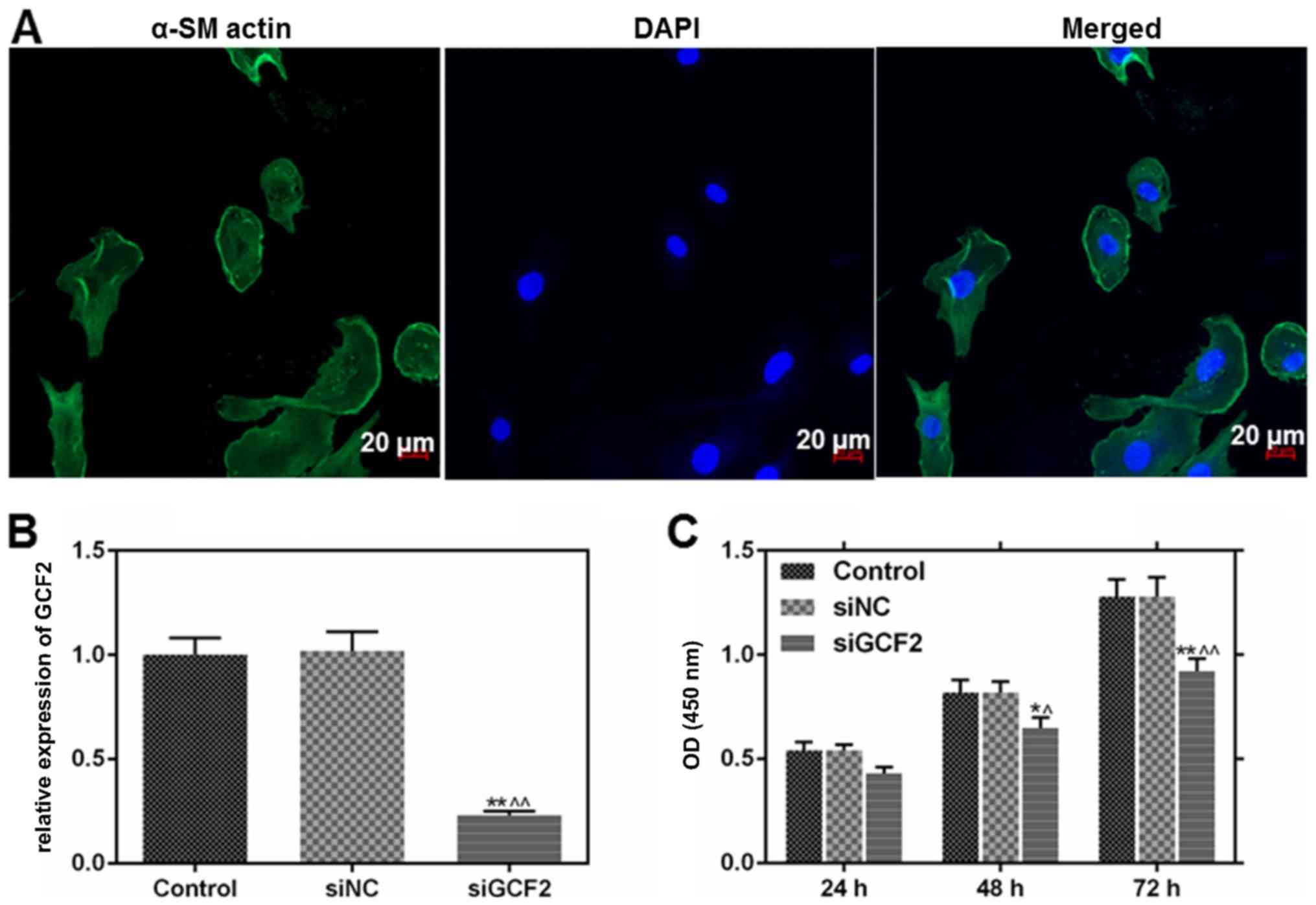
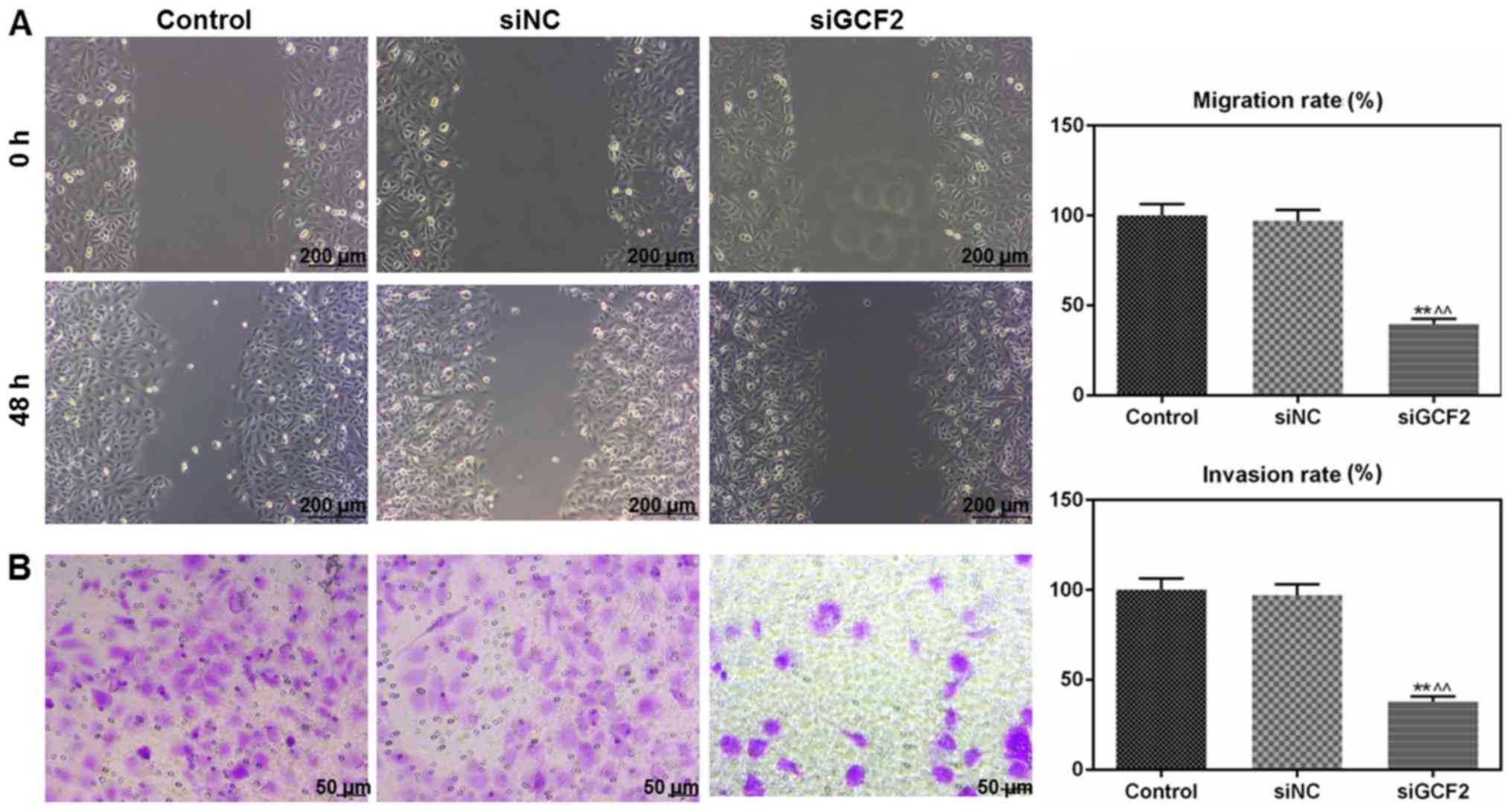
