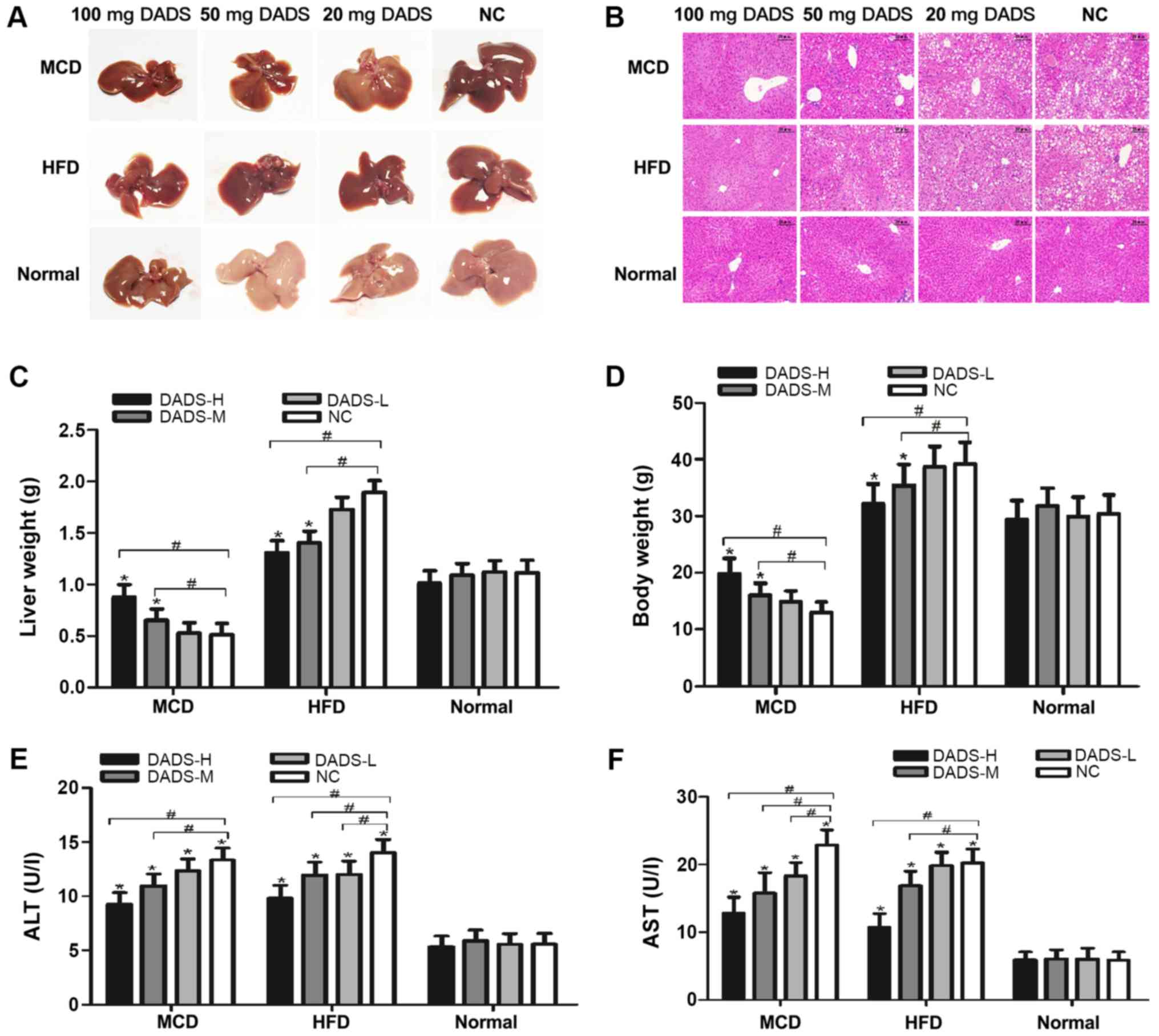
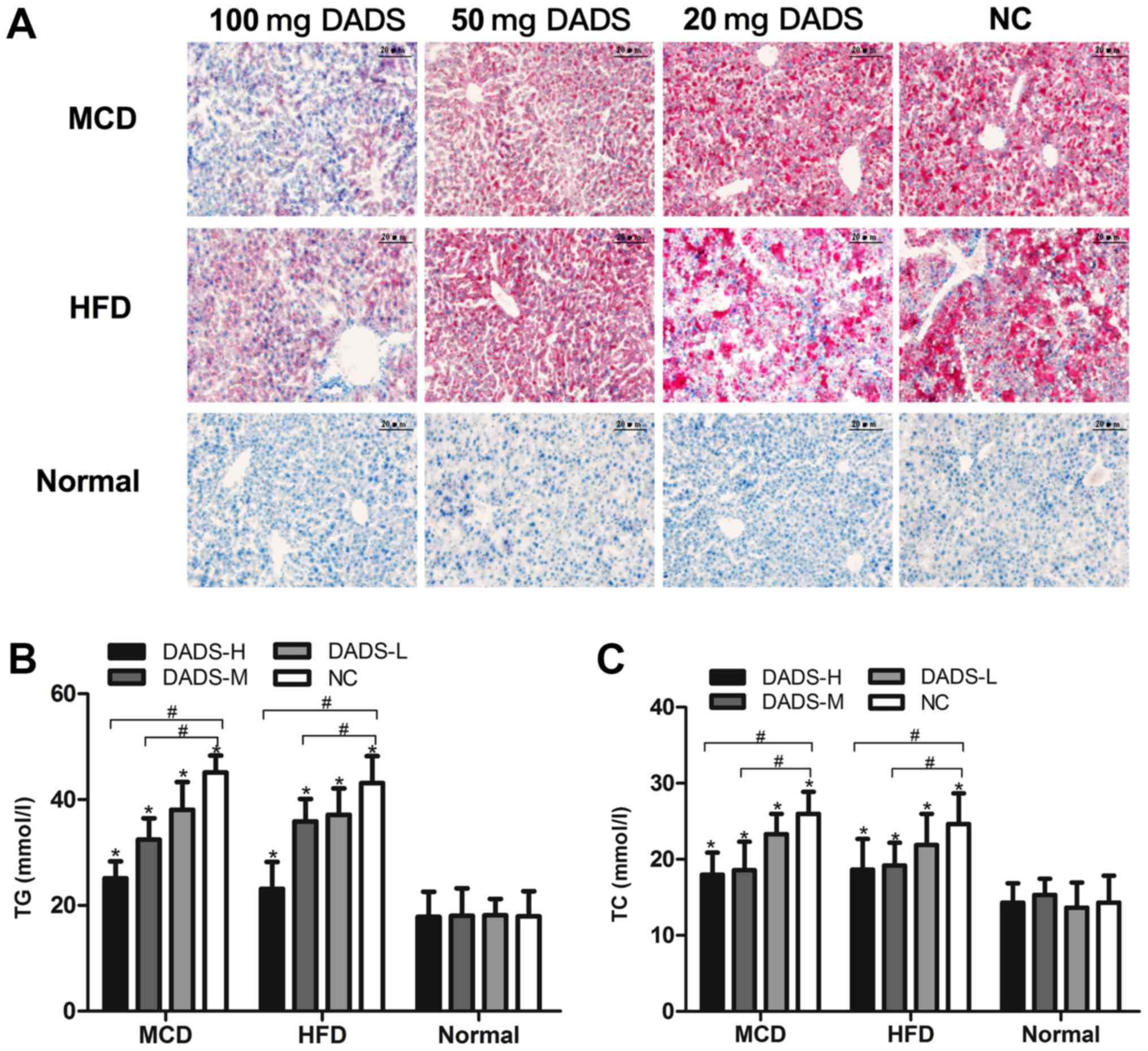
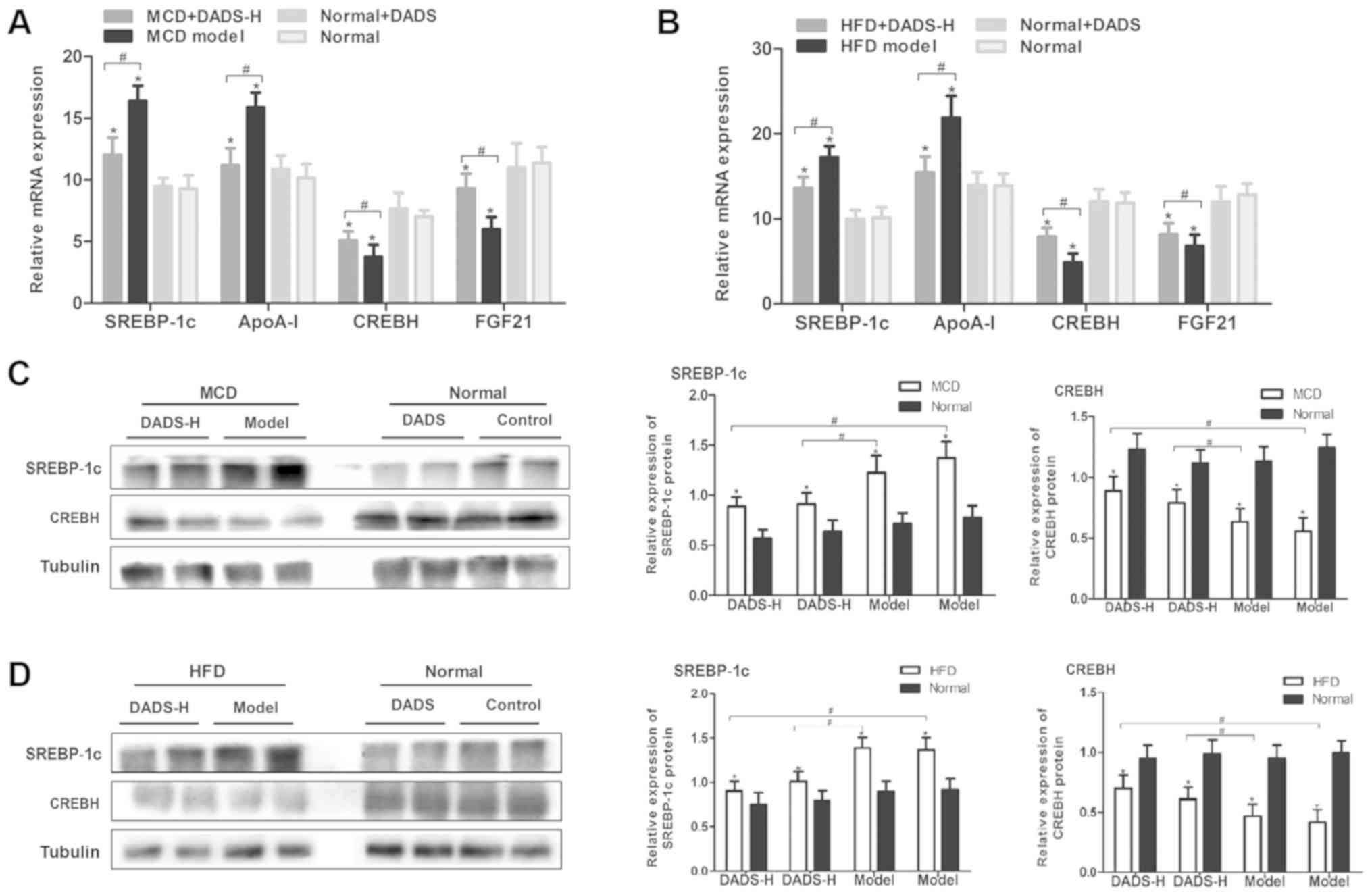
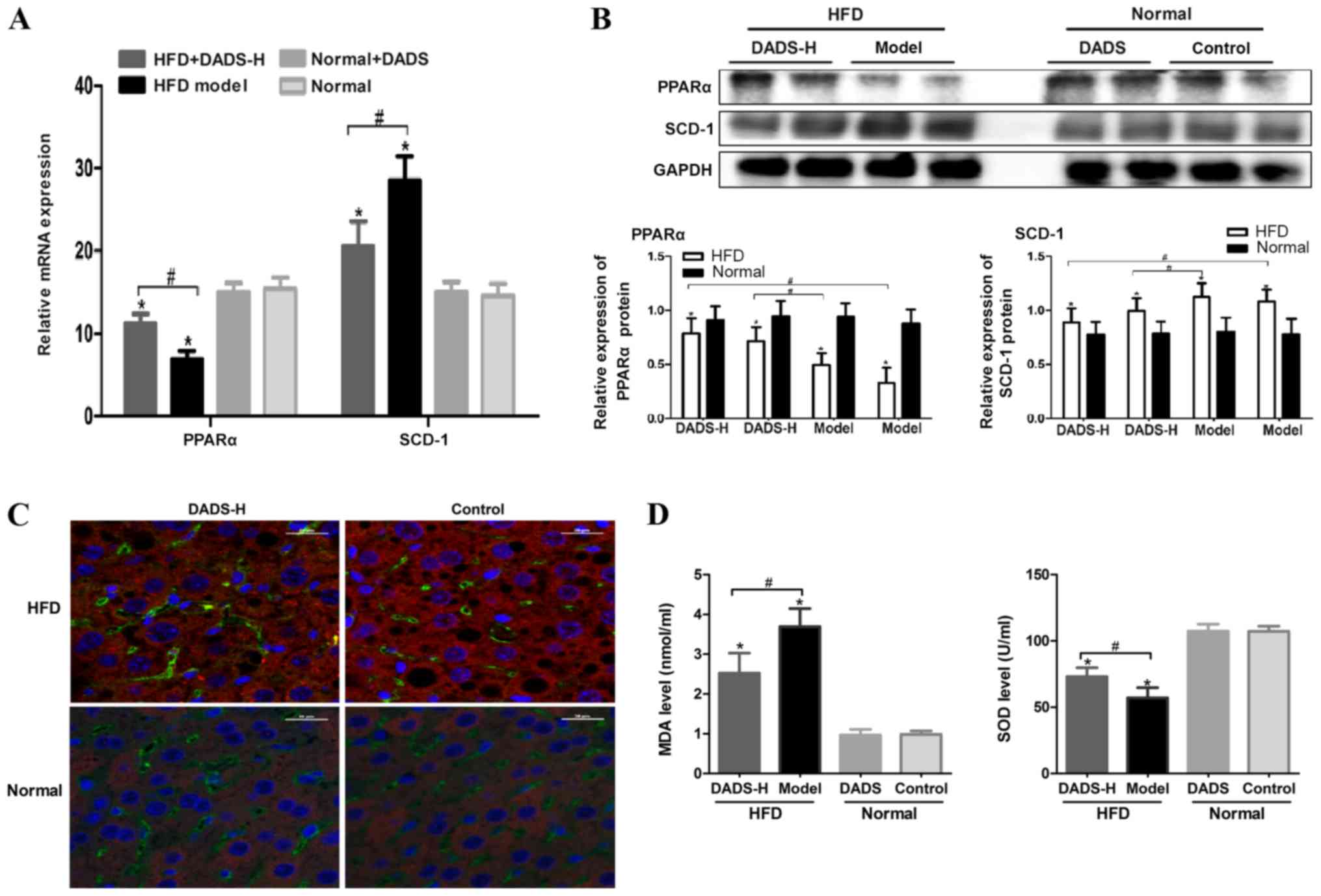
|
1
|
Italian Association for the Study of the
Liver (AISF), . AISF position paper on nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease (NAFLD): Updates and future directions. Dig Liver Dis.
49:471–483. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Caligiuri A, Gentilini A and Marra F:
Molecular pathogenesis of NASH. Int J Mol Sci. 17(pii): E15752016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tilg H and Moschen AR: Evolution of
inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The multiple
parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology. 52:1836–1846. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lassailly G, Caiazzo R, Pattou F and
Mathurin P: Perspectives on treatment for nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 150:1835–1848. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lai YS, Chen WC, Ho CT, Lu KH, Lin SH,
