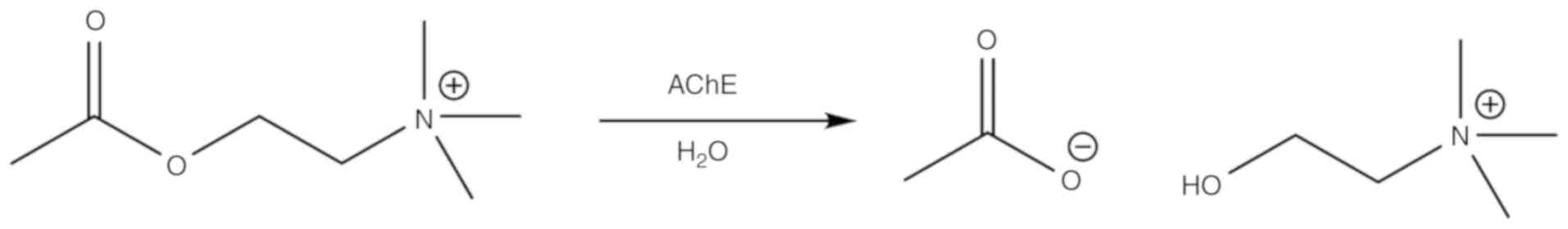
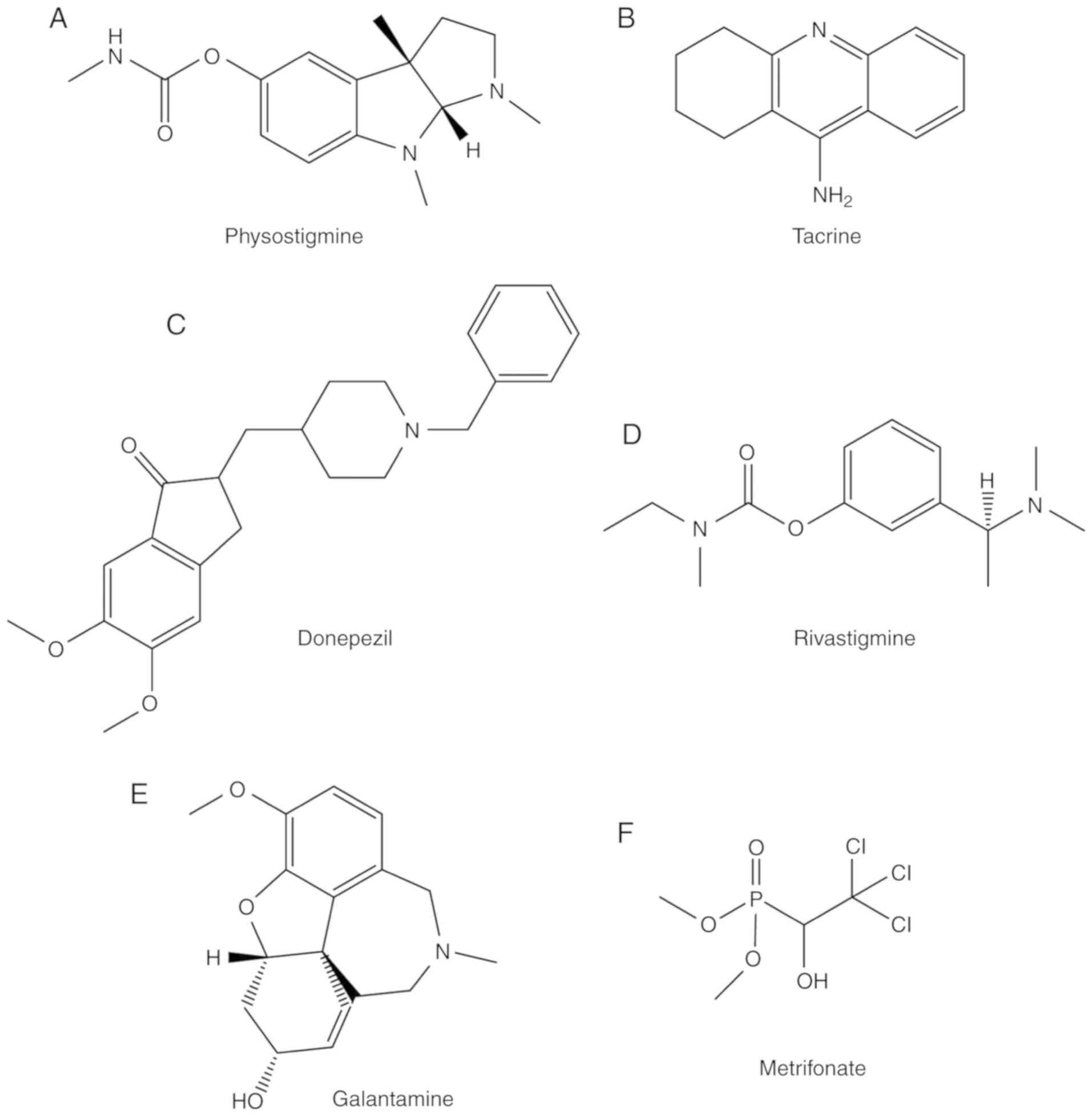
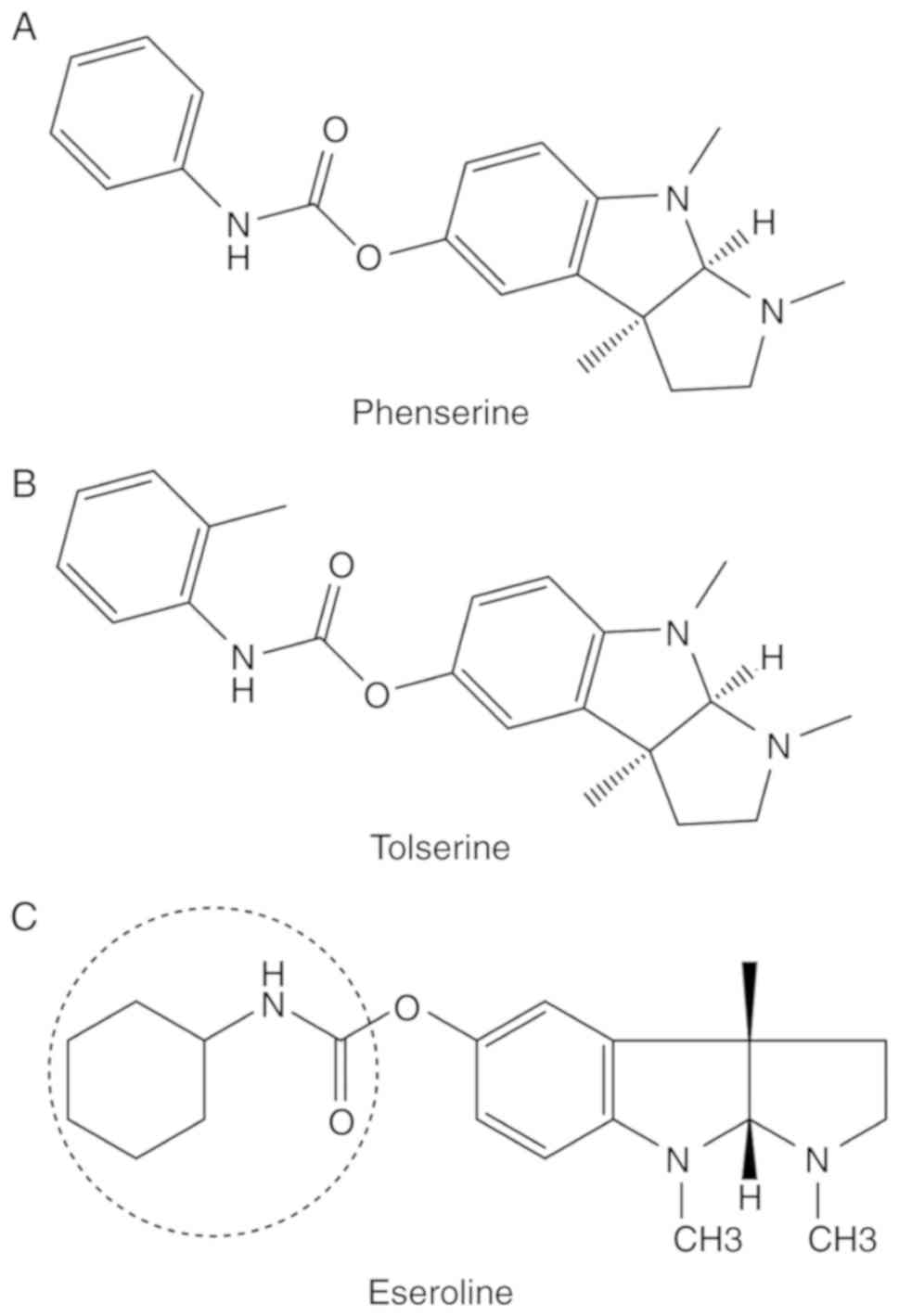
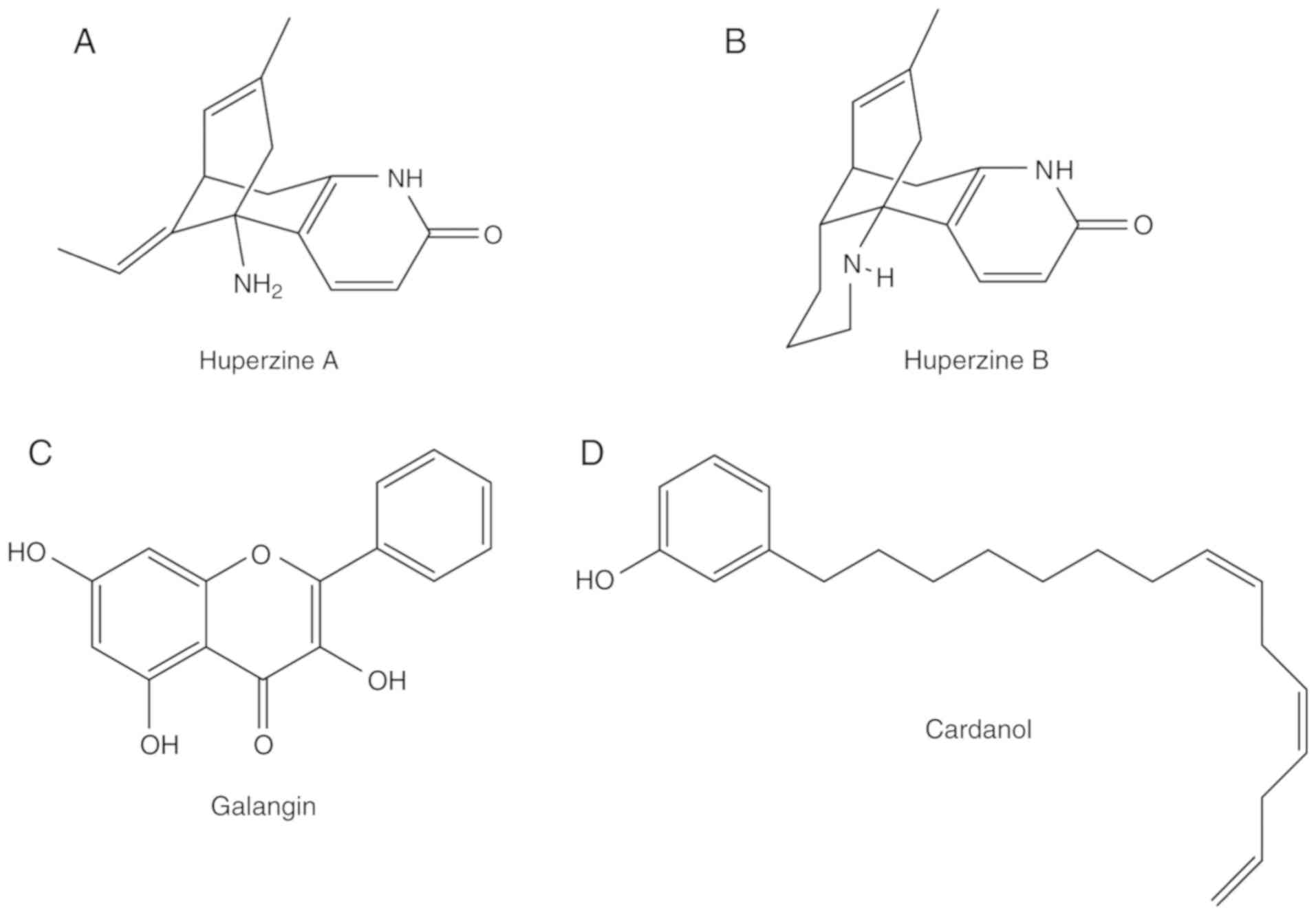
|
1
|
Khachaturian ZS: Diagnosis of alzheimer's
disease. Arch Neurol. 42:1097–1105. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kuhn D: New horizons. Contemporary
longterm care. 26:25–26. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cheng ST: Cognitive reserve and the
prevention of dementia: The role of physical and cognitive
activities. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 18:852016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Silman I and Sussman JL:
Acetylcholinesterase: Classical and non-classical functions and
pharmacology. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 5:293–302. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartus RT, Dean RL III, Beer B and Lippa
AS: The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction.
Science. 217:408–417. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tabet N: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
for alzheimer's disease: Anti-inflammatories in acetylcholine
clothing. Age Ageing. 35:336–338. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Karran E, Mercken M and De Strooper B: The
amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer's disease: An appraisal