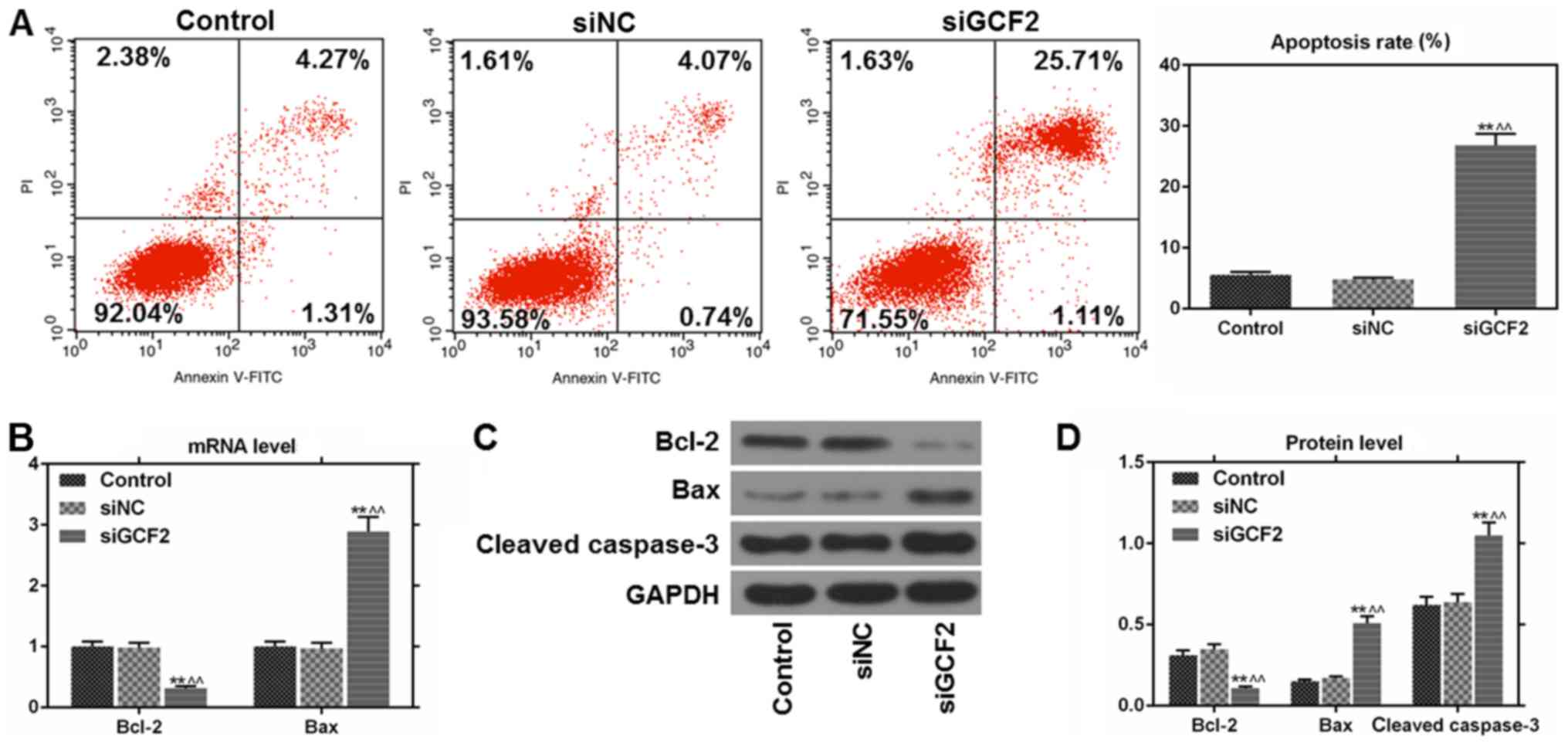
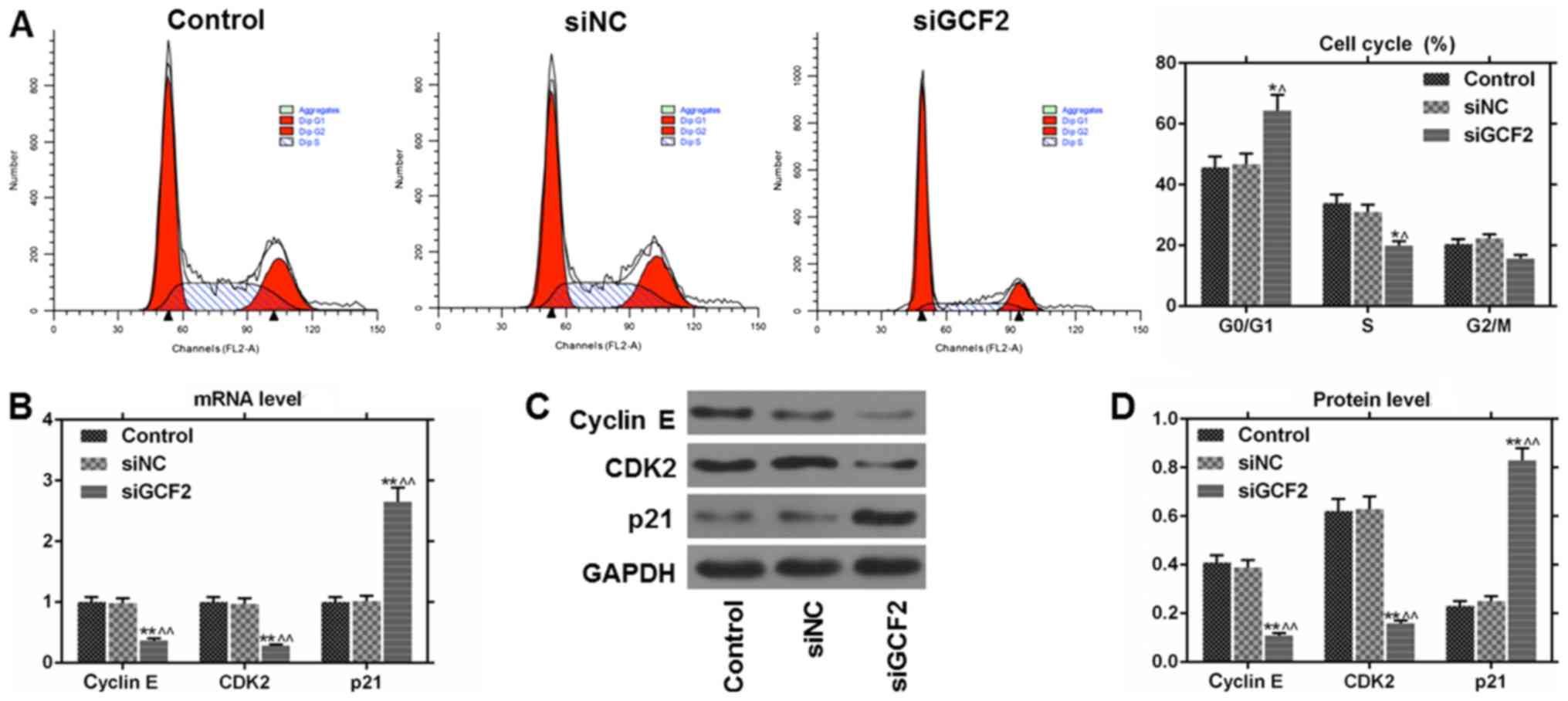
