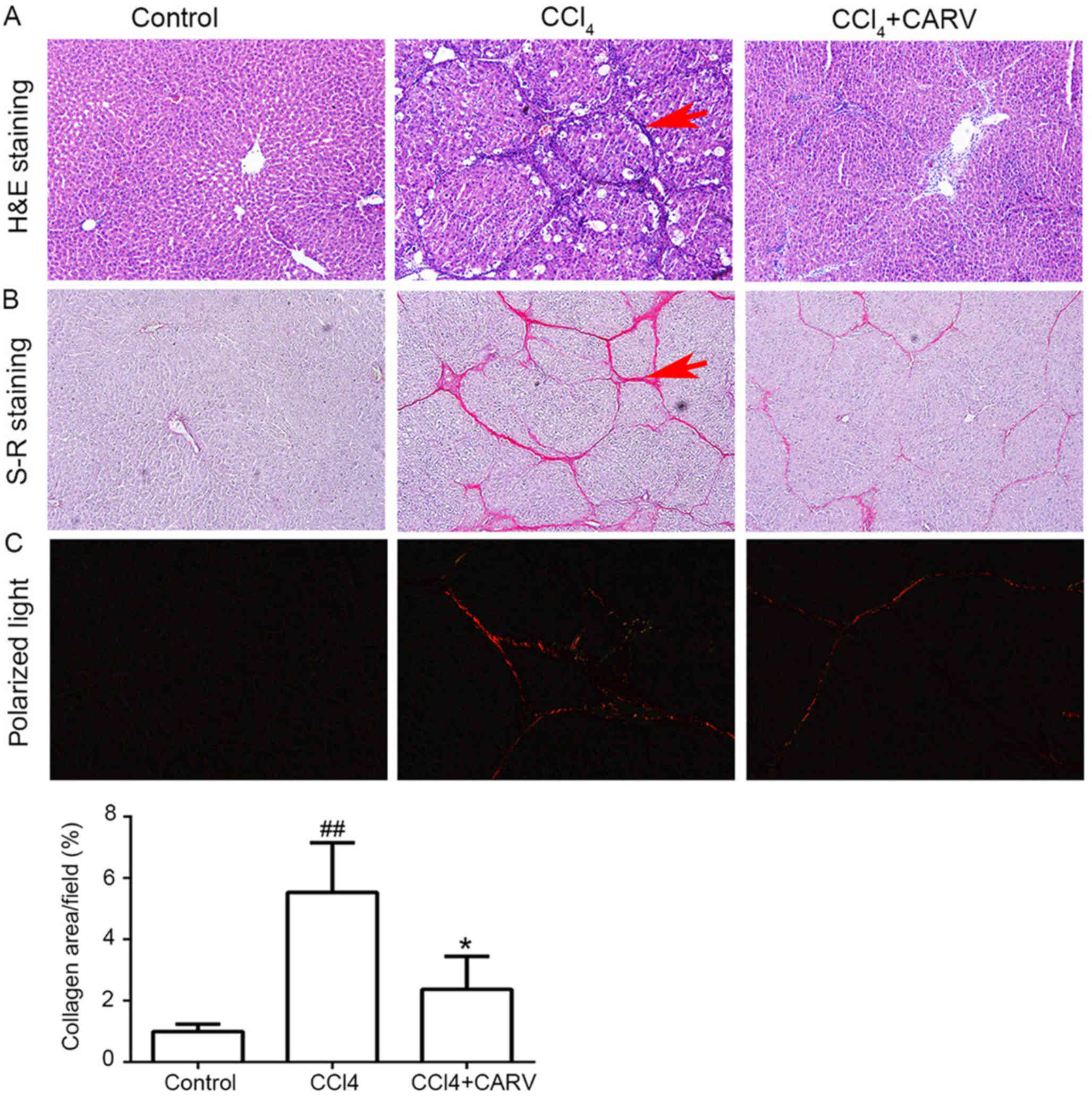
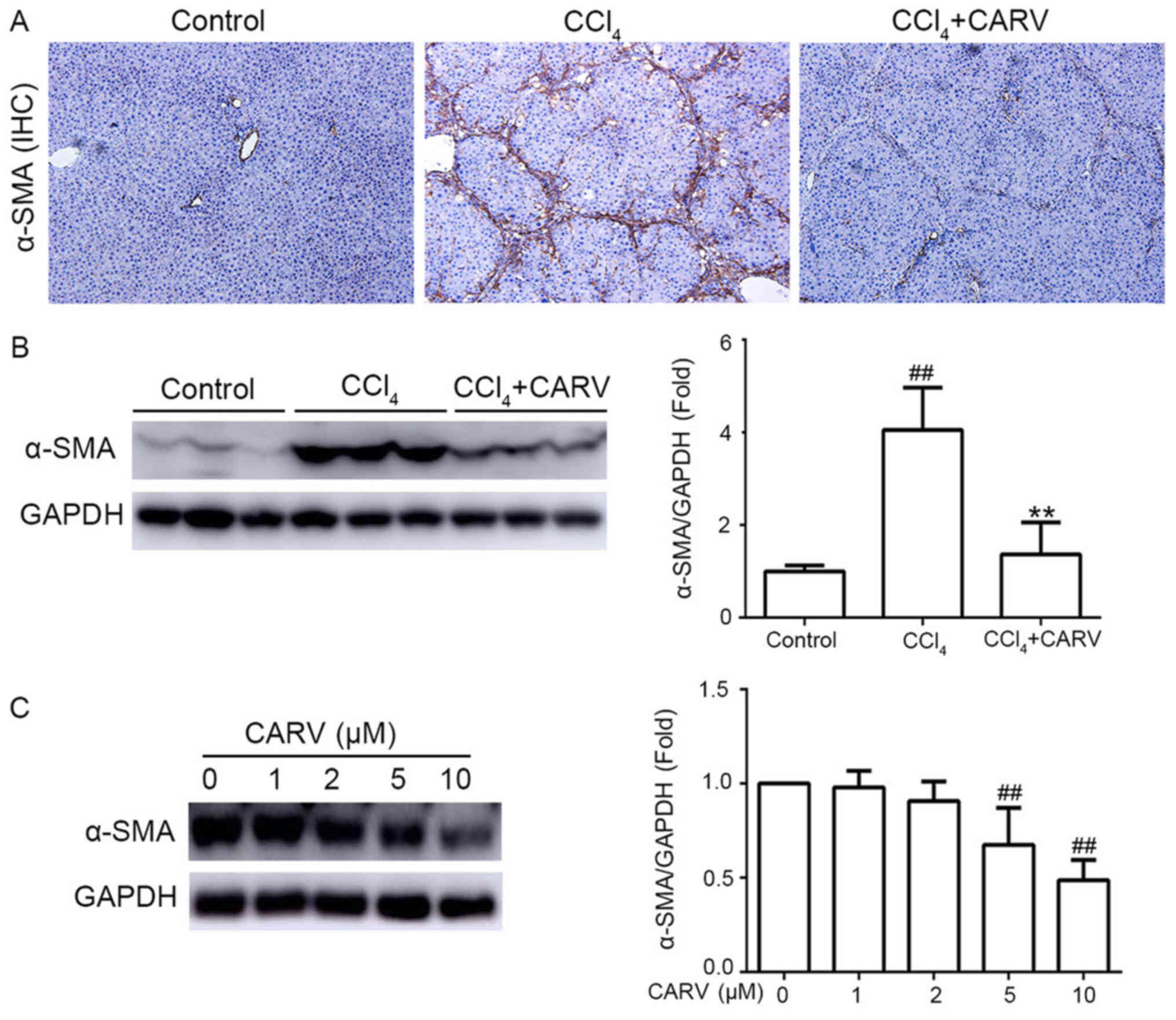
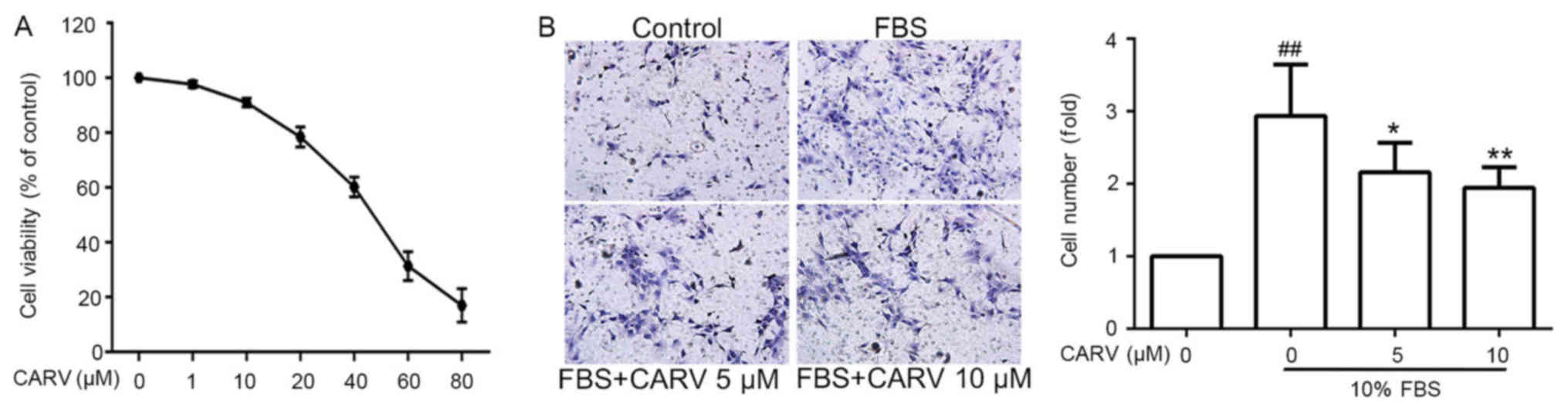
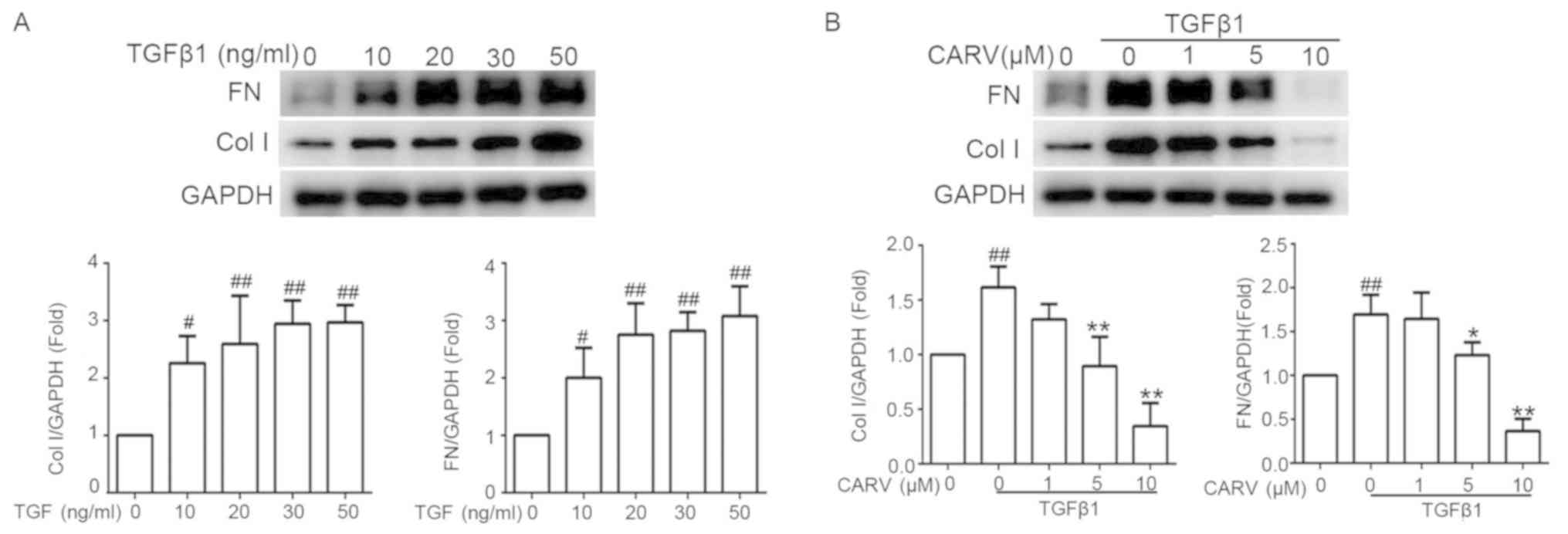
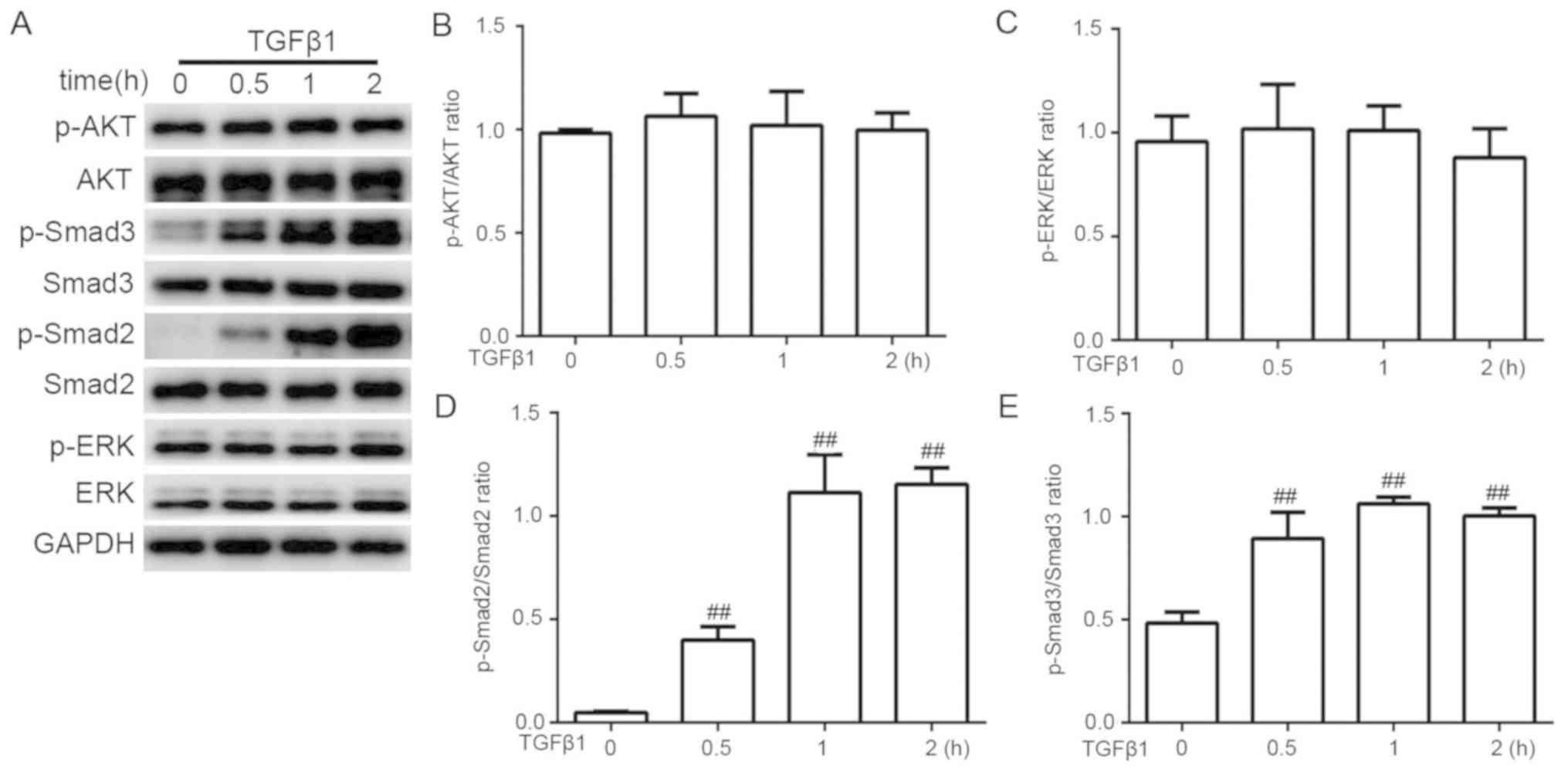
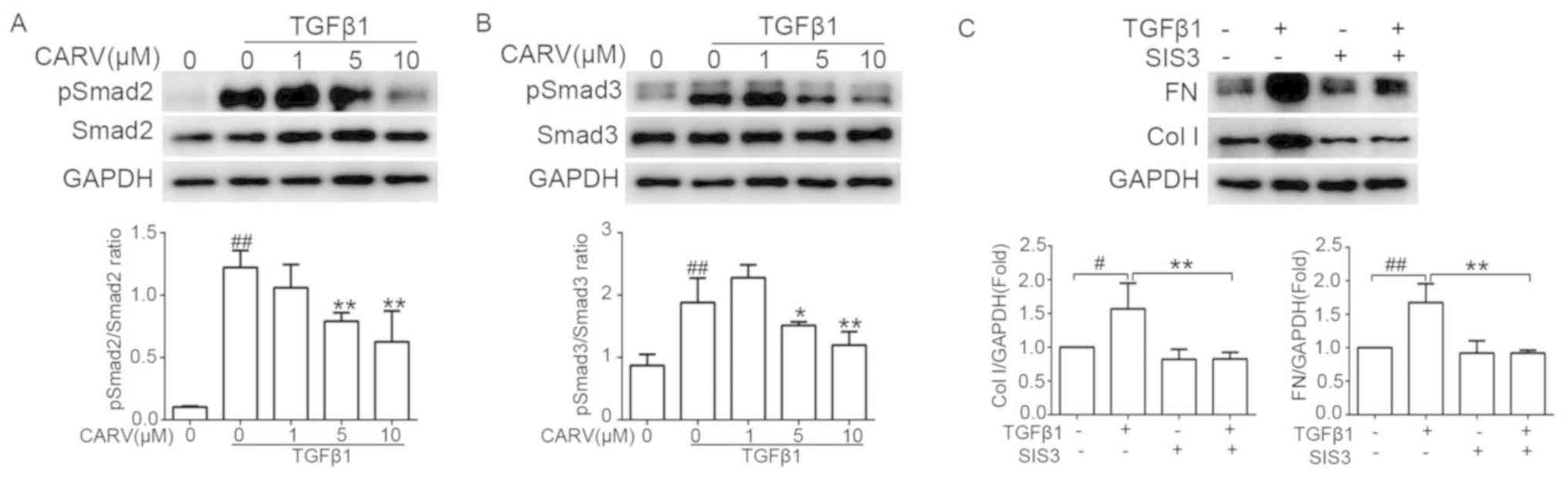
|
1
|
Fernandez M: Molecular pathophysiology of
portal hypertension. Hepatology. 61:1406–1415. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bosch J, Groszmann RJ and Shah VH:
Evolution in the understanding of the pathophysiological basis of
portal hypertension: How changes in paradigm are leading to
successful new treatments. J Hepatol. 62:S121–S130. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reiberger T, Ferlitsch A, Payer BA, Pinter