for the development of therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
10:698–712. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Luo W, Li YP, He Y, Huang SL, Tan JH, Ou
TM, Li D, Gu LQ and Huang ZS: Design, synthesis and evaluation of
novel tacrine-multialkoxybenzene hybrids as dual inhibitors for
cholinesterases and amyloid beta aggregation. Bioorg Med Chem.
19:763–770. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tang H, Zhao LZ, Zhao HT, Huang SL, Zhong
SM, Qin JK, Chen ZF, Huang ZS and Liang H: Hybrids of
oxoisoaporphine-tacrine congeners: Novel acetylcholinesterase and
acetylcholinesterase-induced β-amyloid aggregation inhibitors. Eur
J Med Chem. 46:4970–4979. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Camps P, Formosa X, Galdeano C,
Muñoz-Torrero D, Ramírez L, Gómez E, Isambert N, Lavilla R, Badia
A, Clos MV, et al: Pyrano[3,2-c]quinoline-6-chlorotacrine hybrids
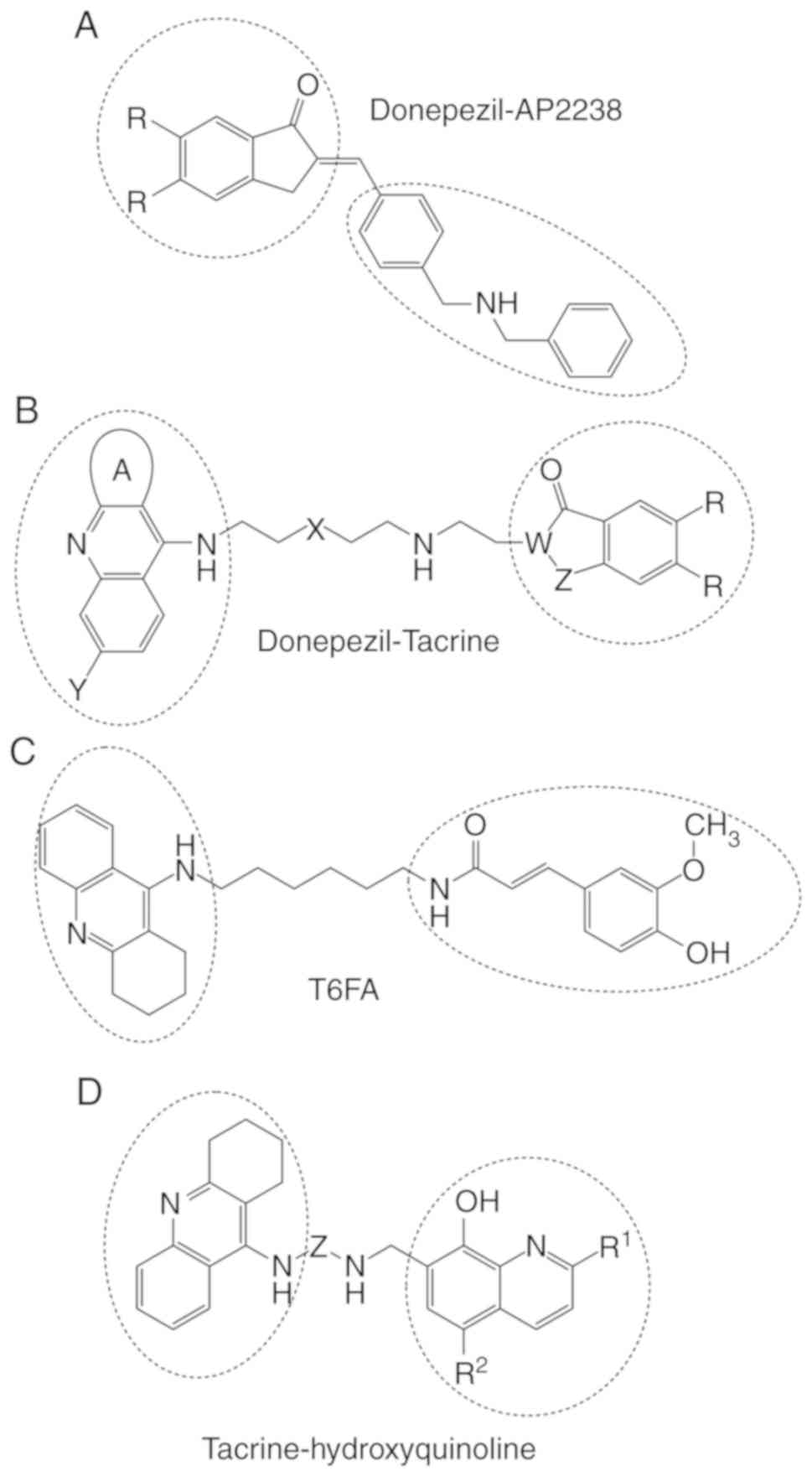
as a novel family of acetylcholinesterase-and beta-amyloid-directed
anti-Alzheimer compounds. J Med Chem. 52:5365–5379. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Camps P, Formosa X, Galdeano C, Gómez T,
Muñoz-Torrero D, Scarpellini M, Viayna E, Badia A, Clos MV, Camins
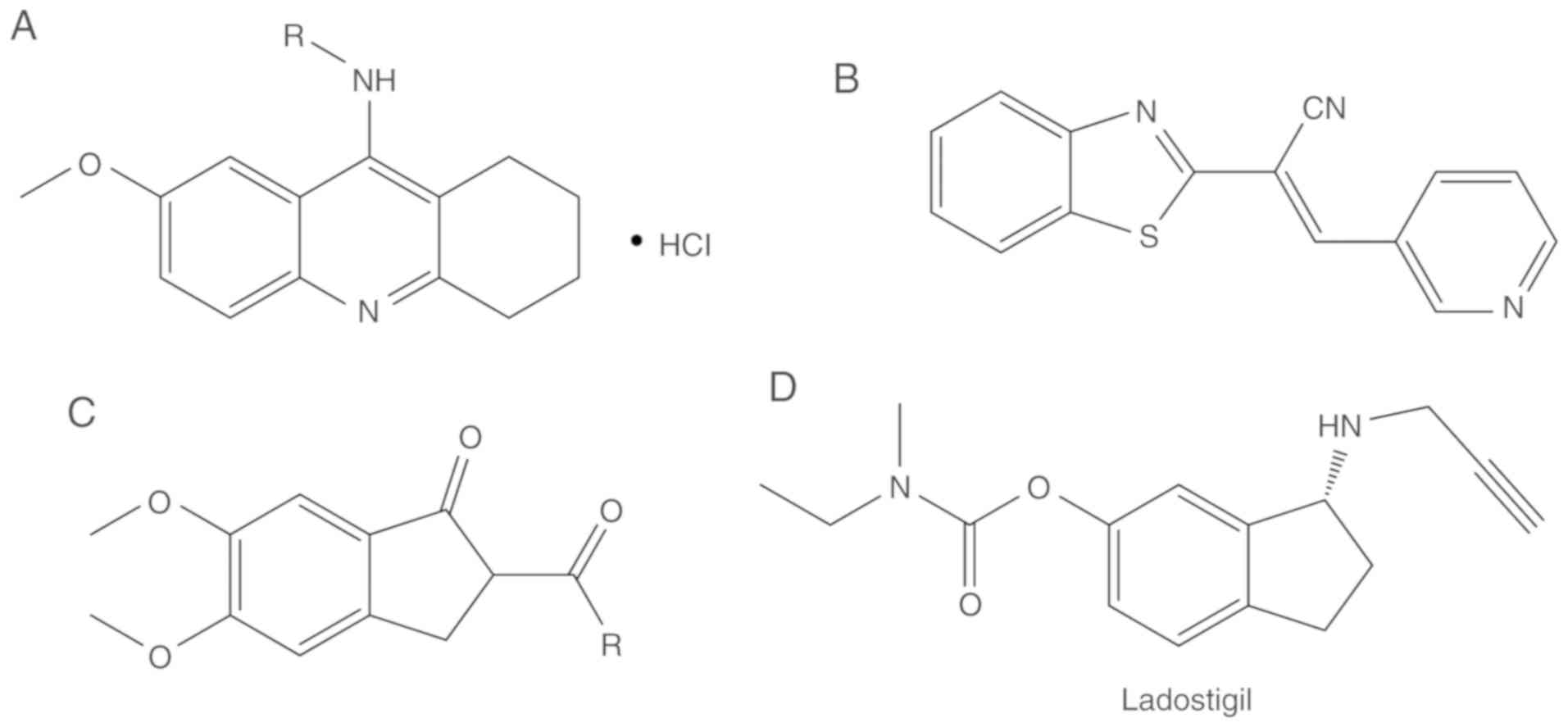
