Introduction
Ovarian cancer is the fifth-leading cause of
worldwide cancer-related deaths among woman. It accounts for more
deaths than other gynecologic tumors. Standard therapy for advanced
ovarian cancer consists of cytoreductive surgery followed by
chemotherapy (1). The 5-year
survival rate for ovarian cancer patients ranges from 30 to 92%
(2). Paclitaxel-platinum treatment
is the standard first-line treatment in ovarian cancer, with
typical response rate of over 70%. However, most patients
eventually experience recurrence, with a median progression-free
survival of 18 months (2).
Although efforts have been focused on overcoming resistance to
chemotherapy drugs for years, mortality rates of patients with
ovarian cancer remain high (3).
Extracellular signal-regulating kinase (ERK) 1/2
pathway plays a major role in the survival of cancer cells via
inhibition of apoptosis controlling Bcl-2 family members such as
Bim, Bad, Bcl-1, and Mcl-1 (4).
However, depending on cell type and stimulus, ERK1/2 activation can
also mediate antiproliferative events such as apoptosis and
autophagy in some studies (4,5).
ERK1/2 phosphorylates and activates direct downstream kinase p90
ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK). ERK1/2/p90RSK activation is involved in
the progression of many cancers (6). It is emerging as a potential
therapeutic target (6). The
purpose of this study was to explore whether ERK1/2/p90RSK
activation could mediate anticancer mechanism in ovarian cancer
cells.
Croton tonkinesis Gagnep. (Euphorbiaceae),
commonly known as ‘Kho sam cho la (or Kho sam Bac Bo)’ in
Vietnamese, is a small medicinal plant indigenous to northern
Vietnam (7). This plant has been
used to treat stomach aches, abscesses, impetigoes, gastric and
duodenal ulcers, and malaria (8).
Crude extract of C. tonkinensis has shown significant
cytotoxicity against breast cancer, lung cancer, and glioblastoma
(9). Some ent-kaurane
diterpenoids isolated from C. tonkinensis also possess
cytotoxic and proapoptotic activities (7,10,11).
They can inhibit lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nuclear factor-κB
(NF-κB) activation with anti-inflammatory properties (12,13).
They can also inhibit silent information regulator two ortholog 1
(SIRT1) and stimulate osteoblast differentiation (14,15).
However, the underlying mechanism by which ent-kaurane
diterpenoids inhibit cancer cell growth remains controversial.
Multiple signaling mechanisms, including PI3K/PKB pathway,
AMP-activated protein kinase pathway, Wnt/β-catenin pathway, and
Akt/mTOR/p70S6K pathway, have been implicated in anticancer
activities of this class of diterpenoids (16–20).
The objective of the present study was to
investigate the effect of a natural ent-kaurane diterpenoid
CRT1 isolated from C. tonkinensis on proliferation,
apoptosis, migration, and invasion of human ovarian cancer cells.
Molecular mechanisms associated with cellular changes were also
examined in this study.
Materials and methods
Plant material and chemical
isolation
The major ent-kauranoid was previously
isolated from leaves of plant Croton tonkinensis and
identified as ent−18-acetoxy-7β-hydroxy
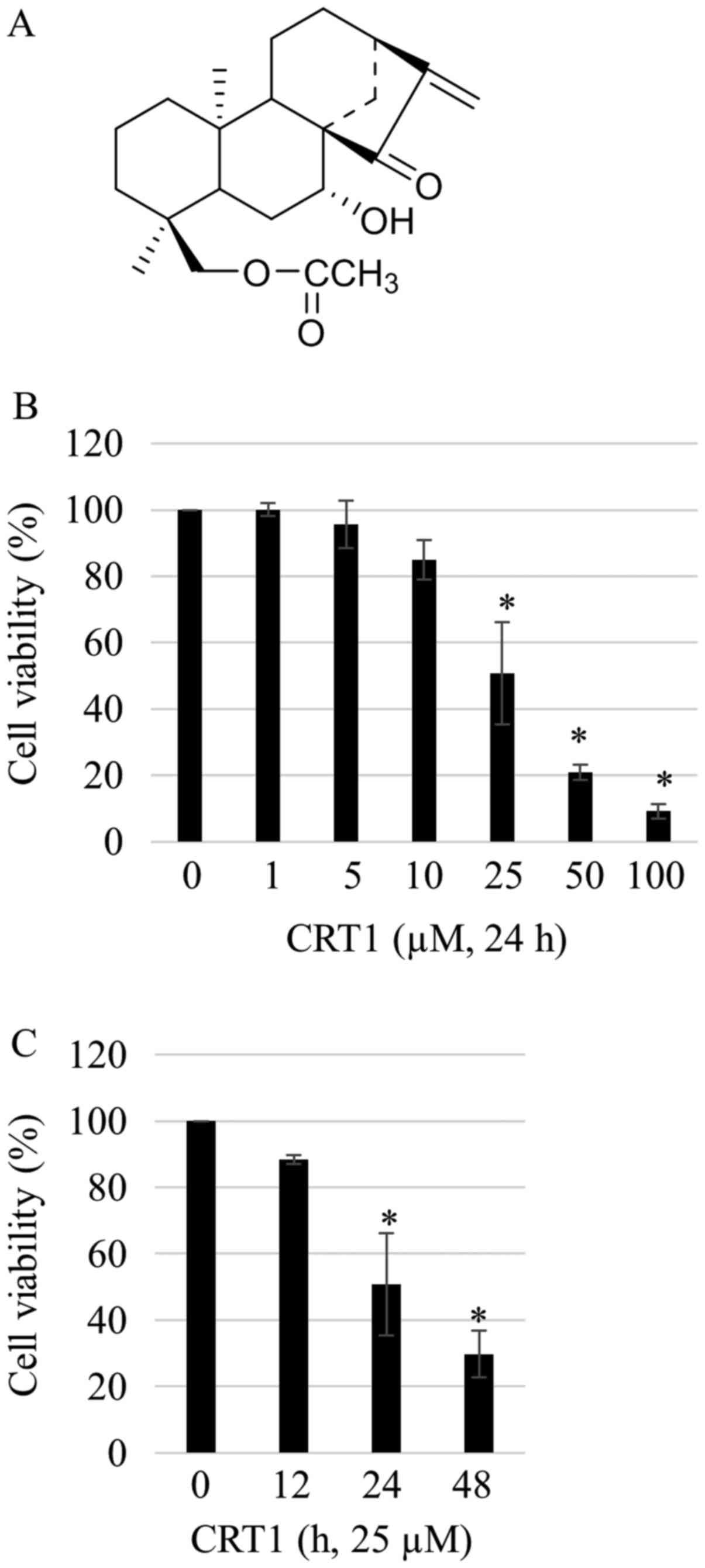
kaur-15-oxo-16-ene (namely CRT1) (Fig.