M, Homoncik M and Peck-Radosavljevic M; Vienna Hepatic Hemodynamic
Lab, : Non-selective β-blockers improve the correlation of liver
stiffness and portal pressure in advanced cirrhosis. J
Gastroenterol. 47:561–568. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bosch J, Abraldes JG, Fernández M and
García-Pagán JC: Hepatic endothelial dysfunction and abnormal
angiogenesis: New targets in the treatment of portal hypertension.
J Hepatol. 53:558–567. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Iwakiri Y and Groszmann RJ: Vascular
endothelial dysfunction in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 46:927–934. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sanyal AJ, Bosch J, Blei A and Arroyo V:
Portal hypertension and its complications. Gastroenterology.
134:1715–1728. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee UE and Friedman SL: Mechanisms of
hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
25:195–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Senoo H, Yoshikawa K, Morii M, Miura M,
Imai K and Mezaki Y: Hepatic stellate cell (vitamin A-storing cell)
and its relative-past, present and future. Cell Biol Int.
34:1247–1272. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu L, Hui AY, Albanis E, Arthur MJ,
O'Byrne SM, Blaner WS, Mukherjee P, Friedman SL and Eng FJ: Human
hepatic stellate cell lines, LX-1 and LX-2: New tools for analysis
of hepatic fibrosis. Gut. 54:142–151. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Reynaert H, Thompson MG, Thomas T and
Geerts A: Hepatic stellate cells: Role in microcirculation and
pathophysiology of portal hypertension. Gut. 50:571–581. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Friedman SL: Molecular regulation of
hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury.
J Biol Chem. 275:2247–2250. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bissell DM, Roulot D and George J:
Transforming growth factor beta and the liver. Hepatology.
34:859–867. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
de Franchis R; Baveno VI Faculty, :
Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno VI
Consensus Workshop: Stratifying risk and individualizing care for
portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 63:743–752. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Arozal W, Sari FR, Watanabe K, Arumugam S,
Veeraveedu PT, Ma M, Thandavarayan RA, Sukumaran V, Lakshmanan AP,
Kobayashi Y, et al: Carvedilol-afforded protection against
daunorubicin-induced cardiomyopathic rats in vivo: Effects on
cardiac fibrosis and hypertrophy. ISRN Pharmacol. 2011:4305492011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wong VY, Laping NJ, Nelson AH, Contino LC,
Olson BA, Gygielko E, Campbell WG Jr, Barone F and Brooks DP:
Renoprotective effects of carvedilol in hypertensive-stroke prone
rats may involve inhibition of TGF beta expression. Br J Pharmacol.
