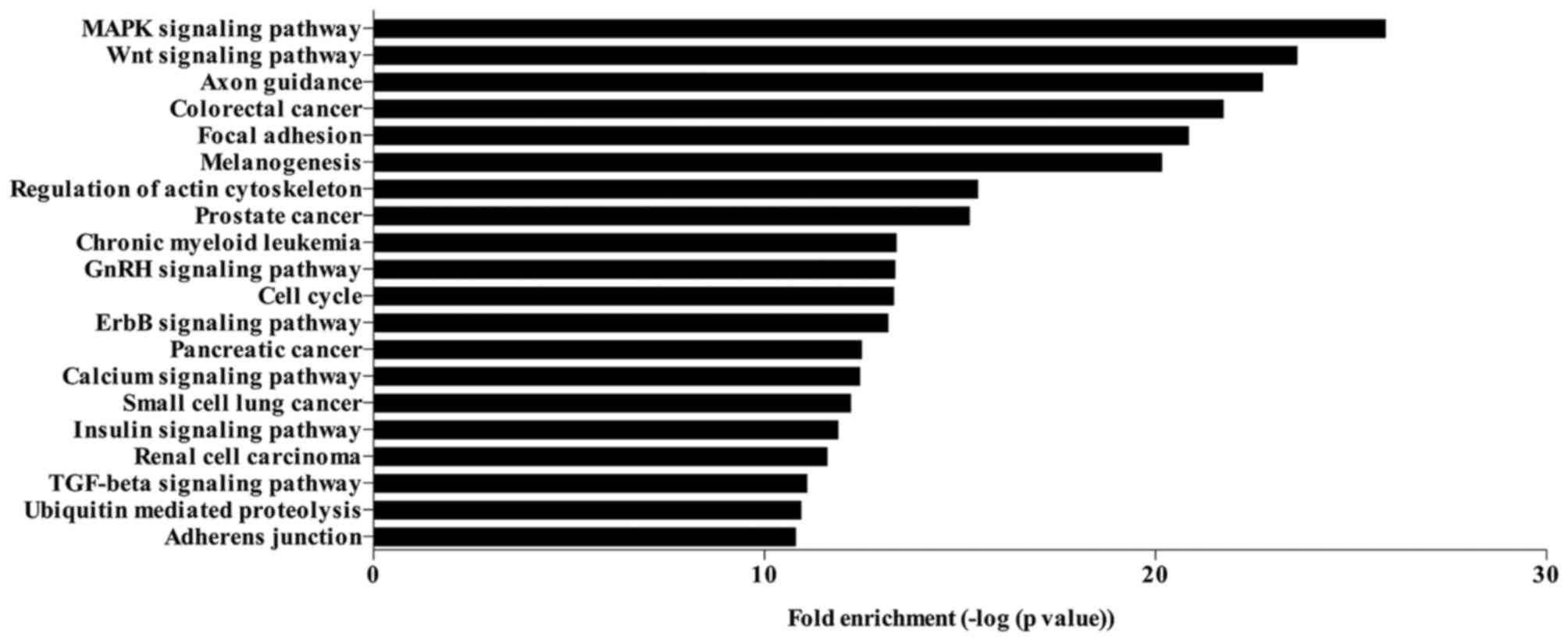
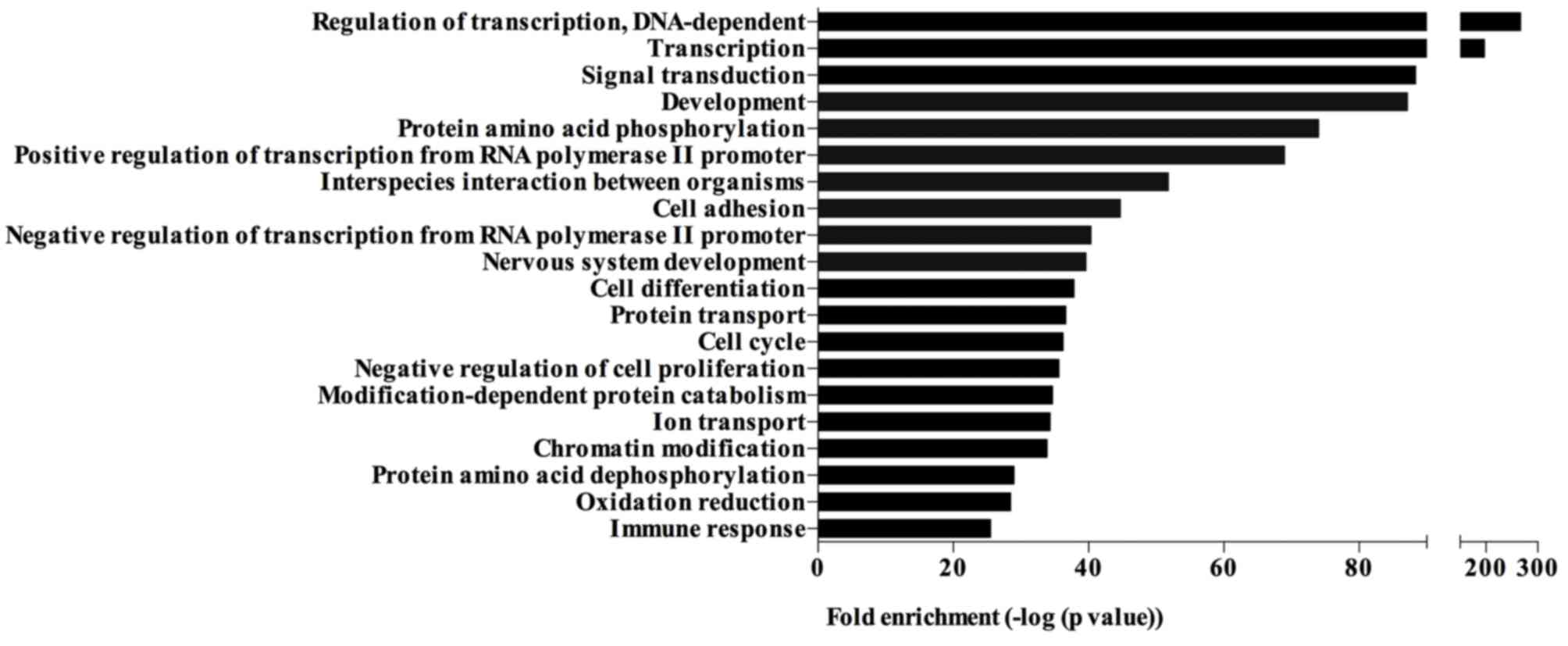
|
1
|
Roberts S, Evans H, Trivedi J and Menage
J: Histology and pathology of the human intervertebral disc. J Bone
Joint Surg Am. 88 Suppl 2:S10–S14. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kanayama M, Togawa D, Takahashi C, Terai T
and Hashimoto T: Cross-sectional magnetic resonance imaging study
of lumbar disc degeneration in 200 healthy individuals. J Neurosurg
Spine. 11:501–507. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cheung KM, Karppinen J, Chan D, Ho DW,
Song YQ, Sham P, Cheah KS, Leong JC and Luk KD: Prevalence and
pattern of lumbar magnetic resonance imaging changes in a
population study of one thousand forty-three individuals. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 34:934–940. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Battie MC, Videman T, Kaprio J, Gibbons
LE, Gill K, Manninen H, Saarela J and Peltonen L: The twin spine
study: Contributions to a changing view of disc degeneration. Spine
J. 9:47–59. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vergroesen PP, Kingma I, Emanuel KS,
Hoogendoorn RJ, Welting TJ, van Royen BJ, van Dieën JH and Smit TH:
Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: A
vicious circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 23:1057–1070. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang D, Nasto LA, Roughley P, Leme AS,
Houghton AM, Usas A, Sowa G, Lee J, Niedernhofer L, Shapiro S, et
al: Spine degeneration in a murine model of chronic human tobacco
