|
1
|
Hudmon A and Schulman H:
Structure-function of the multifunctional
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Biochem J.
364:593–611. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rosenberg OS, Deindl S, Sung RJ, Nairn AC
and Kuriyan J: Structure of the autoinhibited kinase domain of
CaMKII and SAXS analysis of the holoenzyme. Cell. 123:849–860.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Erickson JR, He BJ, Grumbach IM and
Anderson ME: CaMKII in the cardiovascular system: Sensing redox
states. Physiol Rev. 91:889–915. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stratton M, Lee IH, Bhattacharyya M,
Christensen SM, Chao LH, Schulman H, Groves JT and Kuriyan J:
Activation-triggered subunit exchange between CaMKII holoenzymes
facilitates the spread of kinase activity. Elife. 3:e016102013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Erickson JR, Joiner ML, Guan X, Kutschke
W, Yang J, Oddis CV, Bartlett RK, Lowe JS, O'Donnell SE,
Aykin-Burns N, et al: A dynamic pathway for calcium-independent
activation of CaMKII by methionine oxidation. Cell. 133:462–474.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brookes PS, Yoon Y, Robotham JL, Anders MW
and Sheu SS: Calcium, ATP, and ROS: A mitochondrial love-hate
triangle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 287:C817–C833. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nickel AG, Kohlhaas M, Bertero E, Wilhelm
D, Wagner M, Sequeira V, Kreusser MM, Dewenter M, Kappl R, Hoth M,
et al: CaMKII does not control mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake
in cardiac myocytes. J Physiol. Feb 16–2019.(Epub ahead of print).
doi: 10.1113/JP276766. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Luo M, Guan X, Luczak ED, Lang D, Kutschke
W, Gao Z, Yang J, Glynn P, Sossalla S, Swaminathan PD, et al:
Diabetes increases mortality after myocardial infarction by
oxidizing CaMKII. J Clin Invest. 123:1262–1274. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sanders PN, Koval OM, Jaffer OA, Prasad
AM, Businga TR, Scott JA, Hayden PJ, Luczak ED, Dickey DD,
Allamargot C, et al: CaMKII is essential for the proasthmatic
effects of oxidation. Sci Transl Med. 5:195ra972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Viatchenko-Karpinski S Kornyeyev D,
El-Bizri N, Budas G, Fan P, Jiang Z, Yang J, Anderson ME, Shryock
JC, Chang CP, et al: Intracellular Na+ overload causes
oxidation of CaMKII and leads to Ca2+ mishandling in
isolated ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 76:247–256.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ho HT, Liu B, Snyder JS, Lou Q, Brundage
EA, Velez-Cortes F, Wang H, Ziolo MT, Anderson ME, Sen CK, et al:
Ryanodine receptor phosphorylation by oxidized CaMKII contributes
to the cardiotoxic effects of cardiac glycosides. Cardiovasc Res.
101:165–174. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Singh MV, Swaminathan PD, Luczak ED,
Kutschke W, Weiss RM and Anderson ME: MyD88 mediated inflammatory
signaling leads to CaMKII oxidation, cardiac hypertrophy and death
after myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 52:1135–1144.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Swaminathan PD, Purohit A, Soni S, Voigt
N, Singh MV, Glukhov AV, Gao Z, He BJ, Luczak ED, Joiner ML, et al:
Oxidized CaMKII causes cardiac sinus node dysfunction in mice. J
Clin Invest. 121:3277–3288. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
He BJ, Joiner ML, Singh MV, Luczak ED,
Swaminathan PD, Koval OM, Kutschke W, Allamargot C, Yang J, Guan X,
et al: Oxidation of CaMKII determines the cardiotoxic effects of
aldosterone. Nat Med. 17:1610–1618. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Erickson JR, Pereira L, Wang L, Han G,
Ferguson A, Dao K, Copeland RJ, Despa F, Hart GW, Ripplinger CM and
Bers DM: Diabetic hyperglycaemia activates CaMKII and arrhythmias
by O-linked glycosylation. Nature. 502:372–376. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gutierrez DA, Fernandez-Tenorio M,
Ogrodnik J and Niggli E: NO-dependent CaMKII activation during
β-adrenergic stimulation of cardiac muscle. Cardiovasc Res.
