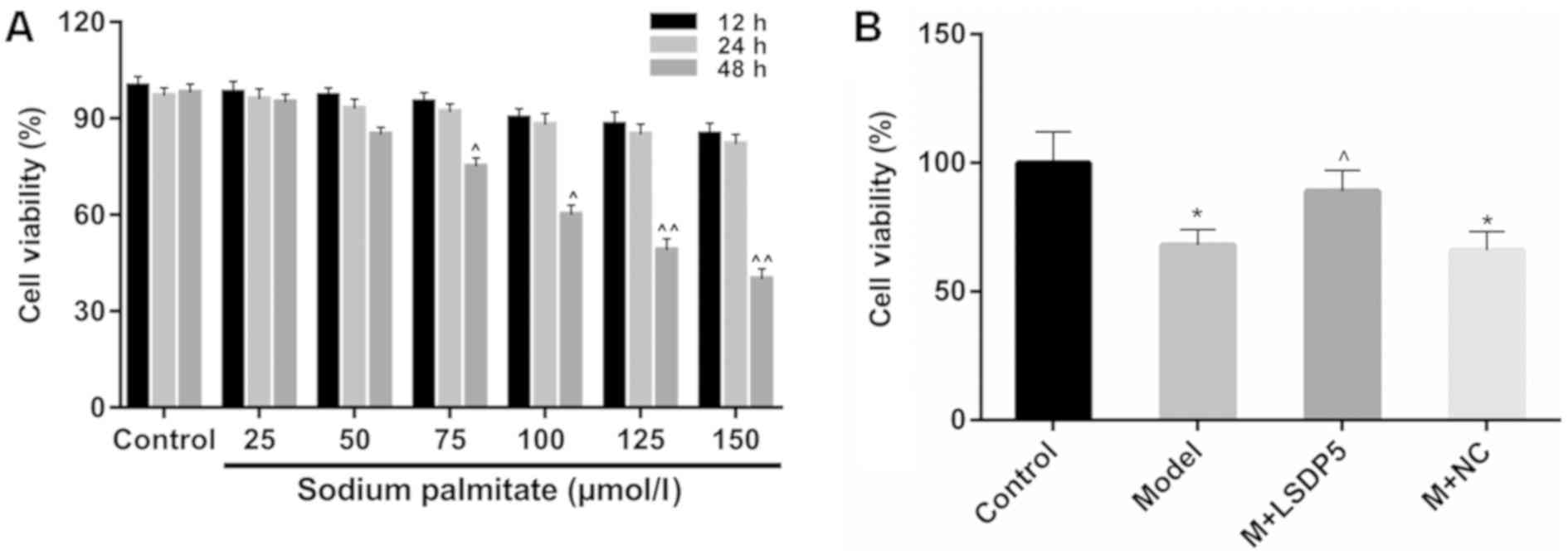
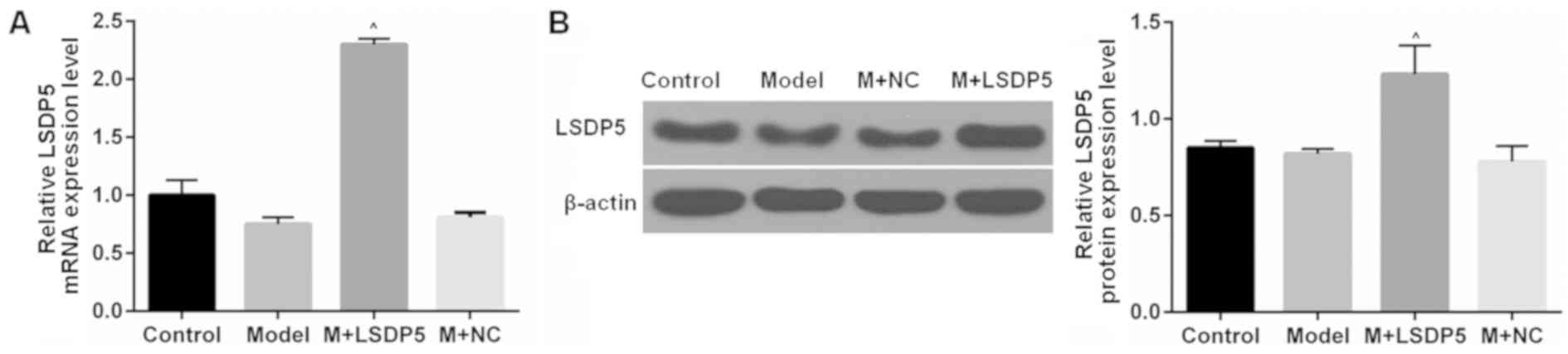
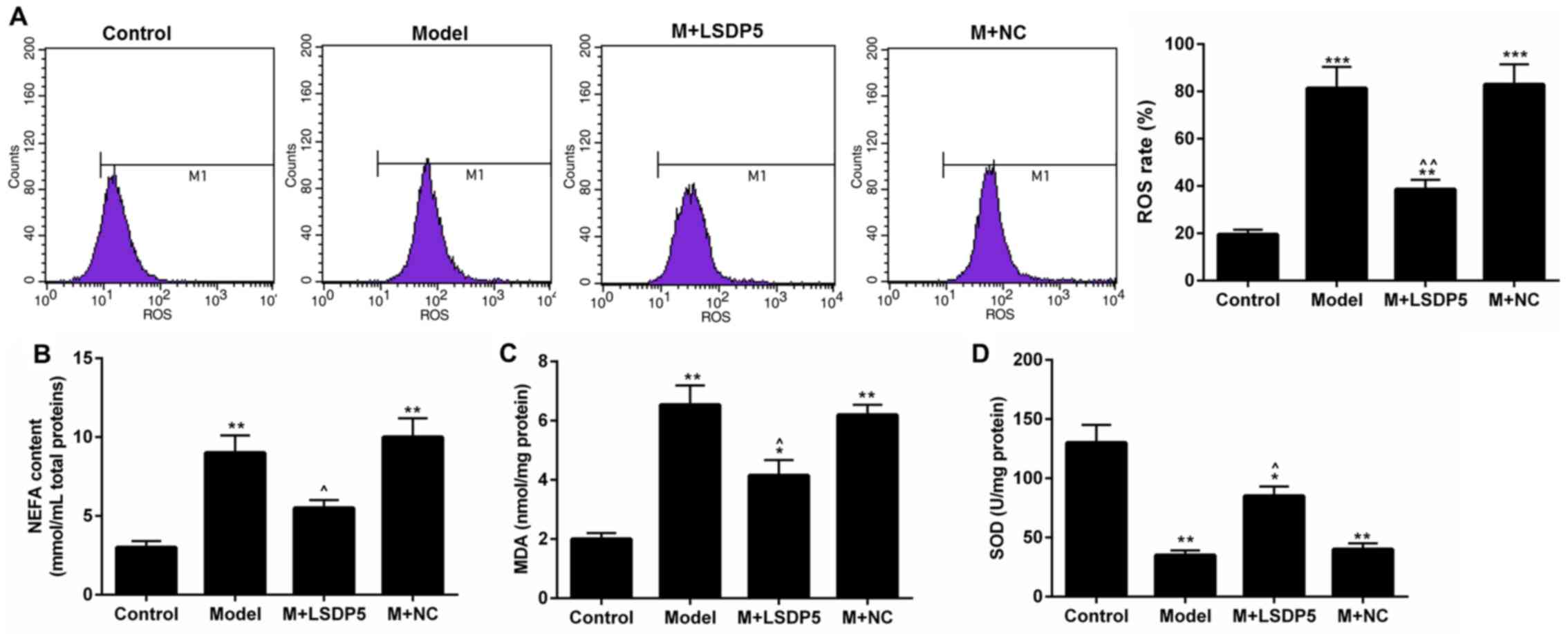
