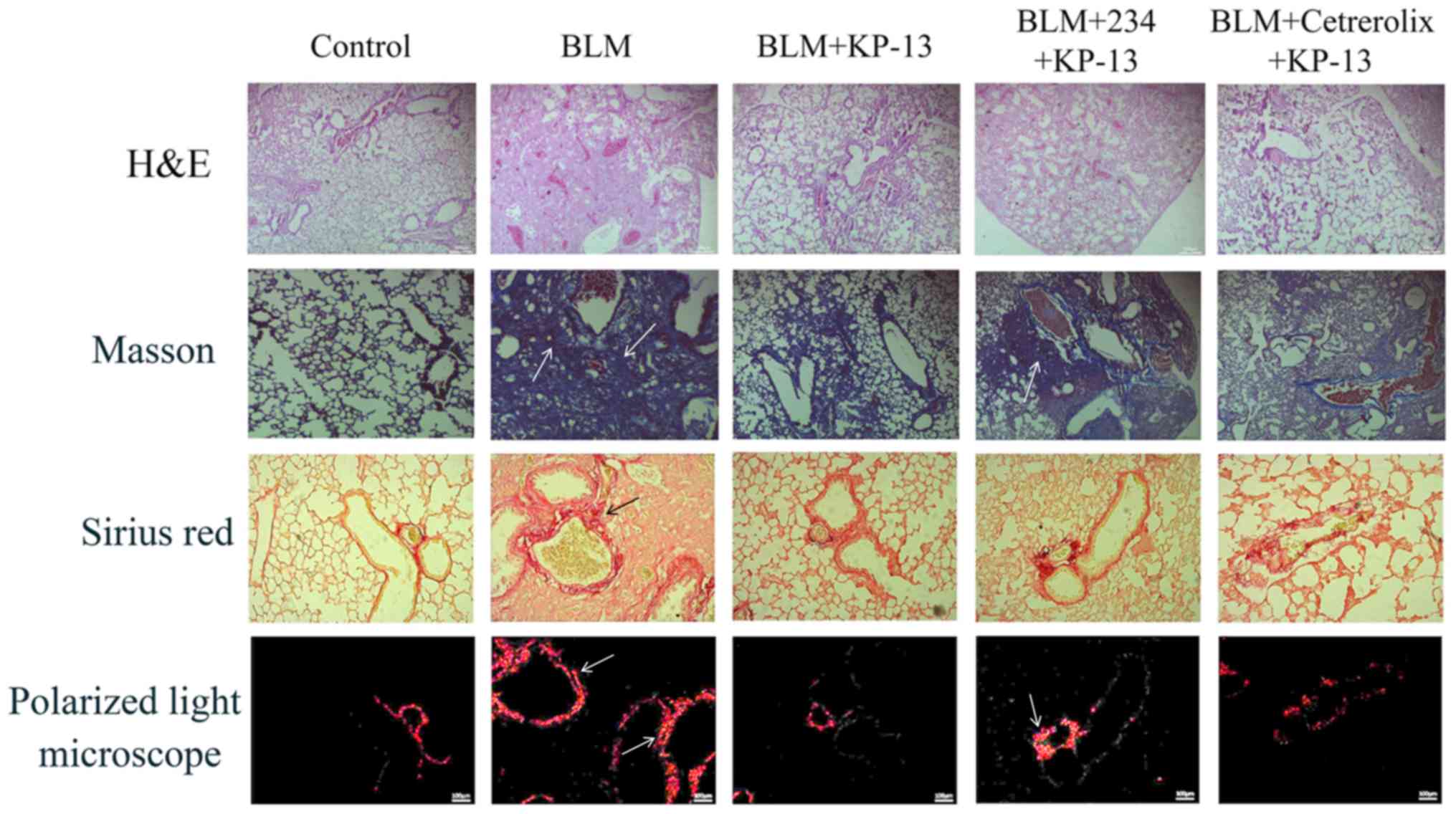
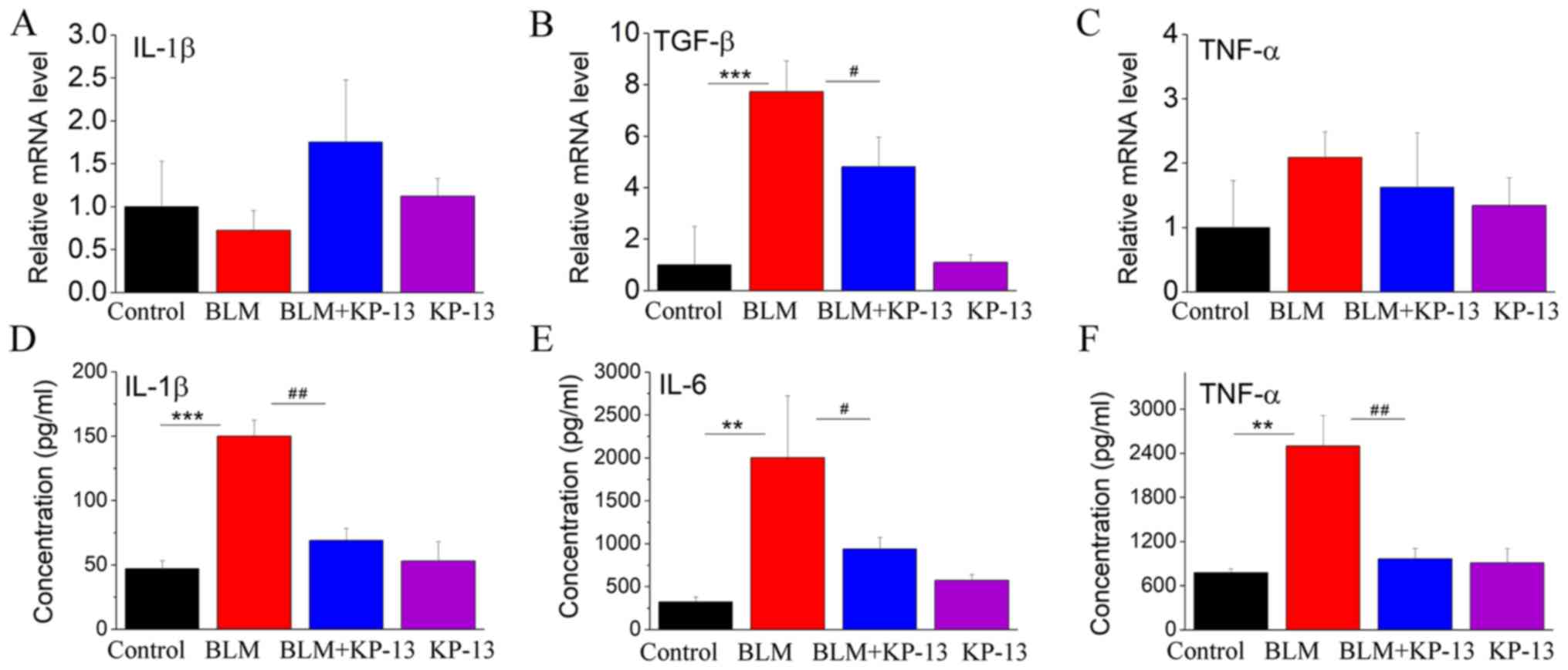
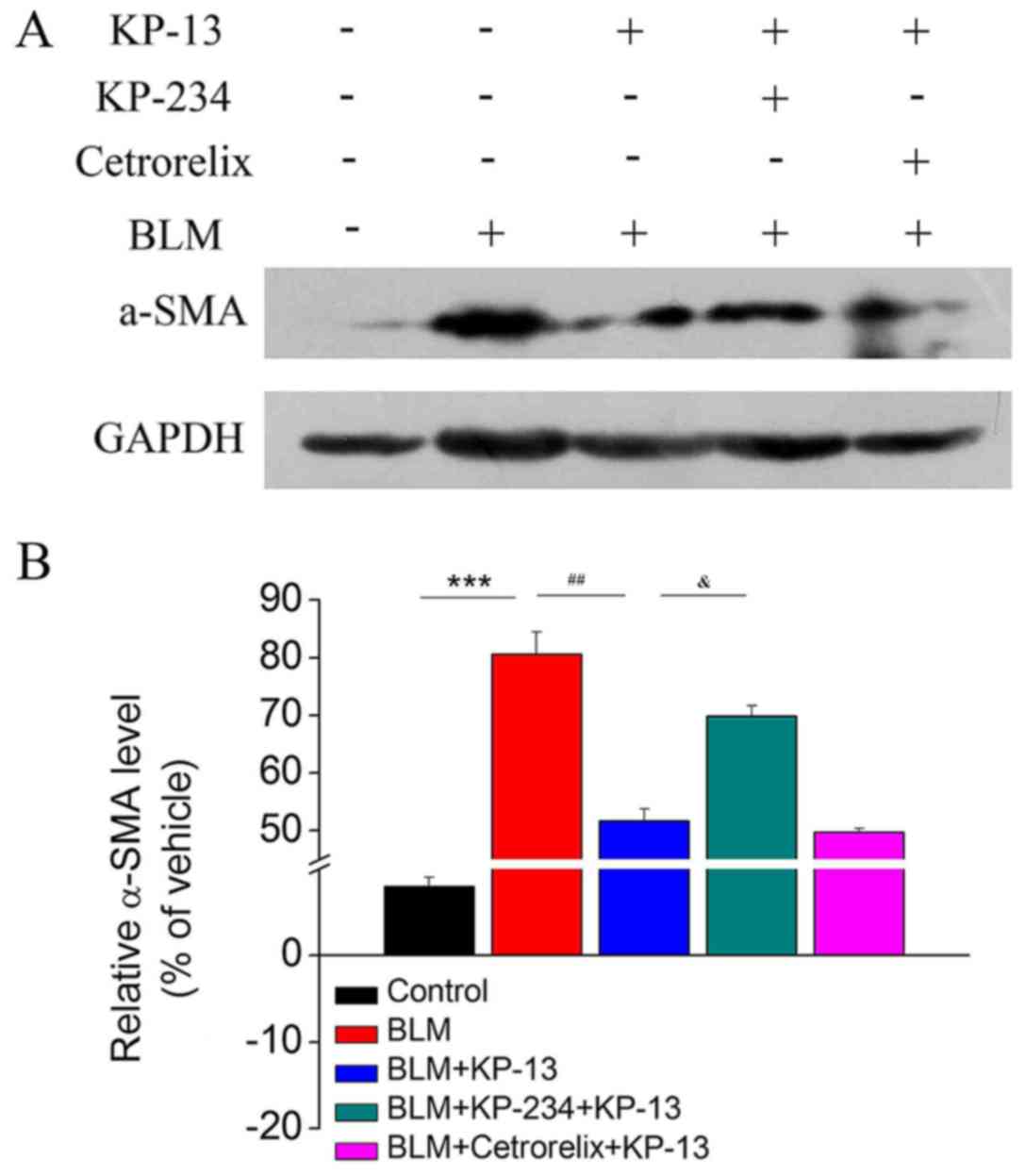
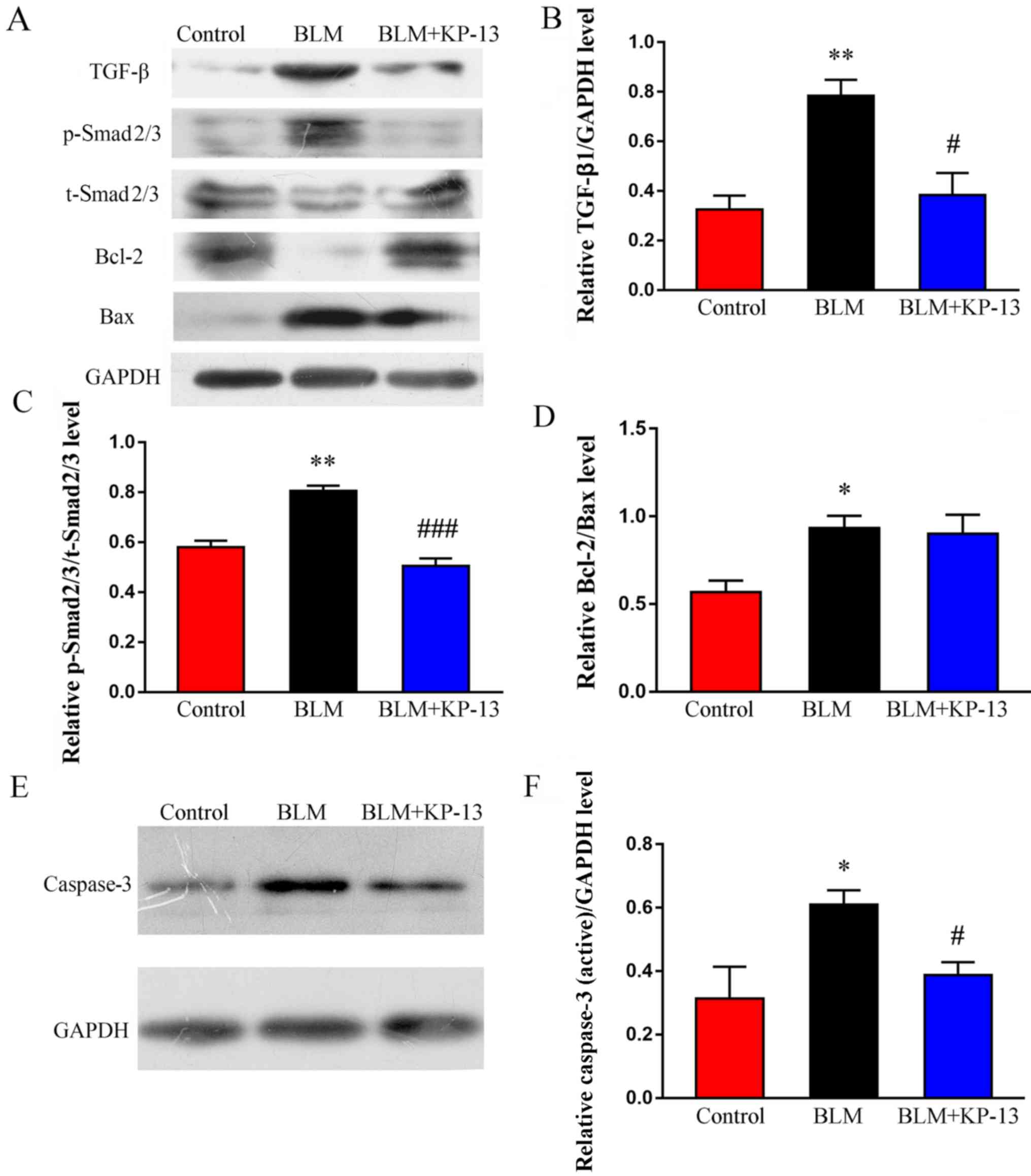
|
1
|
Ferrara G, Luppi F, Birring SS, Cerri S,
Caminati A, Sköld M and Kreuter M: Best supportive care for
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Current gaps and future directions.
Eur Respir Rev. 27(pii): 1700762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xie Y, Wang JJ, Li GY, Li XL and Li JS:
Acupuncture for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Protocol for a
systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e91142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sime PJ: The antifibrogenic potential of
PPARgamma ligands in pulmonary fibrosis. J Investig Med.
56:534–538. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Selman M, King TE and Pardo A; American
Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society; American College of
Chest Physicians, : Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Prevailing and
evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for
therapy. Ann Intern Med. 134:136–151. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tian J, Al-Odaini AA, Wang Y, Korah J, Dai
M, Xiao L, Ali S and Lebrun JJ: KiSS1 gene as a novel mediator of
TGFβ-mediated cell invasion in triple negative breast cancer. Cell
Signal. 42:1–10. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Skorupskaite K, George JT and Anderson RA:
The kisspeptin-GnRH pathway in human reproductive health and
disease. Hum Reprod Update. 20:485–500. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mead EJ, Maguire JJ, Kuc RE and Davenport
AP: Kisspeptins are novel potent vasoconstrictors in humans, with a
discrete localization of their receptor, G protein-coupled receptor
54, to atherosclerosis-prone vessels. Endocrinology. 148:140–147.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang J, Jin W, Peng Y, He Z, Wei L, Li S,
Wang X, Chang M and Wang R: In vivo and vitro characterization of
the effects of kisspeptin-13, endogenous ligands for GPR54, on
mouse gastrointestinal motility. Eur J Pharmacol. 794:216–223.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang JH, He Z, Peng YL, Jin WD, Wang Z,
Han RW, Chang M and Wang R: Kisspeptin-13 enhances memory and
mitigates memory impairment induced by Aβ1–42 in mice novel object
and object location recognition tasks. Neurobiol Learn Mem.
123:187–195. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stathaki M, Armakolas A, Dimakakos A,
Kaklamanis L, Vlachos I, Konstantoulakis MM, Zografos G and
Koutsilieris M: Kisspeptin effect on endothelial monocyte
activating polypeptide II (EMAP-II)-associated lymphocyte cell
death and metastases in colorectal cancer patients. Mol Med.
20:80–92. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kotani M, Detheux M, Vandenbogaerde A,
Communi D, Vanderwinden JM, Le Poul E, Brézillon S, Tyldesley R,
Suarez-Huerta N, Vandeput F, et al: The metastasis suppressor gene
KiSS-1 encodes kisspeptins, the natural ligands of the orphan G
protein-coupled receptor GPR54. J Biol Chem. 276:34631–34636. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meresman GF, Bilotas M, Buquet RA, Barañao
RI, Sueldo C and Tesone M: Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist
induces apoptosis and reduces cell proliferation in eutopic
endometrial cultures from women with endometriosis. Fertility and
sterility. 80 (Suppl 2):S702–S707. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Castellon E, Clementi M, Hitschfeld C,
Sánchez C, Benítez D, Sáenz L, Contreras H and Huidobro C: Effect
of leuprolide and cetrorelix on cell growth, apoptosis, and GnRH
receptor expression in primary cell cultures from human prostate
carcinoma. Cancer Invest. 24:261–268. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kyritsi K, Meng F, Zhou T, Wu N, Venter J,
Francis H, Kennedy L, Onori P, Franchitto A, Bernuzzi F, et al:
Knockdown of hepatic gonadotropin-releasing hormone by
vivo-morpholino decreases liver fibrosis in multidrug resistance
gene 2 knockout mice by down-regulation of miR-200b. Am J Pathol.