1A). Purification and structure identification of CRT1 were
demonstrated elsewhere (13). The
purity of the compound was determined to be 97% by HPLC.
Cell culture
Human ovary adenocarcinoma SKOV3 was purchased from
Korean Cell Line Bank (Seoul, Korea). McCoy's 5A, fetal bovine
serum (FBS), and penicillin/streptomycin were obtained from Gibco
(Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). Trypsin/EDTA
was purchased from Thermo Scientific HyClone (GE Healthcare Life
Sciences, Logan, UT, USA). Cells were grown in McCoy's 5A media
supplemented with 10% (v/v) FBS, penicillin (100 U/ml)/streptomycin
(100 µg/ml) at 37°C in a humidified CO2 (5%)-controlled
incubator.
Cell viability assay
Cells were seeded into 96-well microplates at
density of 5×103 cells/ml and allowed to attach for 24
h. CRT1 and/or PD98059 were added to the medium at various
concentrations. After treatment, cell cytotoxicity and/or
proliferation was assessed using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8;
Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan). Briefly, highly
water-soluble tetrazolium salt,
WST-8[2-(2-methoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(2,4-disulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium,
monosodium salt], produced an orange colored water-soluble product,
formazan. The amount of formazan dye generated by dehydrogenases in
cells was directly proportional to the number of living cells.
CCK-8 (10 µl) was added to each well and incubated at 37°C for 3 h.
Cell proliferation and cytotoxicity were then assessed by measuring
the absorbance at wavelength of 450 nm using a microplate reader.
Three replicated wells were used for each experimental
condition.
Western blot analysis
Cells were incubated with CRT1 (10, 25, and 50 µM)
and/or PD98059 (25 µg/ml) for 24 h, and washed twice in cold
phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Cells were lysed with lysis buffer
[10 mM Tris, pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1% TritonX-100, 0.5%
NP-40, 1 mM propidium iodide (PI), 1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), 1 mM
phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF)], placed on ice for 1 h with
occasional vortexing, and centrifuged at 13,000 × g for 10 min at
4°C to collect the supernatant. Pierce BCA Assay Kit (Pierce;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) was used to determine protein
concentration. Cell lysates (50 µg) were subjected to sodium
dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and
transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane. Blots
were blocked with 5% skim milk in PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20
(PBST) for 1 h at 25°C and then incubated with primary antibodies
(1:1,000) overnight at 4°C. After washing with PBST, membranes were
incubated with anti-rabbit or anti-mouse horseradish
peroxidase-conjugated IgG (1:3,000) at room temperature for 2 h and
visualized with enhanced chemiluminescence using Super
Signal® West Pico Chemiluminescent substrate purchased
from Pierce; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. Antibodies to rabbit
polyclonal anti-human Bax (1:1,000; no. 2772), rabbit polyclonal
anti-human Bcl-2 (1:1,000; no. 2876), rabbit polyclonal anti-human
caspase-3 (1:1,000; no. 9662), mouse monoclonal anti-human cspase-7
(1:1,000; no. 9494), rabbit polyclonal anti-human caspase-9
(1:1,000; no. 9502), rabbit polyclonal anti-human poly-(ADP-ribose)
polymerase (PARP) (1:1,000; no. 9542), rabbit polyclonal anti-human
phospho-p44/p42 MAPK (ERK1/2) (Thr202/Tyr204) (1:1,000; no. 9101),
rabbit monoclonal anti-human RSK1/2/3 (1:1,000; no. 9355), rabbit
polyclonal anti-human phospho-p90RSK (Ser380) (1:1,000; no. 9314),
and rabbit polyclonal anti-human β-actin (1:1,000; no. 4967) were
purchased from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. (Danvers, MA, USA).
Rabbit polyclonal anti-human ERK (1:1,000; sc-94) was obtained from
Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. (Dallas, TX, USA). Horseradish
peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse and anti-rabbit antibodies were
bought from Transduction Lab (Lexington, KY, USA). Band intensity
was quantified by densitometry using ImageJ software and was
normalized to loading controls. Quantification value was expressed
as the fold change vs. band numbered 1.0. ImageJ was downloaded
from NIH website (http:rsbweb.nih.gov/ij/download.html).
Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining
assay
Annexin-V-FLUOS Staining kit was purchased from
Roche Diagnostics GmbH (Penzberg, Germany). Cells were cultured in
6-well plates at cell density of 106 cells/well in
McCoy's 5A medium and treated with CRT1 (10, 25, and 50 µM) and/or
PD98059 (25 µM) for 24 h. Cells were centrifuged and washed three
times with PBS. Cell pellet was then resuspended in 100 µl of
Annexin V-FLUOS labeling solution. After incubating at room
temperature for 30 min, samples were analyzed on a flow cytometer
(BD FACSCanto™II; BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NY,
USA).
Soft agar colony forming assay
For determination of anchorage-independent cell
growth, 104 cells were suspended in growth media
supplemented with 10% FBS (3 ml) containing 0.3% agar. They were
then applied onto pre-solidified 0.6% agar (3 ml) in FBS-free
growth media in 60 mm culture dishes. After 2–3 weeks of
incubation, colonies on soft agar were observed under a
phase-contrast microscope (IX2-ILL100; Olympus Corporation, Tokyo,
Japan) and photographed.
