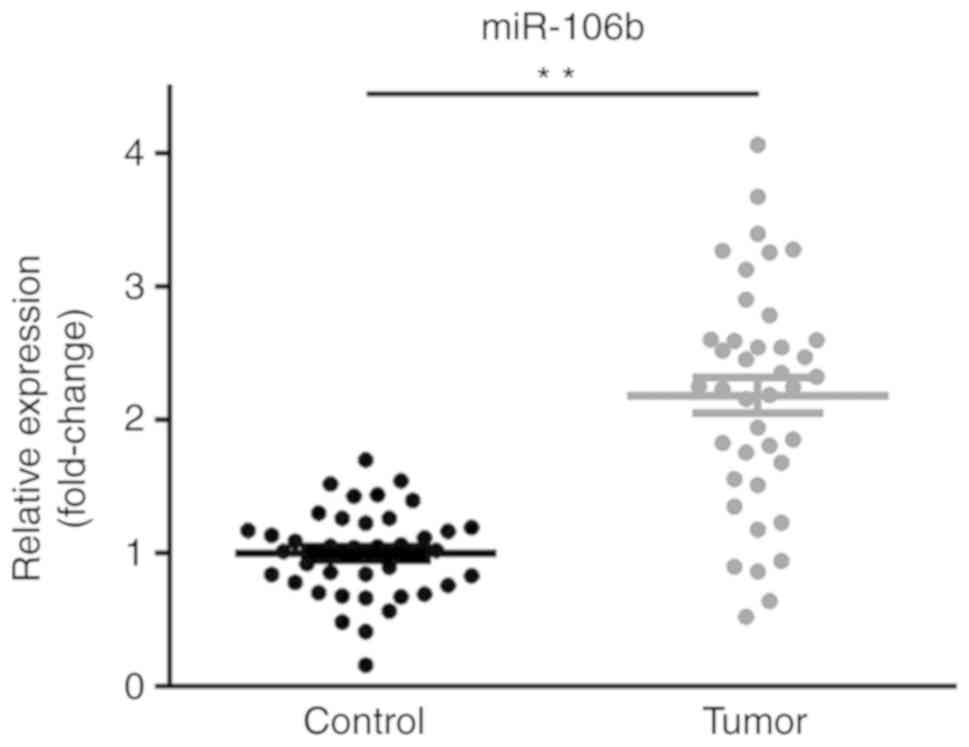
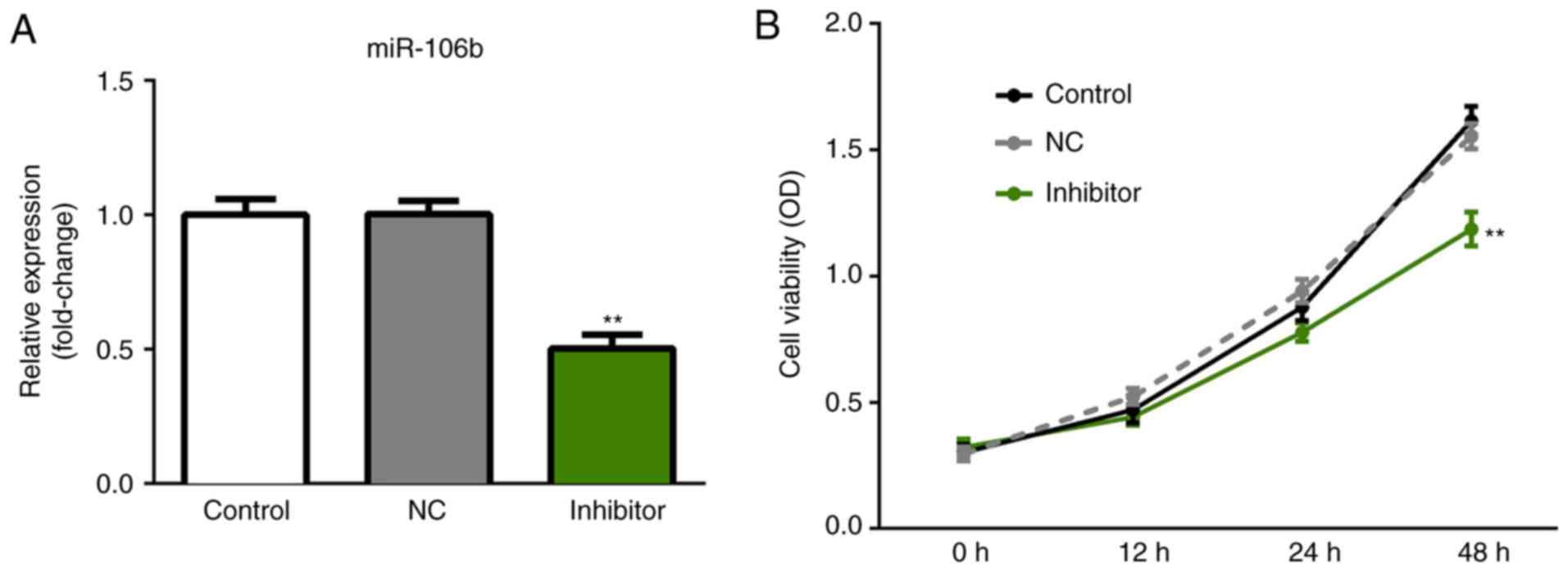
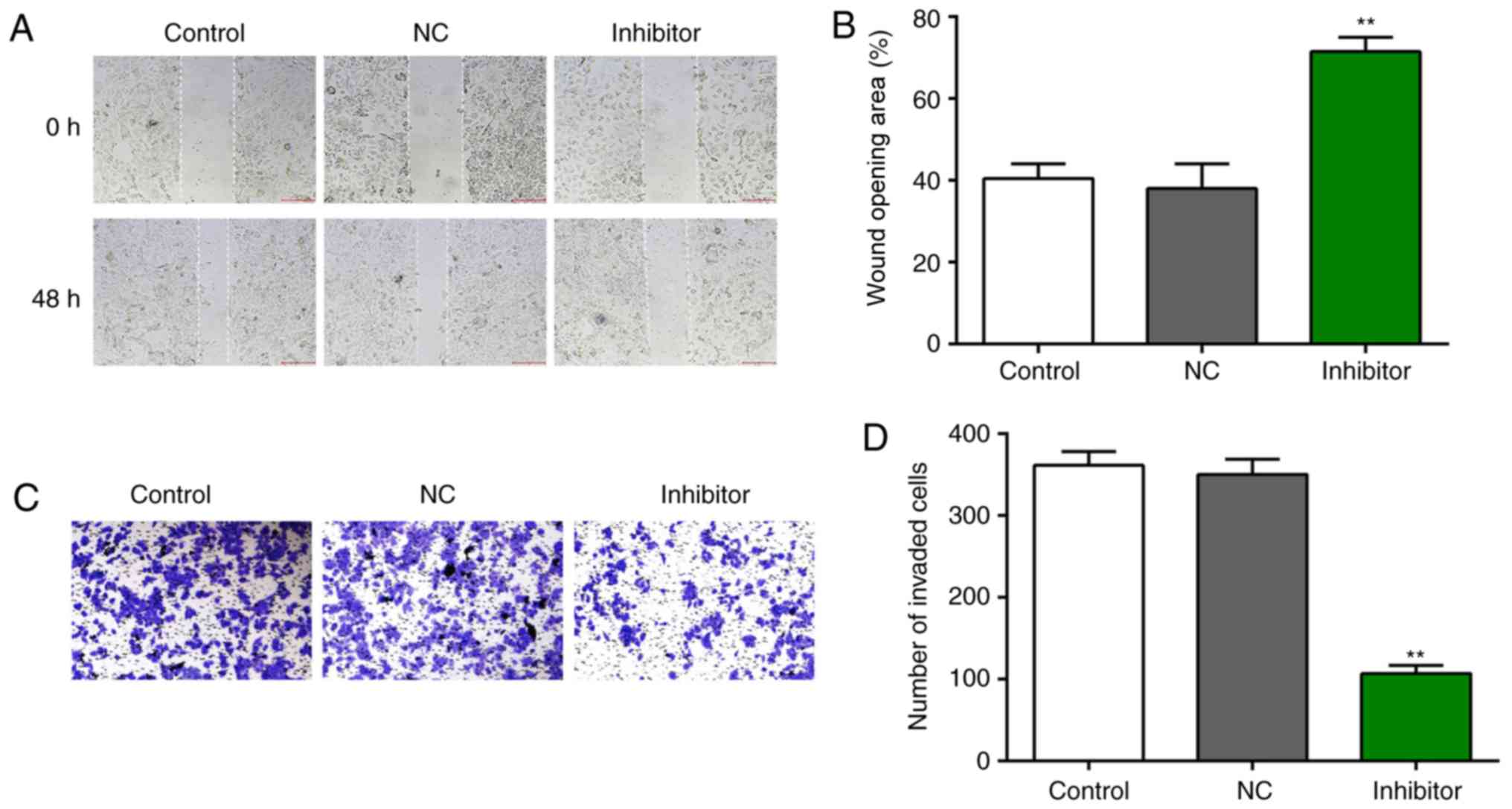
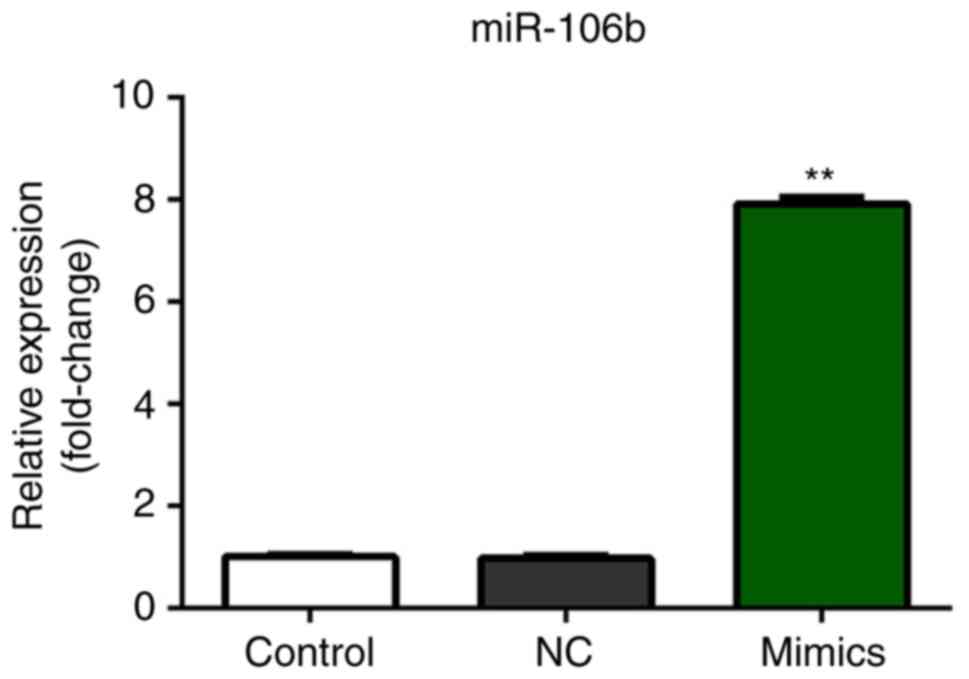
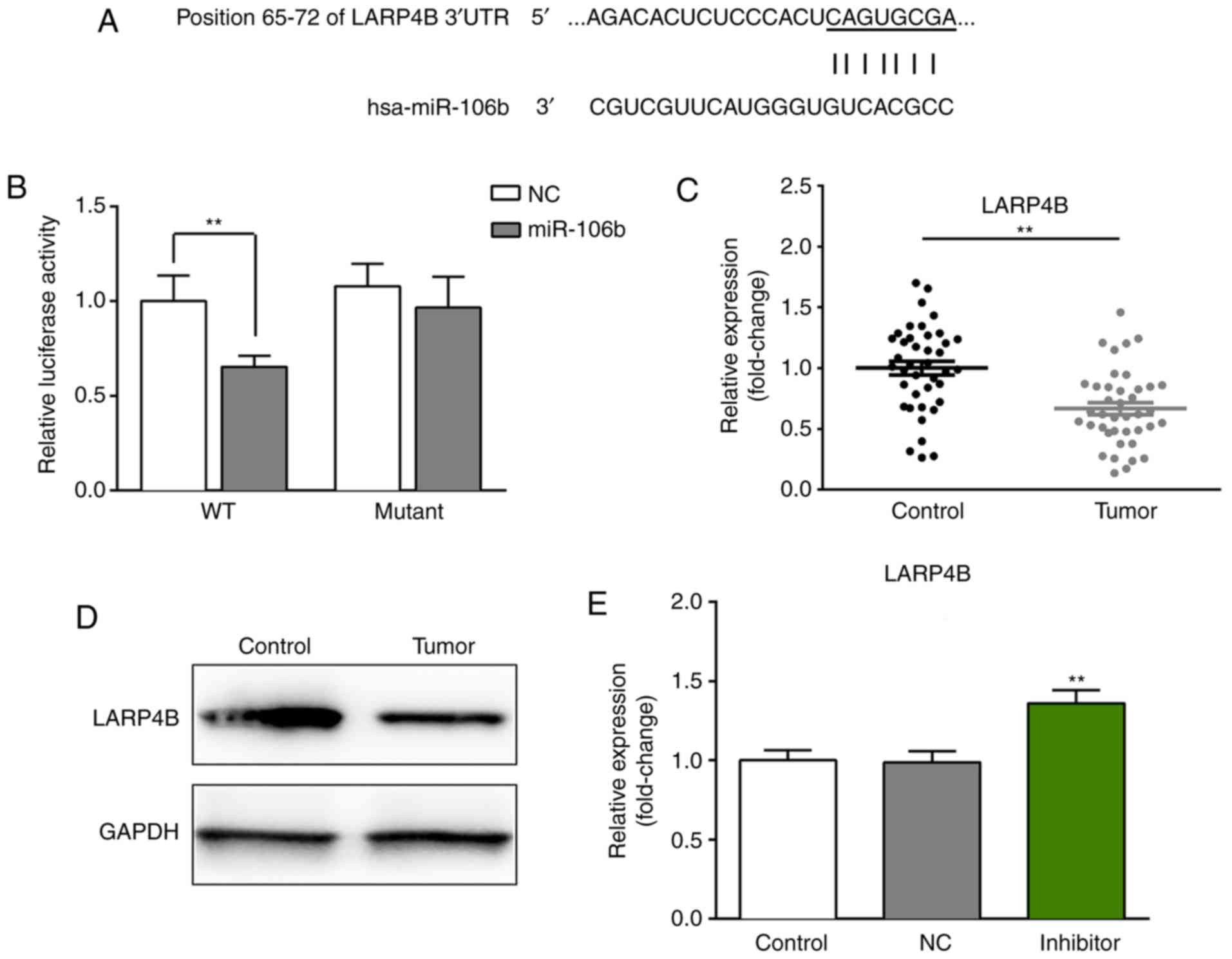
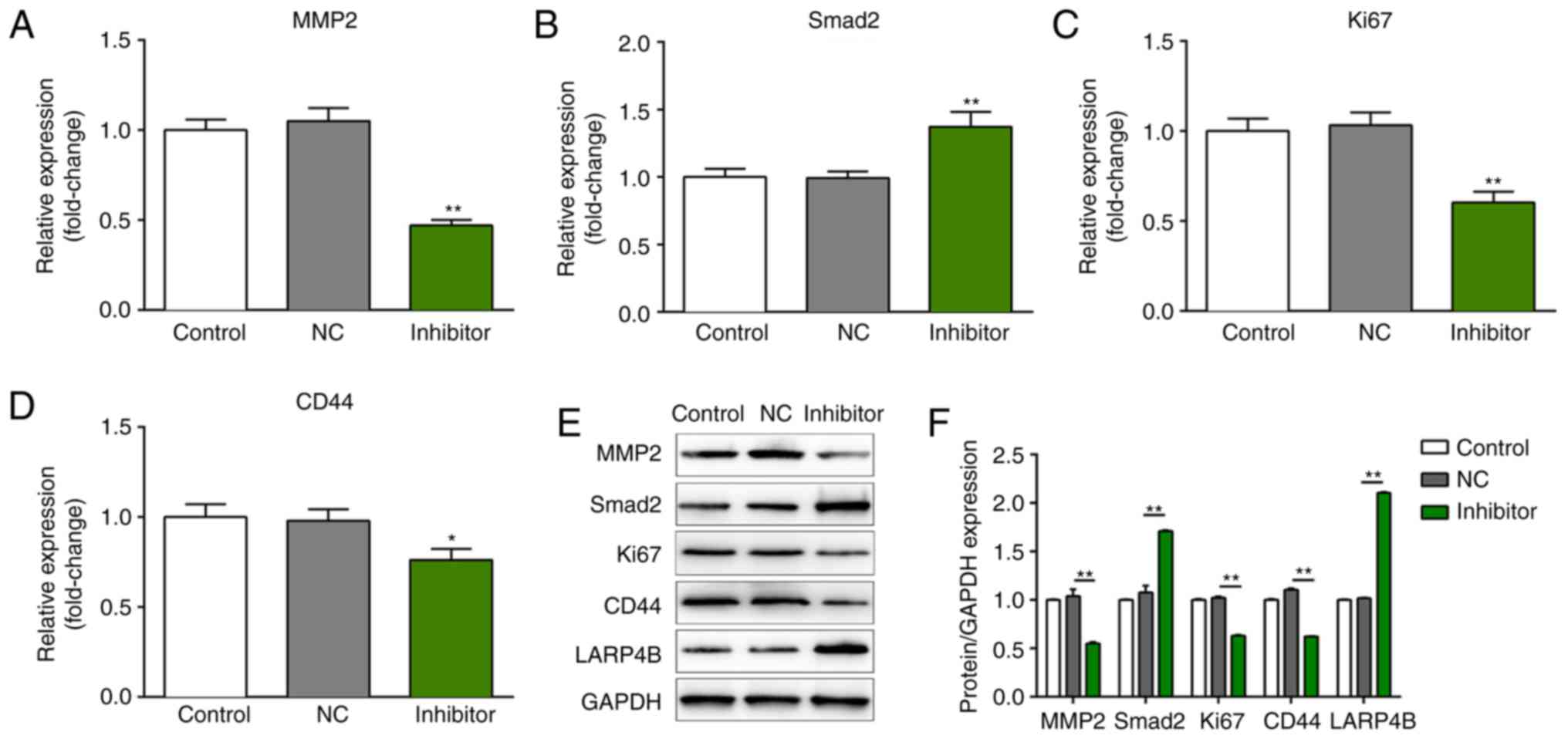
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I,
Dyba T, Randi G, Bettio M, Gavin A, Visser O and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: Estimates for 40
countries and 25 major cancers in 2018. Eur J Cancer. 103:356–387.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ren SC, Chen R and Sun YH: Prostate cancer
research in China. Asian J Androl. 15:350–353. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Naji L, Randhawa H, Sohani Z, Dennis B,
Lautenbach D, Kavanagh O, Bawor M, Banfield L and Profetto J:
Digital rectal examination for prostate cancer screening in primary
care: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Fam Med.
16:149–154. 2018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liss MA, Chen H, Hemal S, Krane S, Kane
CJ, Xu J and Kader AK: Impact of family history on prostate cancer
mortality in white men undergoing prostate specific antigen based
screening. J Urol. 193:75–79. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Durmus T, Baur A and Hamm B:
Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging in the detection of
prostate cancer. Rofo. 186:238–246. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Boesen L, Nørgaard N, Løgager V, Balslev I
and Thomsen HS: A prospective comparison of selective
multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging fusion-targeted and
systematic transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsies for detecting
prostate cancer in men undergoing repeated biopsies. Urol Int.
