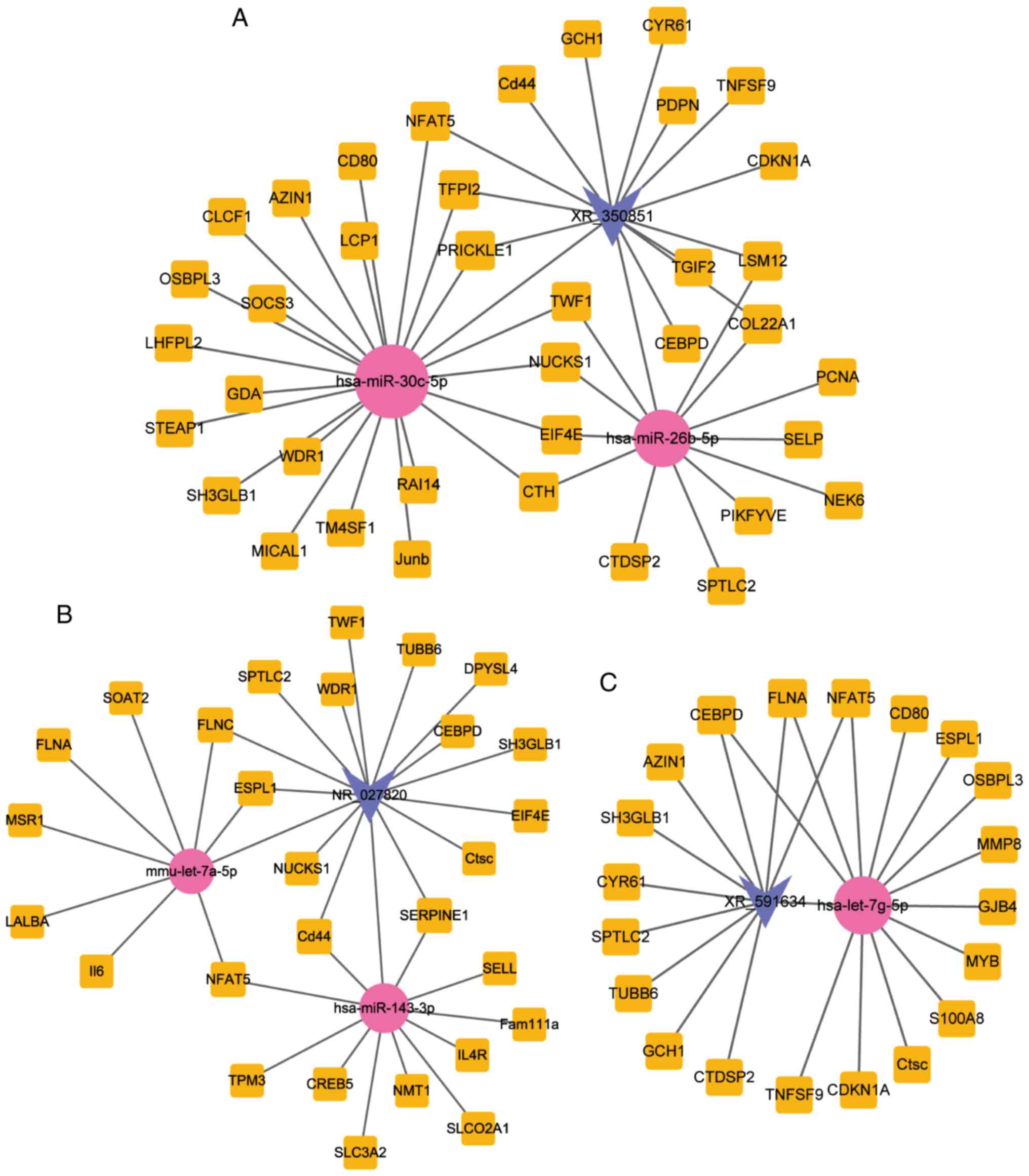
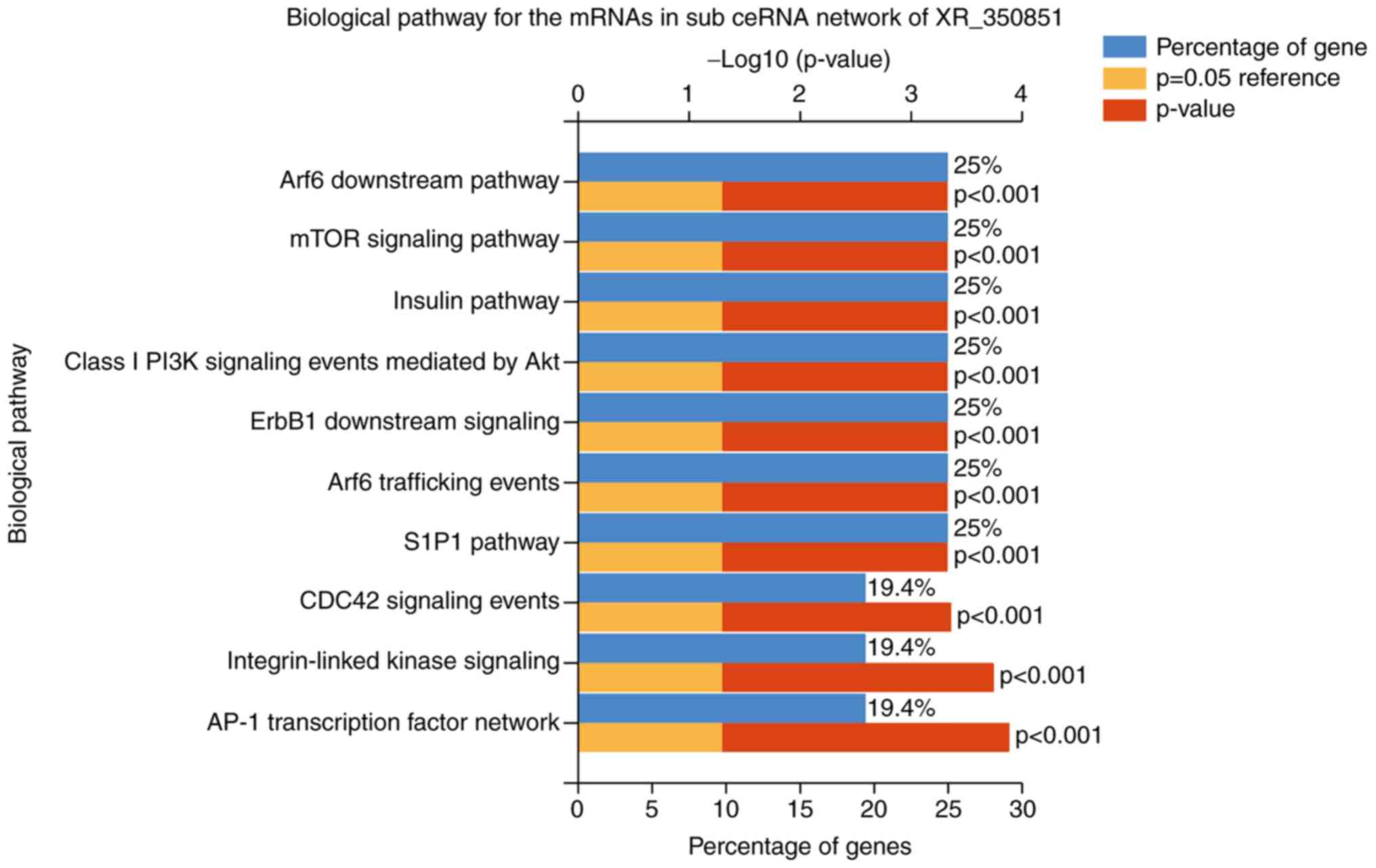
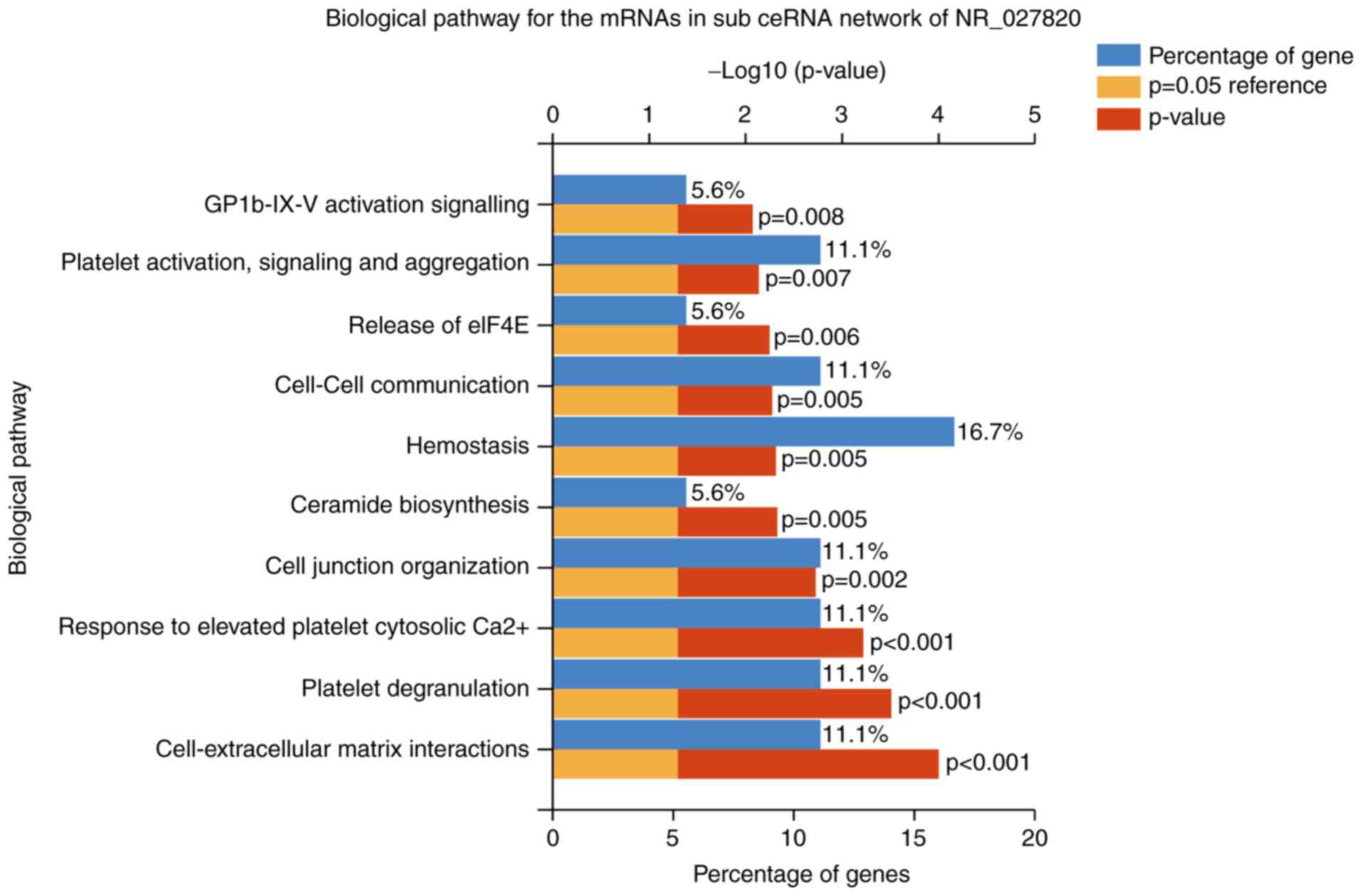
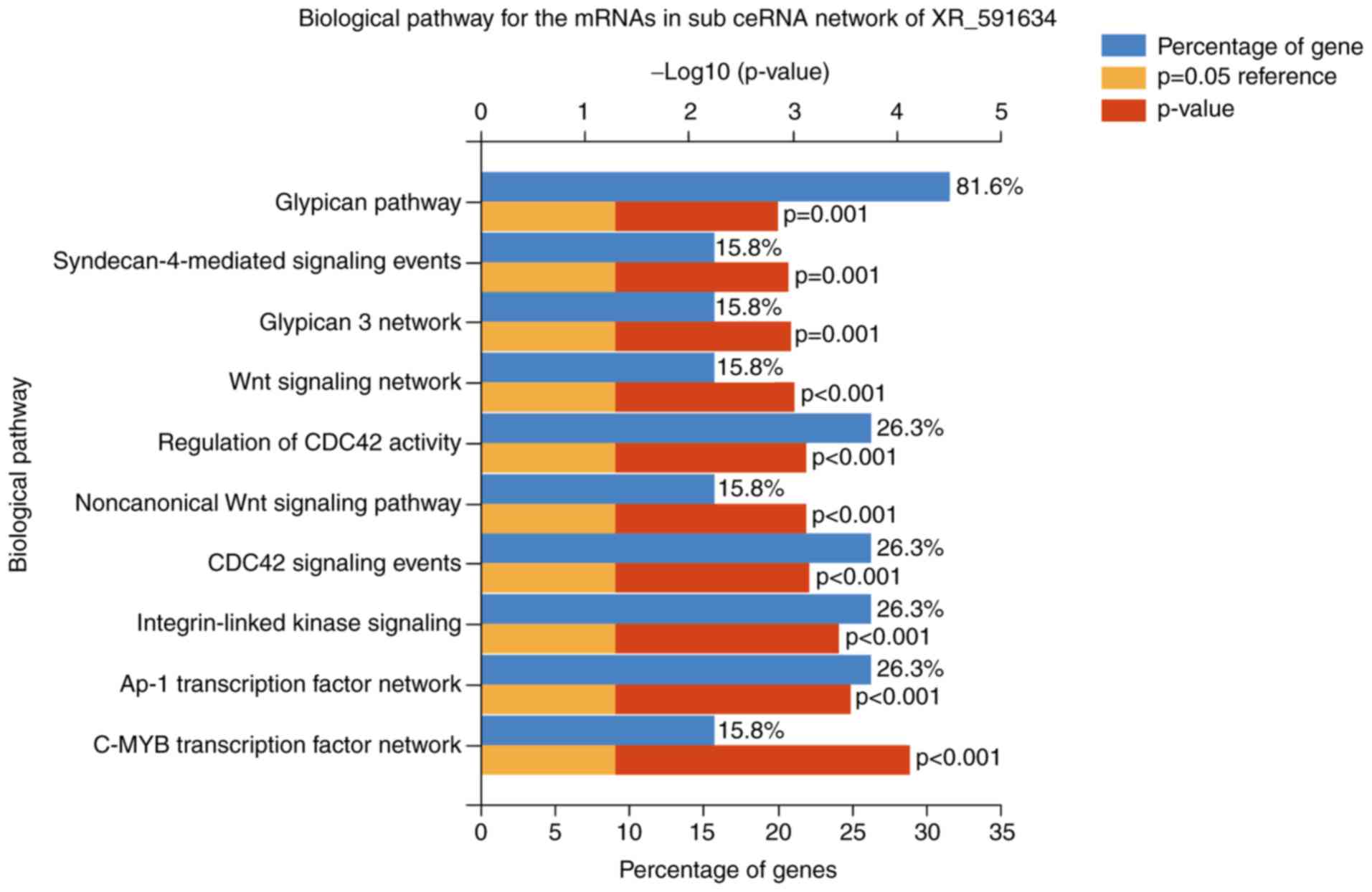
|
1
|
Ramer LM, Ramer MS and Bradbury EJ:
Restoring function after spinal cord injury: Towards clinical
translation of experimental strategies. Lancet Neurol.
13:1241–1256. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Su M, Guan H, Zhang F, Gao Y, Teng X and
Yang W: HDAC6 regulates the chaperone-mediated autophagy to prevent
oxidative damage in injured neurons after experimental spinal cord
injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:72637362016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Walker CL, Walker MJ, Liu NK, Risberg EC,
Gao X, Chen J and Xu XM: Systemic bisperoxovanadium activates
Akt/mTOR, reduces autophagy and enhances recovery following
cervical spinal cord injury. PLoS One. 7:e300122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thuret S, Moon LD and Gage FH: Therapeutic
interventions after spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Neurosci.
7:628–643. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li GL, Brodin G, Farooque M, Funa K, Holtz
A, Wang WL and Olsson Y: Apoptosis and expression of Bcl-2 after
compression trauma to rat spinal cord. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
55:280–289. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Galluzzi L, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Blomgren K
and Kroemer G: Autophagy in acute brain injury. Nat Rev Neurosci.