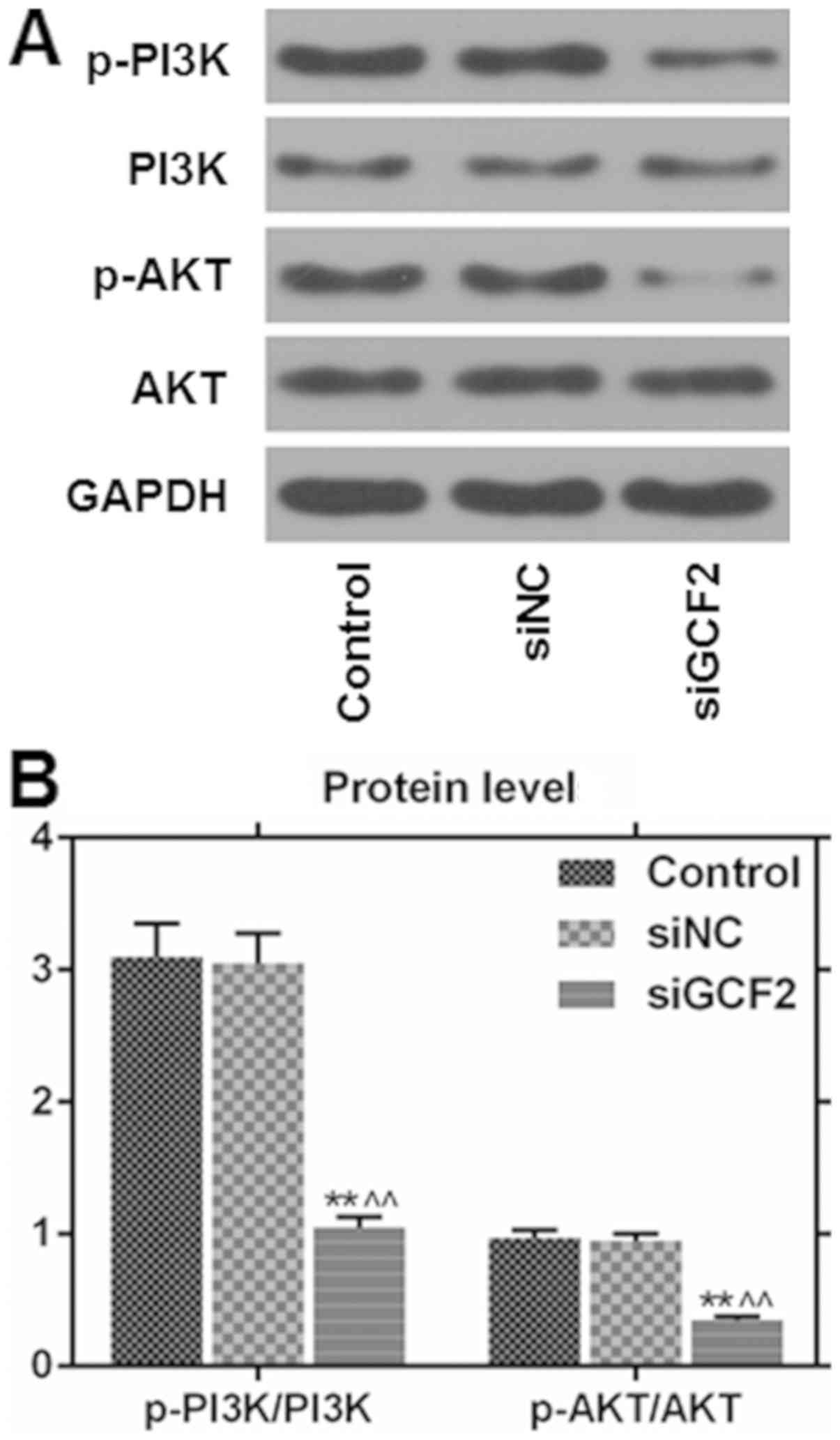
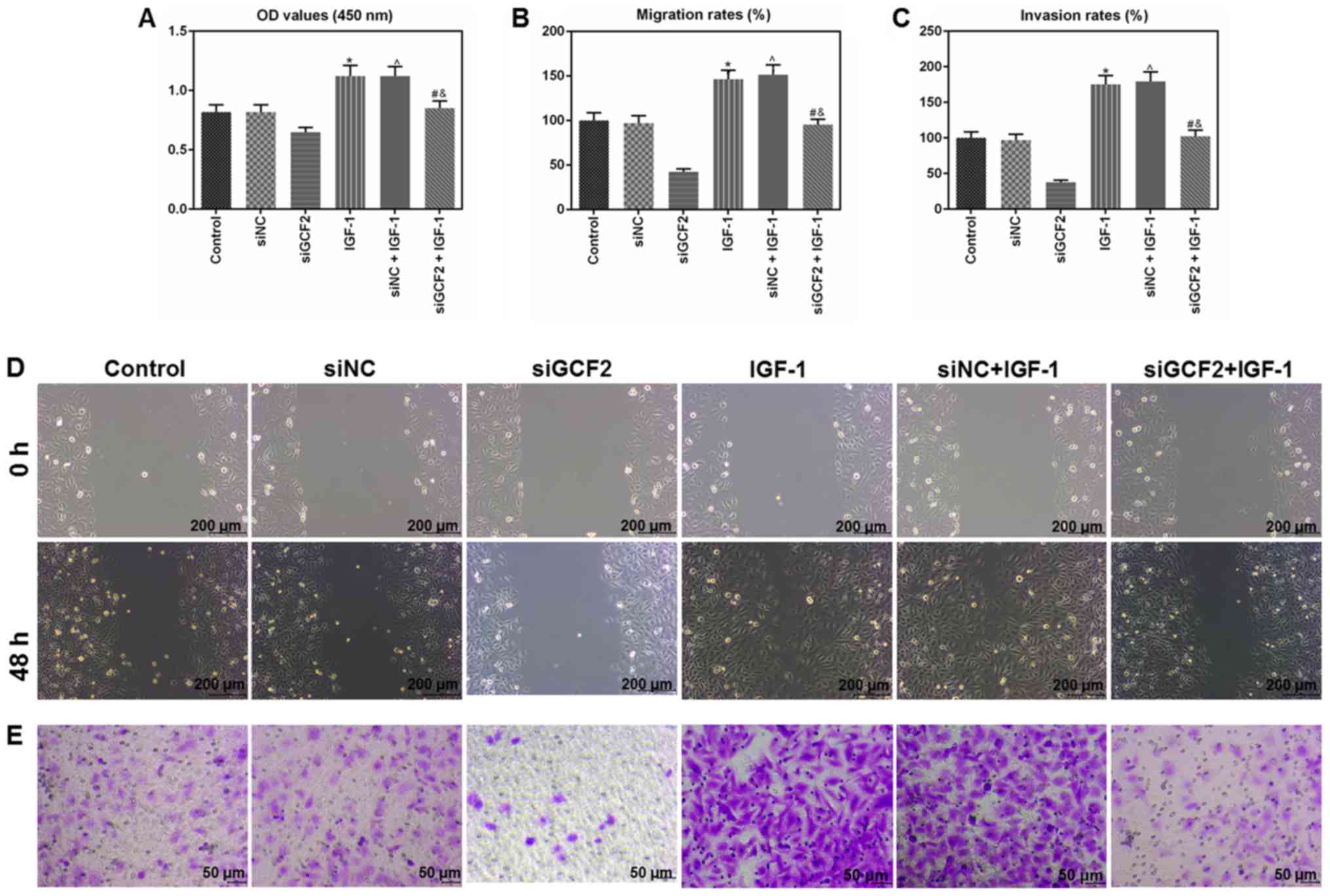
|
1
|
Wang D, Uhrin P, Mocan A, Waltenberger B,
Breuss JM, Tewari D, Mihaly-Bison J, Huminiecki Ł, Starzyński RR,
Tzvetkov NT, et al: Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation as a
therapeutic target. Part 1: Molecular targets and pathways.
