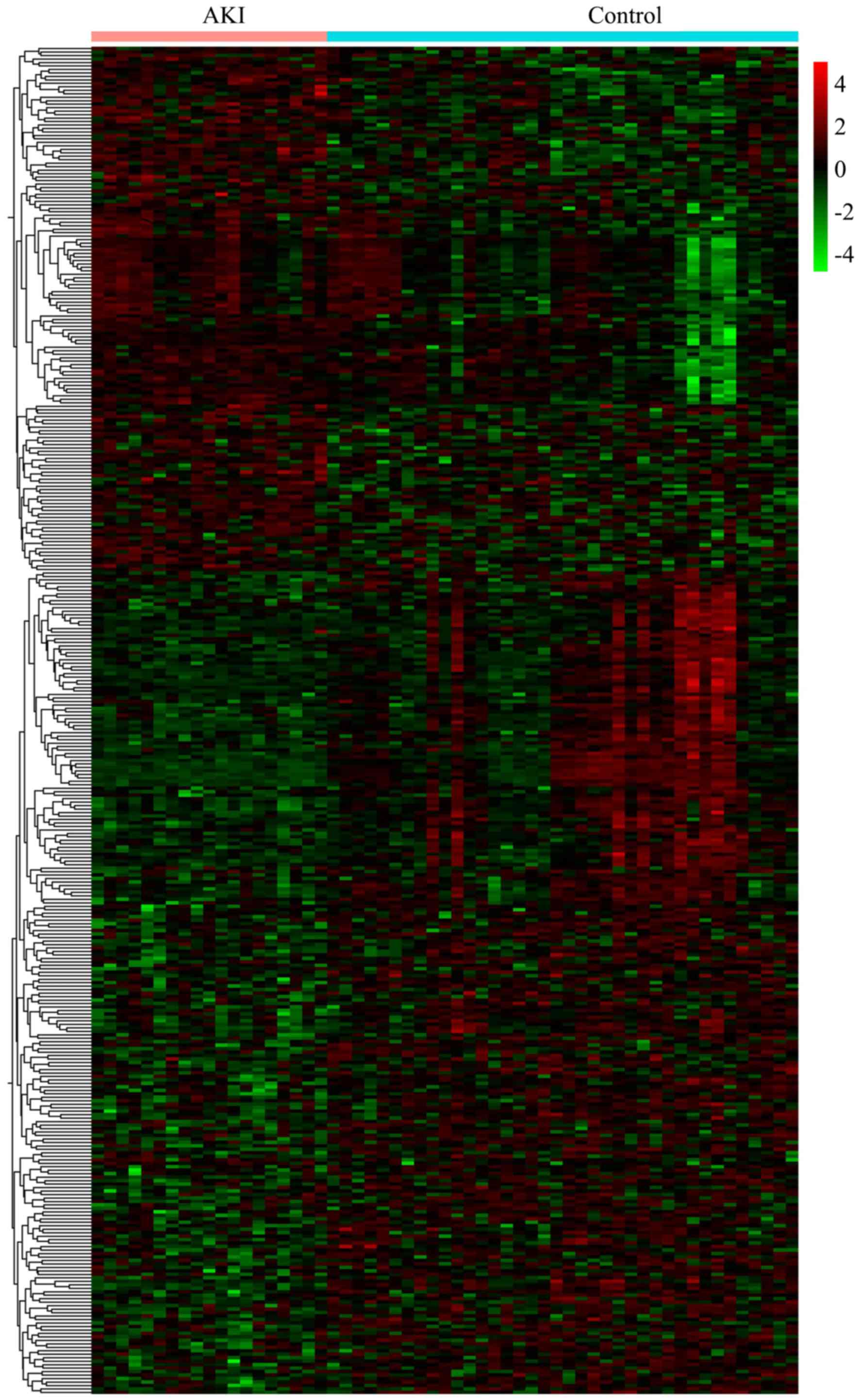
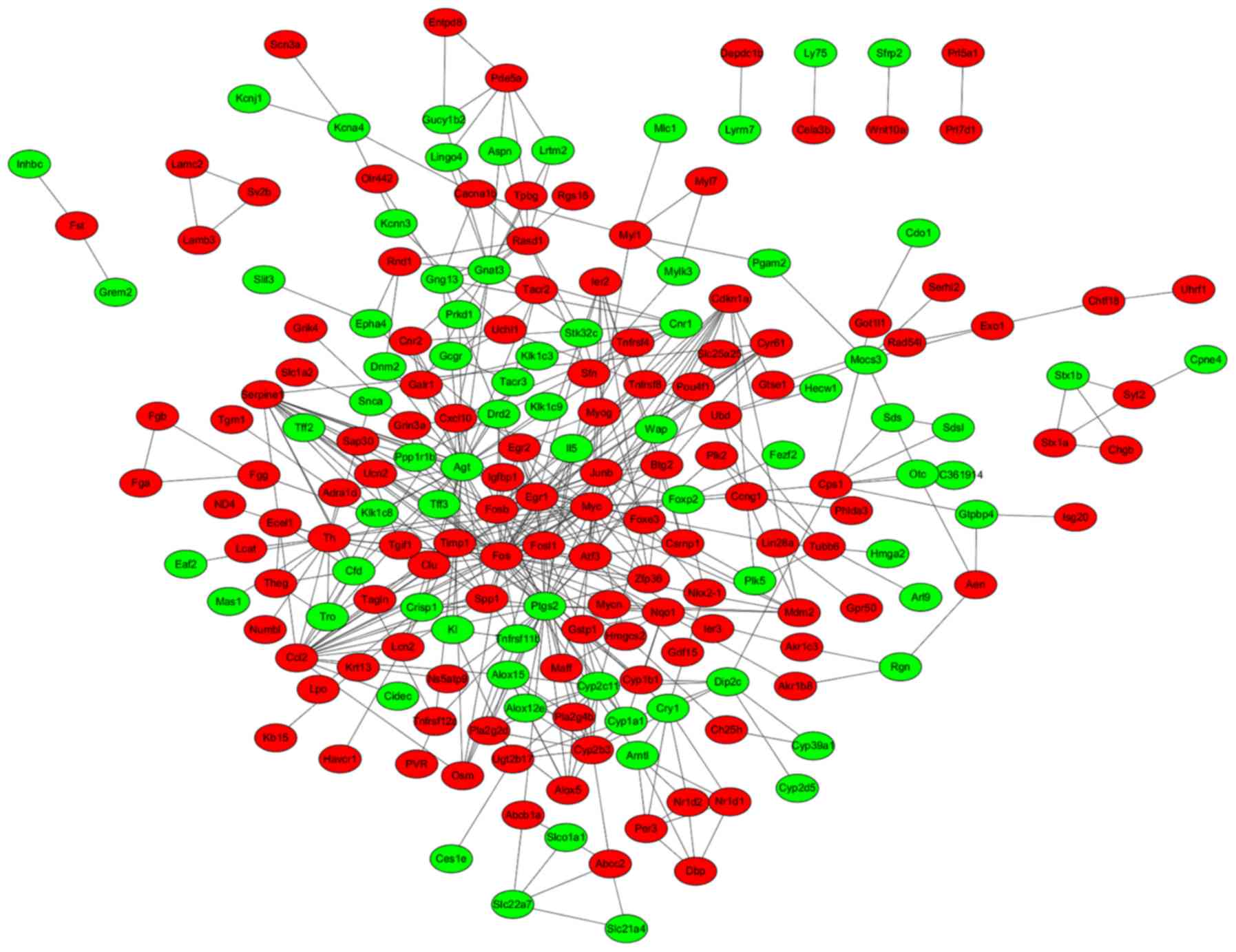
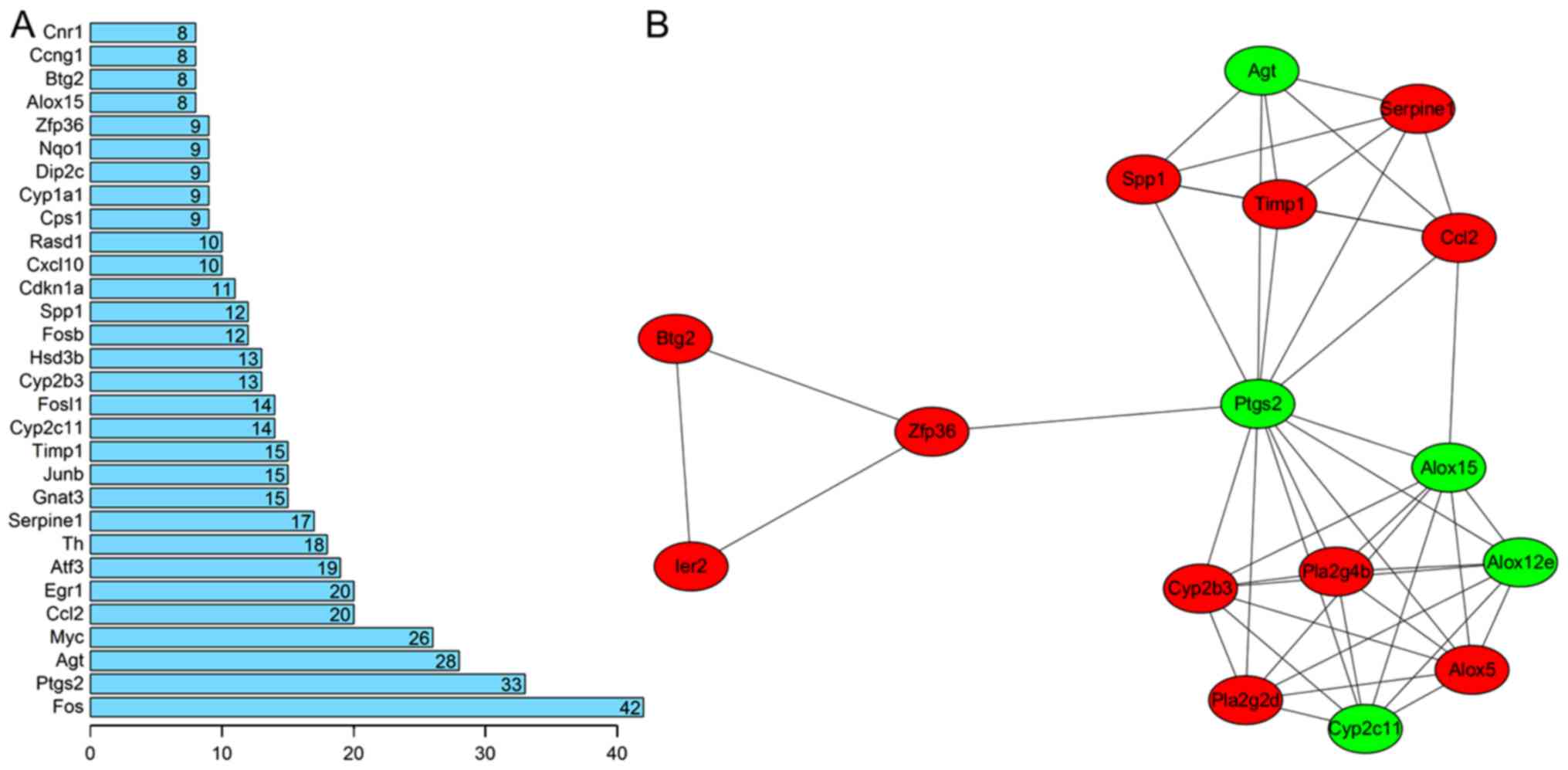
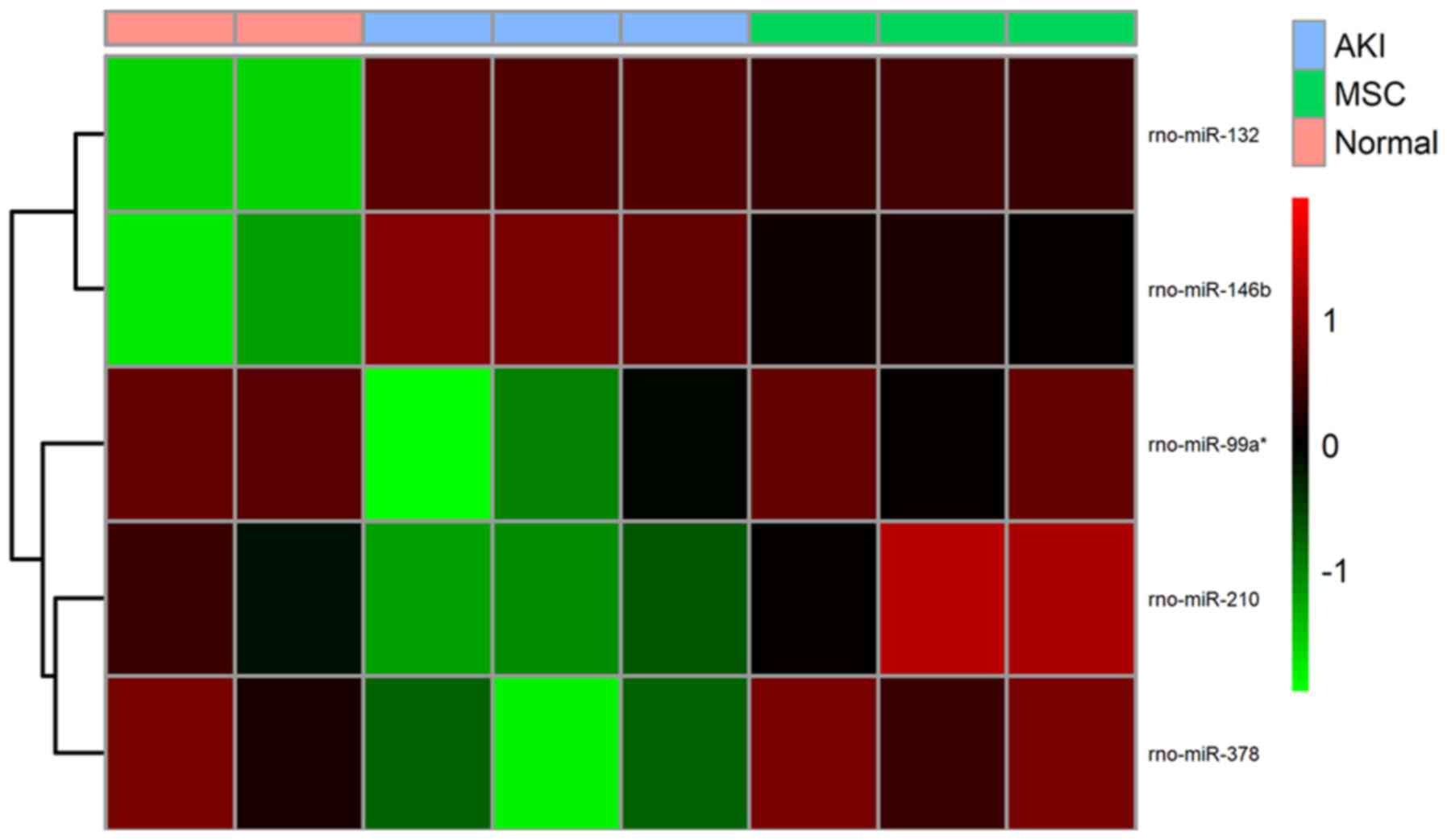
|
1
|
Dasari S and Tchounwou PB: Cisplatin in
cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol.
740:364–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Florea AM and Büsselberg D: Cisplatin as
an anti-tumor drug: Cellular mechanisms of activity, drug
resistance and induced side effects. Cancers (Basel). 3:1351–1371.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bhat ZY, Cadnapaphornchai P, Ginsburg K,
