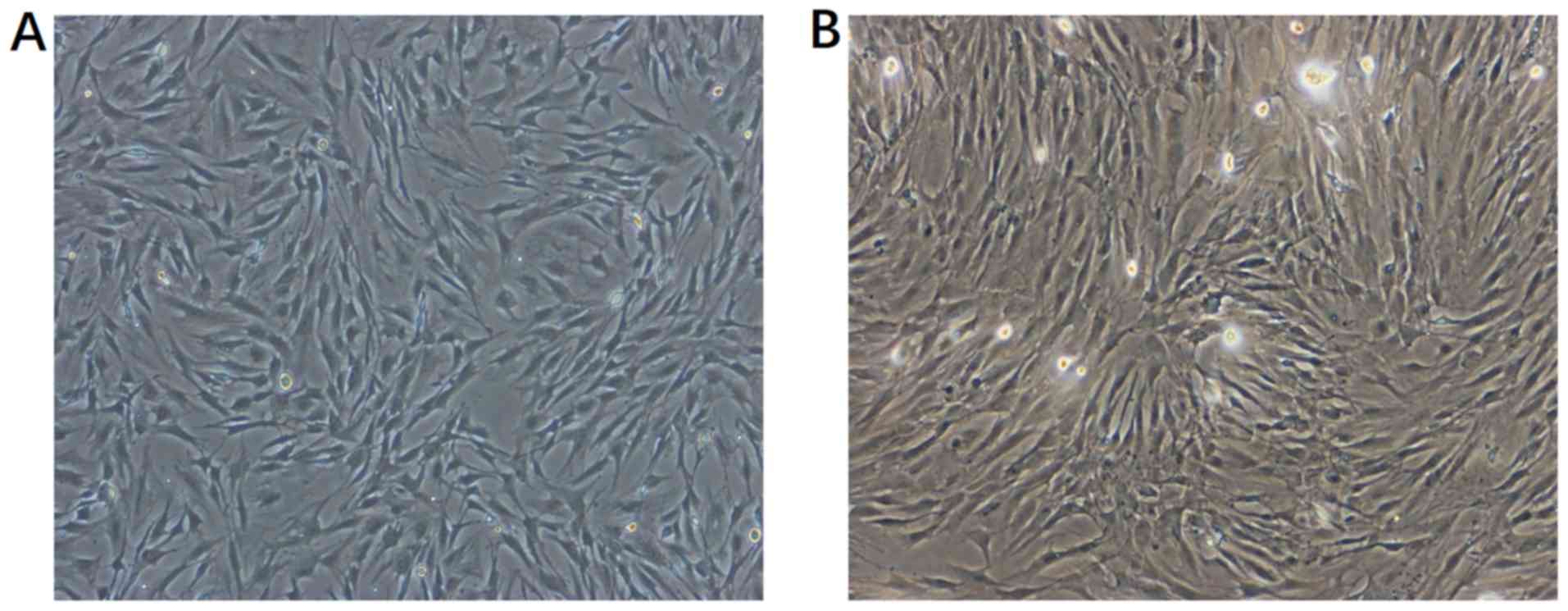
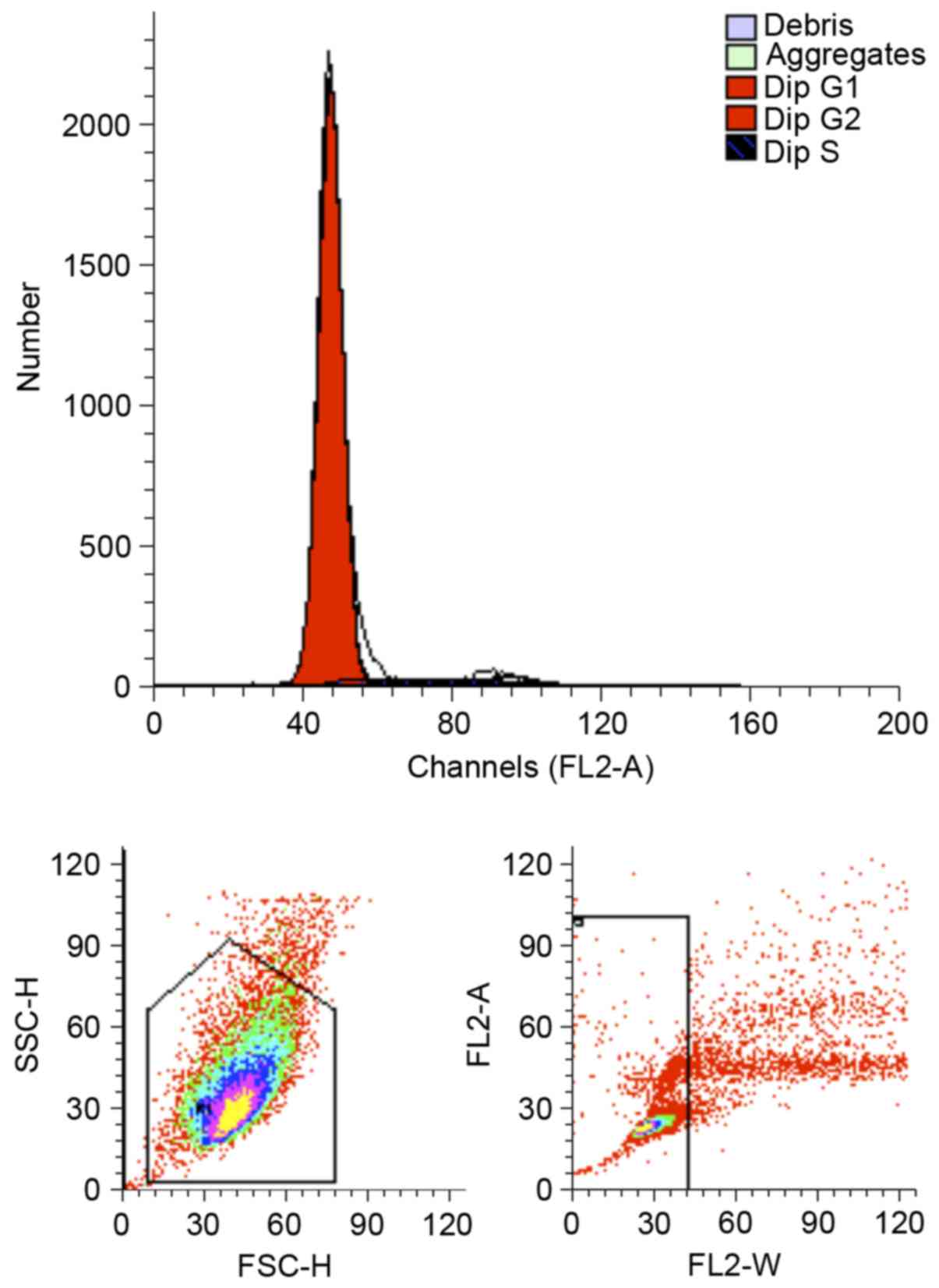
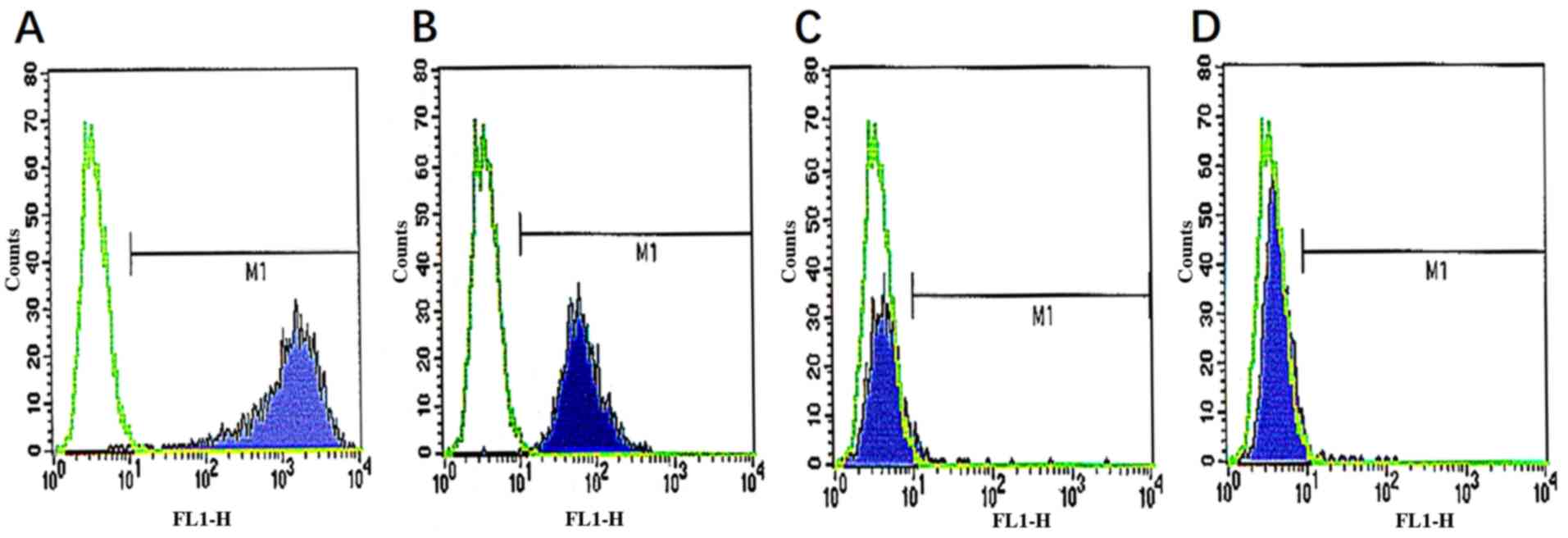
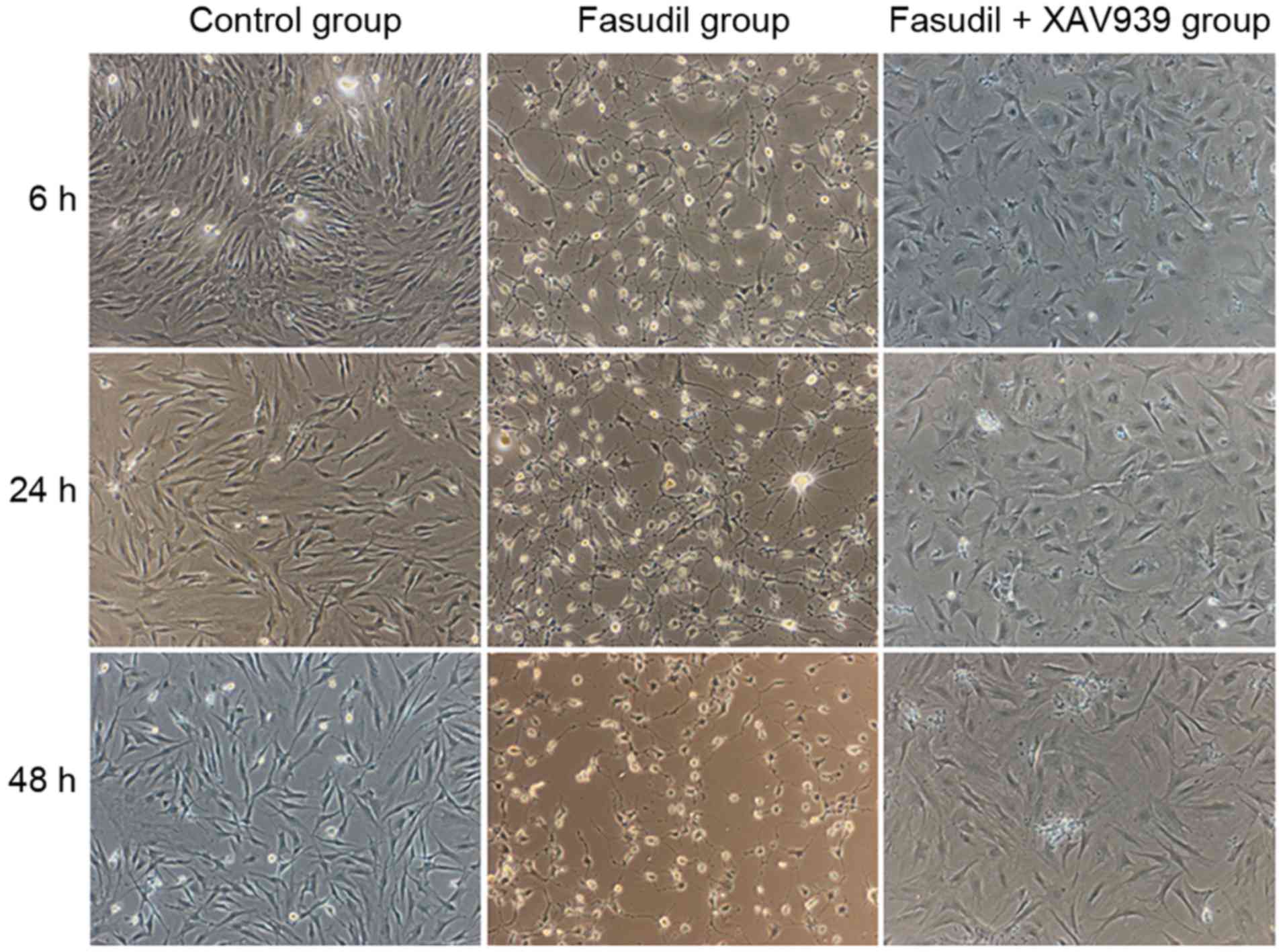
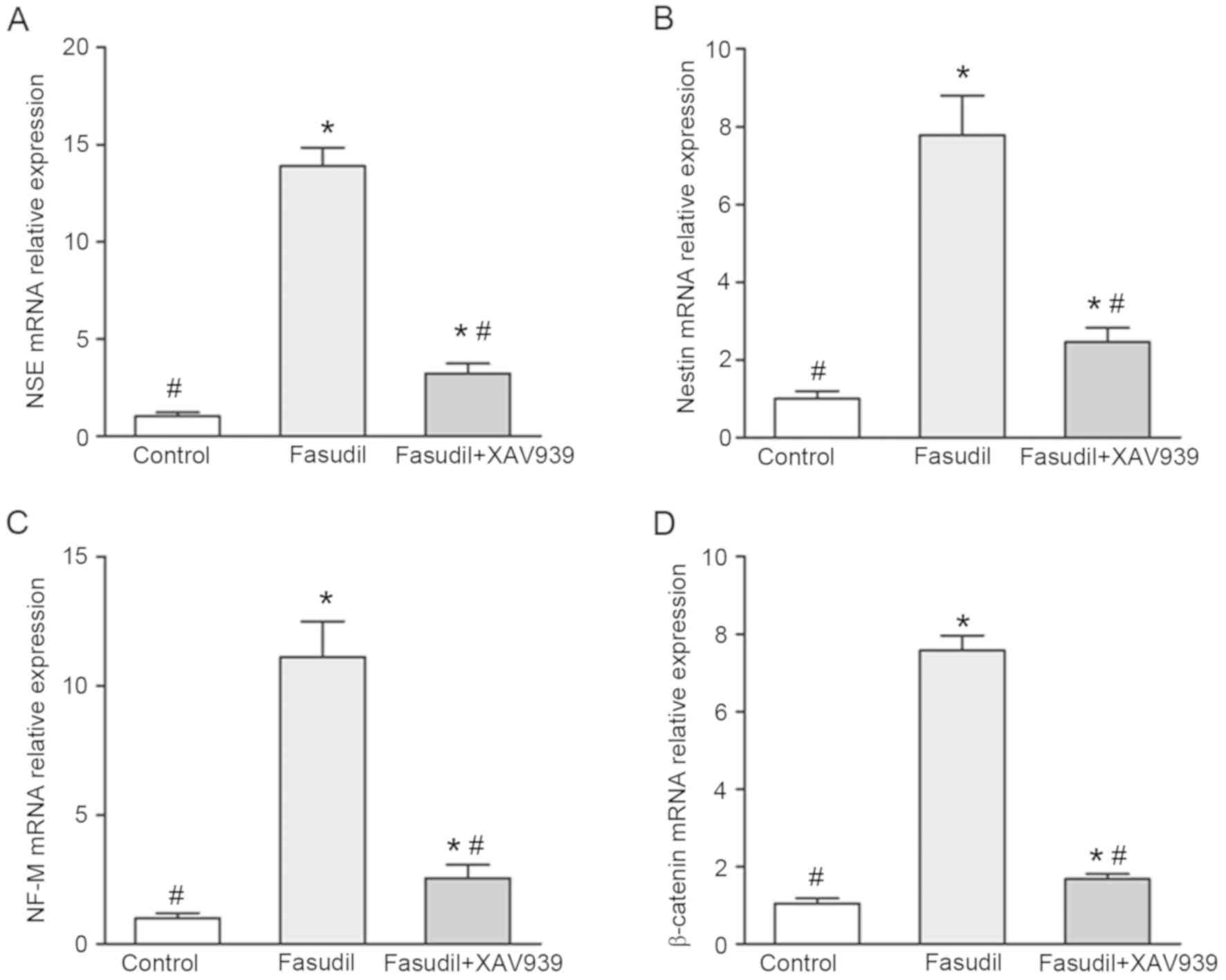
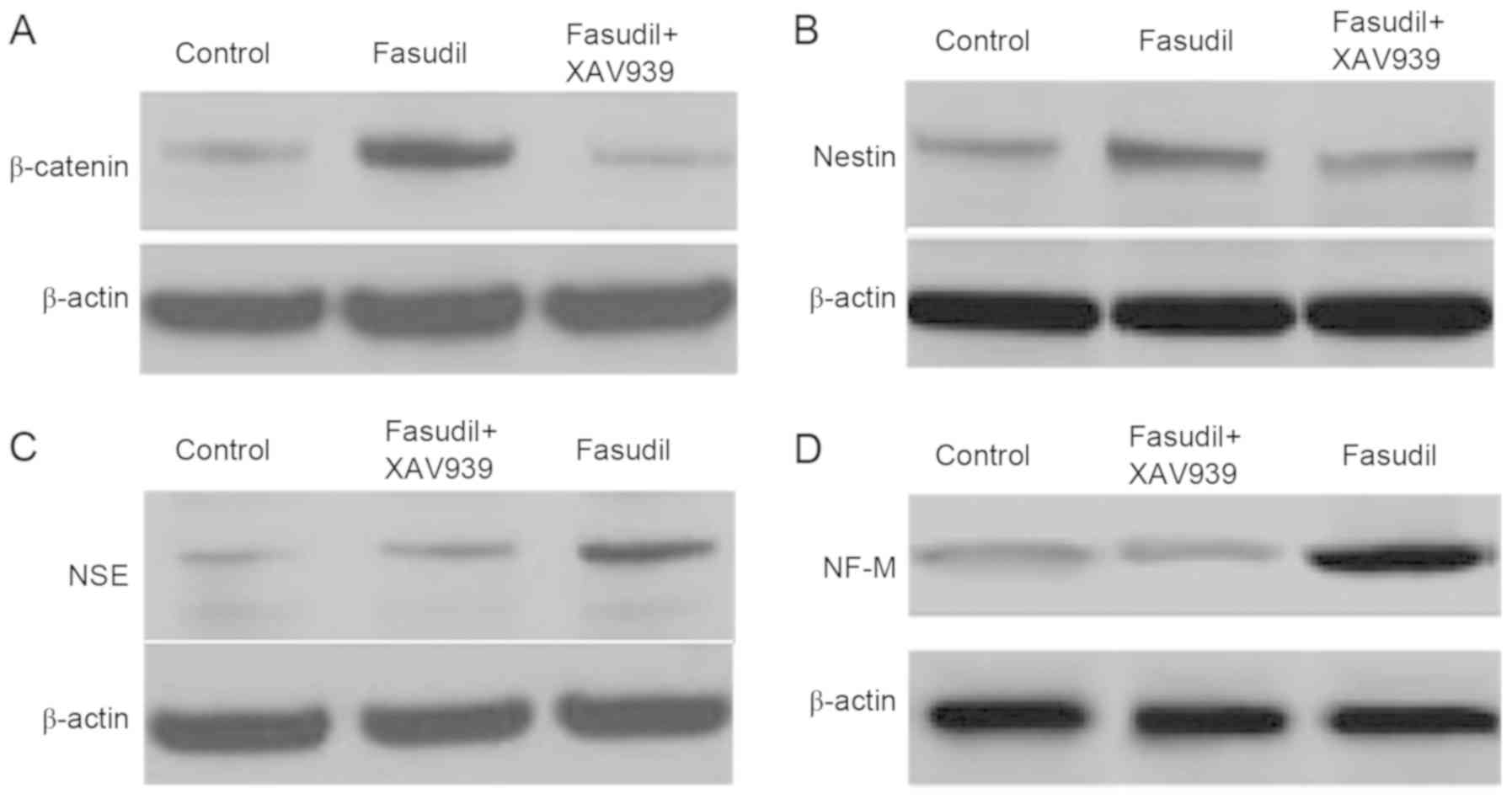
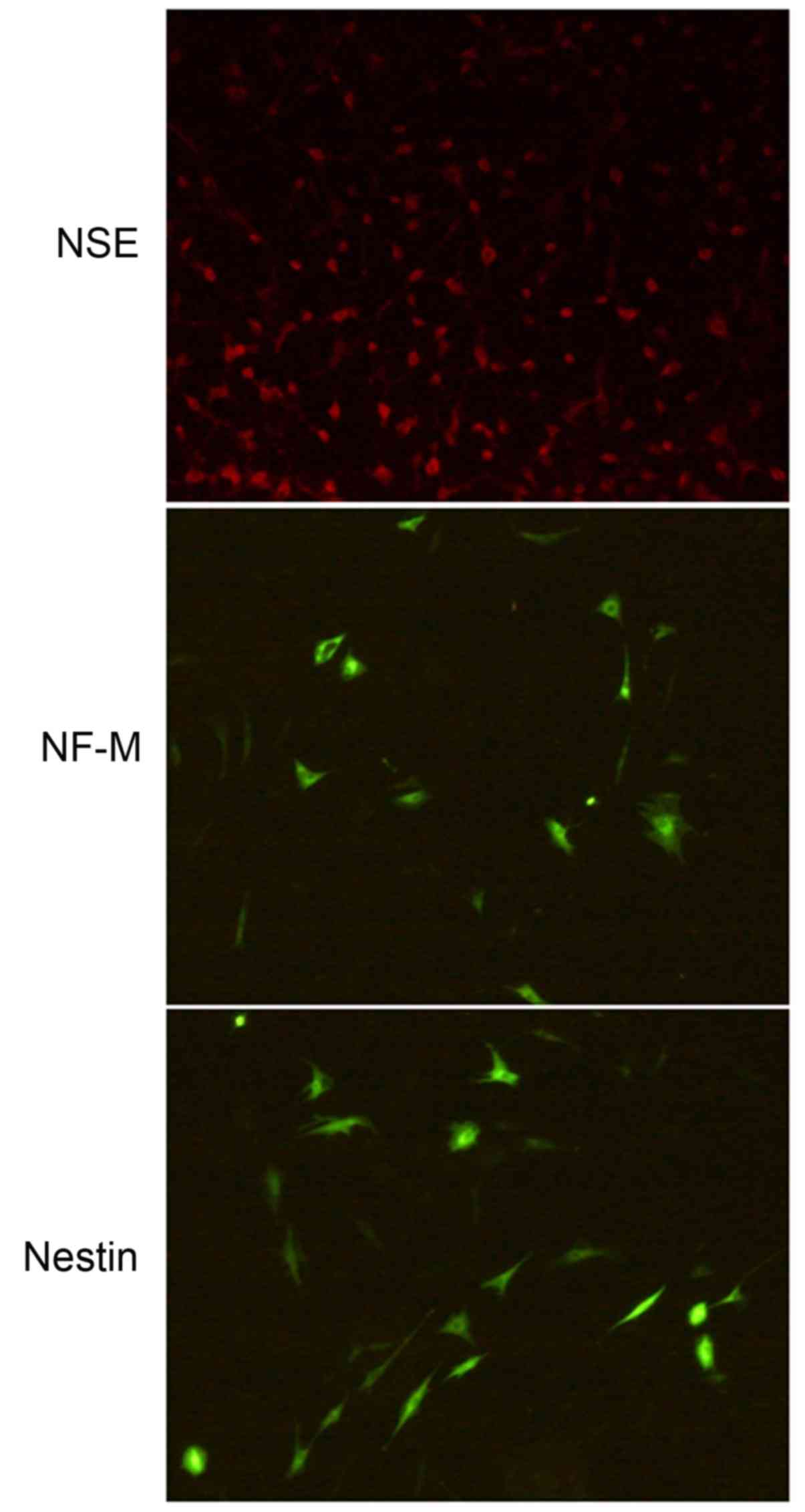
|
1
|
Alvarez-Dolado M, Pardal R, Garcia-Verdugo
JM, Fike JR, Lee HO, Pfeffer K, Lois C, Morrison SJ and
Alvarez-Buylla A: Fusion of bone-marrow-derived cells with Purkinje
neurons, cardiomyocytes and hepatocytes. Nature. 425:968–973. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bjornson CR, Rietze RL, Reynolds BA, Magli
MC and Vescovi AL: Turning brain into blood: A hematopoietic fate
