|
1
|
Pan H, Cheng L, Yang H, Zou W, Cheng R and
Hu T: Lysophosphatidic acid rescues human dental pulp cells from
ischemia-induced apoptosis. J Endod. 40:217–222. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferraz CC, Henry MA, Hargreaves KM and
Diogenes A: Lipopolysaccharide from Porphyromonas gingivalis
sensitizes capsaicin-sensitive nociceptors. J Endod. 37:45–48.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Akira S, Takeda K and Kaisho T: Toll-like
receptors: Critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity.
Nat Immunol. 2:675–680. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mutoh N, Tani-Ishii N, Tsukinoki K, Chieda
K and Watanabe K: Expression of toll-like receptor 2 and 4 in
dental pulp. J Endod. 33:1183–1186. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Omiya S, Omori Y, Taneike M, Protti A,
Yamaguchi O, Akira S, Shah AM, Nishida K and Otsu K: Toll-like
receptor 9 prevents cardiac rupture after myocardial infarction in
mice independently of inflammation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 311:H1485–H1497. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dias AA, Silva CO, Santos JP,
Batista-Silva LR, Acosta CC, Fontes AN, Pinheiro RO, Lara FA,
Machado AM, Nery JA, et al: DNA sensing via TLR-9 constitutes a
major innate immunity pathway activated during erythema nodosum
leprosum. J Immunol. 197:1905–1913. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pei F, Wang HS, Chen Z and Zhang L:
Autophagy regulates odontoblast differentiation by suppressing
NF-κB activation in an inflammatory environment. Cell Death Dis.
7:e21222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mathiassen SG, De Zio D and Cecconi F:
Autophagy and the cell cycle: A complex landscape. Front Oncol.
7:512017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pradhan AK, Talukdar S, Bhoopathi P, Shen
XN, Emdad L, Das SK, Sarkar D and Fisher PB: mda-7/IL-24 mediates
cancer cell-specific death via regulation of miR-221 and the
beclin-1 axis. Cancer Res. 77:949–959. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Klionsky DJ, Baehrecke EH, Brumell JH, Chu
CT, Codogno P, Cuervo AM, Debnath J, Deretic V, Elazar Z, Eskelinen
EL, et al: A comprehensive glossary of autophagy-related molecules
and processes (2nd edition). Autophagy. 7:1273–1294. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lamark T, Svenning S and Johansen T:
Regulation of selective autophagy: The p62/SQSTM1 paradigm. Essays
Biochem. 61:609–624. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Larsen KB, Lamark T, Øvervatn A,
Harneshaug I, Johansen T and Bjorkoy G: A reporter cell system to
monitor autophagy based on p62/SQSTM1. Autophagy. 6:784–793. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Abdel Fattah E, Bhattacharya A, Herron A,
Safdar Z and Eissa N: Critical role for IL-18 in spontaneous lung
inflammation caused by autophagy deficiency. J Immunol.
194:5407–5416. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Deretic V: Autophagy in immunity and
cell-autonomous defense against intracellular microbes. Immunol
Rev. 240:92–104. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi CS, Shenderov K, Huang NN, Kabat J,
Abu-Asab M, Fitzgerald KA, Sher A and Kehrl JH: Activation of
autophagy by inflammatory signals limits IL-1β production by
targeting ubiquitinated inflammasomes for destruction. Nat Immunol.
13:255–263. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Deretic V, Saitoh T and Akira S: Autophagy
in infection, inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol.
13:722–737. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang HY, Wang WC, Lin PY, Huang CP, Chen
CY and Chen YK: The roles of autophagy and hypoxia in human
inflammatory periapical lesions. Int Endod J. 51 (Suppl
2):e125–e145. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Farges J, Alliot-Licht B, Baudouin C,
Msika P, Bleicher F and Carrouel F: Odontoblast control of dental
pulp inflammation triggered by cariogenic bacteria. Front Physiol.