134:977–984. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
El-Demerdash E, Abdel-Sattar SA, El-Bakly
WM and Mohamed EA: Antifibrotic effects of carvedilol and impact of
liver fibrosis on carvedilol pharmacokinetics in a rat model. Eur J
Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 42:767–779. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Krogsgaard K, Gluud C, Henriksen JH and
Christoffersen P: Correlation between liver morphology and portal
pressure in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 4:699–703. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Starkel P and Leclercq IA: Animal models
for the study of hepatic fibrosis. Best Pract Res Clin
Gastroenterol. 25:319–333. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Andrade GB, Montes GS, Conceição GM and
Saldiva PH: Use of the Picrosirius-polarization method to age
fibrotic lesions in the hepatic granulomas produced in experimental
murine schistosomiasis. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 93:265–272. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jinnin M, Ihn H and Tamaki K:
Characterization of SIS3, a novel specific inhibitor of Smad3, and
its effect on transforming growth factor-beta1-induced
extracellular matrix expression. Mol Pharmacol. 69:597–607. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tripathi D and Hayes PC: Beta-blockers in
portal hypertension: New developments and controversies. Liver Int.
34:655–667. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Carlson W and Oberg K: Clinical
pharmacology of carvedilol. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 4:205–218.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ding Q, Tian XG, Li Y, Wang QZ and Zhang
CQ: Carvedilol may attenuate liver cirrhosis by inhibiting
angiogenesis through the VEGF-Src-ERK signaling pathway. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:9566–9576. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Barone FC, Campbell WG Jr, Nelson AH and
Feuerstein GZ: Carvedilol prevents severe hypertensive
cardiomyopathy and remodeling. J Hypertens. 16:871–884. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hamdy N and El-Demerdash E: New
therapeutic aspect for carvedilol: Antifibrotic effects of
carvedilol in chronic carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 261:292–299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Di Pascoli M, Divi M, Rodriguez-Vilarrupla
A, Rosado E, Gracia-Sancho J, Vilaseca M, Bosch J and García-Pagán
JC: Resveratrol improves intrahepatic endothelial dysfunction and
reduces hepatic fibrosis and portal pressure in cirrhotic rats. J
Hepatol. 58:904–910. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu J and Zern MA: Hepatic stellate cells:
A target for the treatment of liver fibrosis. J Gastroenterol.
35:665–672. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schuppan D and Popov Y: Hepatic fibrosis:
From bench to bedside. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17 (Suppl
3):S300–S305. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kaji K, Yoshiji H, Ikenaka Y, Noguchi R,
Aihara Y, Douhara A, Moriya K, Kawaratani H, Shirai Y, Yoshii J, et
al: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor attenuates hepatic fibrosis
via suppression of activated hepatic stellate cell in rats. J
Gastroenterol. 49:481–491. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li J, Li X, Xu W, Wang S, Hu Z, Zhang Q,
Deng X, Wang J, Zhang J and Guo C: Antifibrotic effects of luteolin
on hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis by targeting
AKT/mTOR/p70S6K and TGFβ/Smad signalling pathways. Liver Int.
35:1222–1233. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhu J, Wu J, Frizell E, Liu SL, Bashey R,
Rubin R, Norton P and Zern MA: Rapamycin inhibits hepatic stellate
cell proliferation in vitro and limits fibrogenesis in an in vivo
model of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 117:1198–1204. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Son G, Hines IN, Lindquist J, Schrum LW
and Rippe RA: Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling
in hepatic stellate cells blocks the progression of hepatic
fibrosis. Hepatology. 50:1512–1523. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Trautwein C, Friedman SL, Schuppan D and
Pinzani M: Hepatic fibrosis: Concept to treatment. J Hepatol.
62:S15–S24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Greuter T and Shah VH: Hepatic sinusoids
in liver injury, inflammation, and fibrosis: New pathophysiological
insights. J Gastroenterol. 51:511–519. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kajdaniuk D, Marek B, Borgiel-Marek H and
Kos-Kudła B: Transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1) in physiology
and pathology. Endokrynol Pol. 64:384–396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Inagaki Y and Okazaki I: Emerging insights
into transforming growth factor beta Smad signal in hepatic
fibrogenesis. Gut. 56:284–292. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Derynck R and Zhang YE: Smad-dependent and
Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature.
425:577–584. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bakin AV, Tomlinson AK, Bhowmick NA, Moses
HL and Arteaga CL: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase function is
required for transforming growth factor beta-mediated epithelial to
mesenchymal transition and cell migration. J Biol Chem.
275:36803–36810. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|