A, et al: Novel donepezil-based inhibitors of acetyl- and
butyrylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase-induced beta-amyloid
aggregation. J Med Chem. 51:3588–3598. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gupta S, Pandey A, Tyagi A and Mohan GA:
Computational analysis of Alzheimer's disease drug targets. Curr
Res Inf Pharm Sci. 11:1–10. 2010.
|
|
13
|
Perl DP: Neuropathology of Alzheimer's
disease. Mt Sinai J Med. 77:32–42. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Takashima A: Tau aggregation is a
therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer Res.
7:665–669. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Anand K and Sabbagh M: Early
investigational drugs targeting tau protein for the treatment of
Alzheimer's disease. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 24:1355–1360.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Iqbal K, Gong CX and Liu F:
Microtubule-associated protein tau as a therapeutic target in
Alzheimer's disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 18:307–318. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Noble W, Hanger DP, Miller CC and
Lovestone S: The importance of tau phosphorylation for
neurodegenerative diseases. Front Neurol. 4:832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Panza F, Solfrizzi V, Seripa D, Imbimbo
BP, Lozupone M, Santamato A, Zecca C, Barulli MR, Bellomo A,
Pilotto A, et al: Tau-centric targets and drugs in clinical
development for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Biomed Res
Int. 2016:32459352016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Congdon EE and Sigurdsson EM:
Tau-targeting therapies for Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol.
14:399–415. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Russo P, Frustaci A, Del Bufalo A, Fini M
and Cesario A: Multitarget drugs of plants origin acting on
Alzheimer's disease. Curr Med Chem. 20:1686–1693. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Azam F, Amer AM, Abulifa AR and Elzwawi
MM: Ginger components as new leads for the design and development
of novel multi-targeted anti-alzheimer's drugs: A computational
investigation. Drug Des Devel Ther. 8:2045–2059. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Silman I and Sussman JL:
Acetylcholinesterase: How is structure related to function? Chem
Biol Interact. 175:3–10. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lotta B: Targeting acetylcholinesterase:
Identification of chemical leads by high throughput screening,
structure determination and molecular modeling. PLoS One.
6:e260392011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tripathi A: Acetylcholinsterase: A
versatile enzyme of nervous system. Ann Neurosci. 15:106–111. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
López-Arrieta JM and Schneider L:
Metrifonate for alzheimer's disease. Cochrane Database Sys Rev.
2:1–40. 2006.
|
|
26
|
Tougu V: Acetylcholinesterase: Mechanism
of catalysis and inhibition. Curr Med Chem CNS Agents. 1:155–170.
2001.
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Kua J and McCammon JA: Role of
the catalytic triad and oxyanion hole in acetylcholinesterase
catalysis: An ab initio QM/MM study. J Am Chem Soc.
124:10572–10577. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Weinstock M: Selectivity of cholinesterase
inhibition. CNS Drugs. 12:307–323. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ogura H, Kosasa T, Kuriya Y and Yamanishi
Y: Comparison of inhibitory activities of donepezil and other
cholinesterase inhibitors on acetylcholinesterase and
butyrylcholinesterase in vitro. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol.
22:609–613. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rogers SL and Friedhoff LT: The efficacy
and safety of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease:
Results of a US multicentre randomised double blind
placebo-controlled trial The donepezil study group. Dementia.