smokers. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 20:896–905. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stirling A, Worthington T, Rafiq M,
Lambert PA and Elliott TS: Association between sciatica and
Propionibacterium acnes. Lancet. 357:2024–2025. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Adams MA and Roughley PJ: What is
intervertebral disc degeneration and what causes it? Spine (Phila
Pa 1976). 31:2151–2161. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Risbud MV and Shapiro IM: Role of
cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: Pain and disc
content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 10:44–56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vo NV, Hartman RA, Yurube T, Jacobs LJ,
Sowa GA and Kang JD: Expression and regulation of
metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in intervertebral disc
aging and degeneration. Spine J. 13:331–341. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jiang L, Zhang X, Zheng X, Ru A, Ni X, Wu
Y, Tian N, Huang Y, Xue E, Wang X and Xu H: Apoptosis, senescence
and autophagy in rat nucleus pulposus cells: Implications for
diabetic intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res.
31:692–702. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gruber HE, Ingram JA, Norton HJ, Hanley EN
and Hanley EN Jr: Senescence in cells of the aging and degenerating
intervertebral disc: Immunolocalization of senescence-associated
beta-galactosidase in human and sand rat discs. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 32:321–327. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang YC, Urban JP and Luk KD:
Intervertebral disc regeneration: Do nutrients lead the way? Nat
Rev Rheumatol. 10:561–566. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vo NV, Hartman RA, Patil PR, Risbud MV,
Kletsas D, Iatridis JC, Hoyland JA, Le Maitre CL, Sowa GA and Kang
JD: Molecular mechanisms of biological aging in intervertebral
discs. J Orthop Res. 34:1289–1306. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Urban JP, Smith S and Fairbank JC:
Nutrition of the intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
29:2700–2709. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Grunhagen T, Shirazi-Adl A, Fairbank JC
and Urban JP: Intervertebral disk nutrition: A review of factors
influencing concentrations of nutrients and metabolites. Orthop
Clin North Am. 42:465–477. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bibby SR and Urban JP: Effect of nutrient
deprivation on the viability of intervertebral disc cells. Eur
Spine J. 13:695–701. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bian Q, Liang QQ, Wan C, Hou W, Li CG,
Zhao YJ, Lu S, Shi Q and Wang YJ: Prolonged upright posture induces
calcified hypertrophy in the cartilage end plate in rat lumbar
spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 36:2011–2020. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peng B, Hou S, Shi Q and Jia L: The
relationship between cartilage end-plate calcification and disc
degeneration: An experimental study. Chin Med J (Engl).