Wound healing assay
Cells were seeded into 6-well plates and incubated
in serum-free McCoy's 5A for 18 h. The cellular monolayer was
wounded with a sterile 10 µl-pipette tip and washed with serum free
McCoy's 5A to remove detached cells from plates. These cells were
incubated in the presence or absence of CRT1 for 48 h in McCoy's 5A
containing 10% FBS. The medium was replaced with PBS and cells were
photographed using a phase-contrast microscope (IX2-ILL100; Olympus
Corporation).
Matrigel invasion assay
Cell invasion assay was carried out with 24-well
flat bottom plate with transparent PET membrane with pore size of
8.0 µm (FALCON®; Corning Incorporated, Corning, NY,
USA). Each insert has been coated with Matrigel Matrix (BD
Bioscience, San Jose, CA, USA). Cells (2.5×104)
suspended in 300 µl of serum free McCoy's 5A with or without drugs
were added to the upper chamber while 500 µl of McCoy's 5A
containing 10% FBS were added to the lower chamber of 24-well flat
bottom plate. After incubation for 24 h, non-invading cells were
removed from the upper surface of the membrane by scrubbing while
invading cells on the lower surface of the membrane were stained
with hematoxylin. Membranes were then removed and invading cells
were counted randomly by light microscopy. Each assay was performed
in triplicates and repeated at least three times. Due to variation
in the number of migrated cells from different experiment, results
were normalized to control cells and relative invasion was
expressed as mean ± SD of migrating cells relative to control
cells.
Statistical analysis
All results presented were confirmed in at least
three independent experiments. Data were presented as the mean ±
standard deviation. Statistical differences were analyzed by
one-way analysis of variance followed by a Tukey post hoc test
using SPSS 24.0 software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). P<0.05
was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
CRT1 reduces SKOV3 cellular
proliferation in a dose- and time-dependent manner
To evaluate effects of CRT1 on growth, SKOV3 ovarian
carcinoma cells were treated with increasing concentrations (1 to
100 µM) of CRT1 for various time periods (12, 12, and 48 h) and
cell viabilities were assessed by CCK-8 assay. Viabilities of SKOV3
cells were decreased in a dose- and time-dependent manner after
exposure to different concentrations of CRT1 (Fig. 1B and C).
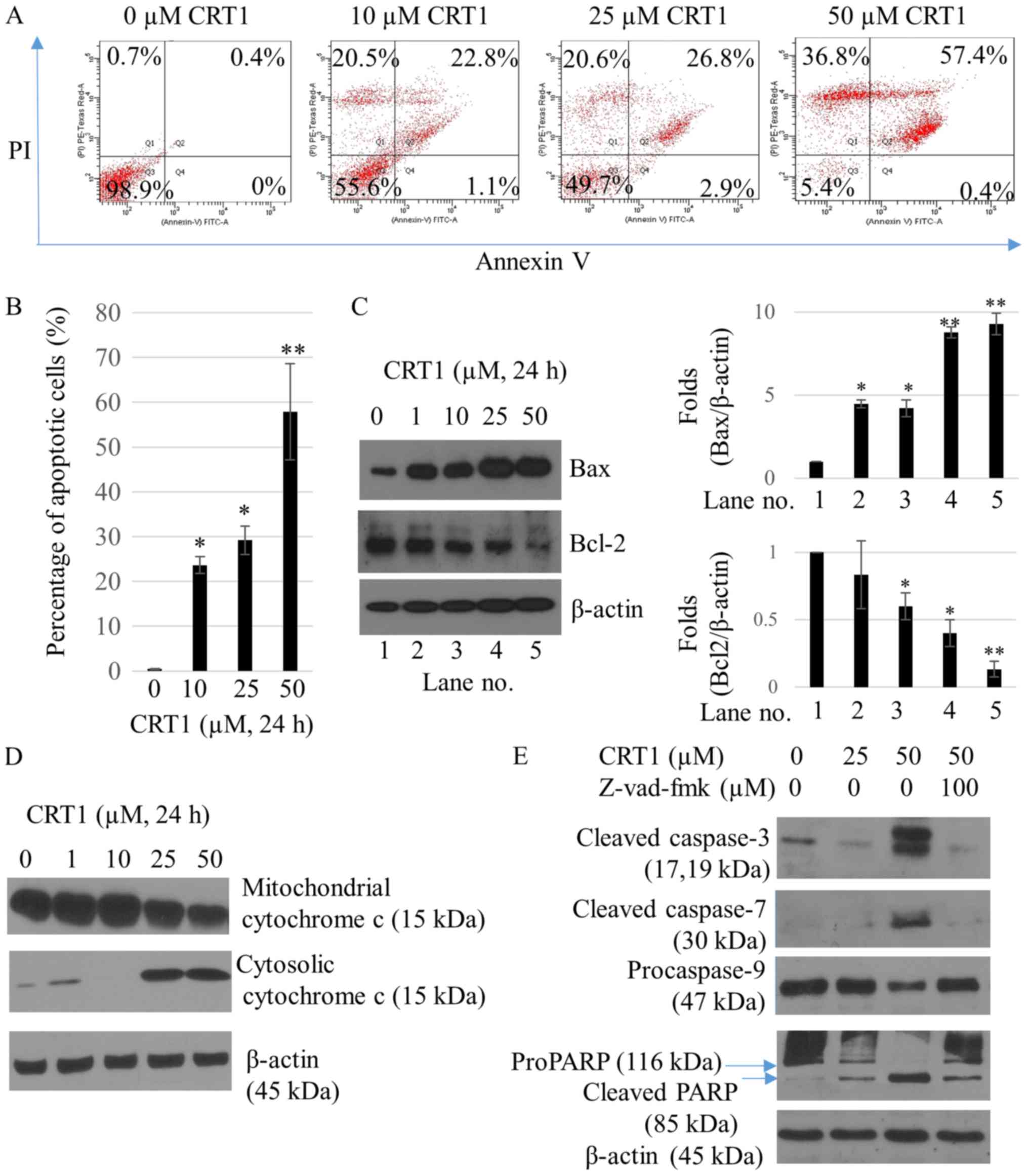
Mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis
induced by CRT1 treatment of SKOV3 cells
To investigate the occurrence of apoptosis following
CRT1 treatment, flow cytometric analysis was performed using a
Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining assay. After SKOV3 cells were
treated with 25 and 50 µM CRT1 for 24 h, the percentage of Annexin
V-positive cells was increased from 0.4% (in the control) to 29.7
and 57.8%, respectively (Fig. 2A and
B). The percentage of necrotic cells was increased from 0.7%
(in the control) to 20.5% (10 µM CRT1), 20.6% (25 µM CRT1), and
36.8% (50 µM CRT1) (Fig. 2A).
