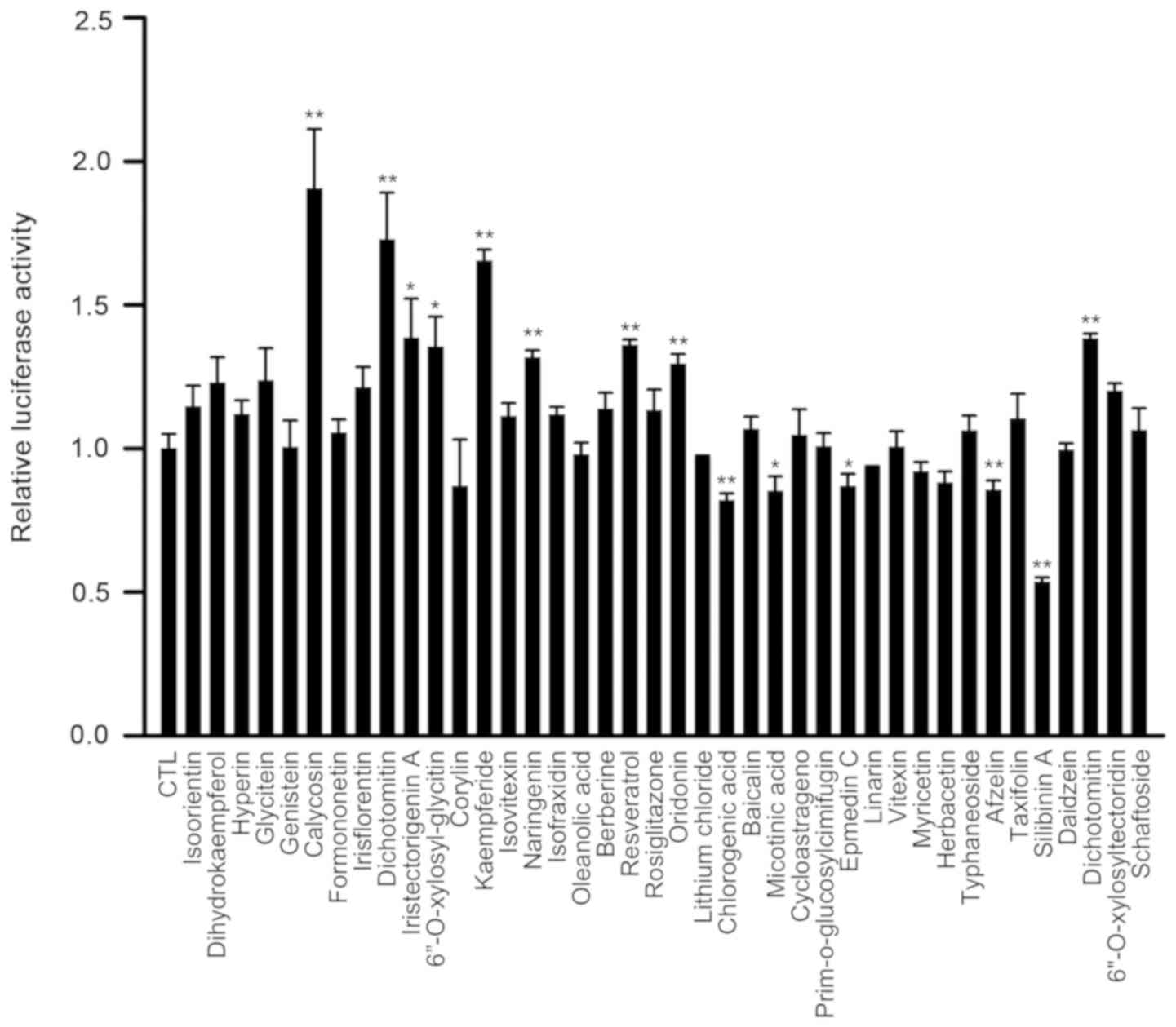
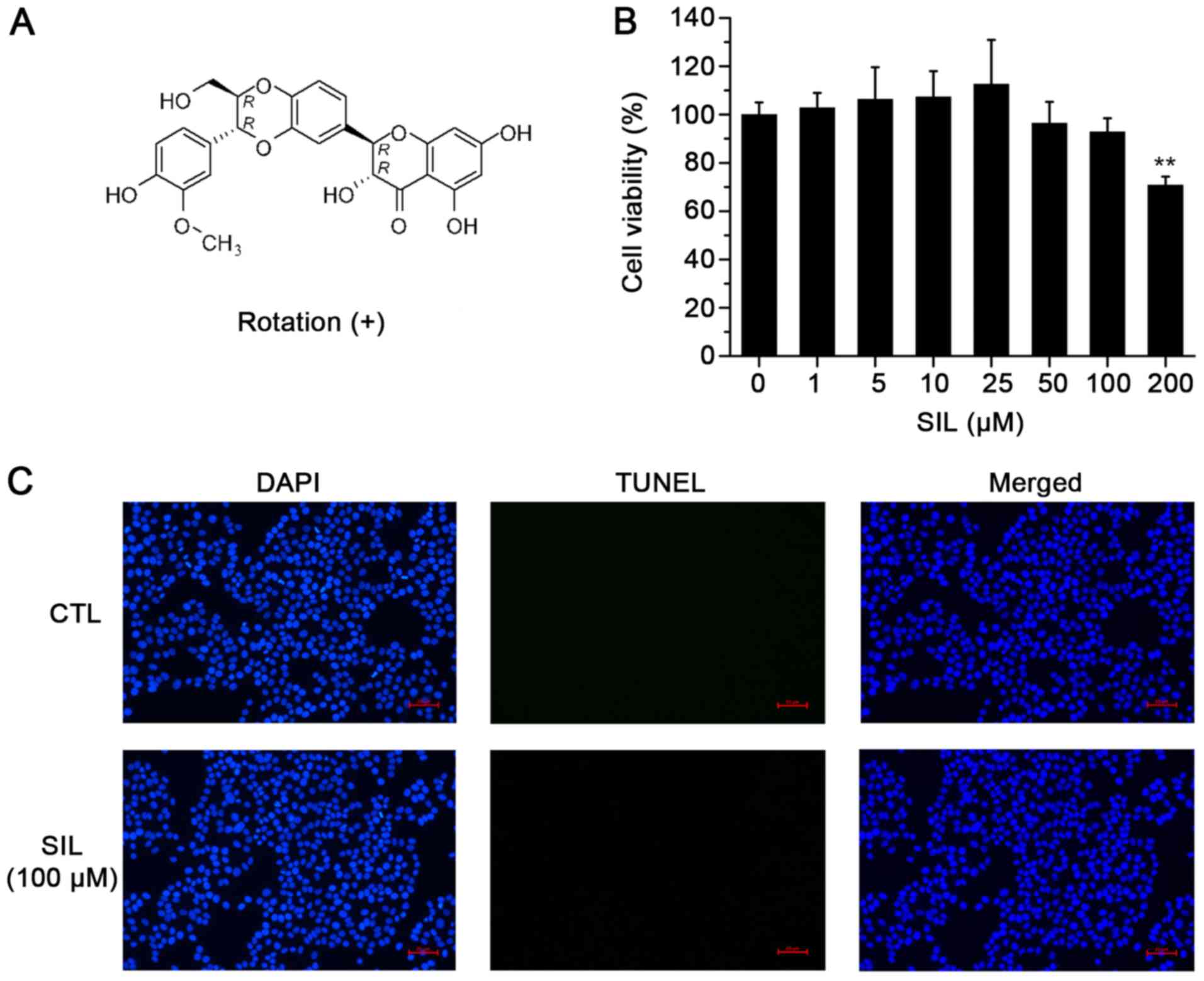
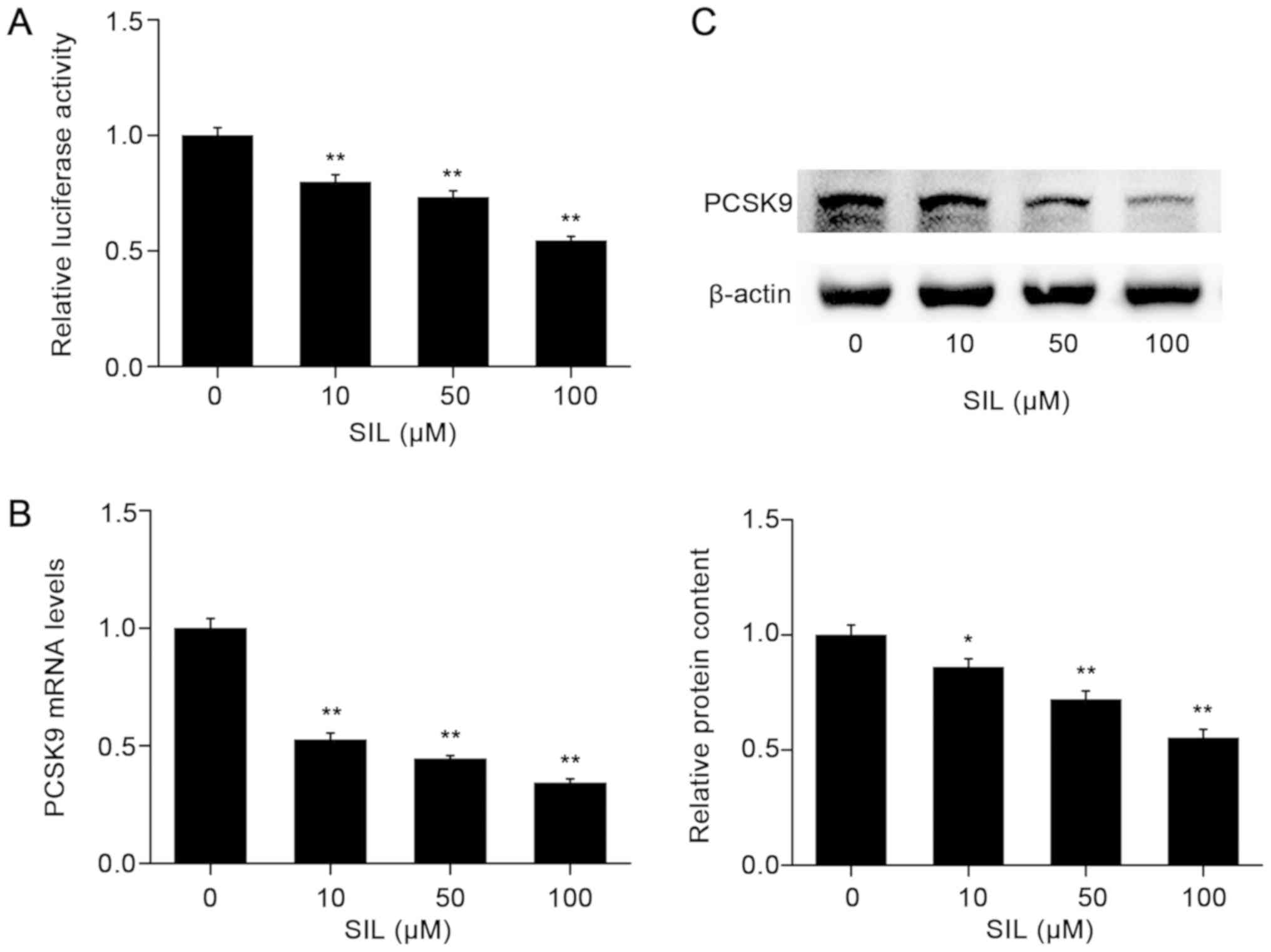
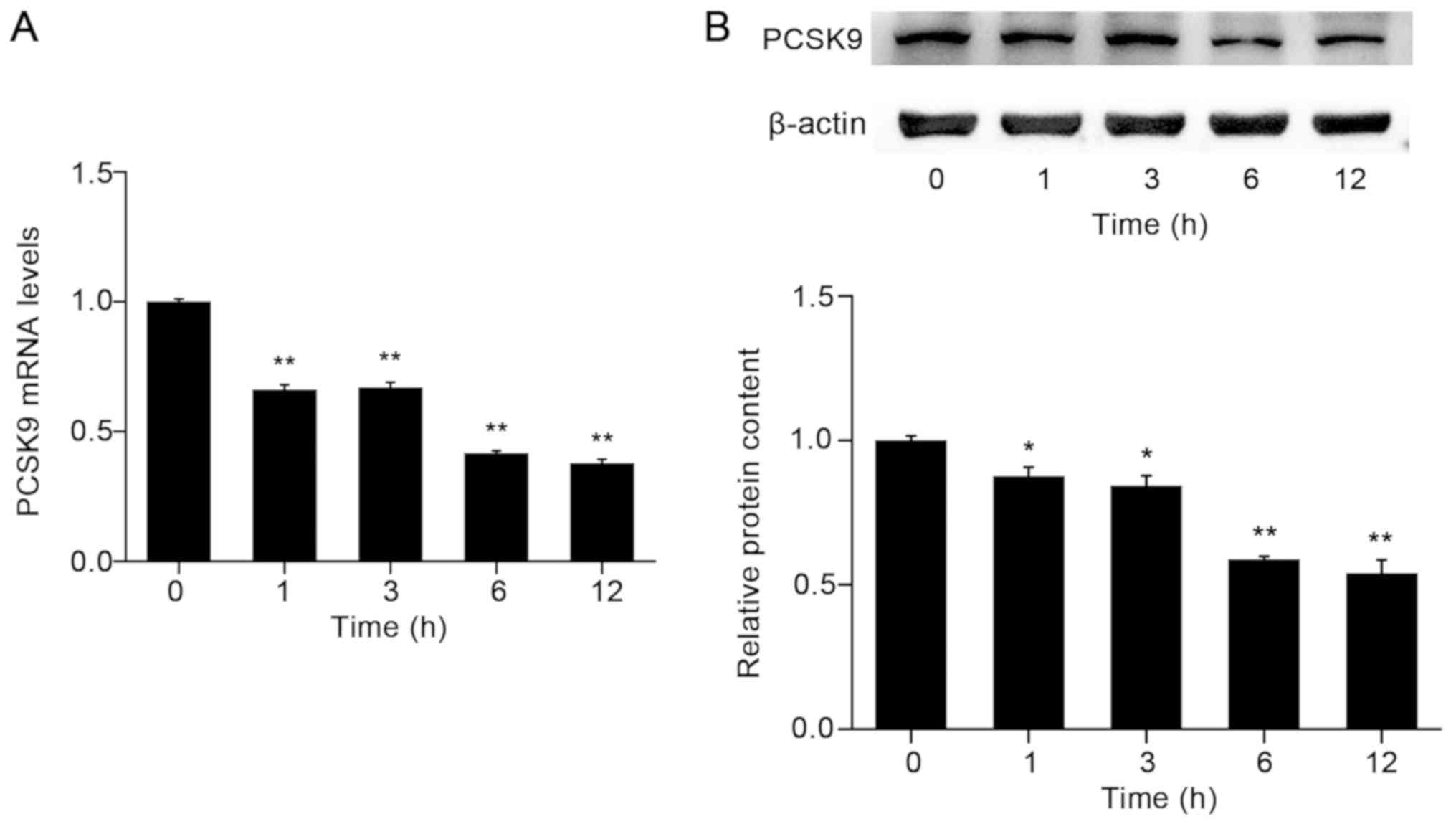
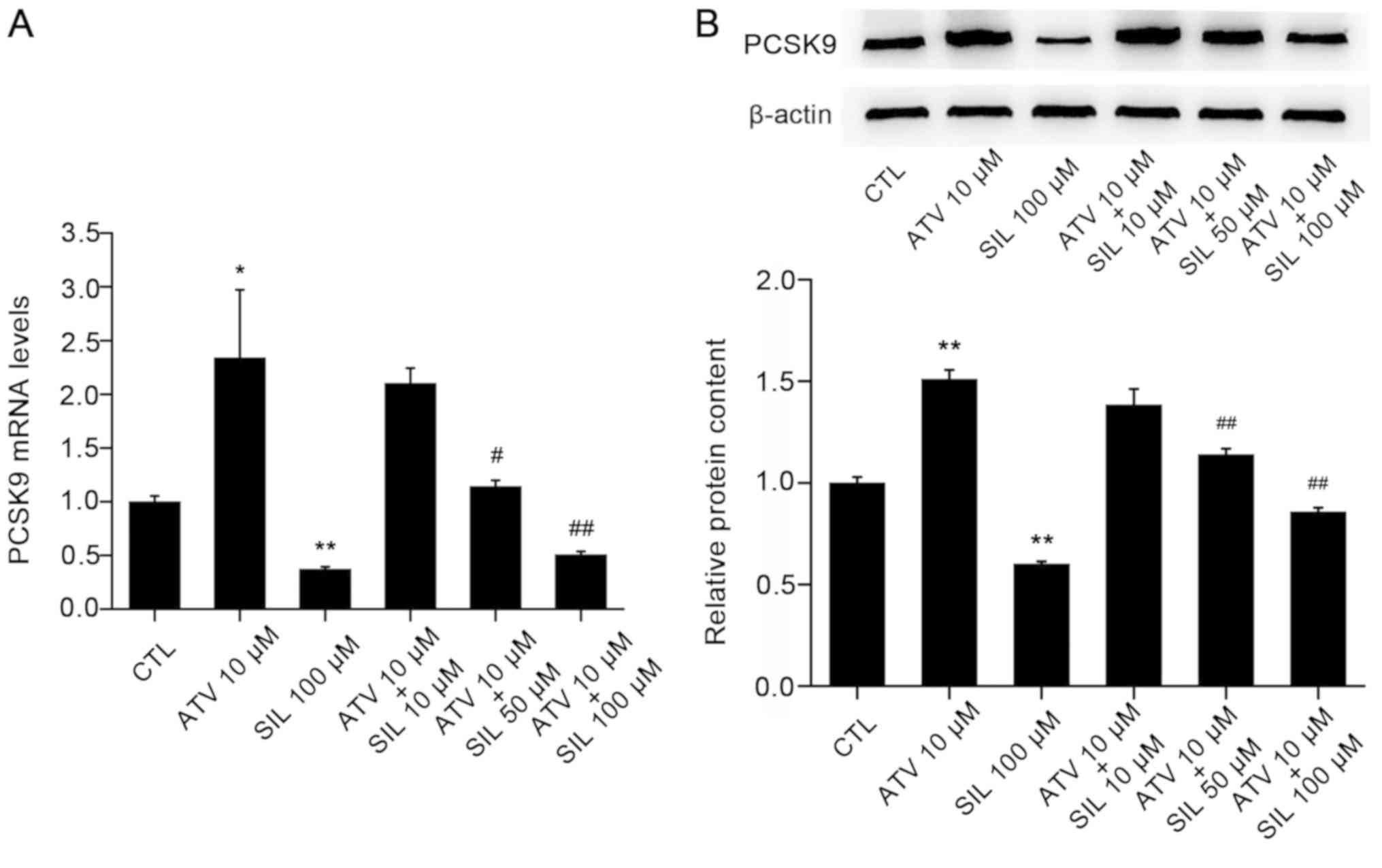
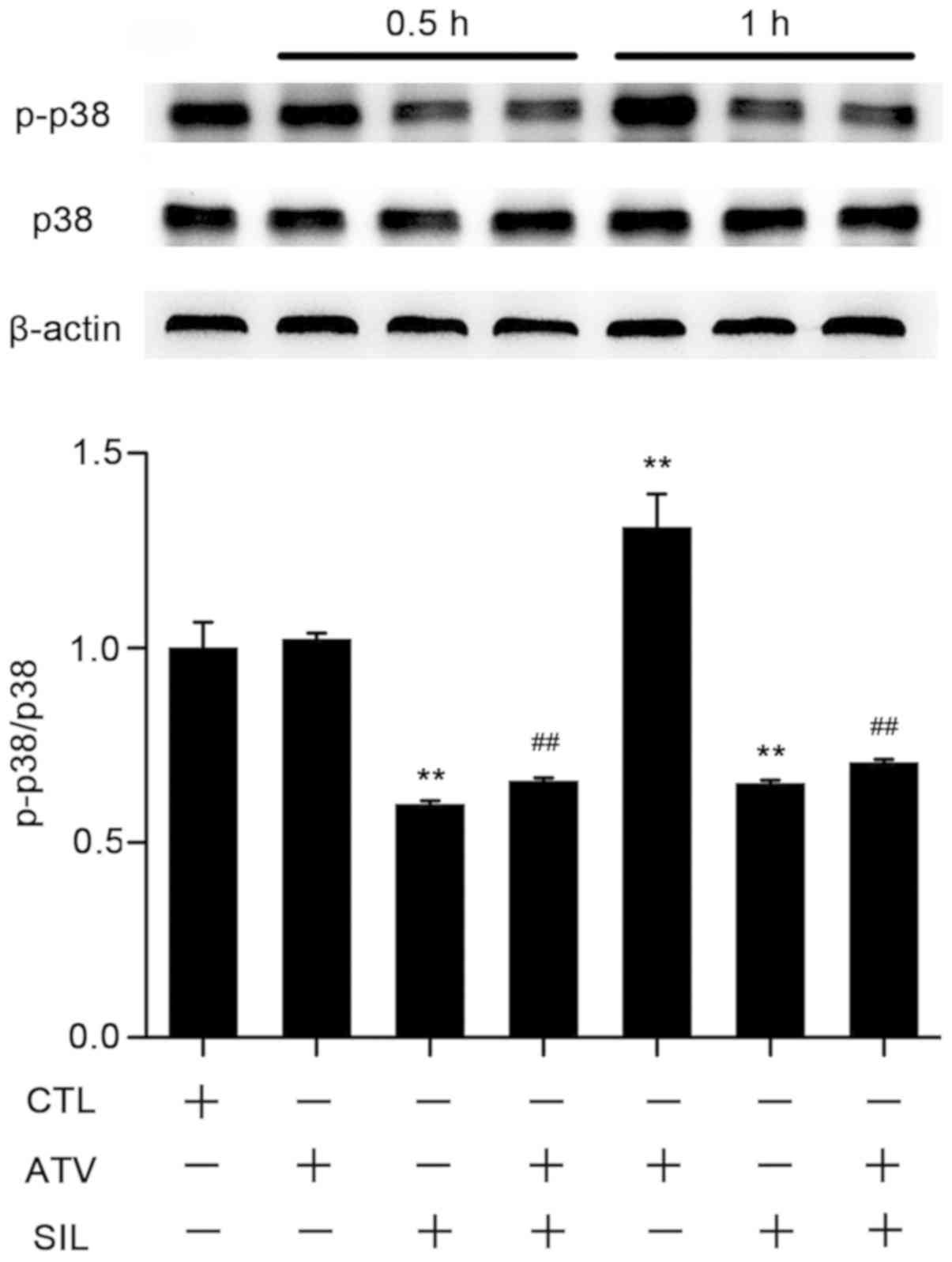
|
1
|
Benito-Vicente A, Uribe KB, Jebari S,
Galicia-Garcia U, Ostolaza H and Martin C: Familial
hypercholesterolemia: The most frequent cholesterol metabolism
disorder caused disease. Int J Mol Sci. 19(pii): E34262018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering
in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease, . The Scandinavian
Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Lancet. 344:1383–1389.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Golomb BA and Evans MA: Statin adverse