4:3262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deretic V: Autophagy as an innate immunity
paradigm: Expanding the scope and repertoire of pattern recognition
receptors. Curr Opin Immunol. 24:21–31. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Konisti S, Kiriakidis S and Paleolog EM:
Hypoxia-a key regulator of angiogenesis and inflammation in
rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 8:153–162. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mazure NM and Pouysségur J:
Hypoxia-induced autophagy: Cell death or cell survival? Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 22:177–180. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vellaisamy K, Li G, Ko CN, Zhong HJ,
Fatima S, Kwan HY, Wong CY, Kwong WJ, Tan W, Leung CH and Ma DL:
Cell imaging of dopamine receptor using agonist labeling iridium
(iii) complex. Chem Sci. 9:1119–1125. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu LJ, Wang W, Huang SY, Hong Y, Li G,
Lin S, Tian J, Cai Z, Wang HD, Ma DL and Leung CH: Inhibition of
the Ras/Raf interaction and repression of renal cancer xenografts
in vivo by an enantiomeric iridium(iii) metal-based compound. Chem
Sci. 8:4756–4763. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang W, Vellaisamy K, Li G, Wu C, Ko CN,
Leung CH and Ma DL: Development of a long-lived luminescence probe
for visualizing β-galactosidase in ovarian carcinoma cells. Anal
Chem. 89:11679–11684. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hori Y, Otomura N, Nishida A, Nishiura M,
Umeno M, Suetake I and Kikuchi K: Synthetic-molecule/protein hybrid
probe with fluorogenic switch for live-cell imaging of DNA
methylation. J Am Chem Soc. 140:1686–1690. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang H, Feng Z, Del Signore SJ, Rodal AA
and Xu B: Active probes for imaging membrane dynamics of live cells
with high spatial and temporal resolution over extended time scales
and areas. J Am Chem Soc. 140:3505–3509. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rubinsztein DC, Codogno P and Levine B:
Autophagy modulation as a potential therapeutic target for diverse
diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 11:709–730. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Y, Zhai S, Wang H, Jia Q, Jiang W,
Zhang X, Zhang A, Liu J and Ni L: Absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) in
rat dental pulp mediates the inflammatory response during pulpitis.
J Endod. 39:1390–1394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gibbs JL, Urban R and Basbaum AI:
Paradoxical surrogate markers of dental injury-induced pain in the
mouse. Pain. 154:1358–1367. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
