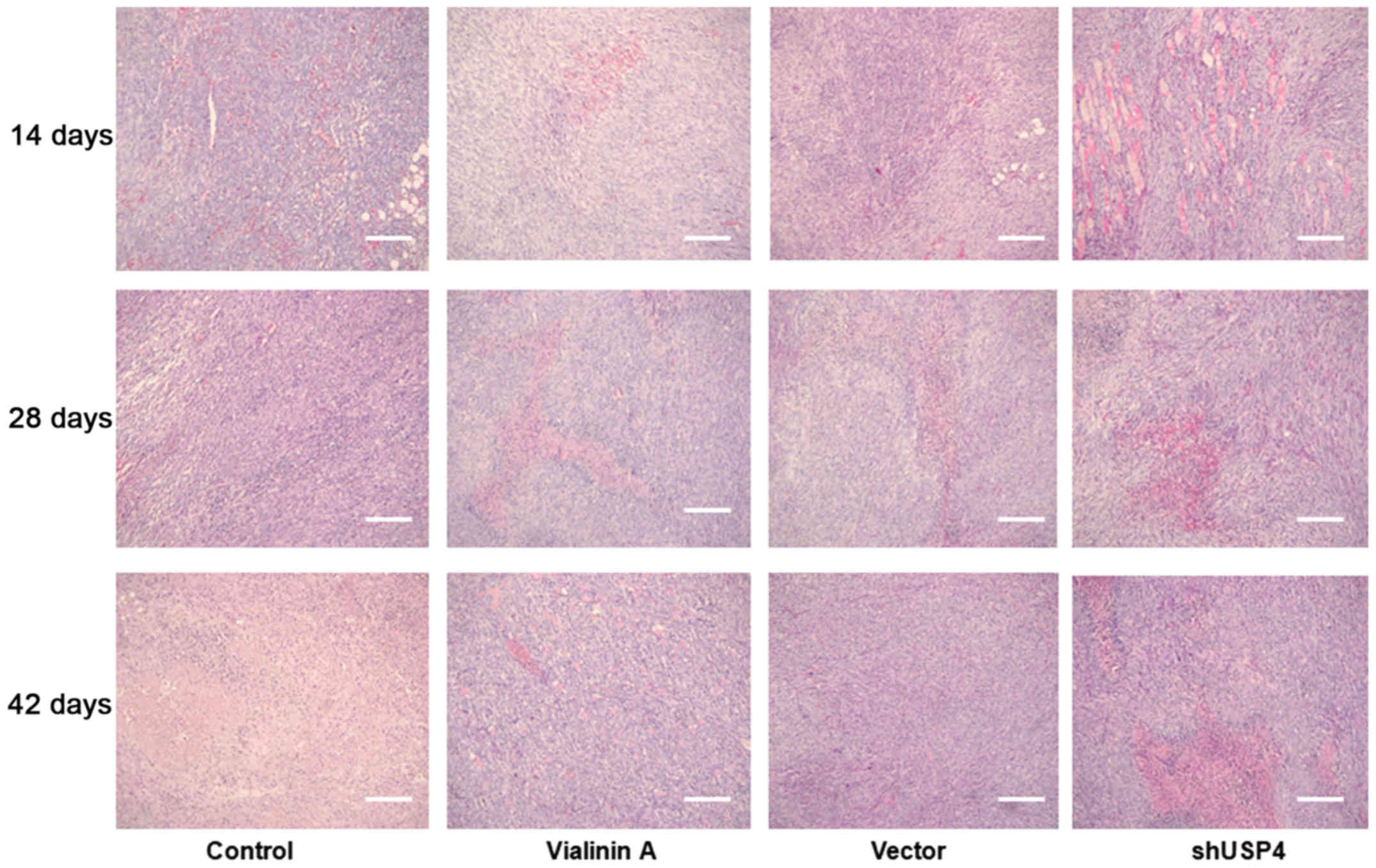
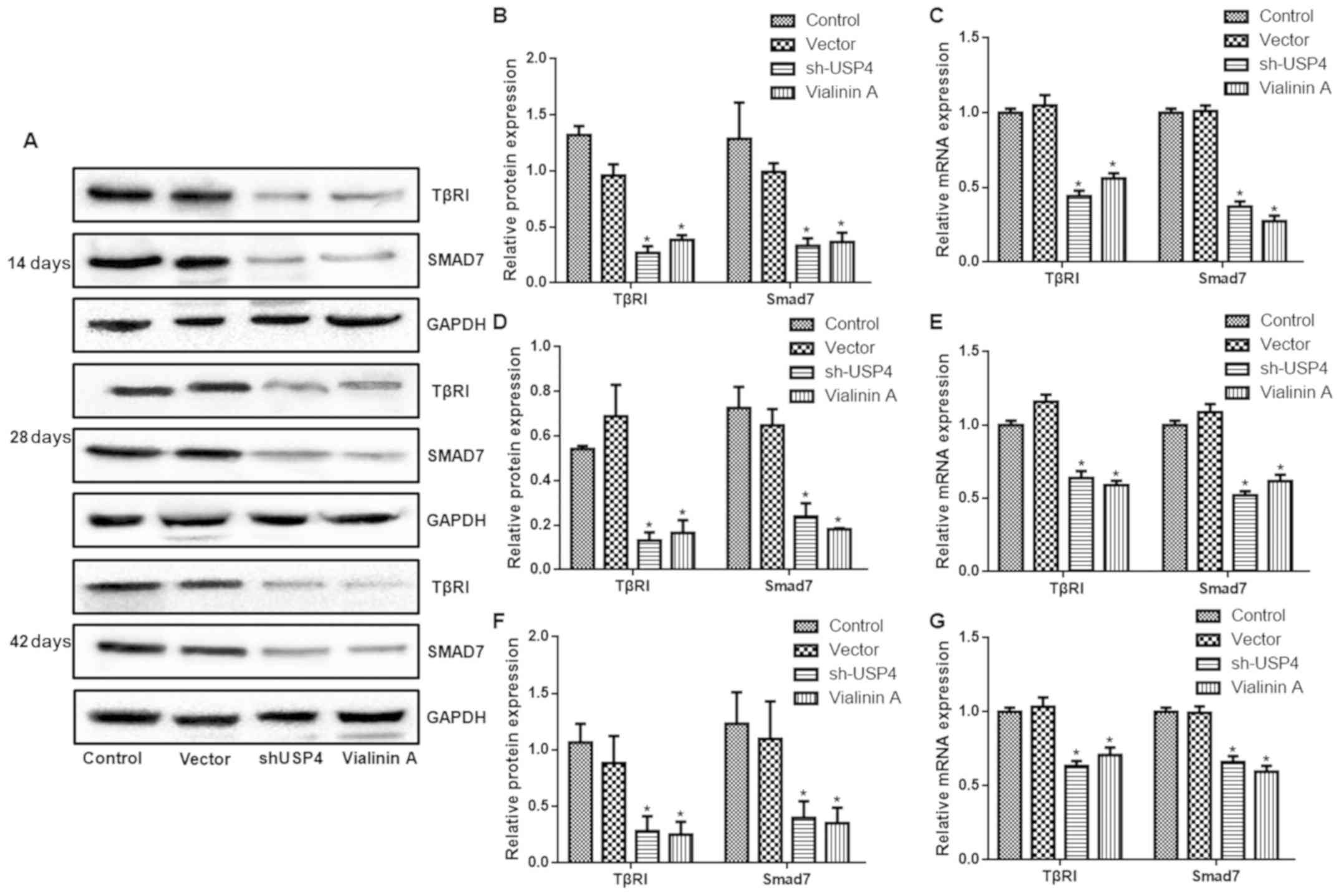
|
1
|
Song H, Tan J, Fu Q, Huang L and Ao M:
Comparative efficacy of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide
injection during early and static stage of pathological scarring. J
Cosmet Dermatol. Jun 22–2018.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
2
|
Liao N, Lu F, Zhao W, Zeng WS, Li YT, Wang
SJ and Gao JH: Relationship between gene p53 codon 72 polymorphism
and pathological scar formation after caesarean section. Zhonghua
Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 29:206–210. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wu WY, Zhang LT, Zheng ZF, Zhu SZ and Wang
ZY: Expression and significance of mRNA and protein of eIF4E,
p-eIF4E and MCl-1 in pathological scar. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke
Za Zhi. 28:360–365. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
DeSalle LM, Latres E, Lin D, Graner E,
Montagnoli A, Baker RT, Pagano M and Loda M: The de-ubiquitinating
enzyme Unp interacts with the retinoblastoma protein. Oncogene.