Sivagnanam M, Chopra S, Treadway CK, Lin HS, Yoo G, Sukari A and
Doshi MD: Understanding the risk factors and long-term consequences
of cisplatin-associated acute kidney injury: An observational
cohort study. PLoS One. 10:e01422252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Faig J, Haughton M, Taylor RC, D'Agostino
RB Jr, Whelen MJ, Porosnicu Rodriguez KA, Bonomi M, Murea M and
Porosnicu M: Retrospective analysis of cisplatin nephrotoxicity in
patients with head and neck cancer receiving outpatient treatment
with concurrent high-dose cisplatin and radiotherapy. Am J Clin
Oncol. 41:432–440. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Saleena UV, Athiyaman MS, Vadhiraja BM,
Fernandes DJ, Prabhu R and Nalini K: Evaluation of urinary tubular
enzymes for the detection of early kidney injury due to cisplatin
chemotherapy. Int J Biol Med Res. 3:2241–2246. 2012.
|
|
6
|
Peres LA, da Cunha AD Jr, Assumpção RA,
Schäfer A Jr, da Silva AL, Gaspar AD, Scarpari DF, Alves JB,
Girelli Neto R and de Oliveira TF: Evaluation of the cisplatin
nephrotoxicity using the urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated
lipocalin (NGAL) in patients with head and neck cancer. J Bras
Nefrol. 36:280–288. 2014.(In Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ozkok A and Edelstein CL: Pathophysiology
of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Biomed Res Int.
2014:9678262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Simovic Markovic B, Gazdic M, Arsenijevic
A, Jovicic N, Jeremic J, Djonov V, Arsenijevic N, Lukic ML and
Volarevic V: Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate cisplatin-induced
nephrotoxicity in iNOS-dependent manner. Stem Cells Int.