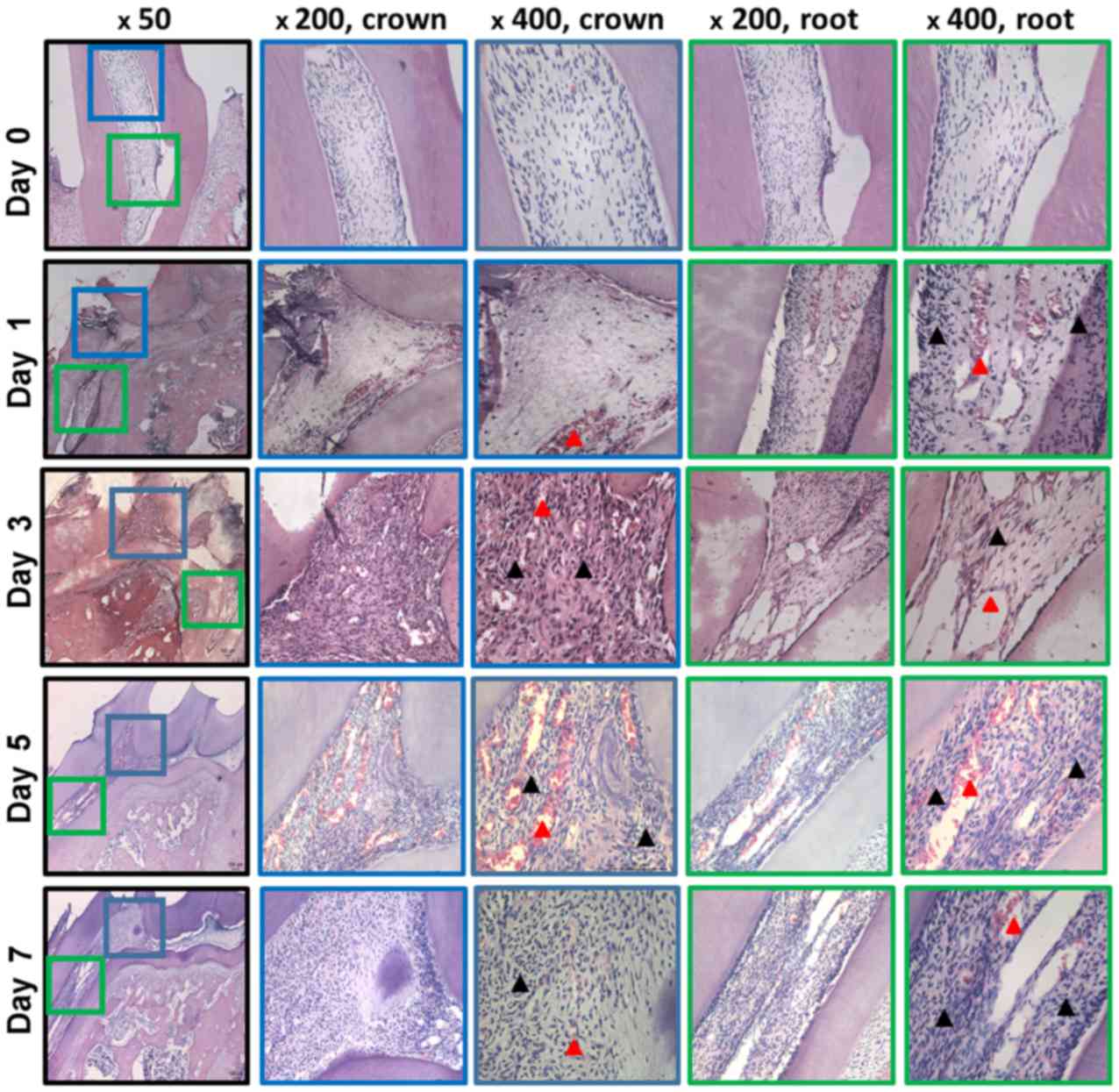
30
|
Ricucci D, Siqueira JF Jr, Loghin S and
Lin LM: Pulp and apical tissue response to deep caries in immature
teeth: A histologic and histobacteriologic study. J Dent. 56:19–32.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimorim T and Levine B:
Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 140:313–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen WR, Liu HB, Chen YD, Sha Y, Ma Q, Zhu
PJ and Mu Y: Melatonin attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury by inhibiting autophagy via an AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 47:2067–2076. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li L, Zhu YQ, Jiang L and Peng W:
Increased autophagic activity in senescent human dental pulp cells.
Int Endod J. 45:1074–1079. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pei F, Lin H, Liu H, Li L, Zhang L and
Chen Z: Dual role of autophagy in lipopolysaccharide-induced
preodontoblastic cells. J Dent Res. 94:175–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhu L, Yang J, Zhang J and Peng B: The
presence of autophagy in human periapical lesions. J Endod.
39:1379–1384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kenmotsu M, Matsuzaka K, Kokubu E, Azuma T
and Inoue T: Analysis of side population cells derived from dental
pulp tissue. Int Endod J. 43:1132–1142. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Matsuoka K, Matsuzaka K, Yoshinari M and
Inoue T: Tenascin-C promotes differentiation of rat dental pulp
cells in vitro. Int Endod J. 46:30–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Duan J, Yu Y, Yu Y, Li Y, Huang P, Zhou X,
Peng S and Sun Z: Silica nanoparticles enhance autophagic activity,
disturb endothelial cell homeostasis and impair angiogenesis. Part
Fibre Toxicol. 11:502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Anand PK, Tait SW, Lamkanfi M, Amer AO,
Nunez G, Pagès G, Pouysségur J, McGargill MA, Green DR and
Kanneganti TD: TLR2 and RIP2 pathways mediate autophagy of Listeria
monocytogenes via extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)
activation. J Biol Chem. 286:42981–42991. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Henault J, Martinez J, Riggs JM, Tian J,
Mehta P, Clarke L, Sasai M, Latz E, Brinkmann MM, Iwasaki A, et al:
Noncanonical autophagy is required for type I interferon secretion
in response to DNA-immune complexes. Immunity. 37:986–997. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu Y, Jagannath C, Liu XD, Sharafkhaneh A,
Kolodziejska KE and Eissa NT: Toll-like receptor 4 is a sensor for
autophagy associated with innate immunity. Immunity. 27:135–144.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|