Tseng HC, Lin SY and Sheen LY: Garlic essential oil protects
against obesity-triggered nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through
modulation of lipid metabolism and oxidative stress. J Agric Food
Chem. 62:5897–5906. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yun HM, Ban JO, Park KR, Lee CK, Jeong HS,
Han SB and Hong JT: Potential therapeutic effects of functionally
active compounds isolated from garlic. Pharmacol Ther. 142:183–195.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sheen LY, Wu CC, Lii CK and Tsai SJ:
Effect of diallyl sulfide and diallyl disulfide, the active
principles of garlic, on the aflatoxin B(1)-induced DNA damage in
primary rat hepatocytes. Toxicol Lett. 122:45–52. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Y, Li A, Feng X, Sun X, Zhu X and Zhao
Z: Pharmacological investigation of the anti-inflammation and
anti-oxidation activities of diallyl disulfide in a rat emphysema
model induced by cigarette smoke extract. Nutrients. 10(pii):
E792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ko JW, Park SH, Shin NR, Shin JY, Kim JW,
Shin IS, Moon C, Heo JD, Kim JC and Lee IC: Protective effect and
mechanism of action of diallyl disulfide against
acetaminophen-induced acute hepatotoxicity. Food Chem Toxicol.
109:28–37. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Raghu R, Liu CT, Tsai MH, Tang X, Kalari
KR, Subramanian S and Sheen LY: Transcriptome analysis of
garlic-induced hepatoprotection against alcoholic fatty liver. J
Agric Food Chem. 60:11104–11119. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shimada M, Liu L, Nussler N, Jonas S,
Langrehr JM, Ogawa T, Kaminishi M, Neuhaus P and Nussler AK: Human
hepatocytes are protected from ethanol-induced cytotoxicity by DADS
via CYP2E1 inhibition. Toxicol Lett. 163:242–249. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jeong HG and Lee YW: Protective effects of
diallyl sulfide on N-nitrosodimethylamine-induced immunosuppression
in mice. Cancer Lett. 134:73–79. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guyonnet D, Siess MH, Le Bon AM and
Suschetet M: Modulation of phase II enzymes by organosulfur
compounds from allium vegetables in rat tissues. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 154:50–58. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Feng C, Luo Y, Nian Y, Liu D, Yin X, Wu J,
Di J, Zhang R and Zhang J: Diallyl disulfide suppresses the
inflammation and apoptosis resistance induced by DCA through ROS
and the NF-κB signaling pathway in human barrett's epithelial
cells. Inflammation. 40:818–831. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Khatua TN, Dinda AK, Putcha UK and
Banerjee SK: Diallyl disulfide ameliorates isoproterenol induced
cardiac hypertrophy activating mitochondrial biogenesis via
eNOS-Nrf2-Tfam pathway in rats. Biochem Biophys Rep. 5:77–88.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Battal M, Kartal A, Citgez B, Yilmaz B,
Akcakaya A and Karatepe O: Impact of allyl disulfide on oxidative
damage and liver regeneration in an experimental hepatectomy model.