2017:13153782017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Elhusseini FM, Saad MA, Anber N, Elghannam
D, Sobh MA, Alsayed A, El-Dusoky S, Sheashaa H, Abdel-Ghaffar H and
Sobh M: Long term study of protective mechanisms of human adipose
derived mesenchymal stem cells on cisplatin induced kidney injury
in sprague-dawley rats. J Stem Cells Regen Med. 12:36–48.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee SJ, Ryu MO, Seo MS, Park SB, Ahn JO,
Han SM, Kang KS, Bhang DH and Youn HY: Mesenchymal stem cells
contribute to improvement of renal function in a canine kidney
injury model. In Vivo. 31:1115–1124. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moghadasali R, Mutsaers HA, Azarnia M,
Aghdami N, Baharvand H, Torensma R, Wilmer MJ and Masereeuw R:
Mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium accelerates regeneration
of human renal proximal tubule epithelial cells after gentamicin
toxicity. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 65:595–600. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park JH, Jang HR, Kim DH, Kwon GY, Lee JE,
Huh W, Choi SJ, Oh W, Oh HY and Kim YG: Early, but not late,
treatment with human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem
cells attenuates cisplatin nephrotoxicity through immunomodulation.
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 313:F984–F996. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sherif IO, Almutabagani LA, Alnakhli AM,
Sobh MA and Mohammed HE: Renoprotective effects of angiotensin
receptor blocker and stem cells in acute kidney injury: Involvement
of inflammatory and apoptotic markers. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
240:1572–1579. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liao W, Fu Z, Zou Y, Wen D, Ma H, Zhou F,
Chen Y, Zhang M and Zhang W: MicroRNA-140-5p attenuated oxidative
stress in Cisplatin induced acute kidney injury by activating
Nrf2/ARE pathway through a Keap1-independent mechanism. Exp Cell
Res. 360:292–302. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee CG, Kim JG, Kim HJ, Kwon HK, Cho IJ,
Choi DW, Lee WH, Kim WD, Hwang SJ, Choi S and Kim SG: Discovery of
an integrative network of microRNAs and transcriptomics changes for
acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 86:943–953. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guo Y, Ni J, Chen S, Bai M, Lin J, Ding G,
Zhang Y, Sun P, Jia Z, Huang S, et al: MicroRNA-709 mediates acute
tubular injury through effects on mitochondrial function. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 29:449–461. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qin W, Xie W, Yang X, Xia N and Yang K:
Inhibiting microRNA-449 attenuates cisplatin-induced injury in
NRK-52E cells possibly via regulating the SIRT1/P53/BAX pathway.
Med Sci Monit. 22:818–823. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu Y, Yu J, Yin L, Zhou Y, Sun Z, Jia H,
Tao Y, Liu W, Zhang B, Zhang J, et al: MicroRNA-146b, a sensitive
indicator of mesenchymal stem cell repair of acute renal injury.
Stem Cells Transl Med. 5:1406–1415. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
de Almeida DC, Bassi ÊJ, Azevedo H,
Anderson L, Origassa CS, Cenedeze MA, de Andrade-Oliveira V,
Felizardo RJ, da Silva RC, Hiyane MI, et al: A regulatory
miRNA-mRNA network is associated with tissue repair induced by
mesenchymal stromal cells in acute kidney injury. Front Immunol.
7:6452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pavkovic M, Riefke B and
Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H: Urinary microRNA profiling for
identification of biomarkers after cisplatin-induced kidney injury.
Toxicology. 324:147–157. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pavkovic M, Riefke B, Gutberlet K, Raschke
M and Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H: Comparison of the MesoScale discovery
and Luminex multiplex platforms for measurement of urinary
biomarkers in a cisplatin rat kidney injury model. J Pharmacol
Toxicol Methods. 69:196–204. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res 43
(Database Issue). D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kohl M, Wiese S and Warscheid B:
Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological
networks. Methods Mol Biol. 696:291–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:22003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dweep H and Gretz N: miRWalk2.0: A
comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat Methods.
12:6972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang W, Sha Y, Wei K, Wu C, Ding D, Yang
Y, Zhu C, Zhang Y, Ding G, Zhang A, et al: Rotenone ameliorates
chronic renal injury caused by acute ischemia/reperfusion.
Oncotarget. 9:24199–24208. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Eren M, Place AT, Thomas PM, Flevaris P,
Miyata T and Vaughan DE: PAI-1 is a critical regulator of FGF23
homeostasis. Sci Adv. 3:e16032592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xue HY, Yuan L, Cao YJ, Fan YP, Chen XL
and Huang XZ: Resveratrol ameliorates renal injury in spontaneously
hypertensive rats by inhibiting renal micro-inflammation. Biosci
Rep. 36(pii): e003392016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jesmin S, Gando S, Zaedi S, Prodhan SH,
Sawamura A, Miyauchi T, Hiroe M and Yamaguchi N: Protease-activated
receptor 2 blocking peptide counteracts endotoxin-induced
inflammation and coagulation and ameliorates renal fibrin
deposition in a rat model of acute renal failure. Shock.