20:5538–5542. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wada K and Kamitani T: UnpEL/Usp4 is
ubiquitinated by Ro52 and deubiquitinated by itself. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 342:253–258. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yan X, Liao H, Cheng M, Shi X, Lin X, Feng
XH and Chen YG: Smad7 protein interacts with receptor-regulated
Smads (R-Smads) to inhibit transforming growth factor-β
(TGF-β)/Smad signaling. J Biol Chem. 291:382–392. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dong X, Zhao B, Iacob RE, Zhu J, Koksal
AC, Lu C, Engen JR and Springer TA: Force interacts with
macromolecular structure in activation of TGF-β. Nature. 542:55–59.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun Q, Guo S, Wang CC, Sun X, Wang D, Xu
N, Jin SF and Li KZ: Cross-talk between TGF-β/Smad pathway and
Wnt/β-catenin pathway in pathological scar formation. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:7631–7639. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Beanes SR, Dang C, Soo C and Ting K: Skin
repair and scar formation: The central role of TGF-beta. Exp Rev
Mol Med. 5:1–22. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Penn JW, Grobbelaar AO and Rolfe KJ: The
role of the TGF-β family in wound healing, burns and scarring: A
review. Int J Burns Trauma. 2:18–28. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang L, Zhou F, Drabsch Y, Gao R,
Snaar-Jagalska BE, Mickanin C, Huang H, Sheppard KA, Porter JA, Lu
CX and ten Dijke P: USP4 is regulated by AKT phosphorylation and
directly deubiquitylates TGF-β type I receptor. Nat Cell Biol.
14:717–726. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li W, Tao S, Wu Q, Wu T, Tao R and Fan J:
Glutamine reduces myocardial cell apoptosis in a rat model of
sepsis by promoting expression of heat shock protein 90. J Surg
Res. 220:247–254. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu G, Li J, He L, Wang X and Hong X:
MPTP-induced changes in hippocampal synaptic plasticity and memory
are prevented by memantine through the BDNF-TrkB pathway. Br J
Pharmacol. 172:2354–2368. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song Z, Chen H, Xu W, Wu S and Zhu G:
Basolateral amygdala calpain is required for extinction of
contextual fear-memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 155:180–188. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xiong G, Huang Z, Jiang H, Pan Z, Xie J
and Wang S: Inhibition of microRNA-21 decreases the invasiveness of
fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis via TGFβ/Smads
signaling pathway. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 19:787–793.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu X, Xu C, Saud SM, Lu X, Liu L, Fang L,
Zhang X, Hu J and Li W: Effect of kuijie granule on the expression
of TGF-β/Smads signaling pathway in patients with ulcerative
colitis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016:26018302016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao B, Schlesiger C, Masucci MG and
Lindsten K: The ubiquitin specific protease 4 (USP4) is a new
player in the Wnt signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 13:1886–1895.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Milojevic T, Reiterer V, Stefan E, Korkhov
VM, Dorostkar MM, Ducza E, Ogris E, Boehm S, Freissmuth M and
Nanoff C: The ubiquitin-specific protease Usp4 regulates the cell
surface level of the A2A receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 69:1083–1094.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wijnhoven P, Konietzny R, Blackford AN,
Travers J, Kessler BM, Nishi R and Jackson SP: USP4
auto-deubiquitylation promotes homologous recombination. Mol Cell.
