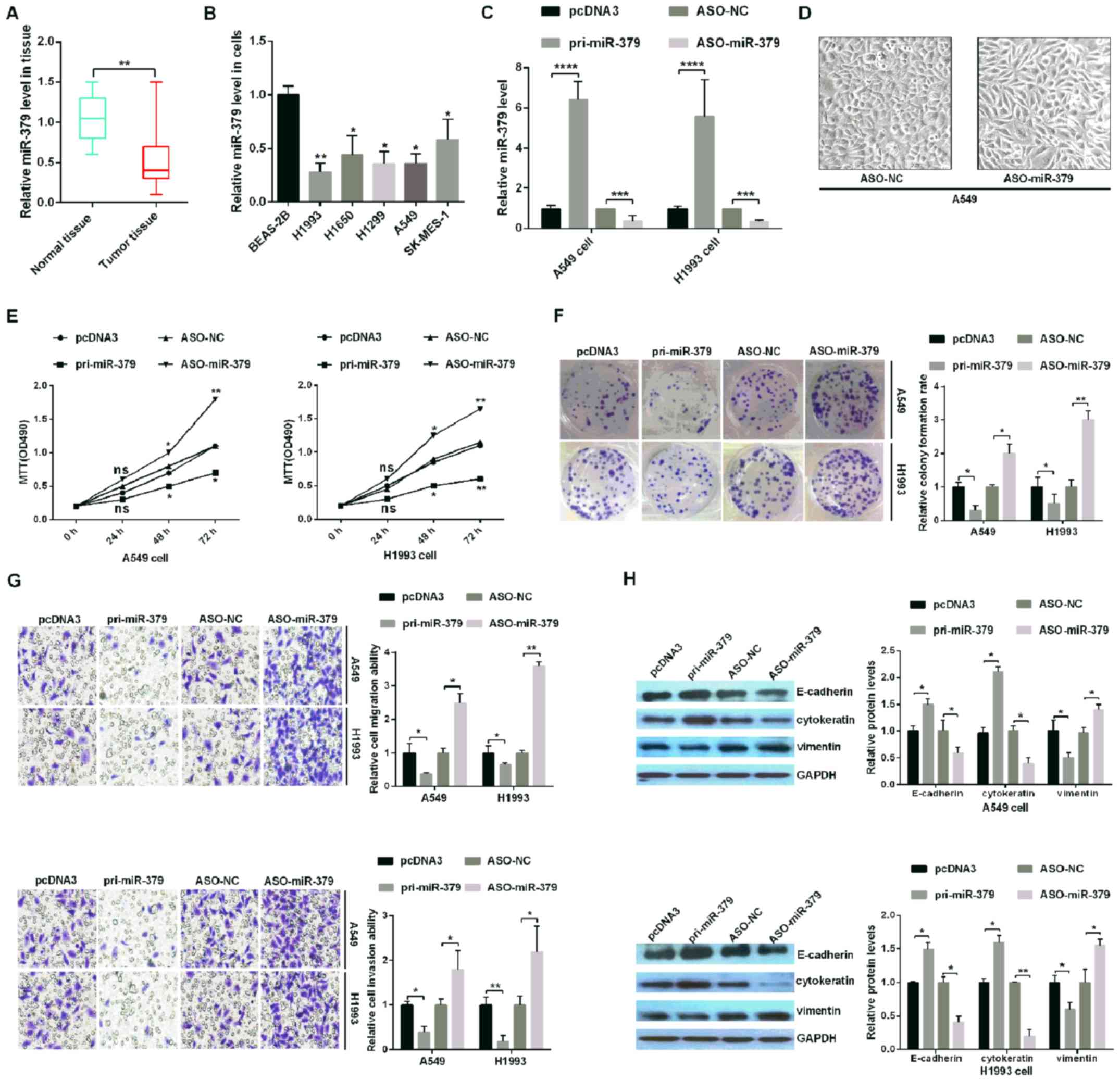
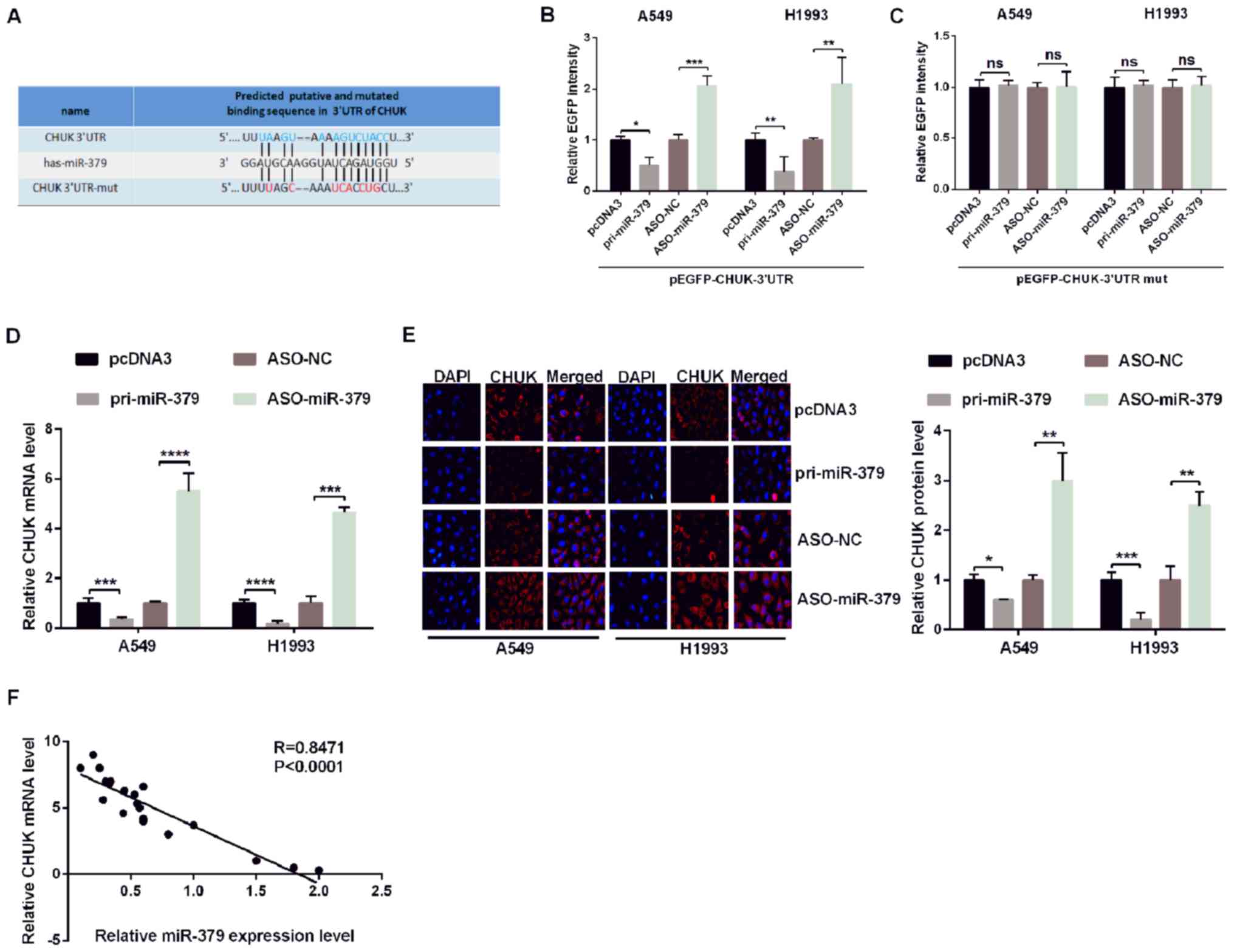
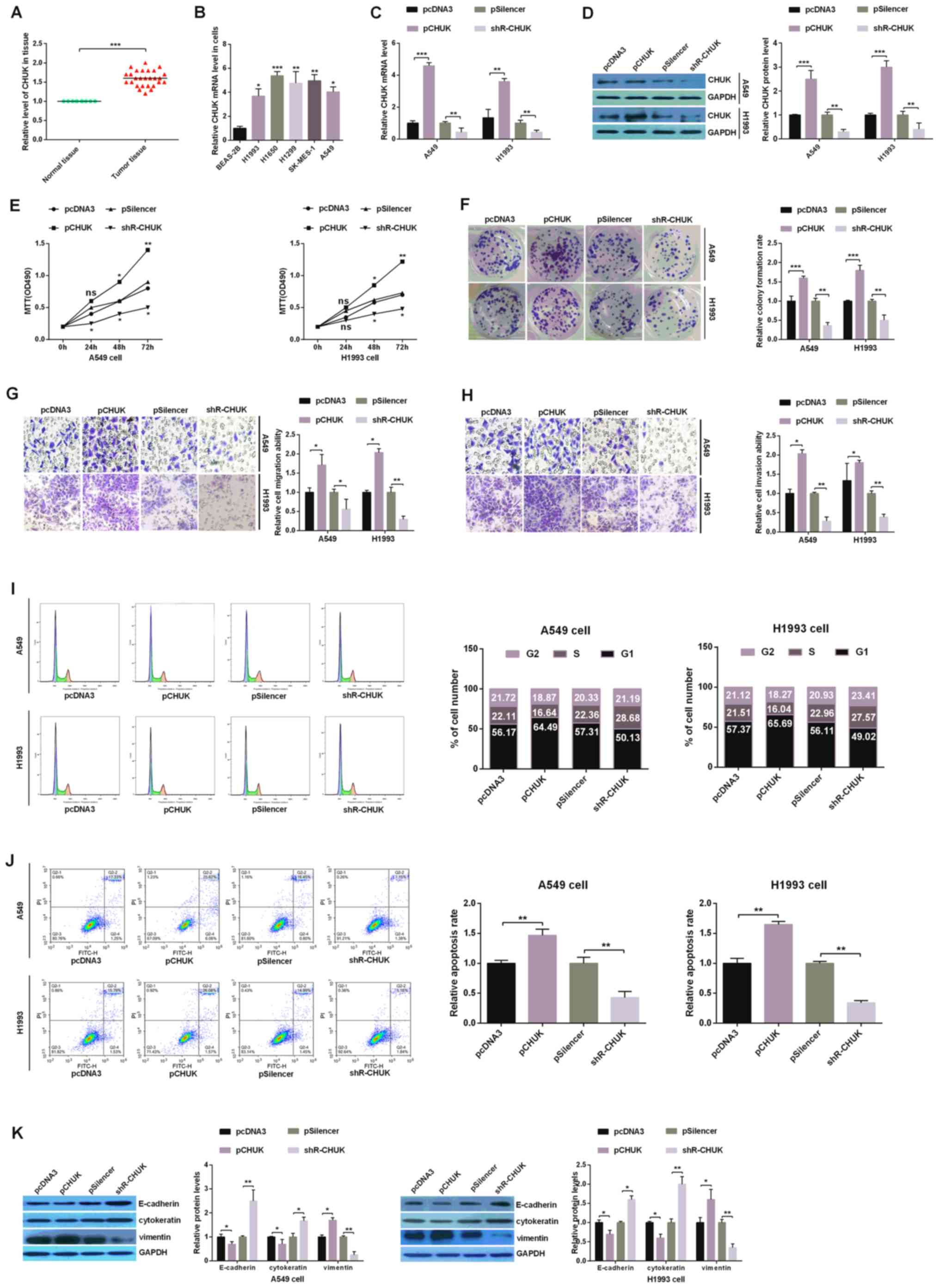
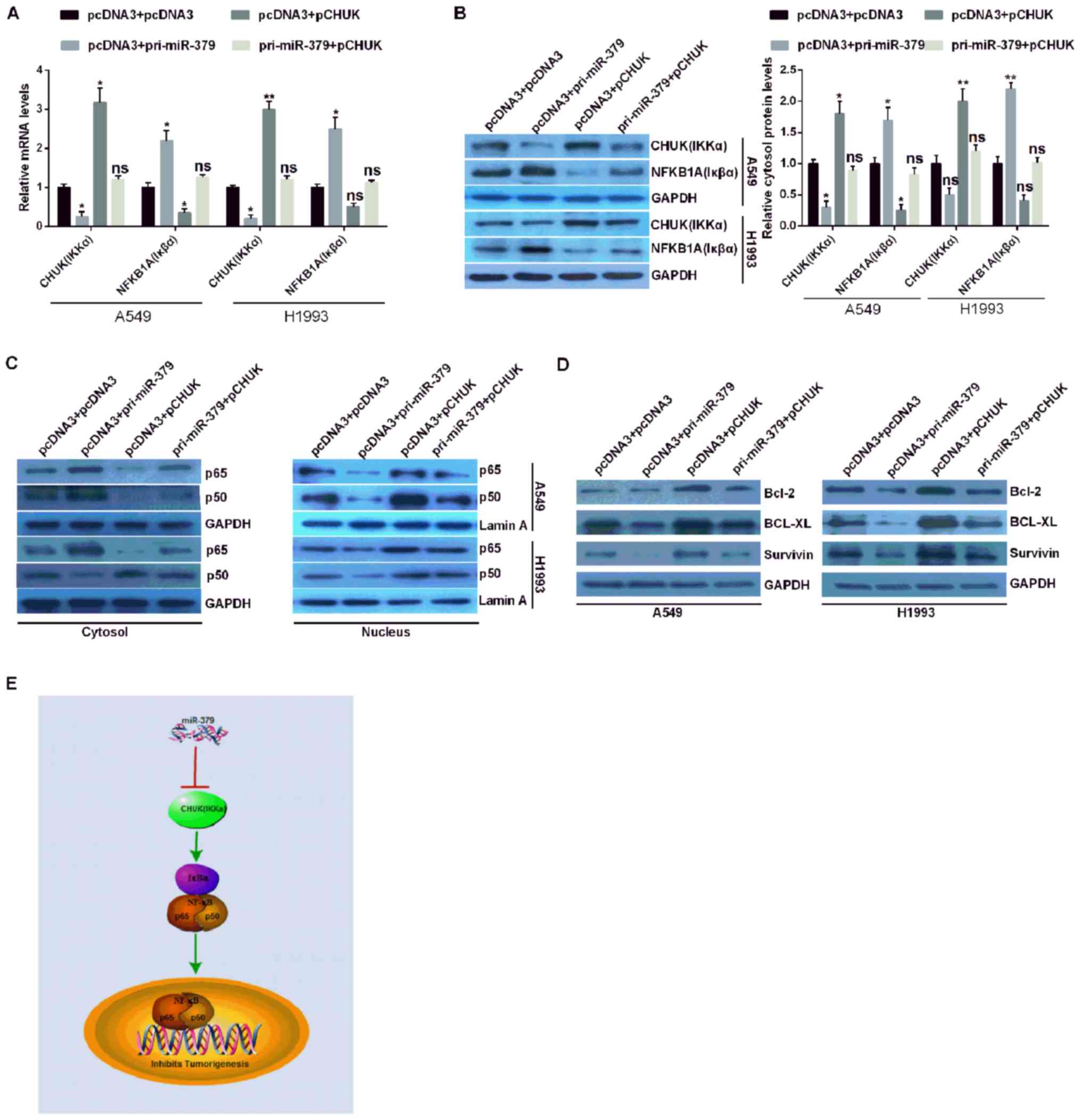
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cheng H, Shcherba M, Kandavelou K, Liang
Y, Liu H and Perez-Soler R: Emerging drugs for squamous cell lung
cancer. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 20:149–160. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Karlsen TA, De Souza GA, Degaard B,
Engebretsen L and Brinchmann JE: MicroRNA-140 inhibits inflammation
and stimulates chondrogenesis in a model of interleukin 1β-induced
osteoarthritis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 5:e3732016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yin J, Wang M, Jin C and Qi Q: MiR-101
sensitizes A549 NSCLC cell line to CDDP by activating caspase
3-dependent apoptosis. Oncol Lett. 7:461–465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zinner R, Visseren-Grul C, Spigel DR and
Obasaju C: Pemetrexed clinical studies in performance status 2
patients with non-small cell lung cancer (review). Int J Oncol.