7:293–303. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Olin J and Schneider L: Galantamine for
Alzheimer's disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
4:CD0017472001.
|
|
32
|
Bar-On P, Millard CB, Harel M, Dvir H, Enz
A, Sussman JL and Silman I: Kinetic and structural studies on the
interaction of cholinesterases with the anti-Alzheimer drug
rivastigmine. Biochem. 41:3555–3564. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Holmstedt B: Plants in the Development of
Modern Medicine. Swain T: Cambridge University Press; Cambridge,
MA: p303 and references cited herein. 1972, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Thal LJ, Fuld PA, Masur DM and Sharpless
NS: Oral physostigmine and lecithin improve memory in alzheimer
disease. Ann Neurol. 13:491–496. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Coelho F and Birks J: Physostigmine for
Alzheimer's disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
2:CD0014992001.
|
|
36
|
Karis JH, Nastuk WL and Katz RL: The
action of tacrine on neuromuscular transmission: A comparison with
hexafluorenium. Brit J Anaesth. 38:762–774. 1966. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Harel M, Schalk I, Ehret-Sabatier L, Bouet
F, Goeldner M, Hirth C, Axelsen PH, Silman I and Sussman JL:
Quaternary ligand binding to aromatic residues in the active-site
gorge of acetylcholinesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
90:9031–9035. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fernández-Bachiller MI, Pérez C,
González-Muñoz GC, Conde S, López MG, Villarrova M, García AG and
Rodríguez-Franco MI: Novel tacrine-8-hydroxyquinoline hybrids as
multifunctional agents for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease,
with neuroprotective, cholinergic, antioxidant and coppercomplexing
properties. J Med Chem. 53:4927–4937. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Farlow M, Gracon SI, Hershey LA, Lewis KW,
Sadowsky CH and Dolan-Ureno J: A controlled trial of tacrine in
Alzheimer's disease. The tacrine study group. JAMA. 268:2523–2529.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Watkins PB, Zimmerman HJ, Knapp MJ, Gracon
SI and Lewis KW: Hepatotoxic effects of tacrine administration in
patients with Alzheimer's disease. JAMA. 271:992–998. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rogers SL, Farlow MR, Doody RS, Mohs R and
Friedhoff LT: A 24 week double blind placebo controlled trial of
donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Donepezil study
group. Neurology. 50:136–145. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jacobson SA and Sabbagh MN: Donepezil:
Potential neuroprotective and disease-modifying effects. Expert
Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 4:1363–1369. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kryger G, Silman I and Sussman JL:
Structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with E2020 (Aricept):
Implications for the design of new anti-Alzheimer drugs. Struct.
7:297–307. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Inglis F: The tolerability and safety of
cholinesterase inhibitors in the treatment of dementia. Int J Clin
Pract Suppl. 127:45–63. 2002.
|
|
45
|
Onor ML, Trevisiol M and Aguglia E:
Rivastigmine in the treatment of alzheimer's disease: An update.
Clin Interv Aging. 2:17–32. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Corey-Bloom J, Anand R and Veach J: A
randomized trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of ENA 713
(rivastigmine tartrate), a new acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, in
patients with mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's disease. Int J
Geriatr Psychopharmacol. 1:55–65. 1998.
|
|
47
|
Fraser MD, Davies JR and Chang X: New gold
in them thar hills: Testing a novel supply route for plant-derived
galanthamine. J Alzheimers Dis. 55:1321–1325. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
de Souza FM, Busquet N, Blatner M, Maclean
KN and Restrepo D: Galantamine improves olfactory learning in the
Ts65Dn mouse model of down syndrome. Sci Rep. 1:1372011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Pernov KG: Nivalin and its curative effect
on disease of the nervous system. Psychiatr Neurol Med Psychol
(Leipz). 13:416–420. 1961.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tariot PN, Solomon PR, Morris JC, Kershaw
P, Lilienfeld S and Ding C: A 5-month, randomized,
placebocontrolled trial of galantamine in AD. The Galantamine
USA-10 Study Group. Neurology. 54:2269–2276. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mehta M, Adem A and Sabbagh M: New
acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease. Int J
Alzheimers Dis. 2012:7289832012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nordgren I, Bengtsson E, Holmstedt B and
Pettersson BM: Levels of metrifonate and dichlorvos in plasma and
erythrocytes during treatment of schistosomiasis with Bilarcil.
Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh). 49 (Suppl 5):S79–S86. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Cummings JL, Cyrus PA, Bieber F, Mas J,
Orazem J and Gulanski B: Metrifonate treatment of the cognitive
deficits of Alzheimer's disease. The metrifonate study group.
Neurology. 50:1214–1221. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Klein J: Phenserine. Exp Opin Investig
Drugs. 16:1087–1097. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Greig NH, De Micheli E, Holloway HW, Yu
QS, Utsuki T, Perry TA, Brossi A, Ingram DK, Deutsch J, Lahiri DK
and Soncrant TT: The experimental Alzheimer drug phenserine:
Preclinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Acta Neurol
Scand Suppl. 176:74–84. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Thatte U: Phenserine Axonyx. Curr Opin
Investig Drugs. 6:729–739. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Winblad B, Giacobini E, Frölich L,
Friedhoff LT, Bruinsma G, Becker RE and Greig NH: Phenserine
efficacy in Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimer's Dis. 22:1201–1208.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Tweedie D, Fukui K, Li Y, Yu QS, Barak S,
Tamargo IA, Rubovitch V, Holloway HW, Lehrmann E, Wood WH III, et
al: Cognitive impairments induced by concussive mild traumatic
brain injury in mouse are ameliorated by treatment with phenserine
via multiple non-cholinergic and cholinergic mechanisms. PLoS One.