60:362–373. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang X, Berger FG, Yang J and Lu X: USP4
inhibits p53 through deubiquitinating and stabilizing ARF-BP1. EMBO
J. 30:2177–2189. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fan YH, Yu Y, Mao RF, Tan XJ, Xu GF, Zhang
H, Lu XB, Fu SB and Yang J: USP4 targets TAK1 to downregulate
TNFα-induced NF-κB activation. Cell Death Differ. 18:1547–1560.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Y, Zhang L, Lei R, Shen Y, Shen H, Wu
Z and Xu J: Effects of blocking two sites of transforming growth
factor-β/Smads signaling on the formation of scar-related proteins
in human skin fibroblasts. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 31:372–377.
2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nong Q, Li S, Wu Y and Liu D: LncRNA
COL1A2-AS1 inhibits the scar fibroblasts proliferation via
regulating miR-21/Smad7 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
495:319–324. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xia W, Phan TT, Lim IJ, Longaker MT and
Yang GP: Complex epithelial-mesenchymal interactions modulate
transforming growth factor-beta expression in keloid-derived cells.
Wound Repair Regen. 12:546–556. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Emami A, Halim AS, Salahshourifar I,
Yussof SJ, Khoo TL and Kannan TP: Association of TGFβ1 and SMAD4
variants in the etiology of keloid scar in the Malay population.
Arch Dermatol Res. 304:541–547. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ward SV, Cadby G, Heyworth JS, Fear MW,
Wallace HJ, Cole JM, Wood FM and Palmer LJ: Association of TGFβ1
and clinical factors with scar outcome following melanoma excision.
Arch Dermatol Res. 304:343–351. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chin GS, Liu W, Peled Z, Lee TY,
Steinbrech DS, Hsu M and Longaker MT: Differential expression of
transforming growth factor-beta receptors I and II and activation
of Smad 3 in keloid fibroblasts. Plast Reconstr Surg. 108:423–429.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bock O, Yu H, Zitron S, Bayat A, Ferguson
MW and Mrowietz U: Studies of transforming growth factors beta 1–3
and their receptors I and II in fibroblast of keloids and
hypertrophic scars. Acta Derm Venereol. 85:216–220. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Goldberg HJ, Huszár T, Mózes MM, Rosivall
L and Mucsi I: Overexpression of the type II transforming growth
factor-beta receptor inhibits fibroblasts proliferation and
activates extracellular signal regulated kinase and c-Jun
N-terminal kinase. Cell Biol Int. 26:165–174. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bran GM, Goessler UR, Schardt C, Hormann
K, Riedel F and Sadick H: Effect of the abrogation of TGF-beta1 by
antisense oligonucleotides on the expression of TGF-beta-isoforms
and their receptors I and II in isolated fibroblasts from keloid
scars. Int J Mol Med. 25:915–921. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li SC, Ma LN, Chen J and Li YK: Effect of
allicin on myocardial fibrosis after myocardial infarction in rats
and its relationship with TGFβ/Smads signal transduction. Zhongguo
Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 41:2517–2521. 2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hu ZC, Shi F, Liu P, Zhang J, Guo D, Cao
XL, Chen CF, Qu SQ, Zhu JY and Tang B: TIEG1 Represses
Smad7-mediated activation of TGF-β1/Smad signaling in keloid
pathogenesis. J Invest Dermatol. 137:1051–1059. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
D'Arpino MC, Fuchs AG, Sánchez SS and
Honoré SM: Extracellular matrix remodeling and TGF-β1/Smad
signaling in diabetic colon mucosa. Cell Biol Int. 42:443–456.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Popovic D, Vucic D and Dikic I:
Ubiquitination in disease pathogenesis and treatment. Nat Med.
20:1242–1253. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wu Y, Kang J, Zhang L, Liang Z, Tang X,
Yan Y, Qian H, Zhang X, Xu W and Mao F: Ubiquitination regulation
of inflammatory responses through NF-κB pathway. Am J Transl Res.
10:881–891. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cheng YF, Zhu GQ, Wang M, Cheng H, Zhou A,
Wang N, Fang N, Wang XC, Xiao XQ, Chen ZW and Li QL: Involvement of
ubiquitin proteasome system in protective mechanisms of Puerarin to
MPP(+)-elicited apoptosis. Neurosci Res. 63:52–58. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|