17:467–484. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ohsumi Y: Historical landmarks of
autophagy research. Cell Res. 24:9–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen ZH, Wang WT, Huang W, Fang K, Sun YM,
Liu SR, Luo XQ and Chen YQ: The lncRNA HOTAIRM1 regulates the
degradation of PML-RARA oncoprotein and myeloid cell
differentiation by enhancing the autophagy pathway. Cell Death
Differ. 24:212–224. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kroemer G: Autophagy: A druggable process
that is deregulated in aging and human disease. J Clin Invest.
125:1–4. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang L, Wang H, Shen Q, Feng L and Jin H:
Long non-coding RNAs involved in autophagy regulation. Cell Death
Dis. 8:e30732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pott J, Kabat AM and Maloy KJ: Intestinal
epithelial cell autophagy is required to protect against
TNF-induced apoptosis during chronic colitis in mice. Cell Host
Microbe. 23:191–202.e4. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Papadakis M, Hadley G, Xilouri M, Hoyte
LC, Nagel S, McMenamin MM, Tsaknakis G, Watt SM, Drakesmith CW,
Chen R, et al: Tsc1 (hamartin) confers neuroprotection against
ischemia by inducing autophagy. Nat Med. 19:351–357. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu F, Wei X, Wu Y, Kong X, Hu A, Tong S,
Liu Y, Gong F, Xie L, Zhang J, et al: Chloroquine promotes the
recovery of acute spinal cord injury by inhibiting
autophagy-associated inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress.
J Neurotrauma. 35:1329–1344. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fritah S, Niclou SP and Azuaje F:
Databases for lncRNAs: A comparative evaluation of emerging tools.
RNA. 20:1655–1665. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gu S, Xie R, Liu X, Shou J, Gu W and Che
X: Long coding RNA XIST contributes to neuronal apoptosis through
the downregulation of AKT phosphorylation and is negatively
regulated by miR-494 in rat spinal cord injury. Int J Mol Sci.
18(pii): E7322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Qiao Y, Peng C, Li J, Wu D and Wang X:
LncRNA MALAT1 is neuroprotective in a rat model of spinal cord
ischemia-reperfusion injury through miR-204 regulation. Curr
Neurovasc Res. 15:211–219. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou HJ, Wang LQ, Wang DB, Yu JB, Zhu Y,
Xu QS, Zheng XJ and Zhan RY: Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 contributes
to inflammatory response of microglia following spinal cord injury
via the modulation of a miR-199b/IKKβ/NF-κB signaling pathway. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 315:C52–C61. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tay Y, Rinn J and Pandolfi PP: The
multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature.
505:344–352. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu J, Li Y, Lu J, Pan T, Ding N, Wang Z,
Shao T, Zhang J, Wang L and Li X: The mRNA related ceRNA-ceRNA
landscape and significance across 20 major cancer types. Nucleic
Acids Res. 43:8169–8182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang X, Sun S, Pu JK, Tsang AC, Lee D,
Man VO, Lui WM, Wong ST and Leung GK: Long non-coding RNA
expression profiles predict clinical phenotypes in glioma.
Neurobiol Dis. 48:1–8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Johnson WE, Li C and Rabinovic A:
Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using
empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics. 8:118–127. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Leek JT, Scharpf RB, Bravo HC, Simcha D,
Langmead B, Johnson WE, Geman D, Baggerly K and Irizarry RA:
Tackling the widespread and critical impact of batch effects in
high-throughput data. Nat Rev Genet. 11:733–739. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Leek JT, Johnson WE, Parker HS, Jaffe AE
and Storey JD: The sva package for removing batch effects and other
unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics.
28:882–883. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang X, Zhu S, Li L, Zhang L, Xian S, Wang
Y and Cheng Y: Identification of differentially expressed genes and
signaling pathways in ovarian cancer by integrated bioinformatics
analysis. Onco Targets Ther. 11:1457–1474. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rehmsmeier M, Steffen P, Hochsmann M and
Giegerich R: Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target
duplexes. RNA. 10:1507–1517. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li J, Ma W, Zeng P, Wang J, Geng B, Yang J
and Cui Q: LncTar: A tool for predicting the RNA targets of long
noncoding RNAs. Brief Bioinform. 16:806–812. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Paraskevopoulou MD, Georgakilas G,
Kostoulas N, Vlachos IS, Vergoulis T, Reczko M, Filippidis C,
Dalamagas T and Hatzigeorgiou AG: DIANA-microT web server v5.0:
Service integration into miRNA functional analysis workflows.