adopted by adult neural stem cells in vivo. Science. 283:534–537.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eglitis MA and Mezey E: Hematopoietic
cells differentiate into both microglia and macroglia in the brains
of adult mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:4080–4085. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Petersen BE, Bowen WC, Patrene KD, Mars
WM, Sullivan AK, Murase N, Boggs SS, Greenberger JS and Goff JP:
Bone marrow as a potential source of hepatic oval cells. Science.
284:1168–1170. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu J, Sun Z, Sun HS, Wu J, Weisel RD,
Keating A, Li ZH, Feng ZP and Li RK: Intravenously administered
bone marrow cells migrate to damaged brain tissue and improve
neural function in ischemic rats. Cell Transplant. 16:993–1005.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yamazaki Y, Kanno H, Maeda K, Yoshida T,
Kobayashi N, Kubo A, Yamaguchi Y and Saito T: Engrafted VHL
peptide-delivered bone marrow stromal cells promote spinal cord
repair in rats. Neuroreport. 21:287–292. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu W, Jiang X, Fu X, Cui S, Du M, Cai Y
and Xu R: Bone marrow stromal cells can be delivered to the site of
traumatic brain injury via intrathecal transplantation in rabbits.
Neurosci Lett. 434:160–164. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chartoff EH, Damez-Werno D, Sonntag KC,
Hassinger L, Kaufmann DE, Peterson J, McPhie D, Cataldo AM and
Cohen BM: Detection of intranasally delivered bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stromal cells in the lesioned mouse brain: A cautionary
report. Stem Cells Int. 2011:5865862011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wakao S, Hayashi T, Kitada M, Kohama M,
Matsue D, Teramoto N, Ose T, Itokazu Y, Koshino K, Watabe H, et al:
Long-term observation of auto-cell transplantation in non-human
primate reveals safety and efficiency of bone marrow stromal
cell-derived Schwann cells in peripheral nerve regeneration. Exp
Neurol. 223:537–547. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cuevas P, Carceller F, Dujovny M,
Garcia-Gómez I, Cuevas B, González-Corrochano R, Diaz-González D
and Reimers D: Peripheral nerve regeneration by bone marrow stromal
cells. Neurol Res. 24:634–638. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shimizu S, Kitada M, Ishikawa H, Itokazu
Y, Wakao S and Dezawa M: Peripheral nerve regeneration by the in
vitro differentiated-human bone marrow stromal cells with Schwann
cell property. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 359:915–920. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Choong PF, Mok PL, Cheong SK, Leong CF and
Then KY: Generating neuron-like cells from BM-derived mesenchymal
stromal cells in vitro. Cytotherapy. 9:170–183. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kondo T, Johnson SA, Yoder MC, Romand R
and Hashino E: Sonic hedgehog and retinoic acid synergistically
promote sensory fate specification from bone marrow-derived
pluripotent stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:4789–4794.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Song S and Sanchez-Ramos J: Preparation of
neural progenitors from bone marrow and umbilical cord blood.