32:626–632. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gupta KK, Donahue DL, Sandoval-Cooper MJ,
Castellino FJ and Ploplis VA: Abrogation of plasminogen activator
inhibitor-1-vitronectin interaction ameliorates acute kidney injury
in murine endotoxemia. PLoS One. 10:e01207282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu KD, Glidden DV, Eisner MD, Parsons PE,
Ware LB, Wheeler A, Korpak A, Thompson BT, Chertow GM and Matthay
MA; National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute ARDS Network Clinical
Trials Group, : Predictive and pathogenetic value of plasma
biomarkers for acute kidney injury in patients with acute lung
injury. Crit Care Med. 35:2755–2761. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Angel P and Karin M: The role of Jun, Fos
and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1072:129–157. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Miyazaki H, Morishita J, Ueki M, Nishina
K, Shiozawa S and Maekawa N: The effects of a selective inhibitor
of c-Fos/activator protein-1 on endotoxin-induced acute kidney
injury in mice. BMC Nephrol. 13:1532012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ishida M, Ueki M, Morishita J, Ueno M,
Shiozawa S and Maekawa N: T-5224, a selective inhibitor of
c-Fos/activator protein-1, improves survival by inhibiting serum
high mobility group box-1 in lethal lipopolysaccharide-induced
acute kidney injury model. J Intensive Care. 3:492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Aguado-Fraile E, Ramos E, Conde E,
Rodríguez M, Martín-Gómez L, Lietor A, Candela Á, Ponte B, Liaño F
and García-Bermejo ML: A pilot study identifying a set of microRNAs
as precise diagnostic biomarkers of acute kidney injury. PLoS One.
10:e01271752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu LL, Li D, He YL, Zhou YZ, Gong SH, Wu
LY, Zhao YQ, Huang X, Zhao T, Xu L, et al: miR-210 protects renal
cell against hypoxia-induced apoptosis by targeting HIF-1 alpha.
Mol Med. 23:258–271. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang D, Cao X, Li J and Zhao G: MiR-210
inhibits NF-κB signaling pathway by targeting DR6 in
osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 5:127752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kopriva SE, Chiasson VL, Mitchell BM and
Chatterjee P: TLR3-induced placental miR-210 down-regulates the
STAT6/interleukin-4 pathway. PLoS One. 8:e677602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pellegrini KL, Han T, Bijol V, Saikumar J,
Craciun FL, Chen WW, Fuscoe JC and Vaidya VS: MicroRNA-155
deficient mice experience heightened kidney toxicity when dosed
with cisplatin. Toxicol Sci. 141:484–492. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lei X, Zhang BD, Ren JG and Luo FL:
Astragaloside suppresses apoptosis of the podocytes in rats with
diabetic nephropathy via miR-378/TRAF5 signaling pathway. Life Sci.
206:77–83. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gu D, Zou X, Ju G, Zhang G, Bao E and Zhu
Y: Mesenchymal stromal cells derived extracellular vesicles
ameliorate acute renal ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibition of
mitochondrial fission through miR-30. Stem Cells Int.
2016:20939402016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu J, Hua R, Gong Z, Shang B, Huang Y,
Guo L, Liu T and Xue J: Human amniotic epithelial cells inhibit
CD4+ T cell activation in acute kidney injury patients by
influencing the miR-101-c-Rel-IL-2 pathway. Mol Immunol. 81:76–84.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang YW, Wang X, Ren X and Zhang M:
Involvement of glucose-regulated protein 78 and spliced X-box
binding protein 1 in the protective effect of gliclazide in
diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 146:41–47. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ezel T, Kocyigit Y, Deveci E, Atamer Y,
Sermet A, Uysal E, Aktaş A and Yavuz D: Biochemical and
histopathological investigation of resveratrol, gliclazide, and
losartan protective effects on renal damage in a diabetic rat
model. Anal Quant Cytopathol Histpathol. 37:187–198.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Onozato ML, Tojo A, Goto A and Fujita T:
Radical scavenging effect of gliclazide in diabetic rats fed with a
high cholesterol diet. Kidney Int. 65:951–960. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|