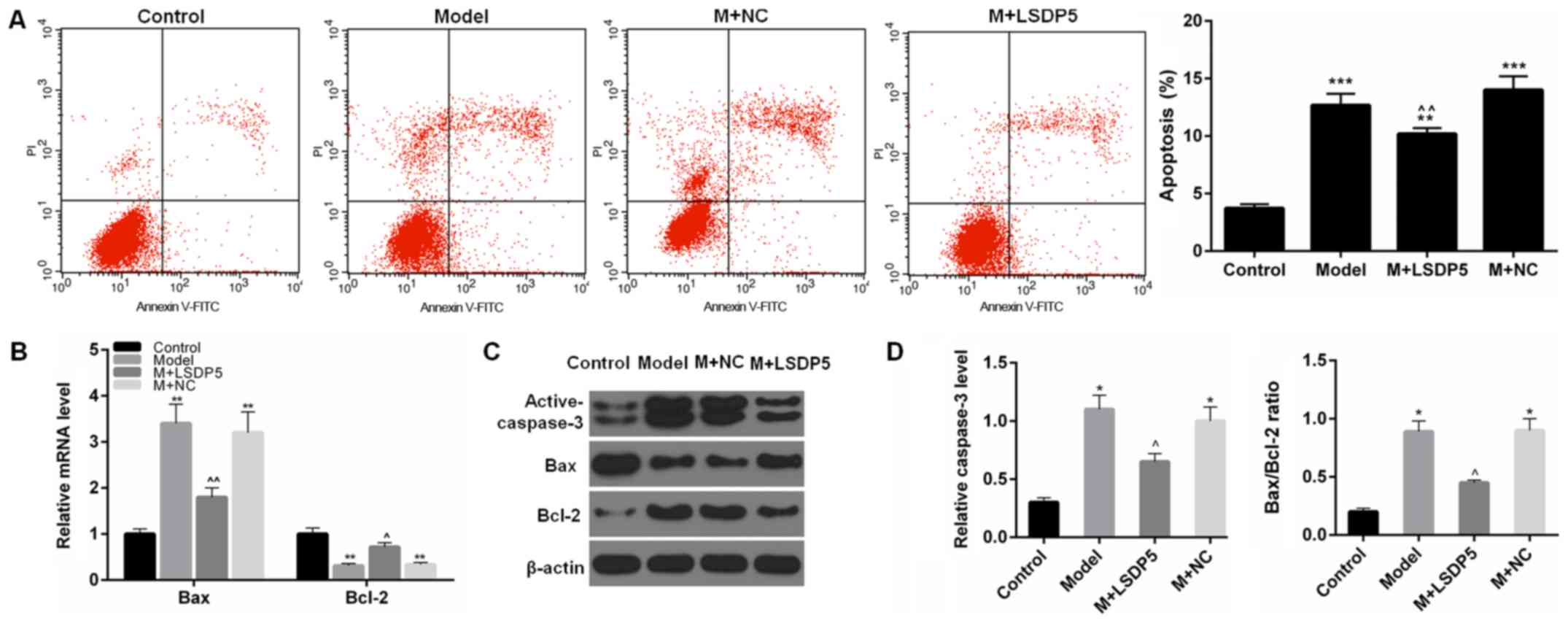
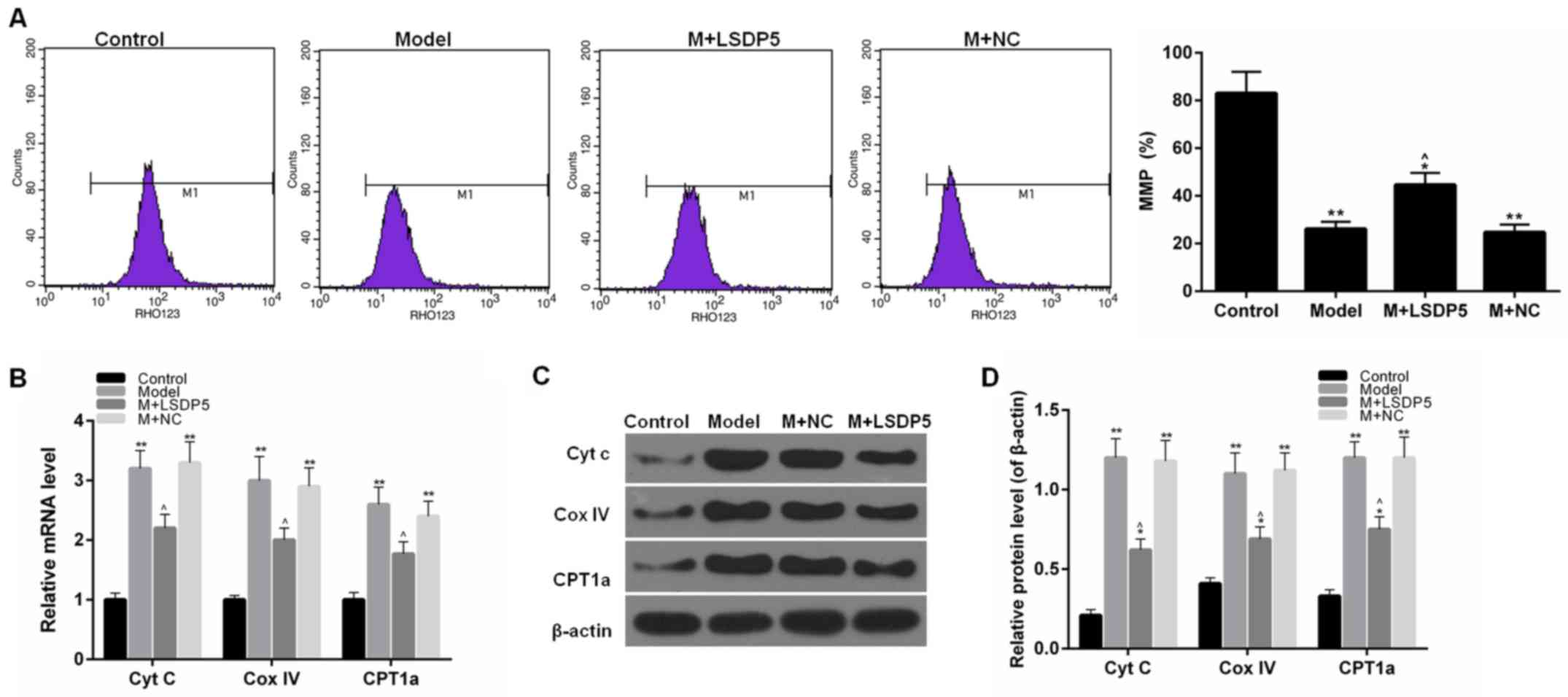