11:e01564932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Becker RE, Greig NH, Lahiri DK, Bledsoe J,
Majercik S, Ballard C, Aarsland D, Schneider LS, Flanagan D,
Govindarajan R, et al: (−)-Phenserine and inhibiting apoptosis: In
pursuit of a novel intervention for Alzheimer's disease. Curr
Alzheimer Res. 15:883–891. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Luo W, Yu QS, Zhan M, Parrish D, Deschamps
JR, Kulkarni SS, Holloway HW, Alley GM, Lahiri DK, Brossi A and
Greig NH: Novel anticholinesterases based on the molecular
skeletons of furobenzofuran and methanobenzodioxepine. J Med Chem.
48:986–994. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yu QS, Holloway HW, Luo W, Lahiri DK,
Brossi A and Greig NH: Long-acting anticholinesterases for
myasthenia gravis: Synthesis and activities of quaternary
phenylcarbamates of neostigmine, pyridostigmine and physostigmine.
Bioorg Med Chem. 18:4687–4693. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kamal MA, Greig NH, Alhomida AS and
Al-Jafari AA: Kinetics of human acetylcholinesterase inhibition by
the novel experimental Alzheimer therapeutic agent, tolserine.
Biochem Pharmacol. 60:561–570. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Fürst S, Friedmann T, Bartolini A,
Bartolini R, Aiello-Malmberg P, Galli A, Somogy GT and Knoll J:
Direct evidence that eseroline possesses morphine-like effects. Eur
J Pharmacol. 83:233–241. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Galli A, Renzi G, Grazzini E, Bartolini R,
Aiello-Malmberg P and Bartolini A: Reversible inhibition of
acetylcholinesterase by eseroline, an opioid agonist structurally
related to physostigmine (eserine) and morphine. Biochemical
Pharmac. 31:1233–1238. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Zhan ZJ, Bian HL, Wang JW and Shan WG:
Synthesis of physostigmine analogues and evaluation of their
anticholinesterase activities. Bioorg Med Chem Letts. 20:1532–1534.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Wang Y, Zeng QG, Zhang ZB, Yan RM, Wang LY
and Zhu D: Isolation and characterization of endophytic
huperzineA-producing fungi from Huperzia serrata. J Ind Microbiol
Biotechnol. 38:1267–1278. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Camps P, El Achab R, Morral J,
Muñoz-Torrero D, Badia A, Baños JE, Vivas NM, Barril X, Orozco M
and Luque FJ: New tacrine-huperzine A hybrids (huprines): Highly
potent tight-binding acetylcholinesterase inhibitors of interest
for the treatment of alzheimer's disease. J Med Chem. 43:4657–4666.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Dvir H, Jiang HL, Wong DM, Harel M,
Chetrit M, He XC, Jin GY, Yu GL, Tang XC, Silman I, et al: X-ray
structures of Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase complexed
with (+)-huperzine A and (−)-huperzine B: Structural evidence for
an active site rearrangement. Biochem. 41:10810–10818. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Li J, Wu HM, Zhou RL, Liu GJ and Dong BR:
Huperzine A for alzheimer's disease. Cochrane Database of Syst Rev.
CD0055922008.
|
|
70
|
Guo AJ, Xie HQ, Choi RC, Zheng KY, Bi CW,
Xu SL, Dong TTX and Tsim KW: Galangin, a flavonol derived from
Rhizoma Alpiniae officinarum, inhibits acetylcholinesterase
activity in vitro. Chem Biol Interact. 187:246–248. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
de Paula AA, Martins JB, dos Santos ML,
Nascente Lde C, Romeiro LA, Areas TF, Vieira KS, Gambôa NF, Castro
NG and Gargano R: New potential AChE inhibitor candidates. Eur J
Med Chem. 44:3754–3759. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Taiwo EA: Cashew nut shell oil - A
renewable and reliable petrochemical feedstock. Advances in
Petrochemicals. Patel V: 2015, View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Piazzi L, Rampa A, Bisi A, Gobbi S,
Belluti F, Cavalli A, Bartolini M, Andrisano V, Valenti P and
Recanatini M: 3-(4-[[Benzyl
(methyl)amino]methyl]phenyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-2H-2-chromenone (AP2238)
inhibits both acetylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase-induced
beta-amyloid aggregation: A dual function lead for Alzheimer's
disease therapy. J Med Chem. 46:2279–2282. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Rizzo S, Bartolini M, Ceccarini L, Piazzi
L, Gobbi S, Cavalli A, Recanatini M, Andrisano V and Rampa A:
Targeting Alzheimer's disease: Novel indanone hybrids bearing a
pharmacophoric fragment of AP2238. Bioorg Med Chem. 18:1749–1760.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Pi R, Xuexuan MX, Chao X, Cheng Z, Liu M,
Duan X, Ye M, Chen X, Mei Z, Liu P, et al: Tacrine-6-ferulic acid,
a novel multifunctional dimer, inhibits amyloid-β-mediated
Alzheimer's disease-associated pathogenesis in vitro and in vivo.
PLoS One. 7:e319212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Tipton KF, Boyce S, O'Sullivan J, Davey GP
and Healy J: Monoamine oxidases: Certainties and uncertainties.