100(392-401): 12013
|
|
17
|
Coultrap SJ and Bayer KU: Nitric oxide
induces Ca2+-independent activity of the
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII). J
Biol Chem. 289:19458–19465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Curran J, Tang L, Roof SR, Velmurugan S,
Millard A, Shonts S, Wang H, Santiago D, Ahmad U, Perryman M, et
al: Nitric oxide-dependent activation of CaMKII increases diastolic
sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release in cardiac myocytes in
response to adrenergic stimulation. PLoS One. 9:e874952014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Erickson JR, Nichols CB, Uchinoumi H,
Stein ML, Bossuyt J and Bers DM: S-Nitrosylation induces both
autonomous activation and inhibition of
Calcium/Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II δ. J Biol Chem.
290:25646–25656. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yilmaz M, Gangopadhyay SS, Leavis P,
Grabarek Z and Morgan KG: Phosphorylation at Ser26 in
the ATP-binding site of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase
II as a mechanism for switching off the kinase activity. Biosci
Rep. 33:e000242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tobimatsu T and Fujisawa H:
Tissue-specific expression of four types of rat
calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II mRNAs. J Biol Chem.
264:17907–17912. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tombes RM and Krystal GW: Identification
of novel human tumor cell-specific CaMK-II variants. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1355:281–292. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Takaishi T, Saito N and Tanaka C: Evidence
for distinct neuronal localization of gamma and delta subunits of
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in the rat
brain. J Neurochem. 58:1971–1974. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bayer KU, Löhler J, Schulman H and Harbers
K: Developmental expression of the CaM kinase II isoforms:
Ubiquitous gamma- and delta-CaM kinase II are the early isoforms
and most abundant in the developing nervous system. Brain Res Mol
Brain Res. 70:147–154. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim I, Je HD, Gallant C, Zhan Q, Riper DV,
Badwey JA, Singer HA and Morgan KG:
Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-dependent
activation of contractility in ferret aorta. J Physiol.
526:367–374. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gangopadhyay SS, Barber AL, Gallant C,
Grabarek Z, Smith JL and Morgan KG: Differential functional
properties of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIgamma variants
isolated from smooth muscle. Biochem J. 372:347–357. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Marganski WA, Gangopadhyay SS, Je HD,
Gallant C and Morgan KG: Targeting of a novel
Ca+2/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II is essential
for extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mediated signaling in
differentiated smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 97:541–549. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guo T, Zhang T, Ginsburg KS, Mishra S,
Brown JH and Bers DM: CaMKIIδC slows Ca]i decline in cardiac
myocytes by promoting Ca sparks. Biophys J. 102:2461–2470. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mishra S, Ling H, Grimm M, Zhang T, Bers
DM and Brown JH: Cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure development
through Gq and CaM kinase II signaling. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
56:598–603. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Singh MV, Kapoun A, Higgins L, Kutschke W,
Thurman JM, Zhang R, Singh M, Yang J, Guan X, Lowe JS, et al:
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II triggers cell
membrane injury by inducing complement factor B gene expression in
the mouse heart. J Clin Invest. 119:986–996. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Crack PJ, Taylor JM, Ali U, Mansell A and
Hertzog PJ: Potential contribution of NF-kappaB in neuronal cell
death in the glutathione peroxidase-1 knockout mouse in response to
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Stroke. 37:1533–1538. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gu SX, Blokhin IO, Wilson KM, Dhanesha N,
Doddapattar P, Grumbach IM, Chauhan AK and Lentz SR: Protein
methionine oxidation augments reperfusion injury in acute ischemic
stroke. JCI Insight. 1(pii): e864602016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kimura W, Muralidhar S, Canseco DC, Puente
B, Zhang CC, Xiao F, Abderrahman YH and Sadek HA: Redox signaling
in cardiac renewal. Antioxid Redox Signal. 21:1660–1673. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fraccarollo D, Galuppo P, Neuser J,
Bauersachs J and Widder JD: Pentaerythritol tetranitrate targeting
myocardial reactive oxygen species production improves left
ventricular remodeling and function in rats with ischemic heart
failure. Hypertension. 66:978–987. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Frantz S, Brandes RP, Hu K, Rammelt K,
Wolf J, Scheuermann H, Ertl G and Bauersachs J: Left ventricular
remodeling after myocardial infarction in mice with targeted
deletion of the NADPH oxidase subunit gp91PHOX. Basic Res Cardiol.