Methods Mol Biol. 438:123–134. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen Y, Teng FY and Tang BL: Coaxing bone
marrow stromal mesenchymal stem cells towards neuronal
differentiation: Progress and uncertainties. Cell Mol Life Sci.
63:1649–1657. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Qin T, Fang F, Song M, Li R, Ma Z and Ma
S: Umbelliferone reverses depression-like behavior in chronic
unpredictable mild stress-induced rats by attenuating neuronal
apoptosis via regulating ROCK/Akt pathway. Behav Brain Res.
317:147–156. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li Q, Huang XJ, He W, Ding J, Jia JT, Fu
G, Wang HX and Guo LJ: Neuroprotective potential of fasudil
mesylate in brain ischemia-reperfusion injury of rats. Cell Mol
Neurobiol. 29:169–180. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Alokam R, Singhal S, Srivathsav GS,
Garigipati S, Puppala S, Sriram D and Perumal Y: Design of dual
inhibitors of ROCK-I and NOX2 as potential leads for the treatment
of neuroinflammation associated with various neurological diseases
including autism spectrum disorder. Mol Biosyst. 11:607–617. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li L, Zhi D, Shen Y, Liu K, Li H and Chen
J: Effects of CC-chemokine receptor 5 on ROCK2 and P-MLC2
expression after focal cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury in
rats. Brain Inj. 30:468–473. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Koyanagi M, Takahashi J, Arakawa Y, Doi D,
Fukuda H, Hayashi H, Narumiya S and Hashimoto N: Inhibition of the
Rho/ROCK pathway reduces apoptosis during transplantation of
embryonic stem cell-derived neural precursors. J Neurosci Res.
86:270–280. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Satoh S, Toshima Y, Hitomi A, Ikegaki I,
Seto M and Asano T: Wide therapeutic time window for Rho-kinase
inhibition therapy in ischemic brain damage in a rat cerebral
thrombosis model. Brain Res. 1193:102–108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ding J, Li QY, Yu JZ, Wang X, Sun CH, Lu
CZ and Xiao BG: Fasudil, a Rho kinase inhibitor, drives
mobilization of adult neural stem cells after hypoxia/reoxygenation
injury in mice. Mol Cell Neurosci. 43:201–208. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee HS, Kim KS, Lim HS, Choi M, Kim HK,
Ahn HY, Shin JC and Joe YA: Priming Wharton's jelly-derived
mesenchymal stromal/stem cells with ROCK inhibitor improves
recovery in an intracerebral hemorrhage model. J Cell Biochem.
116:310–319. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao EY, Wang LD, Wen QQ, Guan WJ, Jing
LJ, Peng T, Wen GQ and Jia YJ: Effect of notch signaling on
differentiation of rat marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neurons
induced by fasudil hydrochloride. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue
Za Zhi. 26:428–432. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao EY, Jia YJ, Wang DM, Wen GQ, Guan WJ,
Jing LJ and Deng YD: Effect of p65 gene inhibited by siRNA on
differention of rat marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neurons.
Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 31:254–258. 2015.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu R, Tang Y, Zang W, Wang Y, Li M, Du Y,
Zhao G and Xu Y: MicroRNA-128 regulates the differentiation of rat
bone mesenchymal stem cells into neuron-like cells by Wnt
signaling. Mol Cell Biochem. 387:151–158. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu Q, Liu L, Duan Y, Wang Y, Xuan X, Zhou
L and Liu W: Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulates neuronal
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 439:297–302. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li L, Tam L, Liu L, Jin T and Ng DS:
Wnt-signaling mediates the anti-adipogenic action of
lysophosphatidic acid through cross talking with the Rho/Rho
associated kinase ROCK) pathway. Biochem Cell Biol. 89:515–521.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao Y, Zhang Q, Xi J, Xiao B, Li Y and Ma
C: Neuroprotective effect of fasudil on inflammation through
PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin dependent pathways in a mice model of
Parkinson's disease. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:2354–2364.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao YF, Zhang Q, Xi JY, Li YH, Ma CG and
Xiao BG: Multitarget intervention of Fasudil in the neuroprotection
of dopaminergic neurons in MPTP-mouse model of Parkinson's disease.