99:384–391. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Moghul M, Somani B, Lane T, Vasdev N,
Chaplin B, Peedell C, KandaSwamy GV and Rai BP: Detection rates of
recurrent prostate cancer: 68Gallium (Ga)-labelled
prostate-specific membrane antigen versus choline PET/CT scans. A
systematic review. Ther Adv Urol. 11:17562872188157932019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Teoh JY, Yuen SK, Tsu JH, Wong CK, Ho BSh,
Ng AT, Ma WK, Ho KL and Yiu MK: Prostate cancer detection upon
transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy in relation to digital rectal
examination and prostate-specific antigen level: What to expect in
the Chinese population? Asian J Androl. 17:821–825. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Javali TD, Dwivedi DK, Kumar R,
Jagannathan NR, Thulkar S and Dinda AK: Magnetic resonance
spectroscopy imaging-directed transrectal ultrasound biopsy
increases prostate cancer detection in men with prostate-specific
antigen between 4–10 ng/ml and normal digital rectal examination.
Int J Urol. 21:257–262. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kash DP, Lal M, Hashmi AH and Mubarak M:
Utility of digital rectal examination, serum prostate specific
antigen, and transrectal ultrasound in the detection of prostate
cancer: A developing country perspective. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:3087–3091. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
McCann JV, Xiao L, Kim DJ, Khan OF,
Kowalski PS, Anderson DG, Pecot CV, Azam SH, Parker JS, Tsai YS, et
al: Endothelial miR-30c suppresses tumor growth via inhibition of
TGF-β-induced Serpine1. J Clin Invest. 130:1654–1670. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee J, Kwon MH, Kim JA and Rhee WJ:
Detection of exosome miRNAs using molecular beacons for diagnosing
prostate cancer. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 46 (Suppl
3):S52–S63. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Malla B, Aebersold DM and Dal Pra A:
Protocol for serum exosomal miRNAs analysis in prostate cancer
patients treated with radiotherapy. J Transl Med. 16:2232018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xiaoli Z, Yawei W, Lianna L, Haifeng L and
Hui Z: Screening of target genes and regulatory function of miRNAs
as prognostic indicators for prostate cancer. Med Sci Monit.
21:3748–3759. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang N, Wang L, Liu J, Liu L, Huang J,
Chen X and Luo Z: MicroRNA-206 regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and inhibits the invasion and metastasis of prostate
cancer cells by targeting Annexin A2. Oncol Lett. 15:8295–8302.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang Y, Xu H, Si L, Li Q, Zhu X, Yu T and
Gang X: MiR-206 inhibits proliferation and migration of prostate
cancer cells by targeting CXCL11. Prostate. 78:479–490. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Karatas OF, Wang J, Shao L, Ozen M, Zhang
Y, Creighton CJ and Ittmann M: miR-33a is a tumor suppressor
microRNA that is decreased in prostate cancer. Oncotarget.
8:60243–60256. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou YJ, Yang HQ, Xia W, Cui L, Xu RF, Lu
H, Xue Z, Zhang B, Tian ZN, Cao YJ, et al: Down-regulation of
miR-605 promotes the proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer
cells by up-regulating EN2. Life Sci. 190:7–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Luo B, Kang N, Chen Y, Liu L and Zhang Y:
Oncogene miR-106a promotes proliferation and metastasis of prostate
cancer cells by directly targeting PTEN in vivo and in vitro.
Minerva Med. 109:24–30. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang ZG, Ma XD, He ZH and Guo YX:
miR-483-5p promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation and invasion
by targeting RBM5. Int Braz J Urol. 43:1060–1067. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu C, Li J, Cheng G, Zhou H, Tao L, Cai
H, Li P, Cao Q, Ju X, Meng X, et al: miR-154 inhibits EMT by
targeting HMGA2 in prostate cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
379:69–75. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Epis MR, Giles KM, Beveridge DJ,
Richardson KL, Candy PA, Stuart LM, Bentel J, Cohen RJ and Leedman
PJ: miR-331-3p and Aurora Kinase inhibitor II co-treatment
suppresses prostate cancer tumorigenesis and progression.