187:1551–1565. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McMillin M, DeMorrow S, Glaser S, Venter
J, Kyritsi K, Zhou T, Grant S, Giang T, Greene JF Jr, Wu N, et al:
Melatonin inhibits hypothalamic gonadotropin-releasing hormone
release and reduces biliary hyperplasia and fibrosis in cholestatic
rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 313:G410–G418. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tian SL, Yang Y, Liu XL and Xu QB: Emodin
attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via
anti-inflammatory and Anti-oxidative activities in rats. Med Sci
Monit. 24:1–10. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luque RM, Kineman RD and Tena-Sempere M:
Regulation of hypothalamic expression of KiSS-1 and GPR54 genes by
metabolic factors: Analyses using mouse models and a cell line.
Endocrinology. 148:4601–4611. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wei YR, Qiu H, Wu Q, Du YK, Yin ZF, Chen
SS, Jin YP, Zhao MM, Wang C, Weng D and Li HP: Establishment of the
mouse model of acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Exp Lung Res. 42:75–86. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dong J and Ma Q: TIMP1 promotes
multi-walled carbon nanotube-induced lung fibrosis by stimulating
fibroblast activation and proliferation. Nanotoxicology. 11:41–51.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Waisberg DR, Parra ER, Barbas-Filho JV,
Fernezlian S and Capelozzi VL: Increased fibroblast telomerase
expression precedes myofibroblast α-smooth muscle actin expression
in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clinics. 67:1039–1046. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun KH, Chang Y, Reed NI and Sheppard D:
α-Smooth muscle actin is an inconsistent marker of fibroblasts
responsible for force-dependent TGFβ activation or collagen
production across multiple models of organ fibrosis. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 310:L824–L836. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cetkovic A, Miljic D, Ljubić A, Patterson
M, Ghatei M, Stamenković J, Nikolic-Djurovic M, Pekic S, Doknic M,
Glišić A, et al: Plasma kisspeptin levels in pregnancies with
diabetes and hypertensive disease as a potential marker of
placental dysfunction and adverse perinatal outcome. Endocr Res.
37:78–88. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hussain MA, Song WJ and Wolfe A: There is
Kisspeptin - and then there is Kisspeptin. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
26:564–572. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jayasena CN, Nijher GM, Comninos AN,
Abbara A, Januszewki A, Vaal ML, Sriskandarajah L, Murphy KG,
Farzad Z, Ghatei MA, et al: The effects of kisspeptin-10 on
reproductive hormone release show sexual dimorphism in humans. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 96:E1963–E1972. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zank DC, Bueno M, Mora AL and Rojas M:
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Aging, mitochondrial dysfunction and
cellular bioenergetics. Front Med (Lausanne). 5:102018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sava P, Ramanathan A, Dobronyi A, Peng X,
Sun H, Ledesma-Mendoza A, Herzog EL and Gonzalez AL: Human
pericytes adopt myofibroblast properties in the microenvironment of
the IPF lung. JCI Insight. 2(pii): 963522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sato K, Shirai R, Hontani M, Shinooka R,
Hasegawa A, Kichise T, Yamashita T, Yoshizawa H, Watanabe R,
Matsuyama TA, et al: Potent vasoconstrictor Kisspeptin-10 induces
atherosclerotic plaque progression and instability: Reversal by its
receptor GPR54 antagonist. J Am Heart Assoc. 6(pii):
e0057902017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Oruqaj G, Karnati S, Vijayan V, Kotarkonda
LK, Boateng E, Zhang W, Ruppert C, Günther A, Shi W and
Baumgart-Vogt E: Compromised peroxisomes in idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis, a vicious cycle inducing a higher fibrotic response via
TGF-β signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:E2048–E2057. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cutroneo KR, White SL, Phan SH and Ehrlich
HP: Therapies for bleomycin induced lung fibrosis through
regulation of TGF-beta1 induced collagen gene expression. J Cell
Physiol. 211:585–589. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|