J Neurol Sci. 353:28–37. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Long X, Olszewski M, Huang W and Kletzel
M: Neural cell differentiation in vitro from adult human bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 14:65–69. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ge L, Liu K, Liu Z and Lu M:
Co-transplantation of autologous OM-MSCs and OM-OECs: A novel
approach for spinal cord injury. Rev Neurosci. 27:259–270.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kumagai G, Tsoulfas P, Toh S, McNiece I,
Bramlett HM and Dietrich WD: Genetically modified mesenchymal stem
cells (MSCs) promote axonal regeneration and prevent
hypersensitivity after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 248:369–380.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kopen GC, Prockop DJ and Phinney DG:
Marrow stromal cells migrate throughout forebrain and cerebellum,
and they differentiate into astrocytes after injection into
neonatal mouse brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:10711–10716.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bianco P, Robey PG and Simmons PJ:
Mesenchymal stem cells: Revisiting history, concepts, and assays.
Cell Stem Cell. 2:313–319. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Deng W, Obrocka M, Fischer I and Prockop
DJ: In vitro differentiation of human marrow stromal cells into
early progenitors of neural cells by conditions that increase
intracellular cyclic AMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 282:148–152.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bae KS, Park JB, Kim HS, Kim DS, Park DJ
and Kang SJ: Neuron-like differentiation of bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells. Yonsei Med J. 52:401–412. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim BJ, Seo JH, Bubien JK and Oh YS:
Differentiation of adult bone marrow stem cells into
neuroprogenitor cells in vitro. Neuroreport. 13:1185–1188. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sagara J and Makino N: Glutathione induces
neuronal differentiation in rat bone marrow stromal cells.
Neurochem Res. 33:16–21. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang N, Xie K, Huo S, Zhao J, Zhang S and
Miao J: Suppressing phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C
and elevating ROS level, NADPH oxidase activity and Rb level
induced neuronal differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell
Biochem. 100:1548–1557. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pacary E, Legros H, Valable S, Duchatelle
P, Lecocq M, Petit E, Nicole O and Bernaudin M: Synergistic effects
of CoCl(2) and ROCK inhibition on mesenchymal stem cell
differentiation into neuron-like cells. J Cell Sci. 119:2667–2678.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pacary E, Petit E and Bernaudin M:
Concomitant inhibition of prolyl hydroxylases and ROCK initiates
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and PC12 towards the
neuronal lineage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 377:400–406. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dickson BJ: Rho GTPases in growth cone
guidance. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 11:103–110. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sit ST and Manser E: Rho GTPases and their
role in organizing the actin cytoskeleton. J Cell Sci. 124:679–683.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Begum R, Nur-E-Kamal MS and Zaman MA: The
role of Rho GTPases in the regulation of the rearrangement of actin
cytoskeleton and cell movement. Exp Mol Med. 36:358–366. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Luo L: Rho GTPases in neuronal
morphogenesis. Nat Rev Neurosci. 1:173–180. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bito H, Furuyashiki T, Ishihara H,
Shibasaki Y, Ohashi K, Mizuno K, Maekawa M, Ishizaki T and Narumiya
S: A critical role for a Rho-associated kinase, p160ROCK, in
determining axon outgrowth in mammalian CNS neurons. Neuron.
26:431–441. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hirose M, Ishizaki T, Watanabe N, Uehata
M, Kranenburg O, Moolenaar WH, Matsumura F, Maekawa M, Bito H and
Narumiya S: Molecular dissection of the Rho-associated protein
kinase (p160ROCK)-regulated neurite remodeling in neuroblastoma
N1E-115 cells. J Cell Biol. 141:1625–1636. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Choi BH, Zhu SJ, Kim BY, Huh JY, Lee SH
and Jung JH: Transplantation of cultured bone marrow stromal cells
to improve peripheral nerve regeneration. Int J Oral Maxillofac
Surg. 34:537–542. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shin HK, Salomone S, Potts EM, Lee SW,
Millican E, Noma K, Huang PL, Boas DA, Liao JK, Moskowitz MA and
Ayata C: Rho-kinase inhibition acutely augments blood flow in focal
cerebral ischemia via endothelial mechanisms. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 27:998–1009. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Impellizzeri D, Mazzon E, Paterniti I,
Esposito E and Cuzzocrea S: Effect of fasudil, a selective
inhibitor of Rho kinase activity, in the secondary injury
associated with the experimental model of spinal cord trauma. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 343:21–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Fournier AE, Takizawa BT and Strittmatter
SM: Rho kinase inhibition enhances axonal regeneration in the
injured CNS. J Neurosci. 23:1416–1423. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang S, Kan Q, Sun Y, Han R, Zhang G, Peng
T and Jia Y: Caveolin-1 regulates neural differentiation of rat
bone mesenchymal stem cells into neurons by modulating Notch
signaling. Int J Dev Neurosci. 31:30–35. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zechner D, Fujita Y, Hülsken J, Müller T,
Walther I, Taketo MM, Crenshaw EB III, Birchmeier W and Birchmeier
C: beta-Catenin signals regulate cell growth and the balance
between progenitor cell expansion and differentiation in the
nervous system. Dev Biol. 258:406–418. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|