Effects of CRT1 treatment on the expression of apoptotic proteins,
Bax and Bcl-2, were also investigated by western blot analysis. As
shown in Fig. 2C, expression
levels of proapoptotic protein Bax were significantly increased in
SKOV3 cells following treatment with CRT1 at 25 and 50 µM for 24 h
compared to those in the control. However, expression levels of
anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 were decreased in cells treated with
CRT1 at 25 and 50 µM for 24 h compared to those in the control. Bax
is a key proapoptotic molecule in the mitochondrially mediated
apoptotic pathway. It is responsible for pore-opening of the
mitochondria to release cytochrome c and activate caspase family of
proteases as part of the apoptotic cascade (21). Therefore, we examined the effect of
CRT1 on the release of cytochrome c and caspase-3, −7, −9, and
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) activation. CRT1 significantly
enhanced cytochrome c release from the mitochondria to the cytosol
(Fig. 2D), leading to increased
expression of cleaved caspase-3, cleaved caspase-7, and cleaved
PARP but decreased expression of procaspase-9 compared with the
control (Fig. 2E). Pretreatment of
SKOV3 cells with z-VAD-fmk, a caspase inhibitor, attenuated the
ability of CRT1 to activate the caspase cascade (Fig. 2E).
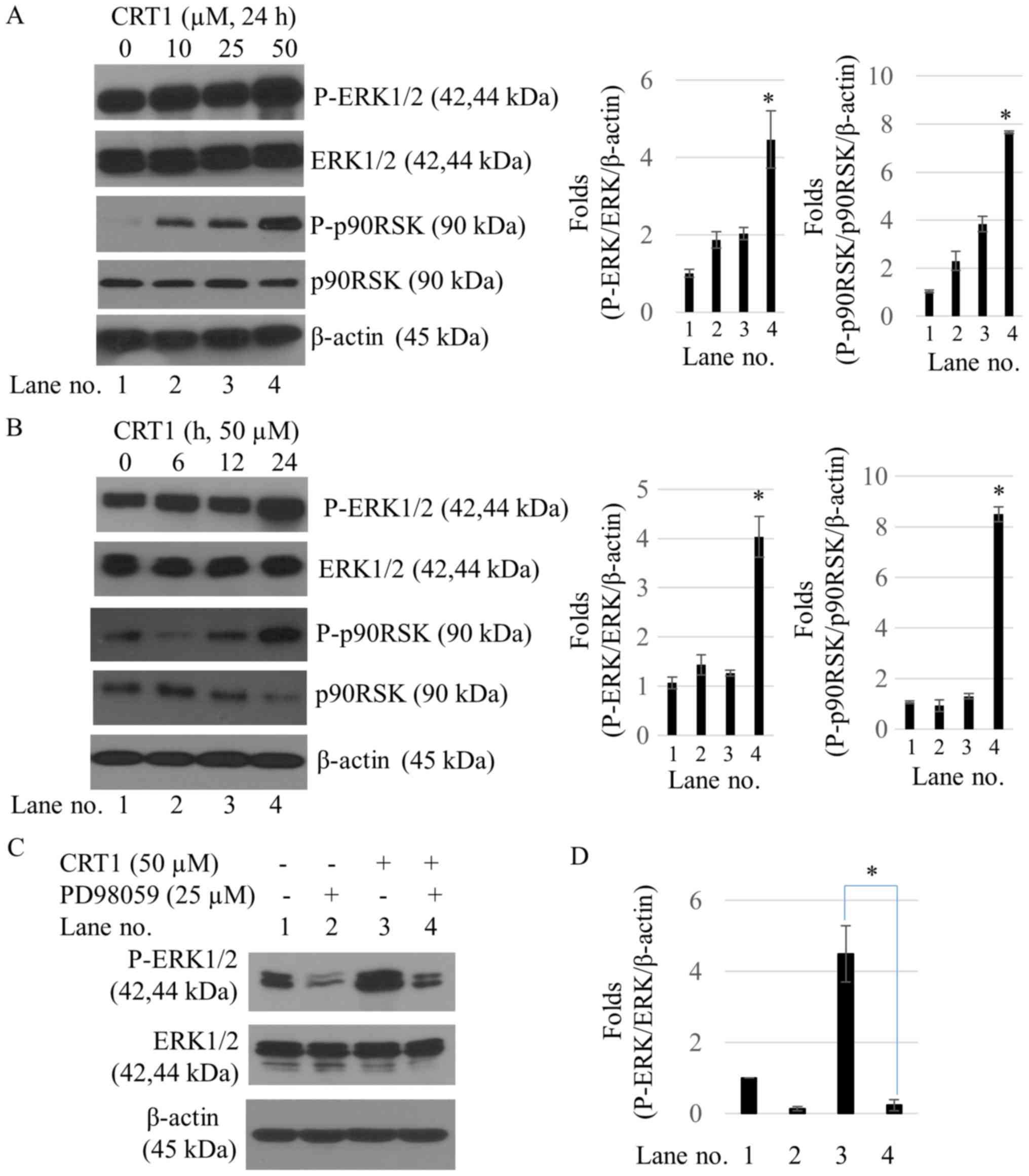
CRT1 increases ERK/p90RSK
phosphorylation of SKOV3 cells
To determine whether the MAPK/ERK1/2 pathway was
involved in the anticancer effect of CRT1, this study examined
phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and its substrate, p90RSK, following
treatment with CRT1. CRT1 significantly increased phosphorylation
levels of ERK1/2 at Thr202/Tyr204 sites and p90RSK at Ser380 site
in a dose- and time-dependent manner. However, there was no
significant difference in total expression levels of ERK1/2 and
p90RSK proteins between control and CRT1 treatment (Fig. 3A and B). PD98059, a specific ERK
inhibitor, failed to increase CRT1-induced ERK1/2 activation
(Fig. 3C) or suppress CRT1-induced
cell viability (Fig. 3D).
