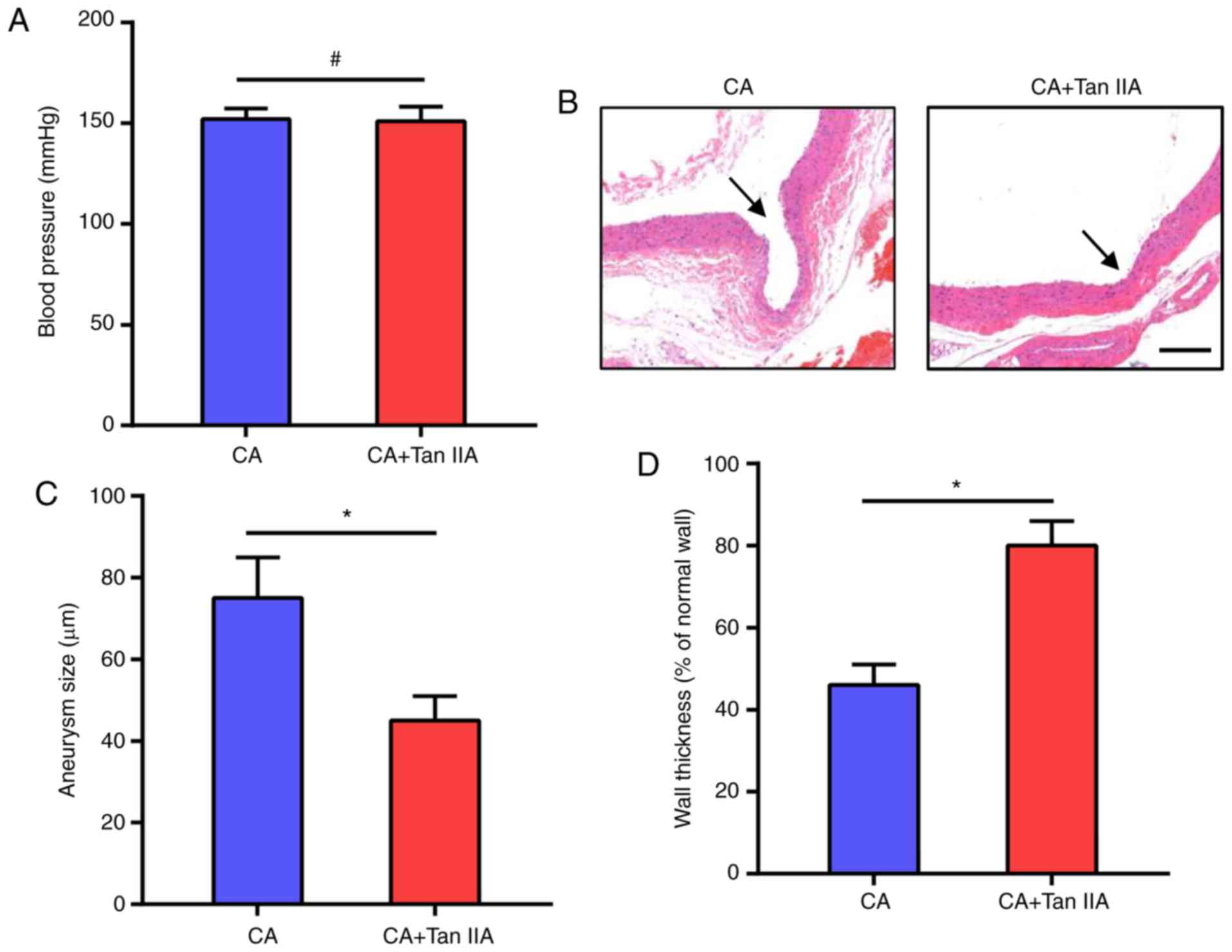
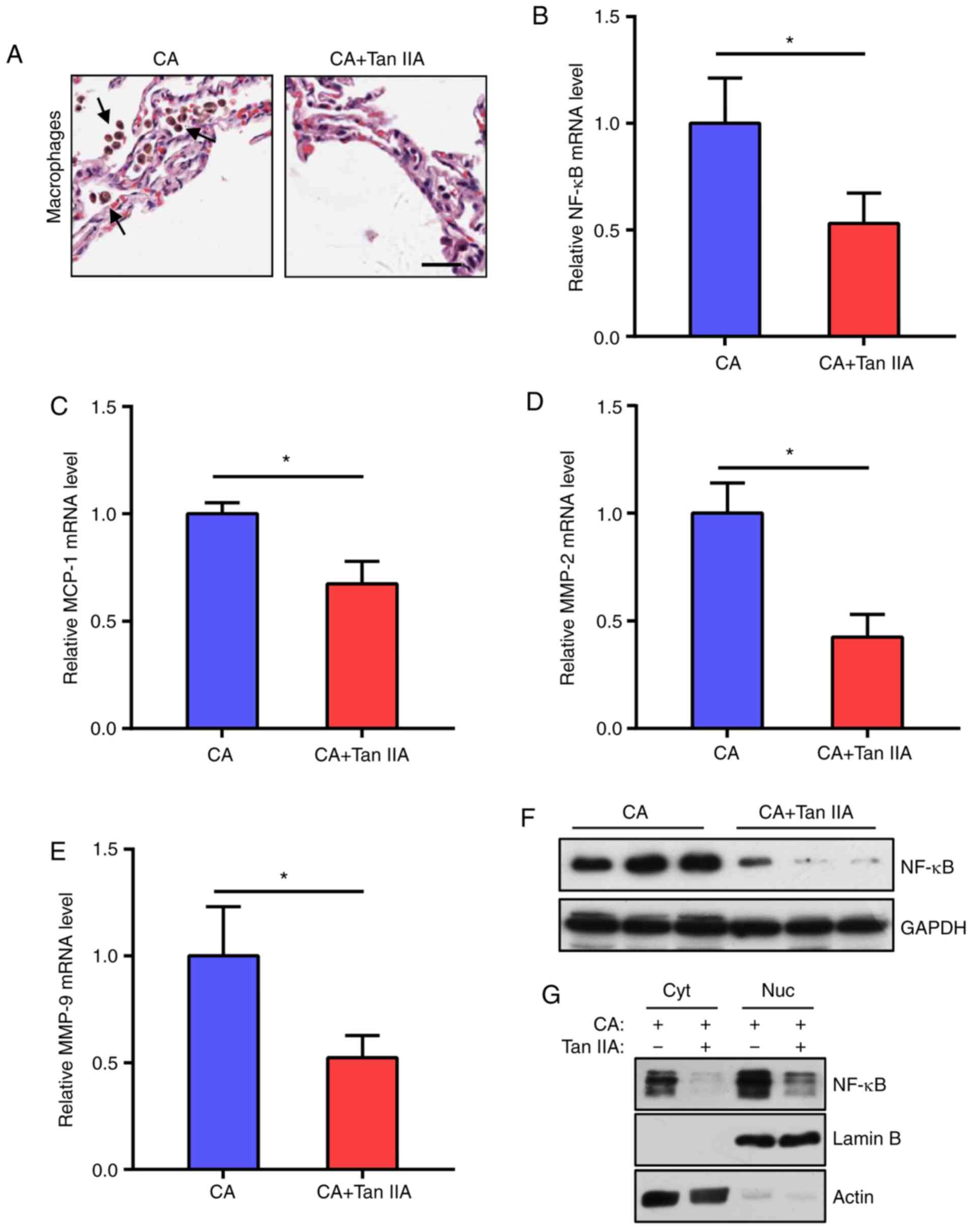
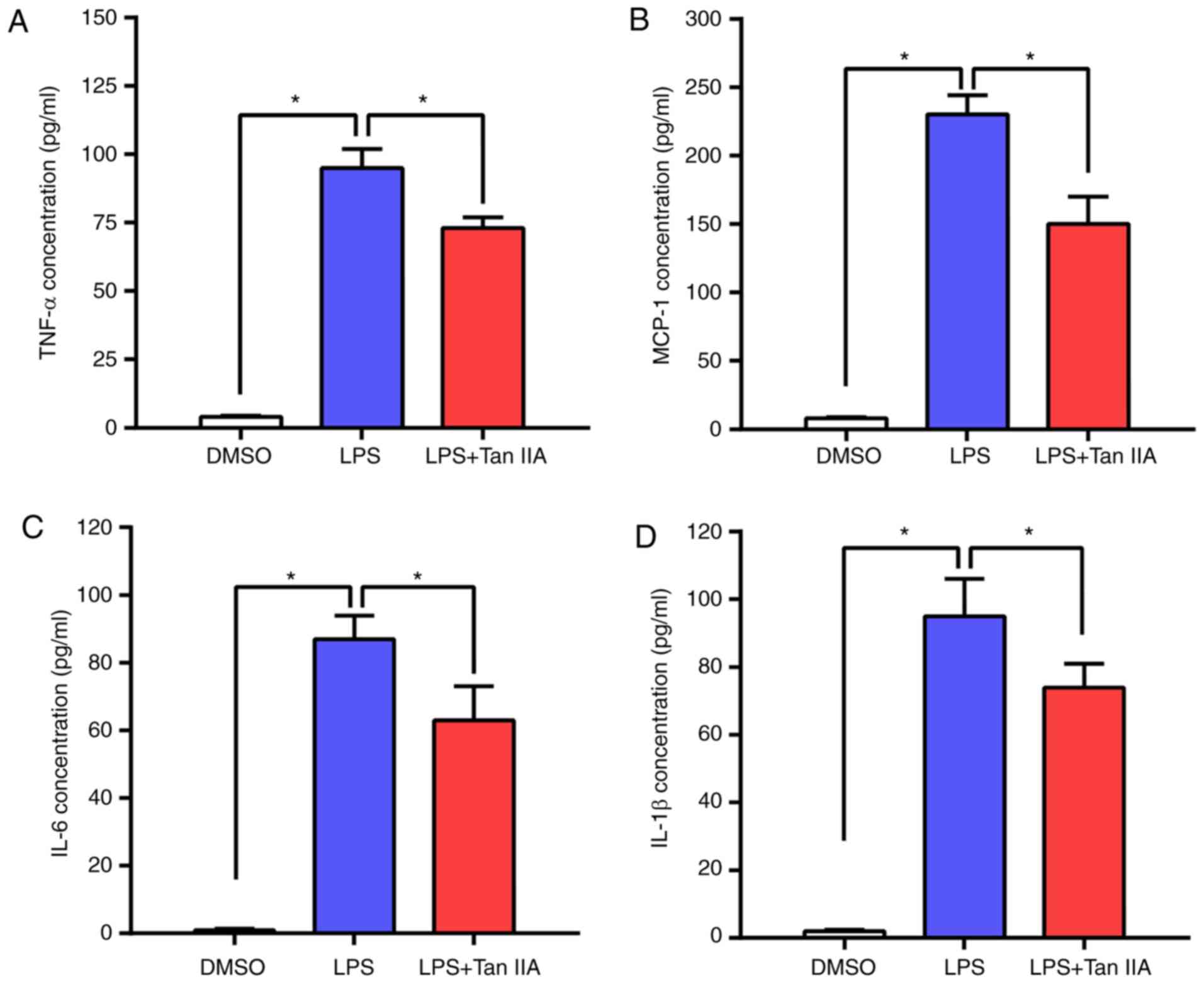
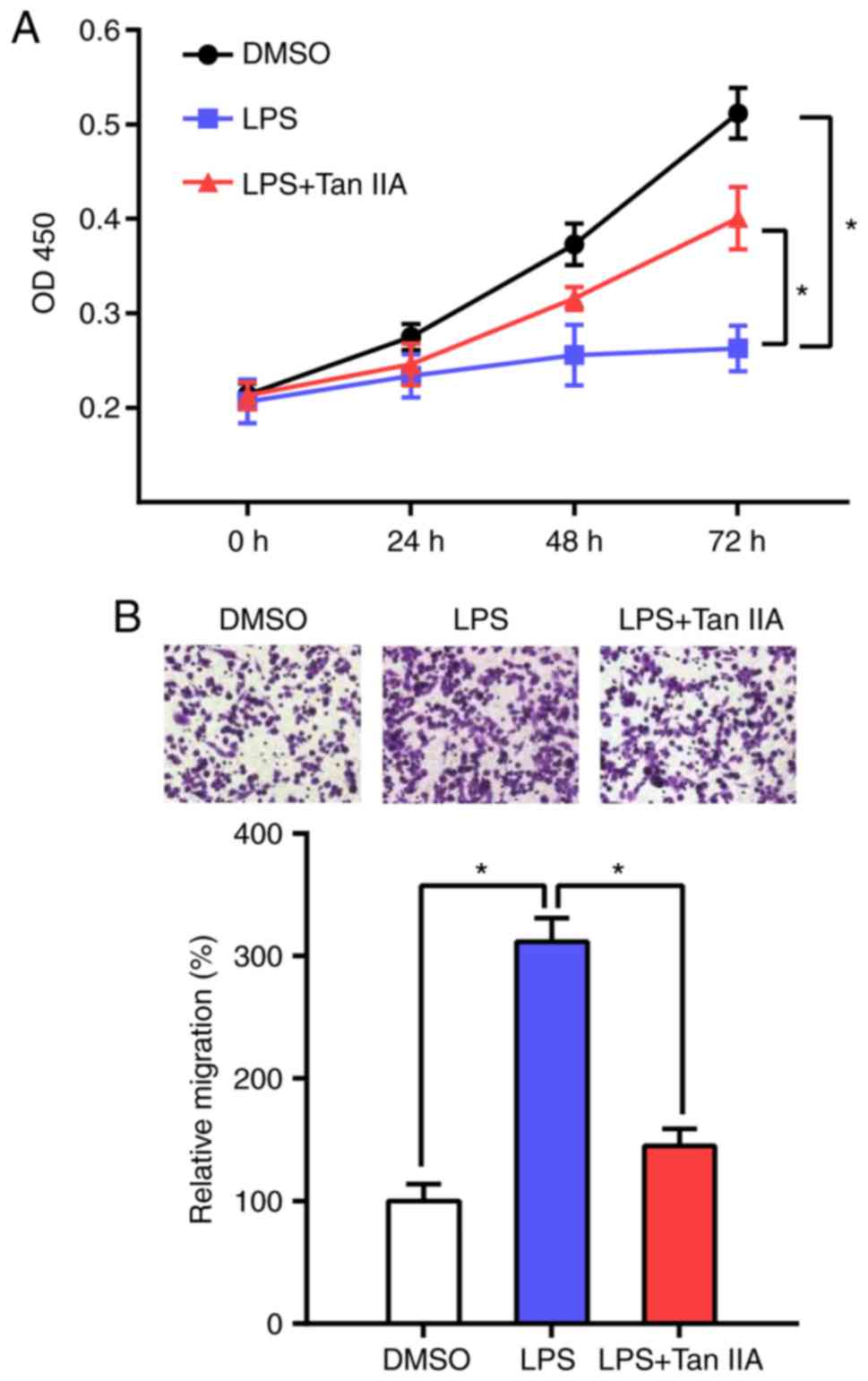
|
1
|
Vlak MHM, Algra A, Brandenburg R and
Rinkel GJ: Prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms, with
emphasis on sex, age, comorbidity, country, and time period: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 10:626–636.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Baron EP: Headache, cerebral aneurysms,
and the use of triptans and ergot derivatives. Headache.
55:739–747. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bowles E: Cerebral aneurysm and aneurysmal
subarachnoid haemorrhage. Nurs Stand. 28:52–59. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