Oncotarget. 8:55116–55134. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jackson BL, Grabowska A and Ratan HL:
MicroRNA in prostate cancer: Functional importance and potential as
circulating biomarkers. BMC Cancer. 14:9302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu Y, Wang K, Gao W, Zhang C, Huang F, Wen
S and Wang B: MicroRNA-106b regulates the tumor suppressor RUNX3 in
laryngeal carcinoma cells. FEBS Lett. 587:3166–3174. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang TS, Yang XH, Chen X, Wang XD, Hua J,
Zhou DL, Zhou B and Song ZS: MicroRNA-106b in cancer-associated
fibroblasts from gastric cancer promotes cell migration and
invasion by targeting PTEN. FEBS Lett. 588:2162–2169. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Smith AL, Iwanaga R, Drasin DJ, Micalizzi
DS, Vartuli RL, Tan AC and Ford HL: The miR-106b-25 cluster targets
Smad7, activates TGF-β signaling, and induces EMT and tumor
initiating cell characteristics downstream of Six1 in human breast
cancer. Oncogene. 31:5162–5171. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Y, Tan W, Neo TW, Aung MO, Wasser S,
Lim SG and Tan TM: Role of the miR-106b-25 microRNA cluster in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 100:1234–1242. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Carvalheira G, Nozima BH and Cerutti JM:
microRNA-106b-mediated down-regulation of C1orf24 expression
induces apoptosis and suppresses invasion of thyroid cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:28357–28370. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dai F, Liu T, Zheng S, Liu Q, Yang C, Zhou
J, Chen Y, Sheyhidin I and Lu X: MiR-106b promotes migration and
invasion through enhancing EMT via downregulation of Smad 7 in
Kazakh's esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
37:14595–14604. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li Y, Chen D, Su Z, Li Y, Liu J, Jin L,
Shi M, Jiang Z, Qi Z, Gui Y, et al: MicroRNA-106b functions as an
oncogene in renal cell carcinoma by affecting cell proliferation,
migration and apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 13:1420–1426. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wei K, Pan C, Yao G, Liu B, Ma T, Xia Y,
Jiang W, Chen L and Chen Y: miR-106b-5p promotes proliferation and
inhibits apoptosis by regulating BTG3 in non-small cell lung
cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:1545–1558. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li N, Miao Y, Shan Y, Liu B, Li Y, Zhao L
and Jia L: miR-106b and miR-93 regulate cell progression by
suppression of PTEN via PI3K/Akt pathway in breast cancer. Cell
Death Dis. 8:e27962017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lu J, Wei JH, Feng ZH, Chen ZH, Wang YQ,
Huang Y, Fang Y, Liang YP, Cen JJ, Pan YH, et al: miR-106b-5p
promotes renal cell carcinoma aggressiveness and stem-cell-like
phenotype by activating Wnt/β-catenin signalling. Oncotarget.
8:21461–21471. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ni S, Weng W, Xu M, Wang Q, Tan C, Sun H,
Wang L, Huang D, Du X and Sheng W: miR-106b-5p inhibits the
invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting CTSA.
Onco Targets Ther. 11:3835–3845. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang J, Chen D, Liang S, Wang J, Liu C,
Nie C, Shan Z, Wang L, Fan Q and Wang F: miR-106b promotes cell
invasion and metastasis via PTEN mediated EMT in ESCC. Oncol Lett.