114:308–312. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu HG, Hu CJ, Wang H, Liu P, Yang XM,
Zhang Y and Wang LT: Effects of mechanical strain on ANK, ENPP1 and
TGF-β1 expression in rat endplate chondrocytes in vitro. Mol Med
Rep. 4:831–835. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu HG, Zhang XH, Wang H, Liu P, Wang LT,
Zuo CJ, Tong WX and Zhang XL: Intermiåttent cyclic mechanical
tension-induced calcification and downregulation of ankh gene
expression of end plate chondrocytes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
37:1192–1197. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu HG, Li ZR, Wang H, Liu P, Wang LT, Zuo
CJ Tong WX and Zhang XL: Intermittent cyclic mechanical
tension-induced down-regulation of ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase
phosphodiesterase 1 gene expression is mainly dependent on TGF-β1
in end-plate chondrocytes. Orthop Surg. 5:40–45. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu H and Zhang X, Wang H, Zhang Y, Shi Y
and Zhang X: Continuous cyclic mechanical tension increases ank
expression in endplate chondrocytes through the TGF-β1 and p38
pathway. Eur J Histochem. 57:e282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu HG, Yu YF, Zheng Q, Zhang W, Wang CD,
Zhao XY, Tong WX, Wang H, Liu P and Zhang XL: Autophagy protects
end plate chondrocytes from intermittent cyclic mechanical tension
induced calcification. Bone. 66:232–239. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu HG, Ma MM, Zheng Q, Shen X, Wang H,
Zhang SF, Xu JJ, Wang CD and Zhang XL: P120-catenin protects
endplate chondrocytes from intermittent cyclic mechanical tension
induced degeneration by inhibiting the expression of RhoA/ROCK-1
signaling pathway. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 41:1261–1271. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu HG, Zheng Q, Song JX, Li J, Wang H, Liu
P, Wang J, Wang CD and Zhang XL: Intermittent cyclic mechanical
tension promotes endplate cartilage degeneration via canonical Wnt
signaling pathway and E-cadherin/β-catenin complex cross-talk.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 24:158–168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ambros V: microRNAs: Tiny regulators with
great potential. Cell. 107:823–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Teague EM, Print CG and Hull ML: The role
of microRNAs in endometriosis and associated reproductive
conditions. Hum Reprod Update. 16:142–165. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Alexandrov PN, Dua P and Lukiw WJ:
Up-Regulation of miRNA-146a in progressive, age-related
inflammatory neurodegenerative disorders of the human CNS. Front
Neurol. 5:1812014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lv Z, Shi Q, Huang W, Xing C, Hao Y, Feng
X, Yang Y, Zhang A, Kong Q, Yuki N and Wang Y: MicroRNA expression
profiling in Guillain-Barre syndrome. J Neuroimmunol. 301:12–15.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Men Y, Fan Y, Shen Y, Lu L and Kallen AN:
The Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) is regulated by
the H19/let-7 Axis. Endocrinology. 158:402–409. 2016.
|
|
33
|
Lu L, Katsaros D, Canuto EM, Biglia N,
Risch HA and Yu H: LIN-28B/let-7a/IGF-II axis molecular subtypes
are associated with epithelial ovarian cancer prognosis. Gynecol
Oncol. 141:121–127. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lu L, Katsaros D, Risch HA, Canuto EM,
Biglia N and Yu H: MicroRNA let-7a modifies the effect of
self-renewal gene HIWI on patient survival of epithelial ovarian
cancer. Mol Carcinog. 55:357–365. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ohrt-Nissen S, Døssing KB, Rossing M,
Lajer C, Vikeså J, Nielsen FC, Friis-Hansen L and Dahl B:
Characterization of miRNA expression in human degenerative lumbar
disks. Connect Tissue Res. 54:197–203. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao B, Yu Q, Li H, Guo X and He X:
Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in patients with
intervertebral disc degeneration. Int J Mol Med. 33:43–50. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yuan HF, Von Roemeling C, Gao HD, Zhang J,
Guo CA and Yan ZQ: Analysis of altered microRNA expression profile
in the reparative interface of the femoral head with osteonecrosis.
Exp Mol Pathol. 98:158–163. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Miyaki S and Asahara H: Macro view of
microRNA function in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 8:543–552.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang X, Qian W, Wu Z, Bian Y and Weng X:
Preliminary screening of differentially expressed circulating
microRNAs in patients with steroidinduced osteonecrosis of the
femoral head. Mol Med Rep. 10:3118–3124. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu X, Che L, Xie YK, Hu QJ, Ma CJ, Pei
YJ, Wu ZG, Liu ZH, Fan LY and Wang HQ: Noncoding RNAs in human
intervertebral disc degeneration: An integrated microarray study.