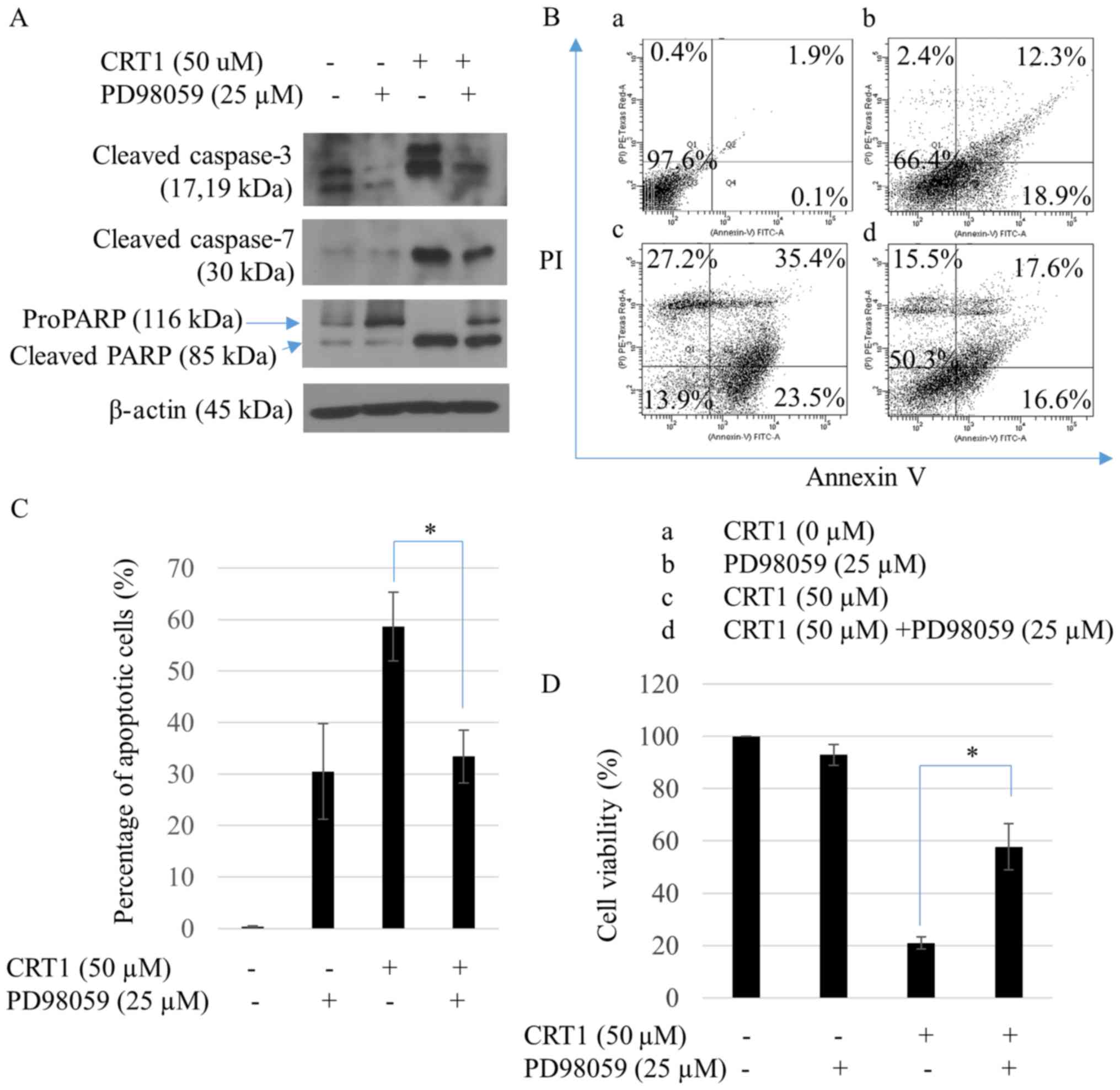
CRT1-induced anti-proliferation and
apoptosis is reversed by ERK inhibitor
To study whether ERK1/2 was involved in CRT1-induced
apoptosis of SKOV3 cells, PD98059, a specific ERK inhibitor, was
used. PD98059 treatment failed to increase CRT1-induced caspase-3,
caspase-7, and PARP cleavages (Fig.
4A) or the percentage of annexin V-positive cells (Fig. 4B and C). To evaluate the reversed
effect of PD98059 on CRT1-induced cell growth, viability of SKOV3
cells was assessed by CCK8 cell-counting assay. CRT1 failed to
decrease cell viability following pretreatment of SKOV3 cells with
PD98059 (Fig. 4D).