101:127–132. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Murdoch CE, Zhang M, Cave AC and Shah AM:
NADPH oxidase-dependent redox signalling in cardiac hypertrophy,
remodelling and failure. Cardiovasc Res. 71:208–215. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Purohit A, Rokita AG, Guan X, Chen B,
Koval OM, Voigt N, Neef S, Sowa T, Gao Z, Luczak ED, et al:
Oxidized Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II triggers
atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 128:1748–1757. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wagner S, Ruff HM, Weber SL, Bellmann S,
Sowa T, Schulte T, Anderson ME, Grandi E, Bers DM, Backs J, et al:
Reactive oxygen species-activated Ca/calmodulin kinase IIδ is
required for late I(Na) augmentation leading to cellular Na and Ca
overload. Circ Res. 108:555–565. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhu LJ, Klutho PJ, Scott JA, Xie L, Luczak
ED, Dibbern ME, Prasad AM, Jaffer OA, Venema AN, Nguyen EK, et al:
Oxidative activation of the Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein
kinase II (CaMKII) regulates vascular smooth muscle migration and
apoptosis. Vascul Pharmacol. 60:75–83. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Scott JA, Xie L, Li H, Li W, He JB,
Sanders PN, Carter AB, Backs J, Anderson ME and Grumbach IM: The
multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II
regulates vascular smooth muscle migration through matrix
metalloproteinase 9. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
302:H1953–H1964. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rajtik T, Carnicka S, Szobi A, Giricz Z,
O-Uchi J, Hassova V, Svec P, Ferdinandy P, Ravingerova T and
Adameova A: Oxidative activation of CaMKIIδ in acute myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury: A role of angiotensin AT1
receptor-NOX2 signaling axis. Eur J Pharmacol. 771:114–122. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE,
Hamman RF, Lachin JM, Walker EA and Nathan DM: Reduction in the
incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or
met-formin. N Engl J Med. 346:393–403. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Donahoe SM, Stewart GC, McCabe CH,
Mohanavelu S, Murphy SA, Cannon CP and Antman EM: Diabetes and
mortality following acute coronary syndromes. JAMA. 298:765–775.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chai S, Qian Y, Tang J, Liang Z, Zhang M,
Si J, Li X, Huang W, Xu R and Wang K: Retracted:
Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIγ, a critical mediator
of the NF-κB network, is a novel therapeutic target in non-small
cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 344:119–128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Britschgi A, Bill A, Brinkhaus H, Rothwell
C, Clay I, Duss S, Rebhan M, Raman P, Guy CT, Wetzel K, et al:
Calcium-activated chloride channel ANO1 promotes breast cancer
progression by activating EGFR and CAMK signaling. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 110:E1026–E1034. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kim JH, Kim TW and Kim SJ: Downregulation
of ARFGEF1 and CAMK2B by promoter hypermethylation in breast cancer
cells. BMB Rep. 44:523–528. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang T, Guo S, Liu Z, Wu L, Li M, Yang J,
Chen R, Liu X, Xu H, Cai S, et al: CAMK2N1 inhibits prostate cancer
progression through androgen receptor-dependent signaling.
Oncotarget. 5:10293–10306. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang C, Li N, Liu X, Zheng Y and Cao X: A
novel endogenous human CaMKII inhibitory protein suppresses tumor
growth by inducing cell cycle arrest via p27 stabilization. J Biol
Chem. 283:11565–11574. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jing Z, Sui X, Yao J, Xie J, Jiang L, Zhou
Y, Pan H and Han W: SKF-96365 activates cytoprotective autophagy to
delay apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells through inhibition of
the calcium/CaMKIIγ/AKT-mediated pathway. Cancer Lett. 372:226–238.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bhat PJ, Darunte L, Kareenhalli V,
Dandekar J and Kumar A: Can metabolic plasticity be a cause for
cancer? Warburg-Waddington legacy revisited. Clin Epigenetics.
