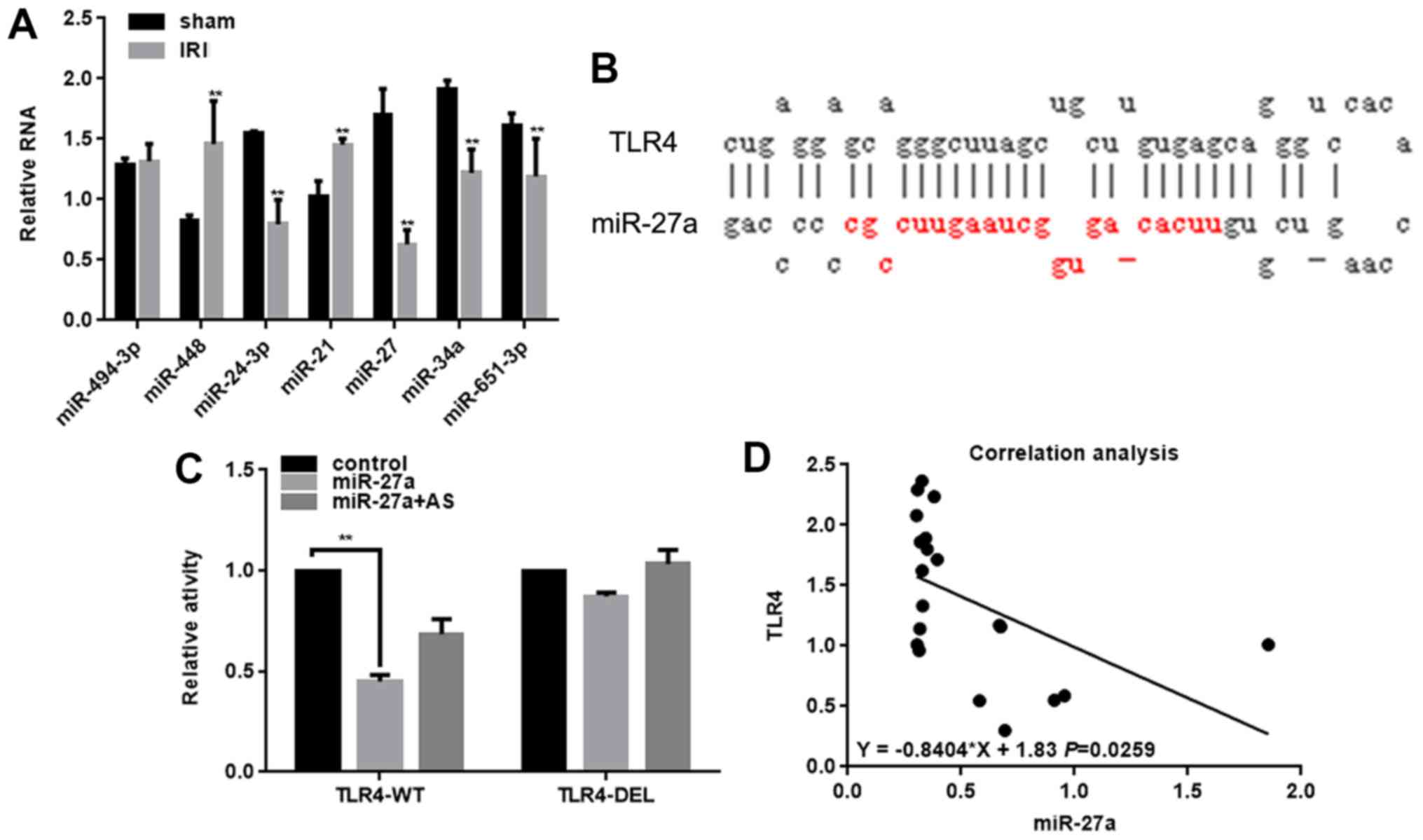
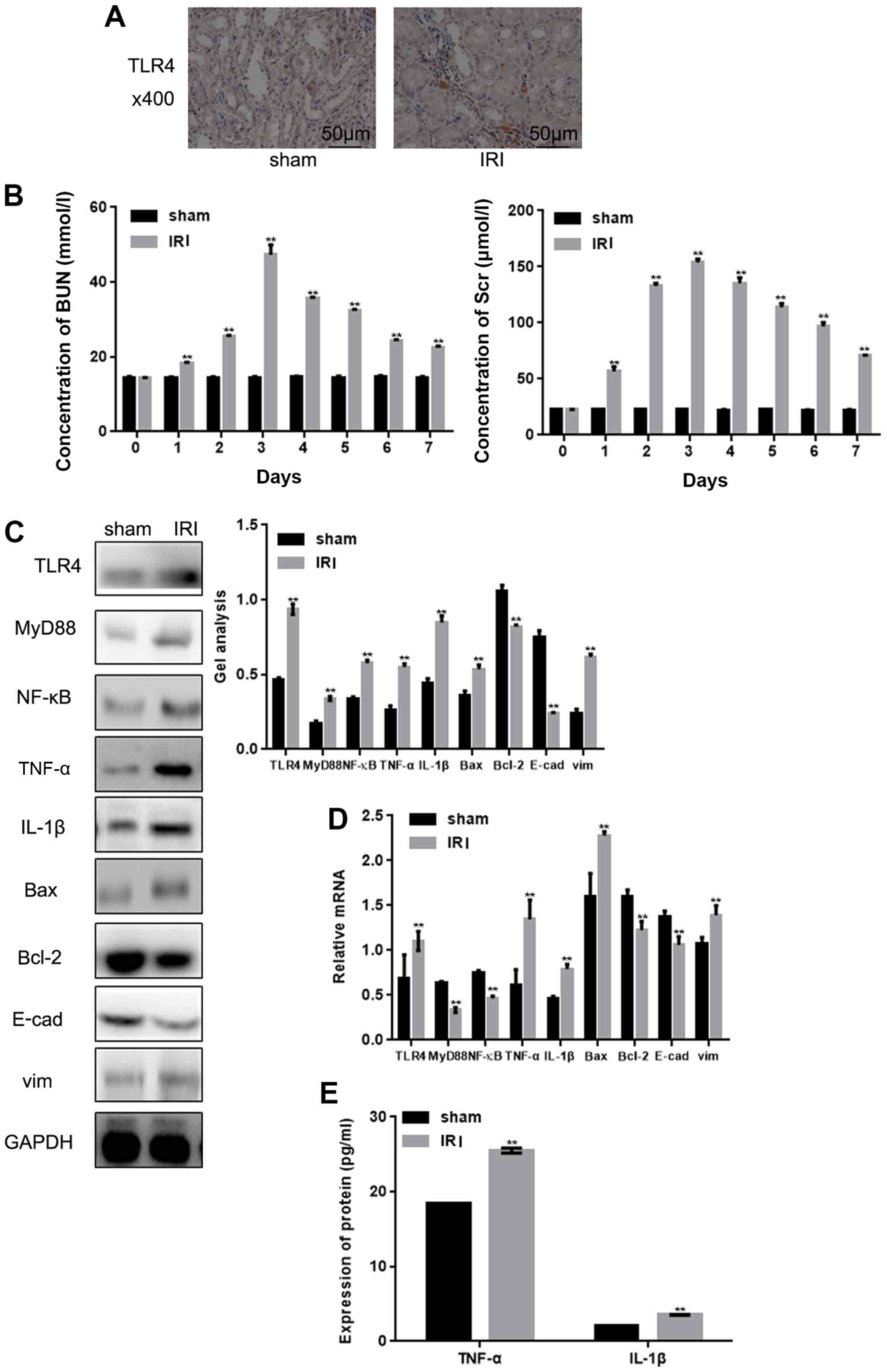
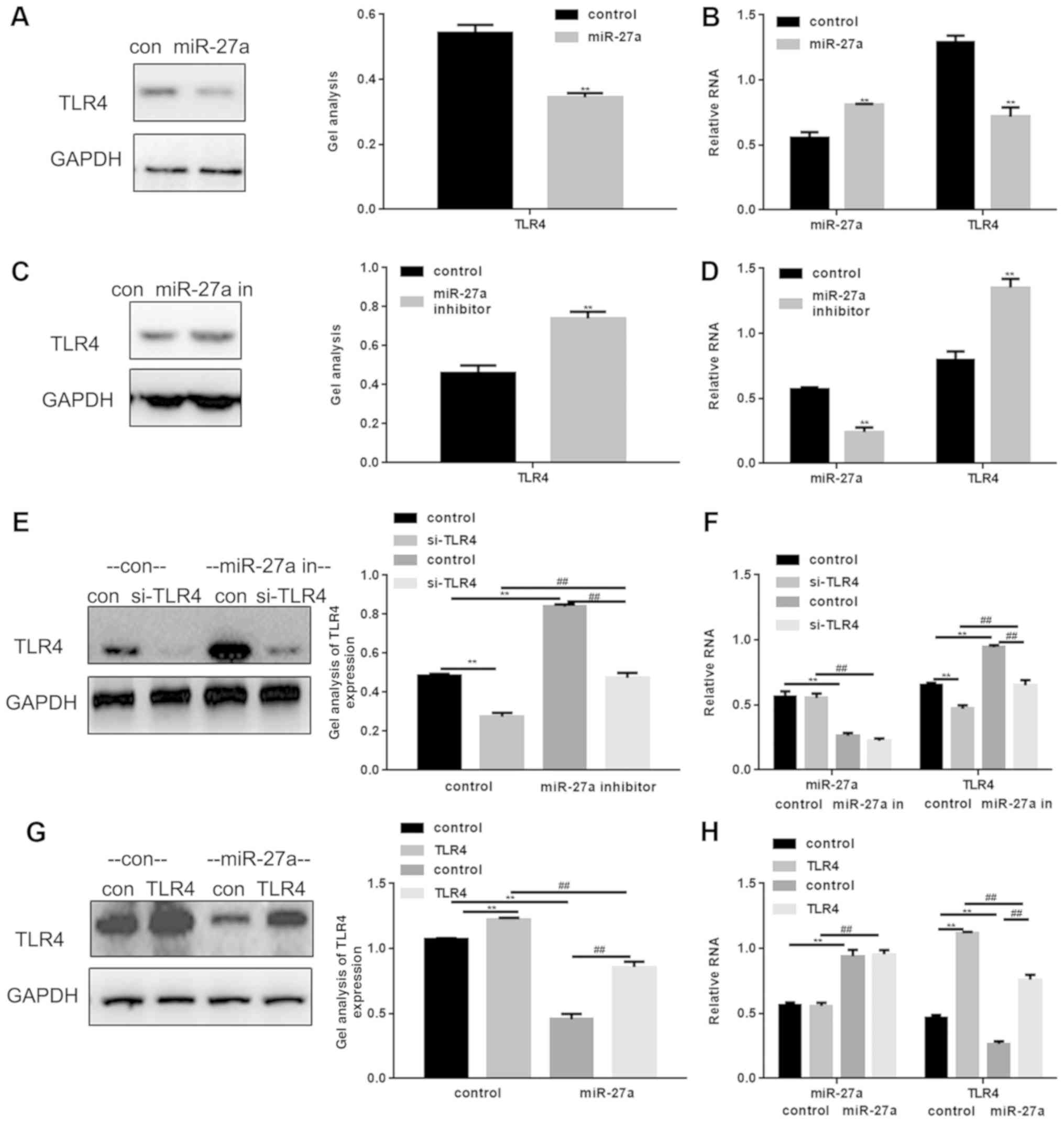
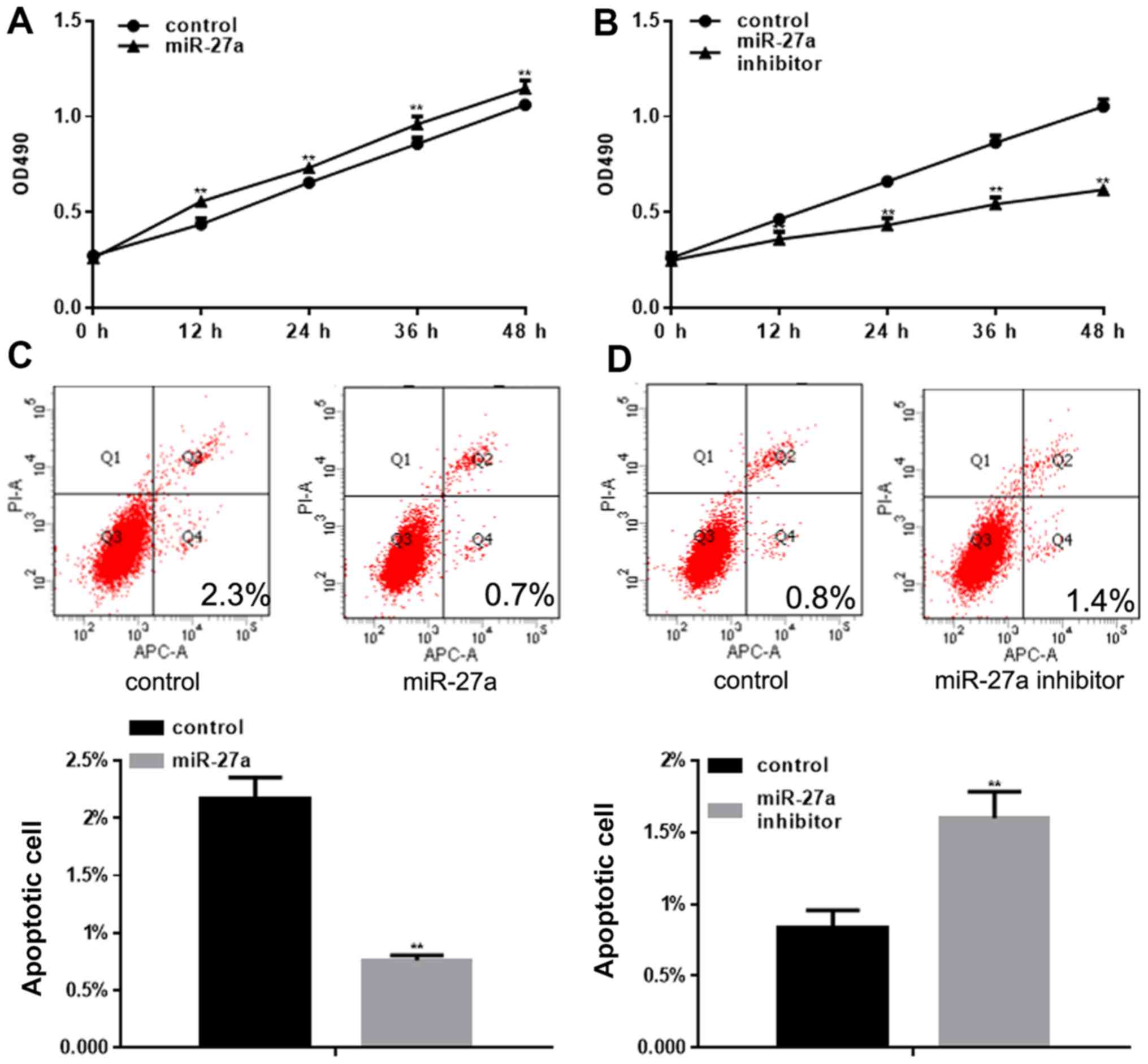
|
1
|
Li W, Ning JZ, Cheng F, Yu WM, Rao T, Ruan
Y, Yuan R, Zhang XB, Du Y and Xiao CC: MALAT1 promotes cell
apoptosis and suppresses cell proliferation in testicular
ischemia-reperfusion injury by sponging miR-214 to modulate TRPV4
expression. Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:802–814. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xie T, Li K, Gong X, Jiang R, Huang W,
Chen X, Tie H, Zhou Q, Wu S, Wan J and Wang B: Paeoniflorin
protects against liver ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice via
inhibiting HMGB1-TLR4 signaling pathway. Phytother Res.