48:13–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ameres SL and Zamore PD: Diversifying
microRNA sequence and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:475–488.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Thayanithy V, Sarver AL, Kartha RV, Li L,
Angstadt AY, Breen M, Steer CJ, Modiano JF and Subramanian S:
Perturbation of 14q32 miRNAs-cMYC gene network in osteosarcoma.
Bone. 50:171–181. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Makeyev EV and Maniatis T: Multilevel
regulation of gene expression by microRNAs. Science. 319:1789–1790.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu N, Zhang Q, Liu Q, Yang J and Zhang S:
A meta-analysis: microRNAs' prognostic function in patients with
nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer Med. 6:2098–2105. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang K, Han X, Zhang Z, Zheng L, Hu Z,
Yao Q, Cui H, Shu G, Si M, Li C, et al: The liver-enriched
lnc-LFAR1 promotes liver fibrosis by activating TGFβ and Notch
pathways. Nat Commun. 8:1442017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Legras A, Pécuchet N, Imbeaud S, Pallier
K, Didelot A, Roussel H, Gibault L, Fabre E, Le Pimpec-Barthes F,
Laurent-Puig P and Blons H: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
and microRNAs in lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). 9(pii): E1012017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang M, Meng B, Liu Y, Yu J and Chen Q:
MiR-124 inhibits growth and enhances radiation-induced apoptosis in
non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting STAT3. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 44:2017–2028. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu J, Bian T, Feng J, Qian L, Zhang J,
Jiang D, Zhang Q, Li X, Liu Y and Shi J: miR-335 inhibited cell
proliferation of lung cancer cells by target Tra2β. Cancer Sci.
109:289–296. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xue X, Fei X, Hou W, Zhang Y, Liu L and Hu
R: miR-342-3p suppresses cell proliferation and migration by
targeting AGR2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett.
412:170–178. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Le F, Zhang JY, Liu W, Huang XM and Luo
WZ: The levels of NF-κB p50 and NF-κB p65 play a role in thyroid
carcinoma malignancy in vivo. J Int Med Res. 46:4092–4099. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu XH, Liu ZL, Sun M, Liu J, Wang ZX and
De W: The long non-coding RNA HOTAIR indicates a poor prognosis and
promotes metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer.
13:4642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen X, Chen S, Hang W, Huang H and Ma H:
MiR-95 induces proliferation and chemo- or radioresistance through
directly targeting sorting nexin1 (SNX1) in non-small cell lung
cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 68:589–595. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Sun S, Liu Z, Zhang Y and
Jiao S: Overexpression of microRNA-221 is associated with poor
prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Tumour Biol.
37:10155–10160. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun S, Schiller JH, Spinola M and Minna
JD: New molecularly targeted therapies for lung cancer. J Clin
Invest. 117:2740–2750. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun C, Liu Z, Li S, Yang C, Xue R, Xi Y,
Wang L, Wang S, He Q, Huang J, et al: Down-regulation of c-Met and
Bcl2 by microRNA-206, activates apoptosis, and inhibits tumor cell
proliferation, migration and colony formation. Oncotarget.