15:4619–4626. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yen CS, Su ZR, Lee YP, Liu IT and Yen CJ:
miR-106b promotes cancer progression in hepatitis B
virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
22:5183–5192. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liang H, Studach L, Hullinger RL, Xie J
and Andrisani OM: Down-regulation of RE-1 silencing transcription
factor (REST) in advanced prostate cancer by hypoxia-induced
miR-106b~25. Exp Cell Res. 320:188–199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hudson RS, Yi M, Esposito D, Glynn SA,
Starks AM, Yang Y, Schetter AJ, Watkins SK, Hurwitz AA, Dorsey TH,
et al: MicroRNA-106b-25 cluster expression is associated with early
disease recurrence and targets caspase-7 and focal adhesion in
human prostate cancer. Oncogene. 32:4139–4147. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Merret R, Martino L, Bousquet-Antonelli C,
Fneich S, Descombin J, Billey E, Conte MR and Deragon JM: The
association of a La module with the PABP-interacting motif PAM2 is
a recurrent evolutionary process that led to the
neofunctionalization of La-related proteins. RNA. 19:36–50. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hussain RH, Zawawi M and Bayfield MA:
Conservation of RNA chaperone activity of the human La-related
proteins 4, 6 and 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:8715–8725. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Stavraka C and Blagden S: The La-related
proteins, a family with connections to cancer. Biomolecules.
5:2701–2722. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Koso H, Yi H, Sheridan P, Miyano S, Ino Y,
Todo T and Watanabe S: Identification of RNA-binding protein LARP4B
as a tumor suppressor in glioma. Cancer Res. 76:2254–2264. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu J, Yang J, Yu L, Rao C, Wang Q, Sun C,
Shi C, Hua D, Zhou X, Luo W, et al: miR-361-5p inhibits glioma
migration and invasion by targeting SND1. Onco Targets Ther.
11:5239–5252. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bao Y, Chen Z, Guo Y, Feng Y, Li Z, Han W,
Wang J, Zhao W, Jiao Y, Li K, et al: Tumor suppressor microRNA-27a
in colorectal carcinogenesis and progression by targeting SGPP1 and
Smad2. PLoS One. 9:e1059912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tu B, Peng ZX, Fan QM, Du L, Yan W and
Tang TT: Osteosarcoma cells promote the production of pro-tumor
cytokines in mesenchymal stem cells by inhibiting their osteogenic
differentiation through the TGF-β/Smad2/3 pathway. Exp Cell Res.
320:164–173. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fleming NI, Jorissen RN, Mouradov D,
Christie M, Sakthianandeswaren A, Palmieri M, Day F, Li S, Tsui C,
Lipton L, et al: SMAD2, SMAD3 and SMAD4 mutations in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Res. 73:725–735. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mattheolabakis G, Milane L, Singh A and
Amiji MM: Hyaluronic acid targeting of CD44 for cancer therapy:
From receptor biology to nanomedicine. J Drug Target. 23:605–618.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Prochazka L, Tesarik R and Turanek J:
Regulation of alternative splicing of CD44 in cancer. Cell Signal.
26:2234–2239. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kinugasa Y, Matsui T and Takakura N: CD44
expressed on cancer-associated fibroblasts is a functional molecule
supporting the stemness and drug resistance of malignant cancer
cells in the tumor microenvironment. Stem Cells. 32:145–156. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chen L, Wang X, Zhu Y, Zhu J and Lai Q:
miR-200b-3p inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in
colorectal cancer by targeting Wnt1. Mol Med Rep. 18:2571–2580.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yadav L, Puri N, Rastogi V, Satpute P,
Ahmad R and Kaur G: Matrix metalloproteinases and cancer-roles in
threat and therapy. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:1085–1091. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ok Atılgan A, Özdemir BH, Akçay EY, Ataol
Demirkan Ö, Tekindal MA and Özkardeş H: Role of tumor-associated
macrophages in the Hexim1 and TGFβ/SMAD pathway, and their
influence on progression of prostatic adenocarcinoma. Pathol Res
Pract. 212:83–92. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lee IH, Sohn M, Lim HJ, Yoon S, Oh H, Shin
S, Shin JH, Oh SH, Kim J, Lee DK, et al: Ahnak functions as a tumor
suppressor via modulation of TGFβ/Smad signaling pathway. Oncogene.
33:4675–4684. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|