CRT1 inhibits migration and invasion
through ERK1/2 activation in SKOV3 cells
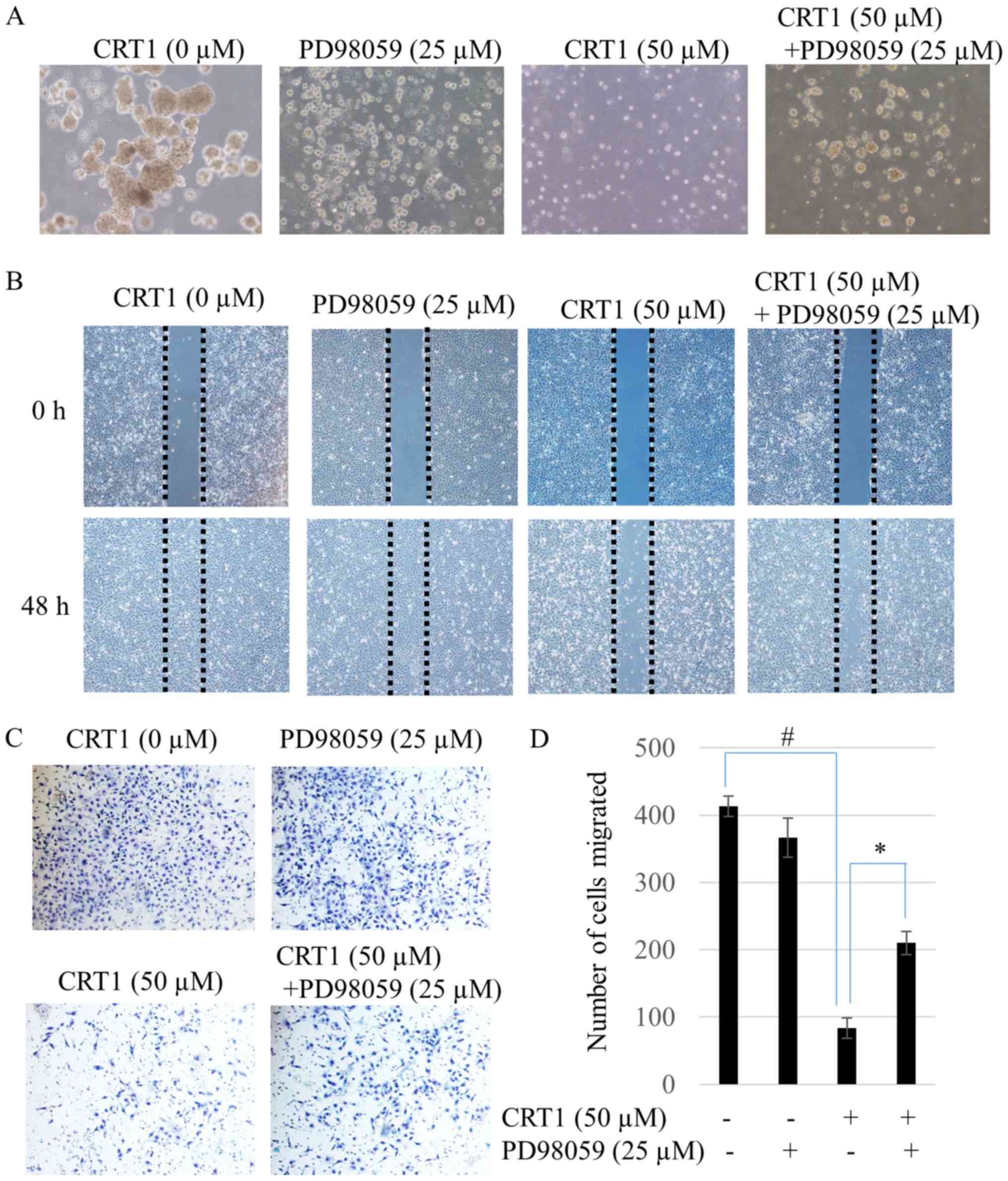
Results from colony survival assays of CRT1 are
presented as photographs. Results showed that activation of ERK1/2
by 50 µM CRT1 treatment strongly diminished colony sizes (Fig. 5A). To evaluate the effect of CRT1
on cell migration, wound healing assay and transwell migration
assay were performed. Results showed that CRT1 (50 µM) suppressed
the migration of SKOV3 cells (Fig.
5B). Consistent with this result, transwell invasion assay also
showed that 50 µM CRT1 significantly weakened the invasion capacity
of SKOV3 cells (Fig. 5C and D). To
investigate whether ERK1/2 was involved in CRT1-induced metastasis
of SKOV3 cells, PD98059, a specific ERK inhibitor, was used in the
experiment. PD98059 reversed CRT1-induced migration and invasion
(Fig. 5B-D) as well as
colony-forming ability (Fig.
5A).
Discussion
A variety of substances such as those present in
dietary and medicinal plants all over the world have inhibitory
effects on several cancers. The genus Croton consists of
about 800 species that are widely distributed throughout tropical
and subtropical regions. About 31 of these medicinal plant species
are cultivated or grow wild in northern Vietnam (9). An ent−18-acetoxy-7β-hydroxy
kaur-15-oxo-16-ene is one of main substances isolated from
Croton tonkinensis. A prior report has shown that this
ent-kaurane diterpenoid compound can regulate cell viability
of SK-HEP1 hepatoma cancer cell line at IC50 of <5 µM
(18). Another ent-kaurane
diterpenoid compound, oridonin, can suppress the proliferation of
human ovarian cancer cells such as SKOV3, OVCAR-3 and A2780 cells
at IC50 values of 17.21, 13.9, and 12.1 µM, respectively
(22). Our results showed that
CRT1, an ent-kaurane diterpenoid compound, significantly
reduced proliferation of SKOV3 ovarian cancer cells, with
IC50 value of 24.6 µM (Fig.
1A). Several papers have suggested that ent-kaurane
diterpenoid possesses apoptotic effects on various cancers such as
colorectal carcinoma, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and ovarian
cancer (23–26). Consistent with these reports, our
study showed that CRT1 increased apoptosis of SKOV3 cells (Fig. 2). Besides, the percentages of
necrotic cells increased after treatment, suggesting that CRT1
could induce necrosis in SKOV3 cells (Fig. 2A). Prior reports have indicated
that ent-kaurane diterpenoids can produce antiproliferation effects
on cancer cells by induction of apoptosis as well as necrosis
(27,28).