effects: A review of the literature and evidence for a
mitochondrial mechanism. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 8:373–418. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dubuc G, Chamberland A, Wassef H, Davignon
J, Seidah NG, Bernier L and Prat A: Statins upregulate PCSK9, the
gene encoding the proprotein convertase neural apoptosis-regulated
convertase-1 implicated in familial hypercholesterolemia.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:1454–1459. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gouni-Berthold I: PCSK9 antibodies: A new
class of lipid-lowering drugs. Atheroscler Suppl. 18:21–27. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Horton JD, Cohen JC and Hobbs HH:
Molecular biology of PCSK9: Its role in LDL metabolism. Trends
Biochem Sci. 32:71–77. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Goldstein JL and Brown MS: A century of
cholesterol and coronaries: From plaques to genes to statins. Cell.
161:161–172. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cunningham D, Danley DE, Geoghegan KF,
Griffor MC, Hawkins JL, Subashi TA, Varghese AH, Ammirati MJ, Culp
JS, Hoth LR, et al: Structural and biophysical studies of PCSK9 and
its mutants linked to familial hypercholesterolemia. Nat Struct Mol
Biol. 14:413–419. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fisher TS, Lo Surdo P, Pandit S, Mattu M,
Santoro JC, Wisniewski D, Cummings RT, Calzetta A, Cubbon RM,
Fischer PA, et al: Effects of pH and low density lipoprotein (LDL)
on PCSK9-dependent LDL receptor regulation. J Biol Chem.
282:20502–20512. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang DW, Lagace TA, Garuti R, Zhao Z,
McDonald M, Horton JD, Cohen JC and Hobbs HH: Binding of proprotein
convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 to epidermal growth factor-like
repeat A of low density lipoprotein receptor decreases receptor
recycling and increases degradation. J Biol Chem. 282:18602–18612.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abifadel M, Varret M, Rabès JP, Allard D,
Ouguerram K, Devillers M, Cruaud C, Benjannet S, Wickham L, Erlich
D, et al: Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant
hypercholesterolemia. Nat Genet. 34:154–156. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maxwell KN and Breslow JL: Proprotein
convertase subtilisin kexin 9: The third locus implicated in
autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Curr Opin Lipidol.
16:167–172. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Allard D, Amsellem S, Abifadel M, Trillard
M, Devillers M, Luc G, Krempf M, Reznik Y, Girardet JP, Fredenrich
A, et al: Novel mutations of the PCSK9 gene cause variable
phenotype of autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Hum Mutat.