Curr Med Chem. 11:1965–1982. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Edmondson DE, Mattevi A, Binda C, Li M and
Hubálek F: Structure and mechanism of monoamine oxidase. Curr Med
Chem. 11:1983–1993. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Pachón-Angona I, Refouvelet B, Andrýs R,
Martin H, Luzet V, Iriepa I, Moraleda I, Diez-Iriepa D, Oset-Gasque
MJ, Marco-Contelles J, et al: Donepezil + chromone + melatonin
hybrids as promising agents for Alzheimer's disease therapy. J
Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 34:479–489. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chufarova N, Czarnecka K, Skibiński R,
Cuchra M, Majsterek I and Szymański P: New tacrine-acridine hybrids
as promising multifunctional drugs for potential treatment of
Alzheimer's disease. Arch Pharm Chem Life Sci. 351:e18000502018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Lopes JPB, Silva L, da Costa Franarin G,
Antonio Ceschi M, Seibert Lüdtke D, Ferreira Dantas R, de Salles
CMC, Paes Silva-Jr F, Roberto Senger M, Alvim Guedes I and Emmanuel
Dardenne L: Design synthesis, cholinesterase inhibition and
molecular modelling study of novel tacrine hybrids with
carbohydrate derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem. 26:5566–5577. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhu J, Yang H, Chen Y, Lin H, Li Q, Mo J,
Bian Y, Pei Y and Sun H: Synthesis, pharmacology and molecular
docking on multifunctional tacrine-ferulic acid hybrids as
cholinesterase inhibitors against Alzheimer's disease. J Enzym
Inhib Med Chem. 33:496–506. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Korabecny J, Musilek K, Holas O, Binder J,
Zemek F, Marek J, Pohanka M, Opletalova V, Dohnal V and Kuca K:
Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of N-alkyl-7-methoxytacrine
hydrochlorides as potential cholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer
disease. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 20:6093–6105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ali MA, Yar MS, Hasan MZ, Ahsan MJ and
Pandian S: Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel
5,6-dimethoxy-1-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-2-indenyl-3,4-substituted phenyl
methanone analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Letts. 19:5075–5077. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
De la Torre P, Saavedra LA, Caballero J,
Quiroga J, Alzate-Morales JH, Cabrera MG and Trilleras J: A novel
class of selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Synthesis and
evaluation of (E)-2-(benzo
d]thiazol-2-yl)-3-heteroarylacrylonitriles. Molecules.
17:12072–12085. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Weinreb O, Amit T, Bar-Am O and Youdim
MBH: A novel anti-Alzheimer's disease drug, ladostigil,
neuroprotective, multimodal brain-selective monoamine oxidase and
cholinesterase inhibitor. Int Rev Neurobiol. 100:191–215. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Yazdani M, Edraki N, Badri R,
Khoshneviszadeh M, Iraji A and Firuzi O: Multi-target inhibitors
against Alzheimer disease derived from 3-hydrazinyl 1,2,4-triazine
scaffold containing pendant phenoxy methyl-1,2,3-triazole: Design,
synthesis and biological evaluation. Bioorg Chem. 84:363–371. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Rastegari A, Nadri H, Mahdavi M, Moradi A,
Mirfazli SS, Edraki N, Moghadam FH, Larijani B, Akbarzadeh T and
Saeedi M: Design, synthesis and anti-Alzheimer's activity of novel
1,2,3-triazole-chromenone carboxamide derivatives. Bioorg Chem.
83:391–1401. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Shah MS, Khan SU, Ejaz SA, Afridi S, Rizvi
SUF, Najam-ul-Haq M and Iqbal J: Cholinesterases inhibition and
molecular modeling studies of piperidyl-thienyl and 2-pyrazoline
derivatives of chalcones. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 482:615–624.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Reis J, Cagide F, Valencia ME, Teixeira J,
Bagetta D, Pérez C, Uriarte E, Oliveira PJ, Ortuso F, Alcaro S, et
al: Multi-target-directed ligands for Alzheimer's disease:
Discovery of chromone-based monoamine oxidase/cholinesterase
inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 158:781–800. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Li Q, He S, Chen Y, Feng F, Qu W and Sun
H: Donepezil-based multi-functional cholinesterase inhibitors for
treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Med Chem. 158:463–477.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Xie SS, Wang XB, Li JY, Yang L and Kong
LY: Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel tacrine-coumarin
hybrids as multifunctional cholinesterase inhibitors against
Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Med Chem. 64:540–553. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Catto M, Pisani L, Leonetti F, Nicolotti
O, Pesce P, Stefanachi A, Cellamare S and Carotti A: Design,
synthesis and biological evaluation of coumarin alkylamines as
potent and selective dual binding site inhibitors of
acetylcholinesterase. Bioorg Med Chem. 21:146–152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Khoobi M, Alipour M, Moradi A, Sakhteman
A, Nadri H, Razavi SF, Ghandi M, Foroumadi A and Shafiee A: Design,
synthesis, docking study and biological evaluation of some novel
tetrahydrochromeno 3′,4′:5,6] pyrano 2,3-b] quinolin-6 (7H)-one
derivatives against acetyland butyrylcholinesterase. Eur J Med
Chem. 68:291–300. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Jin P, Kim JA, Choi DY, Lee YJ, Jung HS
and Hong JT: Anti-inflammatory and anti-amyloidogenic effects of a
small molecule, 2,4-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butenal in Tg2576
Alzheimer's disease mice model. J Neuroinflammation. 10:767–779.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Ramsay RR, Popovic-Nikolic MR, Nikolic K,
Uliassi E and Bolognesi ML: A perspective on multi-target drug
discovery and design for complex diseases. Clin Transl Med.
7:32018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|