To further understand the mechanisms in the
anticancer activity of CRT1 against ovarian cancer, we analyzed the
effect of CRT1 on ERK1/2/p90RSK signaling pathway.
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) are a family of
serine/threonine protein kinases that include ERK, JNK, and p38.
These kinases are involved in the activation of nuclear
transcription factors that control cellular proliferation, cell
cycle progression, apoptosis, and cell migration (29). RSKs, a family member of
serine/threonine protein kinases, are activated by ERK1/2 in
response to many growth factors and hormones. ERK/1/2/p90RSK
pathway is known to modulate a variety of cellular processes,
including cell proliferation, survival, motility, and invasiveness
in ovarian cancers (30–32). However, how this pathway activates
proapoptotic signaling remains largely unknown. Oridonin, one
ent-kaurane diterpenoid, has been previously reported to be
able to induce phosphorylation of ERK, JNK, and p38 MAPK (33). Our study revealed that CRT1
dramatically increased phosphorylation level of ERK1/2 in a
dose-dependent (Fig. 3A) and
time-dependent (Fig. 3B). However,
no significant activation of JNK or p38 was observed under the same
condition (data not shown). A specific ERK inhibitor, PD98059,
prevented the activation of ERK1/2 in CRT1-induced cells (Fig. 3C and D). Moreover, PD98059 blocked
CRT1-mediated increase in cell growth (Fig. 4D) and apoptosis (Figs. 4A-C). These results strongly
support that CRT1-induced anticancer activities are regulated by
ERK1/2 activation in SKOV3 ovarian cancer cells. A prior report has
suggested that ERK1/2 and p90RSK signaling can dynamically regulate
cell motility in cancers (34). We
were interested in investigating the role of ERK1/2 activation in
SKOV3 cells in relation to colony formation, migration, and
invasion. Our results revealed that CRT1-induced ERK1/2 activation
inhibited ovarian cancer cell metastasis while ERK inhibitor
PD98059 prevented CRT1-induced anti-migration and anti-invasive
activity of SKOV3 cells (Fig. 5).
These results suggest that CRT1 plays an important role in cell
proliferation, migration, and the invasive potential of ovarian
cancer cells via ERK1/2 activation.
Primary cells are believed to be more biologically
relevant tools than cell lines for studying cancer biology
(35). Cell lines are known to
grow faster with minimal care. There is a possibility that cell
lines do not behave identically with primary cells. They should not
be used to replace primary cells (35). Although this study was performed
with SKOV3 cell line, we should do confirmation with primary cells
in the future.
Overall, our study showed that CRT1 could inhibit
cell viability, cell migration, and invasion of SKOV3 ovarian
cancer cells through activating the ERK1/2/p90RSK signaling
pathway. These results indicate that a natural ent-kaurane
diterpenoid, CRT1, might have potential as a chemotherapeutic agent
to prevent the spread of ovarian cancer by activating ERK1/2.
Further studies are needed to investigate the biological efficacy
of CRT1 for treating ovarian cancer using in vivo model.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by a research fund
from Chungnam National University (grant no. 2015-0881-01).
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are
included in this published article.
Authors' contributions
JSL designed the study and prepared the manuscript.
MSL, EYC and JBP performed the experiments and analyzed the data.
PTT isolated and identified the structure of CRT1. JYS and YBK
conceived and designed the study, and revised the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Serkies K, Węgrzynowicz E and Jassem J:
Paclitaxel and cisplatin chemotherapy for ovarian cancer during
pregnancy: Case report and review of the literature. Arch Gynecol
Obstet. 283 Suppl 1:S97–S100. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wen W, Wu J, Liu L, Tian Y, Buettner R,
Hsieh MY, Horne D, Dellinger TH, Han ES, Jove R and Yim JH:
Synergistic anti-tumor effect of combined inhibition of EGFR and
JAK/STAT3 pathways in human ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer. 14:1002015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vaughan S, Coward JI, Bast RC Jr, Berchuck
A, Berek JS, Brenton JD, Coukos G, Crum CC, Drapkin R,
Etemadmoghadam D, et al: Rethinking ovarian cancer: Recommendations
for improving outcomes. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:719–725. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lu Z and Xu S: ERK1/2 MAP kinases in cell
survival and apoptosis. IUBMB Life. 58:621–631. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cagnol S and Chambard JC: ERK and cell
death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death-apoptosis, autophagy
and senescence. FEBS J. 277:2–21. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calvo N, Carriere P, Martin MJ and Gentili
C: RSK activation via ERK modulates human colon cancer cells
response to PTHrP. J Mol Endocrinol. 59:13–27. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Giang PM, Son PT, Lee JJ and Otsuka H:
Four ent-kaurane-type diterpenoids from Croton tonkinensis Gagnep.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 52:879–882. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Do TL: Medicinal plants and remedies of
Vietnam. Publishing House Medicine; Hanoi: pp. 826–828. 2001
|
|
9
|
Kuo PC, Shen YC, Yang ML, Wang SH, Thang
TD, Dung NX, Chiang PC, Lee KH, Lee EJ and Wu TS: Crotonkinins A
and B and related diterpenoids from Croton tonkinensis as
anti-inflammatory and antitumor agents. J Nat Prod. 70:1906–1909.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Phan MG, Phan TS, Hamada Y and Otsuka H:
Cytotoxic diterpenoids from Vietnamese medicinal plant Croton
tonkinensis GAGNEP. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 53:296–300. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thuong PT, Khoi NM, Ohta S, Shiota S,
Kanta H, Takeuchi K and Ito F: ent-kaurane diterpenoids from Croton
tonkinensis induce apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells through the
phosphorylation of JNK mediated by reactive oxygen species and
dual-specificity JNK kinase MKK4. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
14:1051–1061. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Giang PM, Jin HZ, Son PT, Lee JH, Hong YS
and Lee JJ: ent-Kaurane diterpenoids from croton tonkinensis
inhibit LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation and NO production. J Nat
Prod. 66:1217–1220. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thuong PT, Dao TT, Pham TH, Nguyen PH, Le
TV, Lee KY and Oh WK: Crotonkinensins A and B, diterpenoids from
the Vietnamese medicinal plant Croton tonkinensis. J Nat Prod.