26:4972005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hallman DM, Srinivasan SR, Chen W,
Boerwinkle E and Berenson GS: Relation of PCSK9 mutations to serum
low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in childhood and adulthood
(from The Bogalusa Heart Study). Am J Cardiol. 100:69–72. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fala L: Repatha (Evolocumab): Second PCSK9
inhibitor approved by the FDA for patients with familial
hypercholesterolemia. Am Health Drug Benefits 9 (Spec Feature).
136–139. 2016.
|
|
16
|
Raedler LA: Praluent (Alirocumab): First
PCSK9 inhibitor approved by the FDA for hypercholesterolemia. Am
Health Drug Benefits 9 (Spec Feature). 123–126. 2016.
|
|
17
|
White CM: Therapeutic potential and
critical analysis of the PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies evolocumab and
alirocumab. Ann Pharmacother. 49:1327–1335. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dai L, Lu A, Zhong LLD, Zheng G and Bian
Z: Chinese herbal medicine for hyperlipidaemia: A review based on
data mining from 1990 to 2016. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 15:520–531.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kong W, Wei J, Abidi P, Lin M, Inaba S, Li
C, Wang Y, Wang Z, Si S, Pan H, et al: Berberine is a novel
cholesterol-lowering drug working through a unique mechanism
distinct from statins. Nat Med. 10:1344–1351. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dong B, Li H, Singh AB, Cao A and Liu J:
Inhibition of PCSK9 transcription by berberine involves
down-regulation of hepatic HNF1α protein expression through the
ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway. J Biol Chem.
290:4047–4058. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Flora K, Hahn M, Rosen H and Benner K:
Milk thistle (Silybum marianum) for the therapy of liver disease.
Am J Gastroenterol. 93:139–143. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wellington K and Jarvis B: Silymarin: A
review of its clinical properties in the management of hepatic
disorders. BioDrugs. 15:465–489. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Saller R, Meier R and Brignoli R: The use
of silymarin in the treatment of liver diseases. Drugs.
61:2035–2063. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zi X and Agarwal R: Silibinin decreases
prostate-specific antigen with cell growth inhibition via G1
arrest, leading to differentiation of prostate carcinoma cells:
Implications for prostate cancer intervention. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 96:7490–7495. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gallo D, Giacomelli S, Ferlini C,
Raspaglio G, Apollonio P, Prislei S, Riva A, Morazzoni P,
Bombardelli E and Scambia G: Antitumour activity of the
silybin-phosphatidylcholine complex, IdB 1016, against human
ovarian cancer. Eur J Cancer. 39:2403–2410. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Saliou C, Rihn B, Cillard J, Okamoto T and
Packer L: Selective inhibition of NF-kappaB activation by the
flavonoid hepatoprotector silymarin in HepG2. Evidence for
different activating pathways. FEBS Lett. 440:8–12. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li H, Dong B, Park SW, Lee HS, Chen W and
Liu J: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1alpha plays a critical role in
PCSK9 gene transcription and regulation by the natural
hypocholesterolemic compound berberine. J Biol Chem.
284:28885–28895. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Costet P, Cariou B, Lambert G, Lalanne F,
Lardeux B, Jarnoux AL, Grefhorst A, Staels B and Krempf M: Hepatic
PCSK9 expression is regulated by nutritional status via insulin and
sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c. J Biol Chem.
281:6211–6218. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ko FN, Chu CC, Lin CN, Chang CC and Teng
CM: Isoorientin-6′-O-glucoside, a water-soluble antioxidant
isolated from Gentiana arisanensis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1389:81–90. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lu CL, Zhu W, Wang DM, Chen WL, Hu MM,
Wang M, Xu XJ and Lu CJ: Inhibitory effects of chemical compounds
isolated from the rhizome of Smilax glabra on nitric oxide and
tumor necrosis factor-α production in lipopolysaccharide-induced
RAW264.7 cell. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015:6024252015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee S, Jung SH, Lee YS, Yamada M, Kim BK,
Ohuchi K and Shin KH: Antiinflammatory activity of hyperin from
Acanthopanax chiisanensis roots. Arch Pharm Res. 27:628–632. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang B, Su JP, Bai Y, Li J and Liu YH:
Inhibitory effects of O-methylated isoflavone glycitein on human
breast cancer SKBR-3 cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:7809–7817.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Matsukawa Y, Marui N, Sakai T, Satomi Y,
Yoshida M, Matsumoto K, Nishino H and Aoike A: Genistein arrests
cell cycle progression at G2-M. Cancer Res. 53:1328–1331.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen J, Zhao X, Ye Y, Wang Y and Tian J:
Estrogen receptor beta-mediated proliferative inhibition and
apoptosis in human breast cancer by Calycosin and Formononetin.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 32:1790–1797. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Auyeung KK, Law PC and Ko JK: Novel
anti-angiogenic effects of formononetin in human colon cancer cells
and tumor xenograft. Oncol Rep. 28:2188–2194. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gao Y, Fang L, Liu F, Zong C, Cai R, Chen
X and Qi Y: Suppressive effects of irisflorentin on LPS-induced
inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 239:1018–1024. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Effect of Dichotomitin on relieving cough
induced by cigarette and infection and serum cytokines of model
guinea pigs. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Xuekan. 34:2902–2904. 2016.