32:2247–2255. 2018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cheng J, Zhu P, Qin H, Li X, Yu H, Yu H
and Peng X: Dexmedetomidine attenuates cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury in neonatal rats by inhibiting TLR4
signaling. J Int Med Res. 46:2925–2932. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen H, Song Z, Ying S, Yang X, Wu W, Tan
Q, Ju X, Wu W, Zhang X, Qu J and Wang Y: Myeloid differentiation
protein 2 induced retinal ischemia reperfusion injury via
upregulation of ROS through a TLR4-NOX4 pathway. Toxicol Lett.
282:109–120. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen J, Yang C, Xu X, Yang Y and Xu B: The
effect of focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury on TLR4 and
NF-κB signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 15:897–903. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
He Q, Zhao X, Bi S and Cao Y: Pretreatment
with erythropoietin attenuates lung ischemia/reperfusion injury via
toll-like receptor-4/nuclear factor-κB (TLR4/NF-κB) pathway. Med
Sci Monit. 24:1251–1257. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Di YF, Li DC, Shen YQ, Wang CL, Zhang DY,
Shang AQ and Hu T: miR-146b protects cardiomyocytes injury in
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion by targeting Smad4. Am J Transl
Res. 9:656–663. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fu BC, Lang JL, Zhang DY, Sun L, Chen W,
Liu W, Liu KY, Ma CY, Jiang SL, Li RK and Tian H: Suppression of
miR-34a expression in the myocardium protects against
ischemia-reperfusion injury through SIRT1 protective pathway. Stem
Cells Dev. 26:1270–1282. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jia P, Teng J, Zou J, Fang Y, Zhang X,
Bosnjak ZJ, Liang M and Ding X: miR-21 contributes to
xenon-conferred amelioration of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
in mice. Anesthesiology. 119:621–630. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Song N, Zhang T, Xu X, Lu Z, Yu X, Fang Y,
Hu J, Jia P, Teng J and Ding X: miR-21 protects against
ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury by preventing
epithelial cell apoptosis and inhibiting dendritic cell maturation.