72:1–2042. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Dao TT, Le TV, Nguyen PH, Thuong PT, Minh
PT, Woo ER, Lee KY and Oh WK: SIRT1 inhibitory diterpenoids from
the Vietnamese medicinal plant Croton tonkinensis. Planta Med.
76:1011–1014. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dao TT, Lee KY, Jeong HM, Nguyen PH, Tran
TL, Thuong PT, Nguyen BT and Oh WK: ent-Kaurane diterpenoids from
Croton tonkinensis stimulate osteoblast differentiation. J Nat
Prod. 74:2526–2531. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu J, Chen X, Qu S, Yao B, Xu Y, Wu J, Jin
Y and Ma C: Oridonin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in hormone-independent
prostate cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 13:2838–2846. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Deng R, Tang J, Xia LP, Li DD, Zhou WJ,
Wang LL, Feng GK, Zeng YX, Gao YH and Zhu XF: ExcisaninA, a
diterpenoid compound purified from Isodon MacrocalyxinD, induces
tumor cells apoptosis and suppresses tumor growth through
inhibition of PKB/AKT kinase activity and blockade of its signal
pathway. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:873–882. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sul YH, Lee MS, Cha EY, Thuong PT, Khoi NM
and Song IS: An ent-kaurane diterpenoid from Croton tonkinensis
induces apoptosis by regulating AMP-activated protein kinase in
SK-HEP1 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biol Pharm Bull.
36:158–164. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ye Q, Yao G, Zhang M, Guo G, Hu Y, Jiang
J, Cheng L, Shi J, Li H, Zhang Y and Liu H: A novel ent-kaurane
diterpenoid executes antitumor function in colorectal cancer cells
by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Carcinogenesis. 36:318–326.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou X, Yue GG, Chan AM, Tsui SK, Fung KP,
Sun H, Pu J and Lau CB: Eriocalyxin B, a novel autophagy inducer,
exerts anti-tumor activity through the suppression of
Akt/mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway in breast cancer. Biochem
Pharmacol. 142:58–70. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chipuk JE, Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L,
Droin NM, Newmeyer DD, Schuler M and Green DR: Direct activation of
Bax by p53 mediates mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and
apoptosis. Science. 303:1010–1014. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xia R, Chen SX, Qin Q, Chen Y, Zhang WW,
Zhu RR and Deng AM: Oridonin suppresses proliferation of human
ovarian cancer cells via blockage of mTOR signaling. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 17:667–671. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qiu S, Wu X, Liao H, Zeng X, Zhang S, Lu
X, He X, Zhang X, Ye W, Wu H and Zhu X: Pteisolic acid G, a novel
ent-kaurane diterpenoid, inhibits viability and induces apoptosis
in human colorectal carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 14:5540–5548.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li L, Yue GG, Lau CB, Sun H, Fung KP,
Leung PC, Han Q and Leung PS: Eriocalyxin B induces apoptosis and
cell cycle arrest in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells through
caspase- and p53-dependent pathways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
262:80–90. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yao R, Chen Z, Zhou C, Luo M, Shi X, Li J,
Gao Y, Zhou F, Pu J, Sun H and He J: Xerophilusin B induces cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
cells and does not cause toxicity in nude mice. J Nat Prod.
78:10–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liao YJ, Bai HY, Li ZH, Zou J, Chen JW,
Zheng F, Zhang JX, Mai SJ, Zeng MS, Sun HD, et al: Longikaurin A, a
natural ent-kaurane, induces G2/M phase arrest via downregulation
of Skp2 and apoptosis induction through ROS/JNK/c-Jun pathway in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 5:e11372014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu JJ, Huang RW, Lin DJ, Wu XY, Peng J,
Pan XL, Lin Q, Hou M, Zhang MH and Chen F: Antiproliferation
effects of oridonin on HPB-ALL cells and its mechanisms of action.
Am J Hematol. 81:86–94. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu GA, Chang JC, Feng XL and Ding L:
Apoptosis induced by weisiensin B isolated from Rabdosia weisiensis
C.Y. Wu in K562. Pharmazie. 70:263–268. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miller CR, Oliver KE and Farley JH: MEK1/2
inhibitors in the treatment of gynecologic malignancies. Gynecol
Oncol. 133:128–137. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Torchiaro E, Lorenzato A, Olivero M,
Valdembri D, Gagliardi PA, Gai M, Erriquez J, Serini G and Di Renzo
MF: Peritoneal and hematogenous metastases of ovarian cancer cells
are both controlled by the p90RSK through a self-reinforcing cell
autonomous mechanism. Oncotarget. 7:712–728. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim JH, Jeong SJ, Kim B, Yun SM, Choi DY
and Kim SH: Melatonin synergistically enhances cisplatin-induced
apoptosis via the dephosphorylation of ERK/p90 ribosomal S6
kinase/heat shock protein 27 in SK-OV-3 cells. J Pineal Res.
52:244–252. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bai RX, Wang WP, Zhao PW and Li CB:
Ghrelin attenuates the growth of HO-8910 ovarian cancer cells
through the ERK pathway. Braz J Med Biol Res. 49(pii):
S0100879×2016000300602. 2016.
|
|
33
|
Kuo LM, Kuo CY, Lin CY, Hung MF, Shen JJ
and Hwang TL: Intracellular glutathione depletion by oridonin leads
to apoptosis in hepatic stellate cells. Molecules. 19:3327–3344.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tanimura S and Takeda K: ERK signalling as
a regulator of cell motility. J Biochem. 162:145–154. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kaur G and Dufour JM: Cell lines: Valuable
tools or useless artifacts. Spermatogenesis. 2:1–5. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|