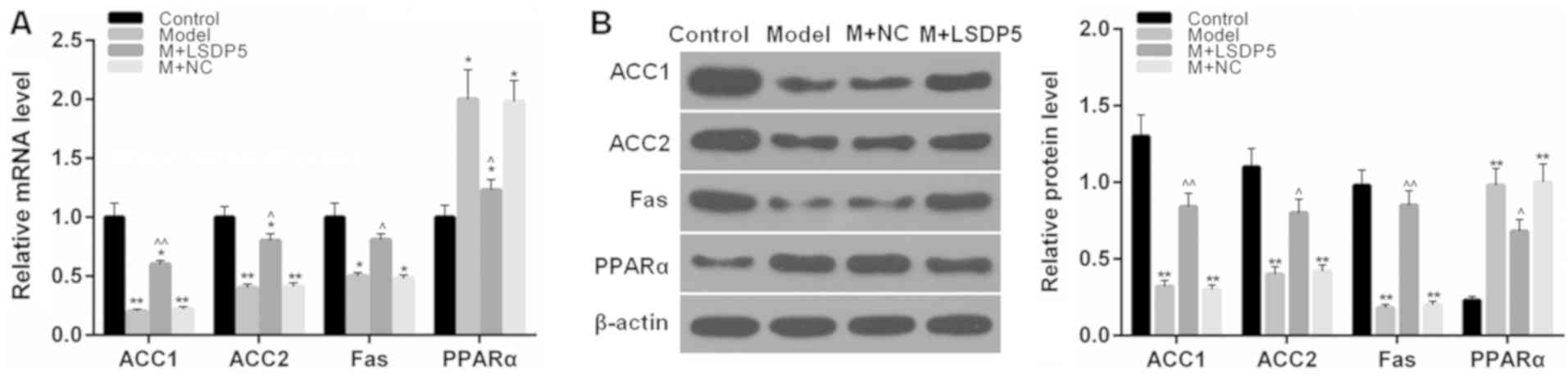
|
1
|
Zheng X, Gong L, Luo R, Chen H, Peng B,
Ren W and Wang Y: Serum uric acid and non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease in non-obesity Chinese adults. Lipids Health Dis.
