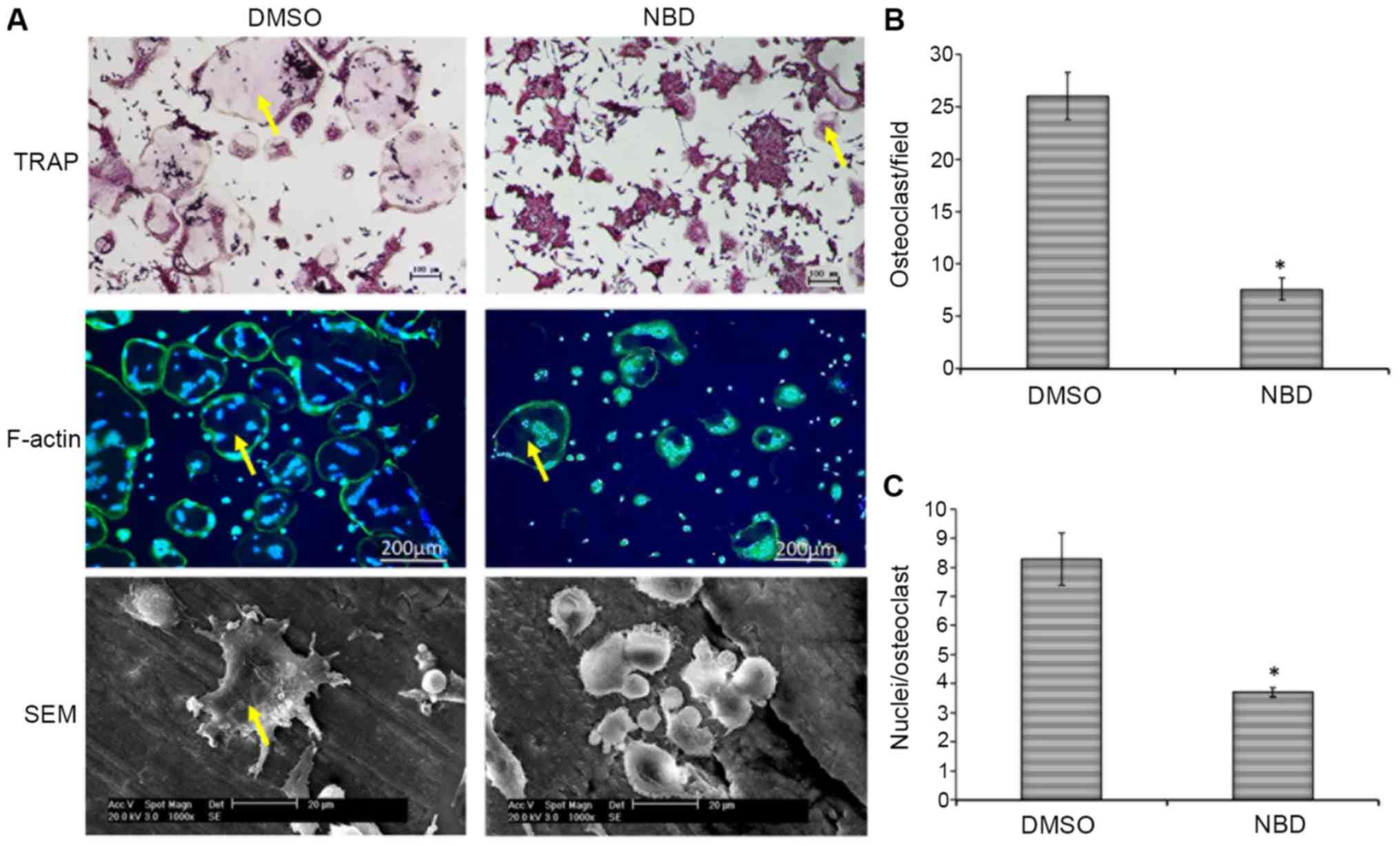
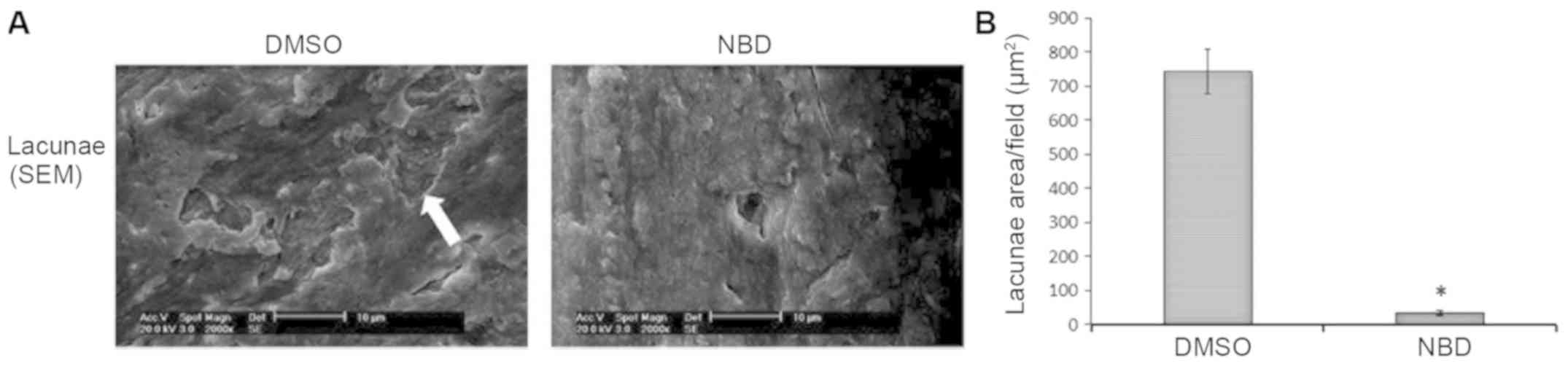
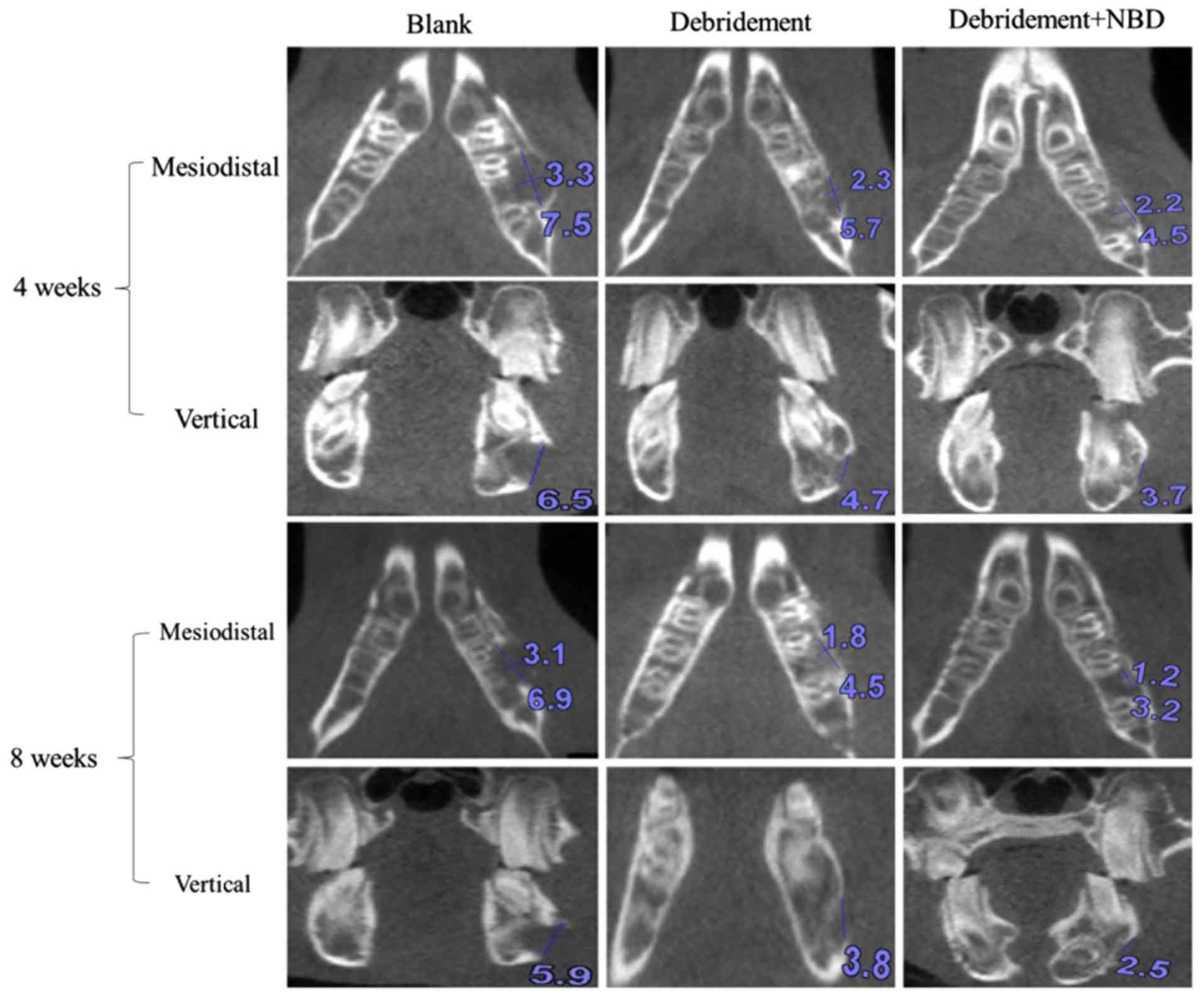
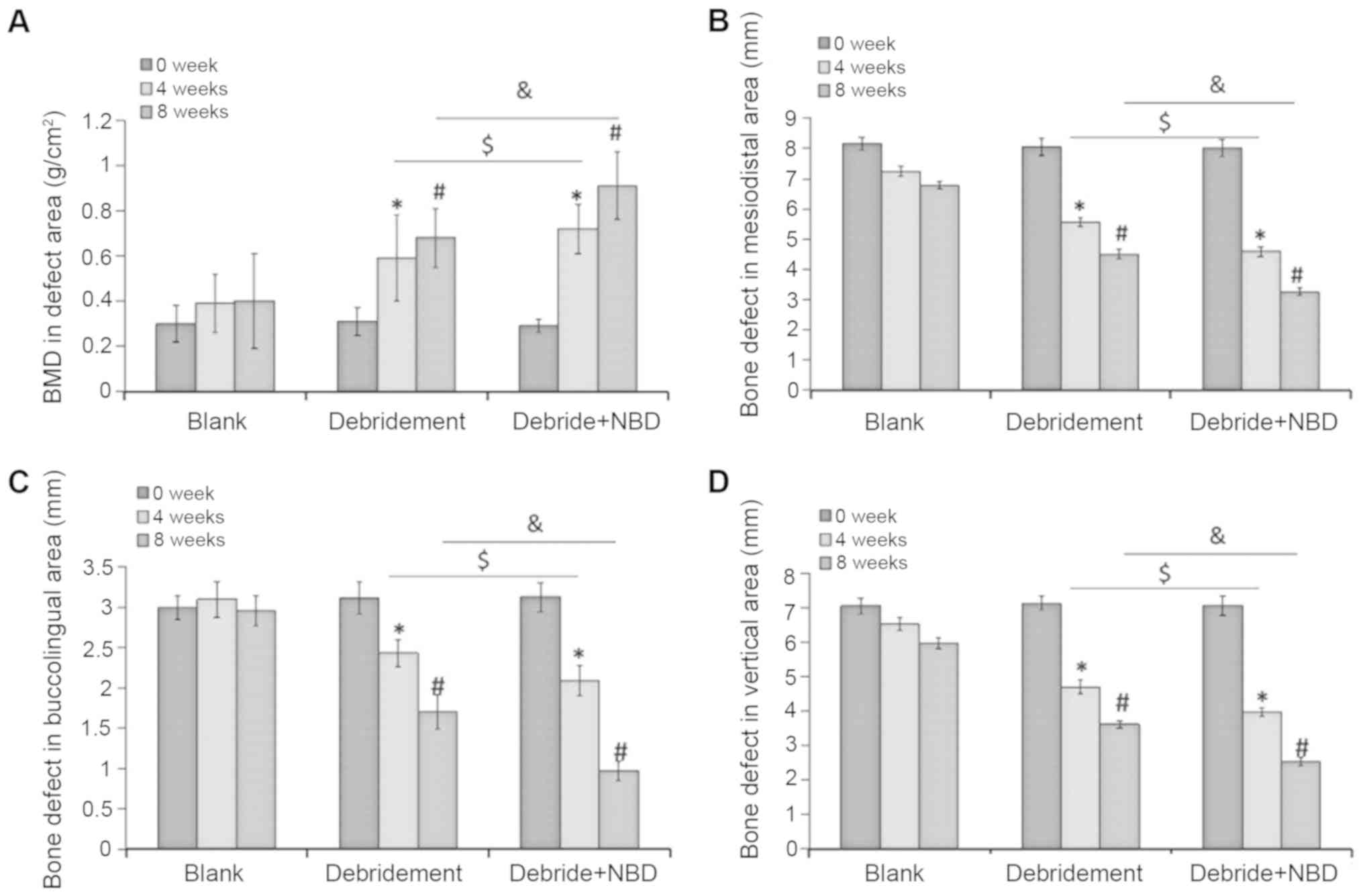
|
1
|
Hajishengallis G, Moutsopoulos NM,
Hajishengallis E and Chavakis T: Immune and regulatory functions of
neutrophils in inflammatory bone loss. Semin Immunol. 28:146–158.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Inzana JA, Schwarz EM, Kates SL and Awad
HA: Biomaterials approaches to treating implant-associated
osteomyelitis. Biomaterials. 81:58–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang R, Braughton KR, Kretschmer D, Bach