Genom Data. 5:80–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Thompson KJ, Dagher AP, Eckel TS, Clark M
and Reinig JW: Modic changes on MR images as studied with
provocative diskography: Clinical relevance-a retrospective study
of 2457 disks. Radiology. 250:849–855. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xiong CJ, Huang B, Zhou Y, Cun YP, Liu LT,
Wang J, Li CQ, Pan Y and Wang H: Macrophage migration inhibitory
factor inhibits the migration of cartilage end plate-derived stem
cells by reacting with CD74. PLoS One. 7:e439842012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu LT, Huang B, Li CQ, Zhuang Y, Wang J
and Zhou Y: Characteristics of stem cells derived from the
degenerated human intervertebral disc cartilage endplate. PLoS One.
6:e262852011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen
S, Bateman A and Enright AJ: miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets
and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:D140–D144. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW,
Bartel DP and Burge CB: Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets.
Cell. 115:787–798. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol.
2:e3632004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hiyama A, Sakai D, Risbud MV, Tanaka M,
Arai F, Abe K and Mochida J: Enhancement of intervertebral disc
cell senescence by WNT/β-catenin signaling-induced matrix
metalloproteinase expression. Arthritis Rheum. 62:3036–3047. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ye W, Xu K, Huang D, Liang A, Peng Y, Zhu
W and Li C: Age-related increases of macroautophagy and
chaperone-mediated autophagy in rat nucleus pulposus. Connect
Tissue Res. 52:472–478. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Jiang W, Zhang X, Hao J, Shen J, Fang J,
Dong W, Wang D, Zhang X, Shui W, Luo Y, et al: SIRT1 protects
against apoptosis by promoting autophagy in degenerative human disc
nucleus pulposus cells. Sci Rep. 4:74562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gruber HE, Hoelscher GL, Ingram JA, Bethea
S and Hanley EN Jr.: Autophagy in the degenerating human
intervertebral disc: In vivo molecular and morphological evidence
and induction of autophagy in cultured annulus cells exposed to
proinflammatory cytokines-implications for disc degeneration. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 40:773–782. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kepler CK, Ponnappan RK, Tannoury CA,
Risbud MV and Anderson DG: The molecular basis of intervertebral
disc degeneration. Spine J. 13:318–330. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Engl W, Arasi B, Yap LL, Thiery JP and
Viasnoff V: Actin dynamics modulate mechanosensitive immobilization
of E-cadherin at adherens junctions. Nat Cell Biol. 16:587–594.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xu Y, Wang Q, Li Y, Gan Y, Li P, Li S,
Zhou Y and Zhou Q: Cyclic tensile strain induces tenogenic
differentiation of tendon-derived stem cells in bioreactor culture.
Biomed Res Int. 2015:7908042015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tamiello C, Buskermolen ABC, Baaijens FPT,
Broers JLV and Bouten CVC: Heading in the Right Direction:
Understanding Cellular Orientation Responses to Complex Biophysical
Environments. Cell Mol Bioeng. 9:12–37. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Walsh AJ, Bradford DS and Lotz JC: In vivo
growth factor treatment of degenerated intervertebral discs. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 29:156–163. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ding L, Heying E, Nicholson N, Stroud NJ,
Homandberg GA, Buckwalter JA, Guo D and Martin JA: Mechanical
impact induces cartilage degradation via mitogen activated protein
kinases. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 18:1509–1517. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Tetsunaga T, Nishida K, Furumatsu T,
Naruse K, Hirohata S, Yoshida A, Saito T and Ozaki T: Regulation of
mechanical stress-induced MMP-13 and ADAMTS-5 expression by RUNX-2
transcriptional factor in SW1353 chondrocyte-like cells.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 19:222–232. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Cailotto F, Bianchi A, Sebillaud S,
Venkatesan N, Moulin D, Jouzeau JY and Netter P: Inorganic
pyrophosphate generation by transforming growth factor-beta-1 is
mainly dependent on ANK induction by Ras/Raf-1/extracellular
signal-regulated kinase pathways in chondrocytes. Arthritis Res
Ther. 9:R1222007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|