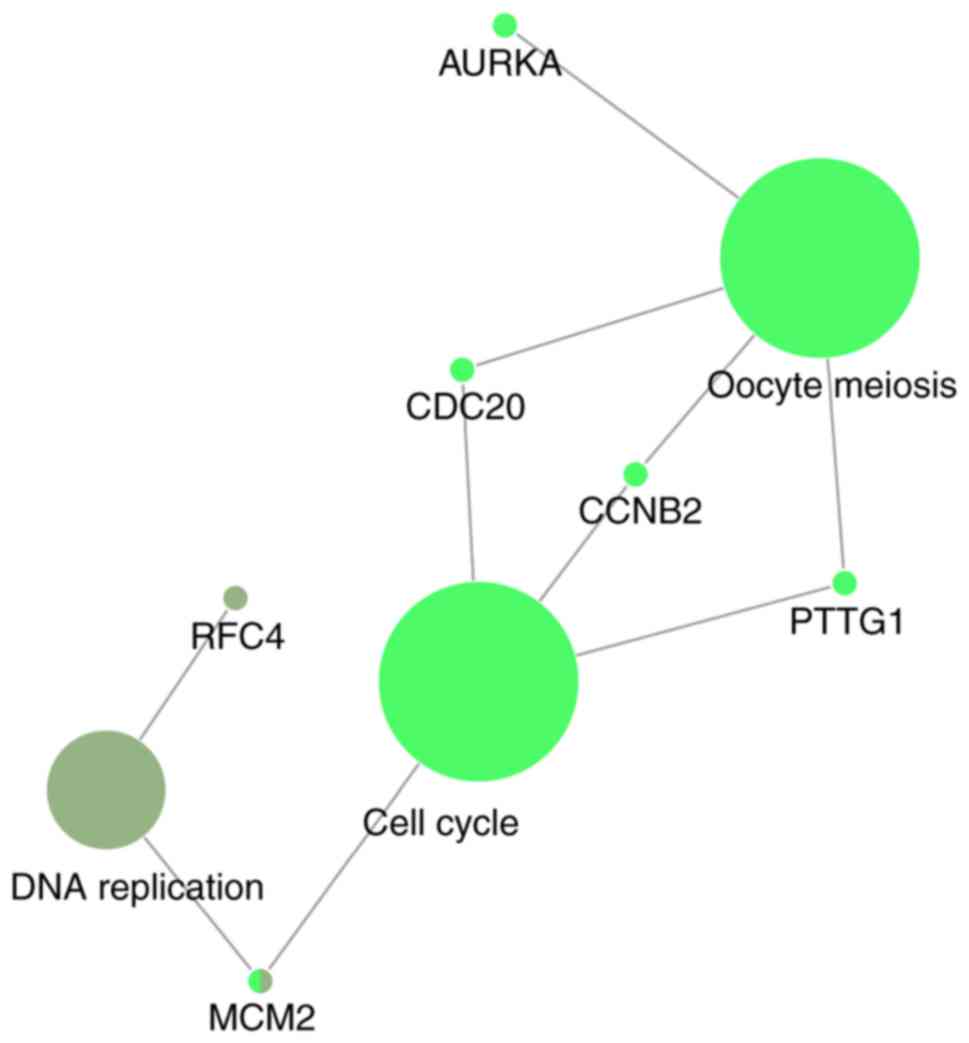
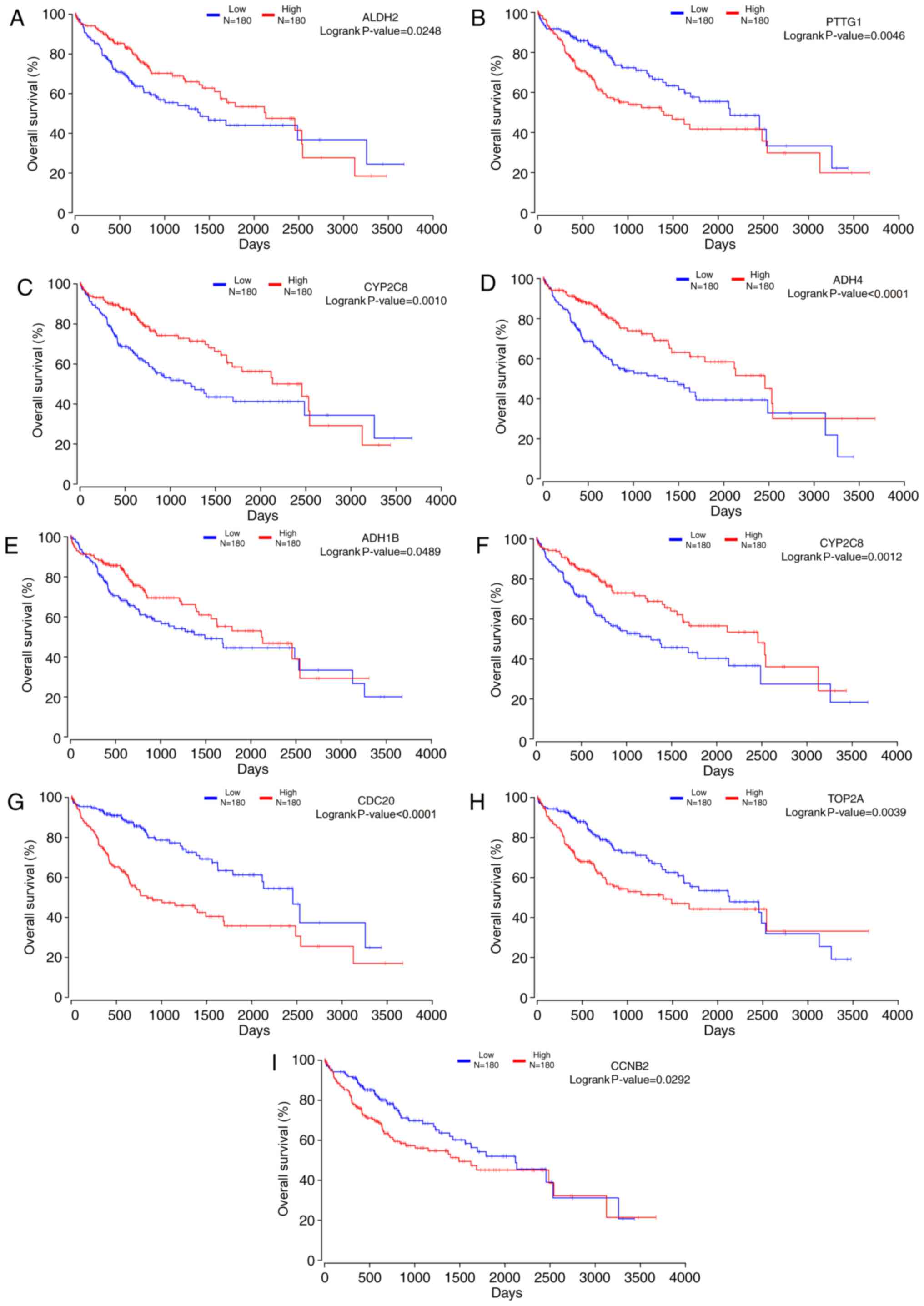
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Walter SR, Thein HH, Gidding HF, Amin J,
Law MG, George J and Dore GJ: Risk factors for hepatocellular
carcinoma in a cohort infected with hepatitis B or C. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:1757–1764. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang JD and Roberts LR: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: A global view. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:448–458.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, Tanaka E, Ohkubo
T, Hasegawa K, Miyagawa S, Sugawara Y, Minagawa M, Takayama T,
Kawasaki S and Makuuchi M: Risk factors contributing to early and
late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma
after hepatectomy. J Hepatol. 38:200–207. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schutte K, Bornschein J and Malfertheiner
P: Hepatocellular carcinoma-epidemiological trends and risk
factors. Dig Dis. 27:80–92. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kononen J, Bubendorf L, Kallioniemi A,
Barlund M, Schraml P, Leighton S, Torhorst J, Mihatsch MJ, Sauter G
and Kallioniemi OP: Tissue microarrays for high-throughput
molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat Med. 4:844–847. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang L, Zang W, Xie D, Ji W, Pan Y, Li Z,
Shen J and Shi Y: Comparison of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC),
cholangiocarcinoma (CC), and combined HCC-CC (CHC) with each other
based on microarray dataset. Tumour Biol. 34:1679–1684. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Grinchuk OV, Yenamandra SP, Iyer R, Singh
M, Lee HK, Lim KH, Chow PK and Kuznetsov VA: Tumor-adjacent tissue
co-expression profile analysis reveals pro-oncogenic ribosomal gene
signature for prognosis of resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol
Oncol. 12:89–113. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mah WC, Thurnherr T, Chow PK, Chung AY,
Ooi LL, Toh HC, Teh BT, Saunthararajah Y and Lee CG: Methylation
profiles reveal distinct subgroup of hepatocellular carcinoma
patients with poor prognosis. PLoS One. 9:e1041582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Irizarry RA, Bolstad BM, Collin F, Cope
LM, Hobbs B and Speed TP: Summaries of Affymetrix GeneChip probe
level data. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:e152003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: Limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
R Core Team R, . A language and
environment for statistical computing. R foundation for statistical
computing. (Vienna). 2013.
|
|
13
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Scardoni G, Petterlini M and Laudanna C:
Analyzing biological network parameters with CentiScaPe.