TH, Queck SY, Li M, Kennedy AD, Dorward DW, Klebanoff SJ, Peschel
A, et al: Identification of novel cytolytic peptides as key
virulence determinants for community-associated MRSA. Nat Med.
13:1510–1514. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park OJ, Kim J, Yang J, Yun CH and Han SH:
Muramyl dipeptide, a shared structural motif of peptidoglycans, is
a novel inducer of bone formation through induction of Runx2. J
Bone Miner Res. 32:1455–1468. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Verdrengh M, Bokarewa M, Ohlsson C,
Stolina M and Tarkowski A: RANKL-targeted therapy inhibits bone
resorption in experimental Staphylococcus aureus-induced arthritis.
Bone. 46:752–758. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xing L, Xiu Y and Boyce BF: Osteoclast
fusion and regulation by RANKL-dependent and independent factors.
World J Orthop. 3:212–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zuo C, Huang Y, Bajis R, Sahih M, Li YP,
Dai K and Zhang X: Osteoblastogenesis regulation signals in bone
remodeling. Osteoporos Int. 23:1653–1663. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gross C, Weber M, Creutzburg K, Möbius P,
Preidl R, Amann K and Wehrhan F: Osteoclast profile of
medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw secondary to
bisphosphonate therapy: A comparison with osteoradionecrosis and
osteomyelitis. J Transl Med. 15:1282017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aurore V, Caldana F, Blanchard M, Kharoubi
Hess S, Lannes N, Mantel PY, Filgueira L and Walch M:
Silver-nanoparticles increase bactericidal activity and radical
oxygen responses against bacterial pathogens in human osteoclasts.