van Gijn J, Kerr RS and Rinkel GJ:
Subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet. 369:306–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pera J, Korostynski M, Krzyszkowski T,
Czopek J, Slowik A, Dziedzic T, Piechota M, Stachura K, Moskala M,
Przewlocki R and Szczudlik A: Gene expression profiles in human
ruptured and unruptured intracranial aneurysms: What is the role of
inflammation? Stroke. 41:224–231. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hosaka K and Hoh BL: Inflammation and
cerebral aneurysms. Transl Stroke Res. 5:190–198. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tuttolomondo A, Di Sciacca R, Di Raimondo
D, Pedone C, La Placa S, Pinto A and Licata G: Effects of clinical
and laboratory variables and of pretreatment with cardiovascular
drugs in acute ischaemic stroke: A retrospective chart review from
the GIFA study. Int J Cardiol. 151:318–322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Di Raimondo D, Tuttolomondo A, Buttà C,
Miceli S, Licata G and Pinto A: Effects of ACE-inhibitors and
angiotensin receptor blockers on inflammation. Curr Pharm Des.
18:4385–4413. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Licata G, Tuttolomondo A, Corrao S, Di
Raimondo D, Fernandez P, Caruso C, Avellone G and Pinto A:
Immunoinflammatory activation during the acute phase of lacunar and
non-lacunar ischemic stroke: Association with time of onset and
diabetic state. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 19:639–646. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Aoki T, Kataoka H, Shimamura M, Nakagami
H, Wakayama K, Moriwaki T, Ishibashi R, Nozaki K, Morishita R and
Hashimoto N: NF-kappaB is a key mediator of cerebral aneurysm
formation. Circulation. 116:2830–2840. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moriwaki T, Takagi Y, Sadamasa N, Aoki T,
Nozaki K and Hashimoto N: Impaired progression of cerebral
aneurysms in interleukin-1β-deficient mice. Stroke. 37:900–905.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aoki T, Kataoka H, Morimoto M, Nozaki K
and Hashimoto N: Macrophage-derived matrix metalloproteinase-2 and
−9 promote the progression of cerebral aneurysms in rats. Stroke.