|
|
38
|
Jun HJ, Hoang MH, Lee JW, Yaoyao J, Lee
JH, Lee DH, Lee HJ, Seo WD, Hwang BY and Lee SJ: Iristectorigenin B
isolated from Belamcanda chinensis is a liver X receptor modulator
that increases ABCA1 and ABCG1 expression in macrophage RAW 264.7
cells. Biotechnol Lett. 34:2213–2221. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen CC, Chen CY, Ueng SH, Hsueh C, Yeh
CT, Ho JY, Chou LF and Wang TH: Corylin increases the sensitivity
of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to chemotherapy through long
noncoding RNA RAD51-AS1-mediated inhibition of DNA repair. Cell
Death Dis. 9:5432018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Martineti V, Tognarini I, Azzari C,
Carbonell Sala S, Clematis F, Dolci M, Lanzotti V, Tonelli F,
Brandi ML and Curir P: Inhibition of in vitro growth and arrest in
the G0/G1 phase of HCT8 line human colon cancer cells by
kaempferide triglycoside from Dianthus caryophyllus. Phytother Res.
24:1302–1308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lin CM, Huang ST, Liang YC, Lin MS, Shih
CM, Chang YC, Chen TY and Chen CT: Isovitexin suppresses
lipopolysaccharide-mediated inducible nitric oxide synthase. Planta
Med. 71:748–753. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zygmunt K, Faubert B, MacNeil J and Tsiani
E: Naringenin, a citrus flavonoid, increases muscle cell glucose
uptake via AMPK. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 398:178–183. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Niu X, Xing W, Li W, Fan T, Hu H and Li Y:
Isofraxidin exhibited anti-inflammatory effects in vivo and
inhibited TNF-α production in LPS-induced mouse peritoneal
macrophages in vitro via the MAPK pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
14:164–171. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shyu MH, Kao TC and Yen GC: Oleanolic acid
and ursolic acid induce apoptosis in HuH7 human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells through a mitochondrial-dependent pathway and
downregulation of XIAP. J Agric Food Chem. 58:6110–6118. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ko BS, Choi SB, Park SK, Jang JS, Kim YE
and Park S: Insulin densitizing and insulinotropic sction of
Berberine from Cortidis Rhizoma. Biol Pharm Bull. 28:1431–1437.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tang FY, Su YC, Chen NC, Hsieh HS and Chen
KS: Resveratrol inhibits migration and invasion of human
breast-cancer cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 52:683–691. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fryer LG, Parbu-Patel A and Carling D: The
Anti-diabetic drugs rosiglitazone and metformin stimulate
AMP-activated protein kinase through distinct signaling pathways. J
Biol Chem. 277:25226–25232. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cui Q, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Minami M and
Ikejima T: Autophagy preceded apoptosis in oridonin-treated human
breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:859–864. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Miyoshi K, Kasahara K, Miyazaki I and
Asanuma M: Factors that influence primary cilium length. Acta Med
Okayama. 65:279–185. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li X, Liu Y, Hou X, Peng H, Zhang L, Jiang
Q, Shi M, Ji Y, Wang Y and Shi W: Chlorogenic acid inhibits the
replication and viability of enterovirus 71 in vitro. PLoS One.
8:e760072013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang CJ and Yu HT: The signal pathways of
immune inflammation mediated By The Tlr3/Nf-Kappab and activator
protein-1 in cells infected with influenza A virus antagonized by
Baicalin. Adv Mat Res. 345:201–209. 2012.
|
|
52
|
Ida C, Ogata S, Okumura K and Taguchi H:
Changes in the gene expression of C-myc and CD38 in HL-60 cells
during differentiation induced by nicotinic acid-related compounds.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 72:868–871. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sun C, Jiang M, Zhang L, Jian Y, Zhang G,
Du B, Ren Y, Li X and Yao J: Cycloastragenol mediates activation
and proliferation suppression in concanavalin A-induced mouse
lymphocyte pan-activation model. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol.
39:131–139. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhou J, Sun YY, Sun MY, Mao WA, Wang L,
Zhang J and Zhang H: Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin attenuates
lipopolysaccharide induced inflammatory response in RAW 264.7
macrophages. Pharmacogn Mag. 13:378–384. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu TZ, Chen CY, Yiin SJ, Chen CH, Cheng
JT, Shih MK, Wang YS and Chern CL: Molecular mechanism of cell
cycle blockage of hepatoma SK-Hep-1 cells by Epimedin C through
suppression of mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and
increased expression of CDK inhibitors p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1).
Food Chem Toxicol. 44:227–235. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li J, Hao L, Wu J, Zhang J and Su J:
Linarin promotes osteogenic differentiation by activating the
BMP-2/RUNX2 pathway via protein kinase A signaling. Int J Mol Med.
37:901–910. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhou J, Hu H, Long J, Wan F, Li L, Zhang
S, Shi YE and Chen Y: Vitexin 6, a novel lignan, induces autophagy
and apoptosis by activating the Jun N-terminal kinase pathway.
Anticancer Drugs. 24:928–936. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lu J, Papp LV, Fang J, Rodriguez-Nieto S,
Zhivotovsky B and Holmgren A: Inhibition of mammalian thioredoxin
reductase by some flavonoids: Implications for myricetin and
quercetin anticancer activity. Cancer Res. 66:4410–4418. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li L, Sapkota M, Kim SW and Soh Y:
Herbacetin inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase via JNK and
nuclear factor-κB in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Eur J
Pharmacol. 765:115–123. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Cao S, Ni B, Feng L, Yin X, Dou H, Fu J,
Lin L and Ni J: Simultaneous determination of typhaneoside and
isorhamnetin-3-O-neohesperidoside in rats after oral administration
of pollen Typhae extract by UPLC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr Sci.