Chirurgia (Bucur). 110:117–122. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee IC, Kim SH, Baek HS, Moon C, Kim SH,
Kim YB, Yun WK, Kim HC and Kim JC: Protective effects of diallyl
disulfide on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity through
activation of Nrf2. Environ Toxicol. 30:538–548. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Germain E, Chevalier J, Siess MH and
Teyssier C: Hepatic metabolism of diallyl disulphide in rat and
man. Xenobiotica. 33:1185–1199. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fan JG and Qiao L: Commonly used animal
models of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis
Int. 8:233–240. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang J, Zhang H, Deng X, Zhang N, Liu B,
Xin S, Li G and Xu K: Baicalin attenuates non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis by suppressing key regulators of lipid metabolism,
inflammation and fibrosis in mice. Life Sci. 192:46–54. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling
C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, Ferrell LD, Liu YC, Torbenson MS,
Unalp-Arida A, et al: Design and validation of a histological
scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology.
41:1313–1321. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bellentani S: The epidemiology of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 37 (Suppl 1):S81–S84.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Musso G, Cassader M and Gambino R:
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Emerging molecular targets and
therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 15:249–274. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Imajo K, Yoneda M, Kessoku T, Ogawa Y,
Maeda S, Sumida Y, Hyogo H, Eguchi Y, Wada K and Nakajima A: Rodent
models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. Int J Mol Sci. 14:21833–21857. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Banini BA and Sanyal AJ: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, natural history,
diagnosis, and current treatment options. Clin Med Insights Ther.
8:75–84. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Benedict M and Zhang X: Non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease: An expanded review. World J Hepatol.
9:715–732. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee IC, Kim SH, Baek HS, Moon C, Kang SS,
Kim SH, Kim YB, Shin IS and Kim JC: The involvement of Nrf2 in the
protective effects of diallyl disulfide on carbon
tetrachloride-induced hepatic oxidative damage and inflammatory
response in rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 63:174–185. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nagaya T, Tanaka N, Suzuki T, Sano K,
Horiuchi A, Komatsu M, Nakajima T, Nishizawa T, Joshita S, Umemura
T, et al: Down-regulation of SREBP-1c is associated with the
development of burned-out NASH. J Hepatol. 53:724–731. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Del Campo JA, Gallego-Durán R, Gallego P
and Grande L: Genetic and epigenetic regulation in nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Int J Mol Sci. 19(pii): E9112018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee JH, Giannikopoulos P, Duncan SA, Wang
J, Johansen CT, Brown JD, Plutzky J, Hegele RA, Glimcher LH and Lee
AH: The transcription factor cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding
protein H regulates triglyceride metabolism. Nat Med. 17:812–815.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee IC, Baek HS, Kim SH, Moon C, Park SH,
Kim SH, Shin IS, Park SC and Kim JC: Effect of diallyl disulfide on
acute gastric mucosal damage induced by alcohol in rats. Hum Exp
Toxicol. 34:227–239. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bauer D, Mazzio E, Soliman KF, Taka E,
Oriaku E, Womble T and Darling-Reed S: Diallyl disulfide inhibits
TNFα-induced CCL2 release by MDA-MB-231 cells. Anticancer Res.
34:2763–2770. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rai SK, Sharma M and Tiwari M: Inhibitory
effect of novel diallyldisulfide analogs on HMG-CoA reductase
expression in hypercholesterolemic rats: CREB as a potential
upstream target. Life Sci. 85:211–219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Y, Cao R, Wei B, Chai X, Sun D, Guan
Y and Liu XM: Diallyl disulfide inhibits proliferation and
transdifferentiation of lung fibroblasts through induction of
cyclooxygenase and synthesis of prostaglandin E2. Mol
Cell Biochem. 393:77–87. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|