Biotechnol Adv. 36:1586–1607. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Alexander MR and Owens GK: Epigenetic
control of smooth muscle cell differentiation and phenotypic
switching in vascular development and disease. Annu Rev Physiol.
74:13–40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Francis DJ, Parish CR, McGarry M, Santiago
FS, Lowe HC, Brown KJ, Bingley JA, Hayward IP, Cowden WB, Campbell
JH, et al: Blockade of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation
and intimal thickening after balloon injury by the sulfated
oligosaccharide PI-88: Phosphomannopentaose sulfate directly binds
FGF-2, blocks cellular signaling, and inhibits proliferation. Circ
Res. 92:e70–77. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Owens GK, Kumar MS and Wamhoff BR:
Molecular regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation
in development and disease. Physiol Rev. 84:767–801. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gabbiani G, Schmid E, Winter S, Chaponnier
C, de Ckhastonay C, Vandekerckhove J, Weber K and Franke WW:
Vascular smooth muscle cells differ from other smooth muscle cells:
Predominance of vimentin filaments and a specific alpha-type actin.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 78:298–302. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hayashi K, Takahashi M, Nishida W, Yoshida
K, Ohkawa Y, Kitabatake A, Aoki J, Arai H and Sobue K: Phenotypic
modulation of vascular smooth muscle cells induced by unsaturated
lysophosphatidic acids. Circ Res. 89:251–258. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Finney AC and Orr AW: Guidance molecules
in vascular smooth muscle. Front Physiol. 9:13112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Low EL, Baker AH and Bradshaw AC: TGFβ,
smooth muscle cells and coronary artery disease: A review. Cell
Signal. 53:90–101. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rikiyama T, Curtis J, Oikawa M, Zimonjic
DB, Popescu N, Murphy BA, Wilson MA and Johnson AC: GCF2:
Expression and molecular analysis of repression. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1629:15–25. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ohtsuka H, Oikawa M, Ariake K, Rikiyama T,
Motoi F, Katayose Y, Unno M and Johnson AC: GC-binding factor 2
interacts with dishevelled and regulates Wnt signaling pathways in
human carcinoma cell lines. Int J Cancer. 129:1599–1610. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Reed AL, Yamazaki H, Kaufman JD,
Rubinstein Y, Murphy B and Johnson AC: Molecular cloning and
characterization of a transcription regulator with homology to
GC-binding factor. J Biol Chem. 273:21594–21602. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li JP, Cao NX, Jiang RT, He SJ, Huang TM,
Wu B, Chen DF, Ma P, Chen L, Zhou SF, et al: Knockdown of
GCF2/LRRFIP1 by RNAi causes cell growth inhibition and increased
apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:2753–2758. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chilakamarthi U, Koteshwar D, Jinka S,
Vamsi Krishna N, Sridharan K, Nagesh N and Giribabu L: Novel
amphiphillic G-quadruplex binding synthetic derivative of TMPyP4
and its effect on cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis
induction. Biochemistry. 57:6514–6527. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Abbastabar M, Kheyrollah M, Azizian K,
Bagherlou N, Tehrani SS, Maniati M and Karimian A: Multiple
functions of p27 in cell cycle, apoptosis, epigenetic modification
and transcriptional regulation for the control of cell growth: A
double-edged sword protein. DNA Repair (Amst). 69:63–72. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fang H, Yang S, Luo Y, Zhang C, Rao Y, Liu
R, Feng Y and Yu J: Notoginsenoside R1 inhibits vascular smooth
muscle cell proliferation, migration and neointimal hyperplasia
through PI3K/Akt signaling. Sci Rep. 8:75952018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li XG and Wang YB: SRPK1 gene silencing
promotes vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and vascular
remodeling via inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in a
rat model of intracranial aneurysms. CNS Neurosci Ther. 25:233–244.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Very N, Vercoutter-Edouart AS, Lefebvre T,
Hardiville S and El Yazidi-Belkoura I: Cross-Dysregulation of
O-GlcNAcylation and PI3K/AKT/mTOR Axis in human chronic diseases.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:6022018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mi XJ, Hou JG, Wang Z, Han Y, Ren S, Hu
JN, Chen C and Li W: The protective effects of maltol on
cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through the AMPK-mediated PI3K/Akt
and p53 signaling pathways. Sci Rep. 8:159222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Khachigian LM, Santiago FS, Rafty LA, Chan
OL, Delbridge GJ, Bobik A, Collins T and Johnson AC: GC factor 2
represses platelet-derived growth factor A-chain gene transcription
and is itself induced by arterial injury. Circ Res. 84:1258–1267.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Suriano AR, Sanford AN, Kim N, Oh M,
Kennedy S, Henderson MJ, Dietzmann K and Sullivan KE: GCF2/LRRFIP1
represses tumor necrosis factor alpha expression. Mol Cell Biol.