53:866–871. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Shin SW, Jung E, Kim S, Kim JH, Kim EG,
Lee J and Park D: Antagonizing effects and mechanisms of Afzelin
against UVB-induced cell damage. PLoS One. 8:e619712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Guo H, Zhang X, Cui Y, Zhou H, Xu D, Shan
T, Zhang F, Guo Y, Chen Y and Wu D: Taxifolin protects against
cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis during biomechanical stress of
pressure overload. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 287:168–177. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chu SC, Chiou HL, Chen PN, Yang SF and
Hsieh YS: Silibinin inhibits the invasion of human lung cancer
cells via decreased productions of urokinase-plasminogen activator
and matrix metalloproteinase-2. Mol Carcinog. 40:143–149. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sugimoto E and Yamaguchi M: Stimulatory
effect of Daidzein in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 59:471–475. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lee KT, Sohn IC, Kim YK, Choi JH, Choi JW,
Park HJ, Itoh Y and Miyamoto K: Tectorigenin, an isoflavone of
Pueraria thunbergiana Benth., induces differentiation and apoptosis
in human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Biol Pharm Bull.
24:1117–1121. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kim PS, Shin JH, Jo DS, Shin DW, Choi DH,
Kim WJ, Park K, Kim JK, Joo CG, Lee JS, et al: Anti-melanogenic
activity of schaftoside in Rhizoma Arisaematis by increasing
autophagy in B16F1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 503:309–315.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Davignon J and Dubuc G: Statins and
ezetimibe modulate plasma proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin-9
(PCSK9) levels. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 120:163–173.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Welder G, Zineh I, Pacanowski MA, Troutt
JS, Cao GQ and Konrad RJ: High-dose atorvastatin causes a rapid
sustained increase in human serum PCSK9 and disrupts its
correlation with LDL cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 51:2714–2721. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Pal S, Ghosh M, Ghosh S, Bhattacharyya S
and Sil PC: Atorvastatin induced hepatic oxidative stress and
apoptotic damage via MAPKs, mitochondria, calpain and caspase12
dependent pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. 83:36–47. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Puccetti L, Acampa M and Auteri A:
Pharmacogenetics of statins therapy. Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug
Discov. 2:228–236. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Taylor BA and Thompson PD: Statins and
their effect on PCSK9-impact and clinical relevance. Curr
Atheroscler Rep. 18:462016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Cameron J, Ranheim T, Kulseth MA, Leren TP
and Berge KE: Berberine decreases PCSK9 expression in HepG2 cells.
Atherosclerosis. 201:266–273. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kumar A, Ekavali, Chopra K, Mukherjee M,
Pottabathini R and Dhull DK: Current knowledge and pharmacological
profile of berberine: An update. Eur J Pharmacol. 761:288–297.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lan J, Zhao Y, Dong F, Yan Z, Zheng W, Fan
J and Sun G: Meta-analysis of the effect and safety of berberine in
the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipemia and
hypertension. J Ethnopharmacol. 161:69–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Wu JW, Lin LC and Tsai TH: Drug-drug
interactions of silymarin on the perspective of pharmacokinetics. J
Ethnopharmacol. 121:185–193. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Flaig TW, Gustafson DL, Su LJ, Zirrolli
JA, Crighton F, Harrison GS, Pierson AS, Agarwal R and Glodé LM: A
phase I and pharmacokinetic study of silybin-phytosome in prostate
cancer patients. Invest New Drugs. 25:139–146. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Stolf AM, Cardoso CC and Acco A: Effects
of silymarin on diabetes mellitus complications: A review.
Phytother Res. 31:366–374. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Lennernäs H: Clinical pharmacokinetics of
atorvastatin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 42:1141–1160. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Wu JW, Lin LC and Tsai TH: Drug-drug
interactions of silymarin on the perspective of pharmacokinetics. J
Ethnopharmacol. 121:185–193. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Pang Y, Zhu H, Xu J, Yang L, Liu L and Li
J: β-arrestin-2 is involved in irisin-induced glucose metabolism in
type 2 diabetes via p38 MAPK signaling. Exp Cell Res. 360:199–204.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Cui CJ, Li S, Zhu CG, Sun J, Du Y, Zhang
Y, Wu NQ, Guo YL, Xu RX, Gao Y and Li JJ: Enhanced pro-protein
convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 expression by C-reactive protein
through p38MAPK-HNF1α pathway in HepG2 cells. J Cell Mol Med.
20:2374–2383. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Du Y, Li S, Cui CJ, Zhang Y, Yang SH and
Li JJ: Leptin decreases the expression of low-density lipoprotein
receptor via PCSK9 pathway: Linking dyslipidemia with obesity. J
Transl Med. 14:2762016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Li J, Huang Q, Long X, Zhang J, Huang X,
Aa J, Yang H, Chen Z and Xing J: CD147 reprograms fatty acid
metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through
Akt/mTOR/SREBP1c and P38/PPARα pathways. J Hepatol. 63:1378–1389.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|