16:2022017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fan JG and Farrell GC: Epidemiology of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in China. J Hepatol. 50:204–210.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Angulo P: GI epidemiology: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 25:883–889. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
de Alwis NM and Day CP: Non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease: The mist gradually clears. J Hepatol. 48
(Suppl 1):S104–S112. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fan JG, Saibara T, Chitturi S, Kim BI,
Sung JJ and Chutaputti A; Asia-Pacific Working Party for NAFLD, :
What are the risk factors and settings for non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease in Asia-Pacific? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22:794–800.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Farrell GC and Larter CZ: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: From steatosis to cirrhosis. Hepatology. 43
(Suppl 1):S99–S112. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Garbarino J and Sturley SL: Saturated with
fat: New perspectives on lipotoxicity. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab
Care. 12:110–116. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weiss TS, Lupke M, Ibrahim S, Buechler C,
Lorenz J, Ruemmele P, Hofmann U, Melter M and Dayoub R: Attenuated
lipotoxicity and apoptosis is linked to exogenous and endogenous
augmenter of liver regeneration by different pathways. PLoS One.
12:e01842822017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kapoor A and Sanyal AJ: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response. Clin Liver Dis.
13:581–590. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bellanti F, Mitarotonda D, Tamborra R,
Blonda M, Iannelli G, Petrella A, Sanginario V, Iuliano L,
Vendemiale G and Serviddio G: Oxysterols induce mitochondrial
impairment and hepatocellular toxicity in non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 75 (Suppl 1):S16–S17. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kusminski CM, Shetty S, Orci L, Unger RH
and Scherer PE: Diabetes and apoptosis: Lipotoxicity. Apoptosis.
14:1484–1495. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Unger RH and Orci L: Lipoapoptosis: Its
mechanism and its diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1585:202–212.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
McCullough AJ: The clinical features,
diagnosis and natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Clin Liver Dis. 8521–533. (viii)2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Murphy DJ: The biogenesis and functions of
lipid bodies in animals, plants and microorganisms. Prog Lipid Res.
40:325–438. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zehmer JK, Huang Y, Peng G, Pu J, Anderson
RG and Liu P: A role for lipid droplets in inter-membrane lipid
traffic. Proteomics. 9:914–921. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Geng F and Guo D: Lipid droplets,
potential biomarker and metabolic target in glioblastoma. Intern
Med Rev (Wash DC). May 3–2017.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.18103/imr.v3i5.443.
|
|
17
|
Bartz R, Zehmer JK, Zhu M, Chen Y, Serrero
G, Zhao Y and Liu P: Dynamic activity of lipid droplets: Protein
phosphorylation and GTP-mediated protein translocation. J Proteome
Res. 6:3256–3265. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brasaemle DL: Thematic review series:
Adipocyte biology. The perilipin family of structural lipid droplet
proteins: Stabilization of lipid droplets and control of lipolysis.
J Lipid Res. 48:2547–2559. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dalen KT, Dahl T, Holter E, Arntsen B,
Londos C, Sztalryd C and Nebb HI: LSDP5 is a PAT protein
specifically expressed in fatty acid oxidizing tissues. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1771:210–227. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wolins NE, Quaynor BK, Skinner JR, Tzekov
A, Croce MA, Gropler MC, Varma V, Yao-Borengasser A, Rasouli N,
Kern PA, et al: OXPAT/PAT-1 is a PPAR-induced lipid droplet protein
that promotes fatty acid utilization. Diabetes. 55:3418–3428. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamaguchi T, Matsushita S, Motojima K,
Hirose F and Osumi T: MLDP, a novel PAT family protein localized to
lipid droplets and enriched in the heart, is regulated by
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. J Biol Chem.