6:25533–25574. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bier A, Giladi N, Kronfeld N, Lee HK,
Cazacu S, Finniss S, Xiang C, Poisson L, Decarvalho AC, Slavin S,
et al: MicroRNA-137 is downregulated in glioblastoma and inhibits
the stemness of glioma stem cells by targeting RTVP-1. Oncotarget.
4:665–676. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun C, Huang C, Li S, Yang C, Xi Y, Wang
L, Zhang F, Fu Y and Li D: Hsa-miR-326 targets CCND1 and inhibits
non-small cell lung cancer development. Oncotarget. 7:8341–8359.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun C, Li S, Zhang F, Xi Y, Wang L, Bi Y
and Li D: Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes non-small cell lung
cancer progression through regulation of miR-377-3p-E2F3 pathway.
Oncotarget. 7:51784–51814. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun CC, Li SJ, Zhang F, Zhang YD, Zuo ZY,
Xi YY, Wang L and Li DJ: The novel miR-9600 suppresses tumor
progression and promotes paclitaxel sensitivity in non-small-cell
lung cancer through altering STAT3 expression. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 5:e3872016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang C, Liu J, Wang X, Wu R, Lin M,
Laddha SV, Yang Q, Chan CS and Feng Z: MicroRNA-339-5p inhibits
colorectal tumorigenesis through regulation of the MDM2/p53
signaling. Oncotarget. 5:9106–9117. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xi Y, Wang L, Sun C, Yang C, Zhang F and
Li D: The novel miR-9501 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and
activates apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Med Oncol.
33:1242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xie X, Li YS, Xiao WF, Deng ZH, He HB, Liu
Q and Luo W: MicroRNA-379 inhibits the proliferation, migration and
invasion of human osteosarcoma cells by targetting EIF4G2. Biosci
Rep. 37(pii): BSR201605422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li K, Wang Y, Zhang A, Liu B and Jia L:
miR-379 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion, and migration of
vascular smooth muscle cells by targeting insulin-like factor-1.
Yonsei Med J. 58:234–240. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen JS, Li HS, Huang JQ, Dong SH, Huang
ZJ, Yi W, Zhan GF, Feng JT, Sun JC and Huang XH: MicroRNA-379-5p
inhibits tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting FAK/AKT
signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 375:73–83.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Majidinia M, Aghazadeh J,
Jahanban-Esfahlani R and Yousefi B: The roles of Wnt/β-catenin
pathway in tissue development and regenerative medicine. J Cell
Physiol. 233:5598–5612. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Perkins ND: Integrating cell-signalling
pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
8:49–62. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wright A, Reiley WW, Chang M, Jin W, Lee
AJ, Zhang M and Sun SC: Regulation of early wave of germ cell
apoptosis and spermatogenesis by deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD. Dev
Cell. 13:705–716. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mabuchi S, Ohmichi M, Nishio Y, Hayasaka
T, Kimura A, Ohta T, Saito M, Kawagoe J, Takahashi K,
Yada-Hashimoto N, et al: Inhibition of NFkappaB increases the
efficacy of cisplatin in in vitro and in vivo ovarian cancer
models. J Biol Chem. 279:23477–23485. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Ahmed F, Ali S, Philip PA, Kucuk O
and Sarkar FH: Inactivation of nuclear factor KB by soy isoflavone
genistein contributes to increased apoptosis induced by
chemotherapeutic agents in human cancer cells. Cancer Res.
65:6934–6942. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Naidu S, Shi L, Magee P, Middleton JD,
Laganá A, Sahoo S, Leong HS, Galvin M, Frese K, Dive C, et al:
PDGFR-modulated miR-23b cluster and miR-125a-5p suppress lung
tumorigenesis by targeting multiple components of KRAS and NF-κB
pathways. Sci Rep. 7:154412017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|