2:113–122. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hart PC, Mao M, de Abreu AL,
Ansenberger-Fricano K, Ekoue DN, Ganini D, Kajdacsy-Balla A,
Diamond AM, Minshall RD, Consolaro ME, et al: MnSOD upregulation
sustains the Warburg effect via mitochondrial ROS and
AMPK-dependent signalling in cancer. Nat Commun. 6:60532015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kirkham P and Rahman I: Oxidative stress
in asthma and COPD: Antioxidants as a therapeutic strategy.
Pharmacol Ther. 111:476–494. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jaffer OA, Carter AB, Sanders PN, Dibbern
ME, Winters CJ, Murthy S, Ryan AJ, Rokita AG, Prasad AM, Zabner J,
et al: Mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant therapy decreases
transforming growth factor-β-mediated collagen production in a
murine asthma model. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 52:106–115. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Anandan C, Nurmatov U, van Schayck OC and
Sheikh A: Is the prevalence of asthma declining? Systematic review
of epidemiological studies. Allergy. 65:152–167. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lambrecht BN and Hammad H: The immunology
of asthma. Nat Immunol. 16:45–56. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Huang SK, Zhang Q, Qiu Z and Chung KF:
Mechanistic impact of outdoor air pollution on asthma and allergic
diseases. J Thorac Dis. 7:23–33. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Casalino-Matsuda SM, Monzón ME and Forteza
RM: Epidermal growth factor receptor activation by epidermal growth
factor mediates oxidant-induced goblet cell metaplasia in human
airway epithelium. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 34:581–591. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Abdala-Valencia H, Earwood J, Bansal S,
Jansen M, Babcock G, Garvy B, Wills-Karp M and Cook-Mills JM:
Nonhematopoietic NADPH oxidase regulation of lung eosinophilia and
airway hyperresponsiveness in experimentally induced asthma. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 292:L1111–L1125. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Spinelli AM, Liu Y, Sun LY, González-Cobos
JC, Backs J, Trebak M and Singer HA: Smooth muscle CaMKIIδ promotes
allergen-induced airway hyper-responsiveness and inflammation.
Pflugers Arch. 467:2541–2554. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Li JM, Mullen AM, Yun S, Wientjes F,
Brouns GY, Thrasher AJ and Shah AM: Essential role of the NADPH
oxidase subunit p47(phox) in endothelial cell superoxide production