25:9073–9081. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Song B, Liu X, Wang Q, Zhang R, Yang T,
Han Z and Xu Y: Adenovirus-mediated shRNA interference against
HSV-1 replication in vitro. J Neurovirol. 22:799–807. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Iyemere VP, Proudfoot D, Weissberg PL and
Shanahan CM: Vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic plasticity and
the regulation of vascular calcification. J Intern Med.
260:192–210. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang MJ, Zhou Y, Chen L, Wang YQ, Wang X,
Pi Y, Gao CY, Li JC and Zhang LL: An overview of potential
molecular mechanisms involved in VSMC phenotypic modulation.
Histochem Cell Biol. 145:119–130. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang YQ, Chen C, Chen Z, Xu Y, Wang Y,
Xiao BK, Chen SM and Tao ZZ: Indole-3-carbinol inhibits cell
proliferation and induces apoptosis in Hep-2 laryngeal cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 30:227–233. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bennetts PS and Pierce JD: Apoptosis:
Understanding programmed cell death for the CRNA. AANA J.
78:237–245. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shibley IA Jr, Gavigan MD and Pennington
SN: Ethanol's effect on tissue polyamines and ornithine
decarboxylase activity: A concise review. Alcohol Clin Exp Res.
19:209–215. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lin SL, Chang DC, Ying SY, Leu D and Wu
DT: MicroRNA miR-302 inhibits the tumorigenecity of human
pluripotent stem cells by coordinate suppression of the CDK2 and
CDK4/6 cell cycle pathways. Cancer Res. 70:9473–9482. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Narasimha AM, Kaulich M, Shapiro GS, Choi
YJ, Sicinski P and Dowdy SF: Cyclin D activates the Rb tumor
suppressor by mono-phosphorylation. Elife. 32014.
|
|
30
|
Karimian A, Ahmadi Y and Yousefi B:
Multiple functions of p21 in cell cycle, apoptosis and
transcriptional regulation after DNA damage. DNA Repair (Amst).
42:63–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ye G, Fu Q, Jiang L and Li Z: Vascular
smooth muscle cells activate PI3K/Akt pathway to attenuate
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis and autophagy by
secreting bFGF. Biomed Pharmacother. 107:1779–1785. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang Q, Chen L, Zhao Z, Wu Y, Zhong J,
Wen G, Cao R, Zu X and Liu J: HMGA1 mediated high-glucose-induced
vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in diabetes mellitus:
Association between PI3K/Akt signaling and HMGA1 expression. DNA
Cell Biol. 37:389–397. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang Q, Cao Y, Luo Q, Wang P, Shi P, Song
C, E M, Ren J, Fu B and Sun H: The transient receptor potential
vanilloid-3 regulates hypoxia-mediated pulmonary artery smooth
muscle cells proliferation via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell
Prolif. 51:e124362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|