281:14232–14240. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gandotra S, Le Dour C, Bottomley W,
Cervera P, Giral P, Reznik Y, Charpentier G, Auclair M, Delépine M,
Barroso I, et al: Perilipin deficiency and autosomal dominant
partial lipodystrophy. N Engl J Med. 364:740–748. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tansey JT, Sztalryd C, Gruia-Gray J, Roush
DL, Zee JV, Gavrilova O, Reitman ML, Deng CX, Li C, Kimmel AR and
Londos C: Perilipin ablation results in a lean mouse with aberrant
adipocyte lipolysis, enhanced leptin production, and resistance to
diet-induced obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:6494–6499. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cao J, Feng XX, Yao L, Ning B, Yang ZX,
Fang DL and Shen W: Saturated free fatty acid sodium
palmitate-induced lipoapoptosis by targeting glycogen synthase
kinase-3β activation in human liver cells. Dig Dis Sci. 59:346–357.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li F, Gu Y, Dong W, Li H, Zhang L, Li N,
Li W, Zhang L, Song Y, Jiang L, et al: Cell death-inducing
DFF45-like effector, a lipid droplet-associated protein, might be
involved in the differentiation of human adipocytes. FEBS J.
277:4173–4183. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bhala N, Younes R and Bugianesi E:
Epidemiology and natural history of patients with NAFLD. Curr Pharm
Des. 19:5169–5176. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cao J, Dai DL, Yao L, Yu HH, Ning B, Zhang
Q, Chen J, Cheng WH, Shen W and Yang ZX: Saturated fatty acid
induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in human
liver cells via the PERK/ATF4/CHOP signaling pathway. Mol Cell
Biochem. 364:115–129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Malhi H and Gores GJ: Molecular mechanisms
of lipotoxicity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Semin Liver
Dis. 28:360–369. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ning B, Bai M and Shen W: Reduced
glutathione protects human hepatocytes from palmitate-mediated
injury by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress response.
Hepatogastroenterology. 58:1670–1679. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cao SS and Kaufman RJ: Targeting
endoplasmic reticulum stress in metabolic disease. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 17:437–448. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li H, Song Y, Zhang LJ, Gu Y, Li FF, Pan
SY, Jiang LN, Liu F, Ye J and Li Q: LSDP5 enhances triglyceride
storage in hepatocytes by influencing lipolysis and fatty acid
β-oxidation of lipid droplets. PLoS One. 7:e367122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kuramoto K, Okamura T, Yamaguchi T,
Nakamura TY, Wakabayashi S, Morinaga H, Nomura M, Yanase T, Otsu K,
Usuda N, et al: Perilipin 5, a lipid droplet-binding protein,
protects heart from oxidative burden by sequestering fatty acid
from excessive oxidation. J Biol Chem. 287:23852–23863. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Engin A: Non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 960:443–467. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kishikawa N and Kuroda N:
Chemiluminescence assay for the investigation of reactive oxygen
species generator. Yakugaku Zasshi. 135:191–196. 2015.(In
Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Feldstein AE, Canbay A, Angulo P, Taniai
M, Burgart LJ, Lindor KD and Gores GJ: Hepatocyte apoptosis and fas
expression are prominent features of human nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 125:437–443. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schattenberg JM, Galle PR and Schuchmann
M: Apoptosis in liver disease. Liver Int. 26:904–911. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cao Z, Zhang H, Cai X, Fang W, Chai D, Wen
Y, Chen H, Chu F and Zhang Y: Luteolin promotes cell apoptosis by
inducing autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 43:1803–1812. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Diamantis A, Magiorkinis E, Sakorafas GH
and Androutsos G: A brief history of apoptosis: From ancient to
modern times. Onkologie. 31:702–706. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Granneman JG, Moore HP, Mottillo EP and
Zhu Z: Functional interactions between Mldp (LSDP5) and Abhd5 in
the control of intracellular lipid accumulation. J Biol Chem.
284:3049–3057. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang H, Bell M, Sreenivasan U, Hu H, Liu
J, Dalen K, Londos C, Yamaguchi T, Rizzo MA, Coleman R, et al:
Unique regulation of adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) by
perilipin 5, a lipid droplet-associated protein. J Biol Chem.
286:15707–15715. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mansour M, Schwartz D, Judd R, Akingbemi
B, Braden T, Morrison E, Dennis J, Bartol F, Hazi A, Napier I and
Abdel-Mageed AB: Thiazolidinediones/PPARγ agonists and fatty acid
synthase inhibitors as an experimental combination therapy for
prostate cancer. Int J Oncol. 38:537–546. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|