38:162–169. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang M, Qian Y and Tang A: Research
progress of pharmacologic actions of TanshinoneIIA. Med
Recapitulate. 16:2661–2664. 2010.
|
|
14
|
Wang X: Progress of pharmacological
research and clinical application of Tanshinone II A. Guang Ming J
Chin Med. 26:1514–1517. 2011.
|
|
15
|
Hosaka K, Downes DP, Nowicki KW and Hoh
BL: Modified murine intracranial aneurysm model: Aneurysm formation
and rupture by elastase and hypertension. J Neurointerv Surg.
6:474–479. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Toth M, Sohail A and Fridman R: Assessment
of gelatinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) by gelatin zymography. Methods Mol
Biol. 878:121–135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li Y, Gu B, Liu J, Xiong X, Zhou C and Wu
G: Research progress of Tanshinone II A. Li ShiZhen Med Materia Med
Res. 21:1770–1772. 2010.
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jin UH, Suh SJ, Chang HW, Son JK, Lee SH,
Son KH, Chang YC and Kim CH: Tanshinone IIA from Salvia
miltiorrhiza BUNGE inhibits human aortic smooth muscle cell
migration and MMP-9 activity through AKT signaling pathway. J Cell
Biochem. 104:15–26. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hartley JW, Evans LH, Green KY, Naghashfar
Z, Macias AR, Zerfas PM and Ward JM: Expression of infectious
murine leukemia viruses by RAW264.7 cells, a potential complication
for studies with a widely used mouse macrophage cell line.
Retrovirology. 5:12008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Saxena RK, Vallyathan V and Lewis DM:
Evidence for lipopolysaccharide-induced differentiation of RAW264.7
murine macrophage cell line into dendritic like cells. J Biosci.
28:129–134. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jou LD, Lee DH, Morsi H and Mawad ME: Wall
shear stress on ruptured and unruptured intracranial aneurysms at
the internal carotid artery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 29:1761–1767.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chalouhi N, Ali MS, Jabbour PM,
Tjoumakaris SI, Gonzalez LF, Rosenwasser RH, Koch WJ and Dumont AS:
Biology of intracranial aneurysms: Role of inflammation. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 32:1659–1676. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Starke RM, Raper DM, Ding D, Chalouhi N,
Owens GK, Hasan DM, Medel R and Dumont AS: Tumor necrosis factor-α
modulates cerebral aneurysm formation and rupture. Transl Stroke
Res. 5:269–277. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Starke RM, Chalouhi N, Ali MS, Jabbour PM,
Tjoumakaris SI, Gonzalez LF, Rosenwasser RH, Koch WJ and Dumont AS:
The role of oxidative stress in cerebral aneurysm formation and
rupture. Curr Neurovasc Res. 10:247–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tang FT, Cao Y, Wang TQ, Wang LJ, Guo J,
Zhou XS, Xu SW, Liu WH, Liu PQ and Huang HQ: Tanshinone IIA
attenuates atherosclerosis in ApoE(−/-) mice through
down-regulation of scavenger receptor expression. Eur J Pharmacol.
650:275–284. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ji X, Tan BK, Zhu YC, Linz W and Zhu YZ:
Comparison of cardioprotective effects using ramipril and DanShen
for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction in rats. Life Sci.
73:1413–1426. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ren ZH, Tong YH, Xu W, Ma J and Chen Y:
Tanshinone II A attenuates inflammatory responses of rats with
myocardial infarction by reducing MCP-1 expression. Phytomedicine.
17:212–218. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ota R, Kurihara C, Tsou TL, Young WL,
Yeghiazarians Y, Chang M, Mobashery S, Sakamoto A and Hashimoto T:
Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in flow-induced outward vascular
remodeling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 29:1547–1558. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jin D, Sheng J, Yang X and Gao B: Matrix
metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases
expression in human cerebral ruptured and unruptured aneurysm. Surg
Neurol. 68 (Suppl):S11–S16. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nuki Y, Matsumoto MM, Tsang E, Young WL,
van Rooijen N, Kurihara C and Hashimoto T: Roles of macrophages in
flow-induced outward vascular remodeling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
29:495–503. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pannu H, Kim DH, Guo D, King TM, Van
Ginhoven G, Chin T, Chang K, Qi Y, Shete S and Milewicz DM: The
role of MMP-2 and MMP-9 polymorphisms in sporadic intracranial
aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 105:418–423. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fujiwara N and Kobayashi K: Macrophages in
inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 4:281–286. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|