Bioinformatics. 25:2857–2859. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:22003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H, Charoentong
P, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Fridman WH, Pagès F, Trajanoski Z and
Galon J: ClueGO: A Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally
grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks.
Bioinformatics. 25:1091–1093. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bindea G, Galon J and Mlecnik B: CluePedia
cytoscape plugin: Pathway insights using integrated experimental
and in silico data. Bioinformatics. 29:661–663. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Anaya J: OncoLnc: Linking TCGA survival
data to mRNAs, miRNAs, and lncRNAs. Peer J Comp Sci. 2:e672016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Razumilava N and Gores GJ: Sorafenib for
HCC: A pragmatic perspective. Oncology. 25:300–302. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Killock D: Liver cancer: Regorafenib-A new
RESORCE in HCC. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:70–71. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nebert DW and Gonzalez FJ: P450 genes:
Structure, evolution, and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 56:945–993.
1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chavan H, Li F, Tessman R, Mickey K, Dorko
K, Schmitt T, Kumer S, Gunewardena S, Gaikwad N and Krishnamurthy
P: Functional coupling of ATP-binding cassette transporter Abcb6 to
cytochrome P450 expression and activity in liver. J Biol Chem.
290:7871–7886. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Raunio H, Juvonen R, Pasanen M, Pelkonen
O, Pääkkö P and Soini Y: Cytochrome P4502A6 (CYP2A6) expression in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 27:427–432. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tsunedomi R, Iizuka N, Hamamoto Y,
Uchimura S, Miyamoto T, Tamesa T, Okada T, Takemoto N, Takashima M,
Sakamoto K, et al: Patterns of expression of cytochrome P450 genes
in progression of hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 27:661–667. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu XR, Huang J, Xu ZG, Qian BZ, Zhu ZD,
Yan Q, Cai T, Zhang X, Xiao HS, Qu J, et al: Insight into
hepatocellular carcinogenesis at transcriptome level by comparing
gene expression profiles of hepatocellular carcinoma with those of
corresponding noncancerous liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:15089–15094. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wong N, Yeo W, Wong WL, Wong NL, Chan KY,
Mo FK, Koh J, Chan SL, Chan AT, Lai PB, et al: TOP2A overexpression
in hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with early age onset,
shorter patients survival and chemoresistance. Int J Cancer.
124:644–652. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li J, Gao JZ, Du JL, Huang ZX and Wei LX:
Increased CDC20 expression is associated with development and
progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 45:1547–1555.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fujii T, Nomoto S, Koshikawa K, Yatabe Y,
Teshigawara O, Mori T, Inoue S, Takeda S and Nakao A:
Overexpression of pituitary tumor transforming gene 1 in HCC is
associated with angiogenesis and poor prognosis. Hepatology.
43:1267–1275. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Edman K and Maret W: Alcohol dehydrogenase
genes: Restriction fragment length polymorphisms for ADH4 (pi-ADH)
and ADH5 (chi-ADH) and construction of haplotypes among different
ADH classes. Hum Genet. 90:395–401. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wei RR, Zhang MY, Rao HL, Pu HY, Zhang HZ
and Wang HY: Identification of ADH4 as a novel and potential
prognostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol.
29:2737–2743. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Goode EL, White KL, Vierkant RA, Phelan
CM, Cunningham JM, Schildkraut JM, Berchuck A, Larson MC, Fridley
BL, Olson JE, et al: Xenobiotic-Metabolizing gene polymorphisms and
ovarian cancer risk. Mol Carcinog. 50:397–402. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jin S, Chen J, Chen L, Histen G, Lin Z,
Gross S, Hixon J, Chen Y, Kung C, Chen Y, et al: ALDH2 (E487K)
mutation increases protein turnover and promotes murine
hepatocarcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:9088–9093. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|