Nanomedicine. 14:601–607. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
May MJ, D'Acquisto F, Madge LA, Glöckner
J, Pober JS and Ghosh S: Selective inhibition of NF-kappaB
activation by a peptide that blocks the interaction of NEMO with
the IkappaB kinase complex. Science. 289:1550–1554. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
May MJ, Marienfeld RB and Ghosh S:
Characterization of the Ikappa B-kinase NEMO binding domain. J Biol
Chem. 277:45992–46000. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kleppe M, Koche R, Zou L, van Galen P,
Hill CE, Dong L, De Groote S, Papalexi E, Hanasoge Somasundara AV,
Cordner K, et al: Dual targeting of oncogenic activation and
inflammatory signaling increases therapeutic efficacy in
myeloproliferative neoplasms. Cancer Cell. 33:785–787. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Luo G, Li F, Li X, Wang ZG and Zhang B:
TNF-α and RANKL promote osteoclastogenesis by upregulating RANK via
the NF-κB pathway. Mol Med Rep. 17:6605–6611. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Oeckinghaus A and Ghosh S: The NF-kappaB
family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Biol. 1:a0000342009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vancurova I and Vancura A: Regulation and
function of nuclear IκBα in inflammation and cancer. Am J Clin Exp
Immunol. 1:56–66. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dai S, Hirayama T, Abbas S and Abu-Amer Y:
The IkappaB kinase (IKK) inhibitor, NEMO-binding domain peptide,
blocks osteoclastogenesis and bone erosion in inflammatory
arthritis. J Biol Chem. 279:37219–37222. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Strickland I and Ghosh S: Use of cell
permeable NBD peptides for suppression of inflammation. Ann Rheum
Dis. 65 (Suppl 3):iii75–iii82. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jimi E, Aoki K, Saito H, D'Acquisto F, May
MJ, Nakamura I, Sudo T, Kojima T, Okamoto F, Fukushima H, et al:
Selective inhibition of NF-kappa B blocks osteoclastogenesis and
prevents inflammatory bone destruction in vivo. Nat Med.
10:617–624. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Y, Dong G, Jeon HH, Elazizi M, La LB,
Hameedaldeen A, Xiao E, Tian C, Alsadun S, Choi Y and Graves DT:
FOXO1 mediates RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and activity. J
Immunol. 194:2878–2887. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Swarnkar G and Abu-Amer Y: Regulation of
NF-κB signaling in osteoclasts and myeloid progenitors. Methods Mol
Biol. 1280:527–542. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu J, Wu HF, Ang ES, Yip K, Woloszyn M,
Zheng MH and Tan RX: NF-kappaB modulators in osteolytic bone
diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 20:7–17. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chacon GE, Bower DL, Larsen PE, McGlumphy
EA and Beck FM: Heat production by 3 implant drill systems after
repeated drilling and sterilization. J Oral Maxillofac Surg.
64:265–269. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Moskowitz JS, Blaisse MR, Samuel RE, Hsu
HP, Harris MB, Martin SD, Lee JC, Spector M and Hammond PT: The
effectiveness of the controlled release of gentamicin from
polyelectrolyte multilayers in the treatment of Staphylococcus
aureus infection in a rabbit bone model. Biomaterials.
31:6019–6030. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sánchez AR, Sheridan PJ, Lohse C and
Weaver A: Assessment of peripheral dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
measurements in peri-implant bone defects in dogs. J Periodontol.
75:658–662. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kröpil P, Hakimi AR, Jungbluth P, Riegger
C, Rubbert C, Miese F, Lanzman RS, Wild M, Schek A, Scherer A, et
al: Cone beam CT in assessment of tibial bone defect healing: An
animal study. Acad Radiol. 19:320–325. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hotokezaka H, Sakai E, Kanaoka K, Saito K,
Matsuo K, Kitaura H, Yoshida N and Nakayama K: U0126 and PD98059,
specific inhibitors of MEK, accelerate differentiation of RAW264.7
cells into osteoclast-like cells. J Biol Chem. 277:47366–47372.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang Y, Liu X, Dou C, Cao Z, Liu C, Dong S
and Fei J: Staphylococcal protein A promotes osteoclastogenesis
through MAPK signaling during bone infection. J Cell Physiol.
232:2396–2406. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|