in response to phorbol ester and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Circ
Res. 90:143–150. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ikeda RK, Nayar J, Cho JY, Miller M,
Rodriguez M, Raz E and Broide DH: Resolution of airway inflammation
following ovalbumin inhalation: Comparison of ISS DNA and
corticosteroids. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 28:655–663. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Anderson ME: Oxidant stress promotes
disease by activating CaMKII. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 89:160–167. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Fujisawa T, Velichko S, Thai P, Hung LY,
Huang F and Wu R: Regulation of airway MUC5AC expression by
IL-1beta and IL-17A; the NF-kappaB paradigm. J Immunol.
183:6236–6243. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Qu J, Do DC, Zhou Y, Luczak E, Mitzner W,
Anderson ME and Gao P: Oxidized CaMKII promotes asthma through the
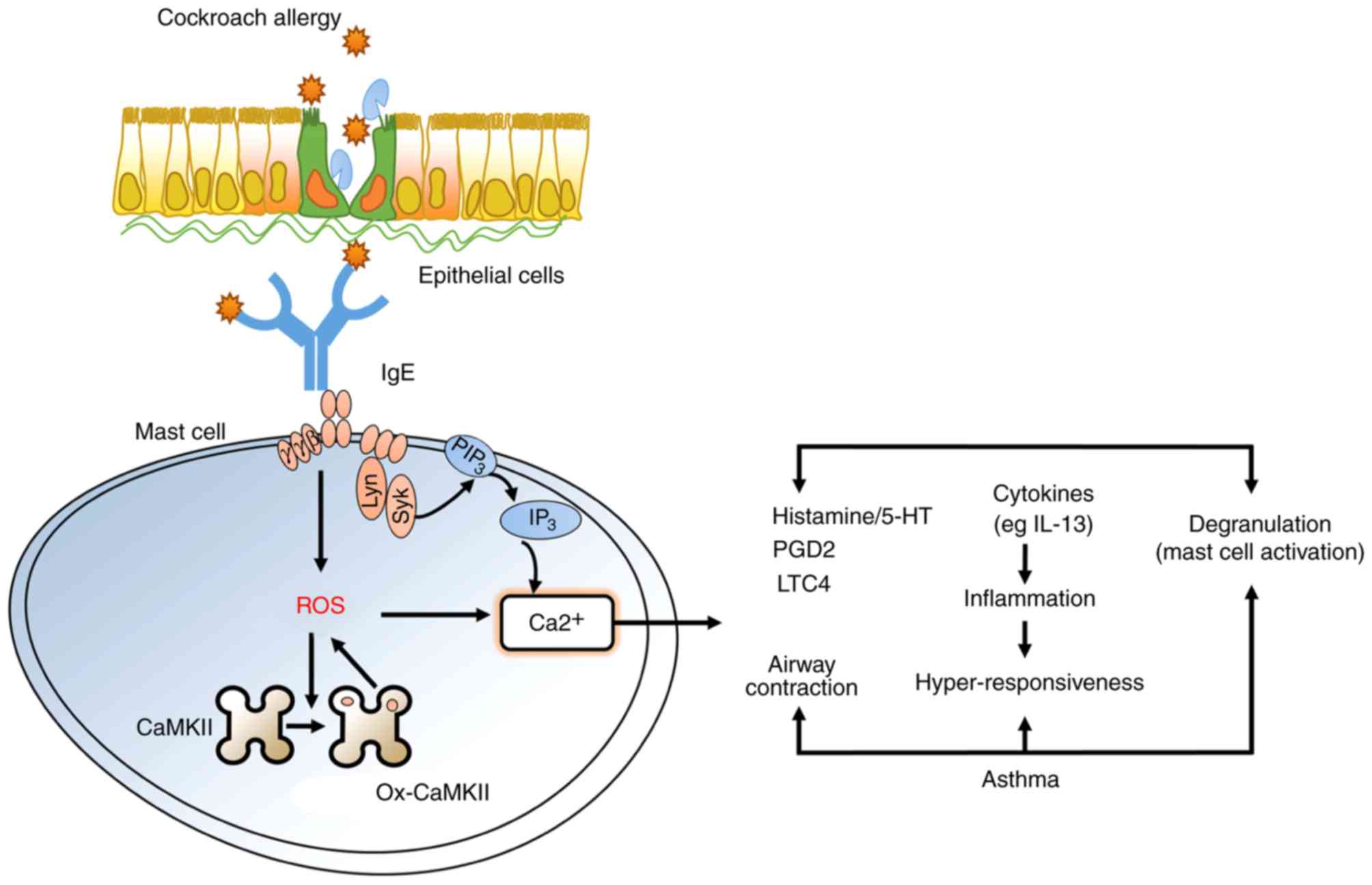
activation of mast cells. JCI Insight. 2:e901392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhou Y, Tung HY, Tsai YM, Hsu SC, Chang
HW, Kawasaki H, Tseng HC, Plunkett B, Gao P, Hung CH, et al: Aryl
hydrocarbon receptor controls murine mast cell homeostasis. Blood.
121:3195–3204. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Mahdavinia M, Suh LA, Carter RG, Stevens
WW, Norton JE, Kato A, Tan BK, Kern RC, Conley DB, Chandra R, et
al: Increased noneosinophilic nasal polyps in chronic
rhinosinusitis in US second-generation Asians suggest genetic
regulation of eosinophilia. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 135:576–579.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Totlandsdal AI, Cassee FR, Schwarze P,
Refsnes M and Låg M: Diesel exhaust particles induce CYP1A1 and
pro-inflammatory responses via differential pathways in human
bronchial epithelial cells. Part Fibre Toxicol. 7:412010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Manners S, Alam R, Schwartz DA and Gorska
MM: A mouse model links asthma susceptibility to prenatal exposure
to diesel exhaust. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 134:63–72. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wang H, Do DC, Liu J, Wang B, Qu J, Ke X,
Luo X, Tang HM, Tang HL, Hu C, et al: Functional role of kynurenine
and aryl hydrocarbon receptor axis in chronic rhinosinusitis with
nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 141:586–600.e6. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|