Nucleic Acids Res. 41:(Web Server Issue). W169–W173. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Reczko M, Maragkakis M, Alexiou P, Grosse
I and Hatzigeorgiou AG: Functional microRNA targets in protein
coding sequences. Bioinformatics. 28:771–776. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jiang H, Ma R, Zou S, Wang Y, Li Z and Li
W: Reconstruction and analysis of the lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network
based on competitive endogenous RNA reveal functional lncRNAs in
rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Biosyst. 13:1182–1192. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sun J, Yan J, Yuan X, Yang R, Dan T, Wang
X, Kong G and Gao S: A computationally constructed ceRNA
interaction network based on a comparison of the SHEE and SHEEC
cell lines. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 21:212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Morris JH, Wu A, Yamashita RA,
Marchler-Bauer A and Ferrin TE: cddApp: A Cytoscape app for
accessing the NCBI conserved domain database. Bioinformatics.
31:134–136. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pathan M, Keerthikumar S, Ang CS, Gangoda
L, Quek CY, Williamson NA, Mouradov D, Sieber OM, Simpson RJ, Salim
A, et al: FunRich: An open access standalone functional enrichment
and interaction network analysis tool. Proteomics. 15:2597–2601.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou M, Diao Z, Yue X, Chen Y, Zhao H,
Cheng L and Sun J: Construction and analysis of dysregulated
lncRNA-associated ceRNA network identified novel lncRNA biomarkers
for early diagnosis of human pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget.
7:56383–56394. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jackson A and Zimmermann JB: Neural
interfaces for the brain and spinal cord-restoring motor function.
Nat Rev Neurol. 8:690–699. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Blesch A and Tuszynski MH: Spinal cord
injury: Plasticity, regeneration and the challenge of translational
drug development. Trends Neurosci. 32:41–47. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tsuboyama K, Koyama-Honda I, Sakamaki Y,
Koike M, Morishita H and Mizushima N: The ATG conjugation systems
are important for degradation of the inner autophagosomal membrane.
Science. 354:1036–1041. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sekiguchi A, Kanno H, Ozawa H, Yamaya S
and Itoi E: Rapamycin promotes autophagy and reduces neural tissue
damage and locomotor impairment after spinal cord injury in mice. J
Neurotrauma. 29:946–956. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ge D, Han L, Huang S, Peng N, Wang P,
Jiang Z, Zhao J, Su L, Zhang S, Zhang Y, et al: Identification of a
novel MTOR activator and discovery of a competing endogenous RNA
regulating autophagy in vascular endothelial cells. Autophagy.
10:957–971. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen JF, Wu P, Xia R, Yang J, Huo XY, Gu
DY, Tang CJ, De W and Yang F: STAT3-induced lncRNA HAGLROS
overexpression contributes to the malignant progression of gastric
cancer cells via mTOR signal-mediated inhibition of autophagy. Mol
Cancer. 17:62018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kim YC and Guan KL: mTOR: A pharmacologic
target for autophagy regulation. J Clin Invest. 125:25–32. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zinzalla V, Stracka D, Oppliger W and Hall
MN: Activation of mTORC2 by association with the ribosome. Cell.
144:757–768. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bai L, Mei X, Shen Z, Bi Y, Yuan Y, Guo Z,
Wang H, Zhao H, Zhou Z, Wang C, et al: Netrin-1 improves functional
recovery through autophagy regulation by activating the AMPK/mTOR
signaling pathway in rats with spinal cord injury. Sci Rep.
7:422882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Saiki S, Sasazawa Y, Imamichi Y, Kawajiri
S, Fujimaki T, Tanida I, Kobayashi H, Sato F, Sato S, Ishikawa K,
et al: Caffeine induces apoptosis by enhancement of autophagy via
PI3K/Akt/mTOR/p70S6K inhibition. Autophagy. 7:176–187. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|