Front Physiol. 9:7902018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Su S, Luo, Liu X, Liu J, Peng F, Fang C
and Li B: miR-494 up-regulates the PI3K/Akt pathway via targetting
PTEN and attenuates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat
model. Biosci Rep. 37(pii): BSR20170798. 2017.
|
|
12
|
Martin-Sole O, Rodo J, Garcia-Aparicio L,
Blanch J, Cusi V and Albert A: Effects of platelet-rich plasma
(PRP) on a model of renal ischemia-reperfusion in rats. PLoS One.
11:e01607032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang X, Gao Y, Qin J and Lu S: The role
of miR-34a in the hepatoprotective effect of hydrogen sulfide on
ischemia/reperfusion injury in young and old rats. PLoS One.
9:e1133052014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Feng J, Wang K, Liu X, Chen S and Chen J:
The quantification of tomato microRNAs response to viral infection
by stem-loop real-time RT-PCR. Gene. 437:14–21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee
DH, Nguyen JT, Barbisin M, Xu NL, Mahuvakar VR, Andersen MR, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e1792005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hua F, Ma J, Ha T, Kelley JL, Kao RL,
Schweitzer JB, Kalbfleisch JH, Williams DL and Li C: Differential
roles of TLR2 and TLR4 in acute focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
injury in mice. Brain Res. 1262:100–108. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li D, Wang J, Hou J, Fu J, Liu J and Lin
R: Salvianolic acid B induced upregulation of miR-30a protects
cardiac myocytes from ischemia/reperfusion injury. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 16:3362016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Diaz I, Calderon-Sanchez E, Toro RD,
Ávila-Médina J, de Rojas-de Pedro ES, Domínguez-Rodríguez A, Rosado
JA, Hmadcha A, Ordóñez A and Smani T: miR-125a, miR-139 and miR-324
contribute to Urocortin protection against myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Sci Rep. 7:88982017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dai Y, Jia P, Fang Y, Liu H, Jiao X, He JC
and Ding X: miR-146a is essential for lipopolysaccharide
(LPS)-induced cross-tolerance against kidney ischemia/reperfusion
injury in mice. Sci Rep. 6:270912016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xie YL, Zhang B and Jing L: miR-125b
blocks bax/cytochrome C/caspase-3 apoptotic signaling pathway in
rat models of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by targeting
p53. Neurol Res. 40:828–837. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li XQ, Lv HW, Wang ZL, Tan WF, Fang B and
Ma H: miR-27a ameliorates inflammatory damage to the blood-spinal
cord barrier after spinal cord ischemia: Reperfusion injury in rats
by downregulating TICAM-2 of the TLR4 signaling pathway. J
Neuroinflammation. 12:252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee JW, Kim SC, Ko YS, Lee HY, Cho E, Kim
MG, Jo SK, Cho WY and Kim HK: Renoprotective effect of paricalcitol
via a modulation of the TLR4-NF-κB pathway in
ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 444:121–127. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Luo SY, Li R, Le ZY, Li QL and Chen ZW:
Anfibatide protects against rat cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
injury via TLR4/JNK/caspase-3 pathway. Eur J Pharmacol.
807:127–137. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Han Y, Liao X, Gao Z, Yang S, Chen C, Liu
Y, Wang WE, Wu G, Chen X, Jose PA, et al: Cardiac troponin I
exacerbates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inducing the
adhesion of monocytes to vascular endothelial cells via
TLR4/NF-κB-dependent pathway. Clin Sci (Lond). 130:2279–2293. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu X, Zhang L, Qin H, Han X, Zhang Z,
Zhang Z, Qin SY and Niu J: Inhibition of TRA F3 expression
alleviates cardiac ischemia reperfusion (IR) injury: A mechanism
involving in apoptosis, inflammation and oxid ative stress. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 506:298–305. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|