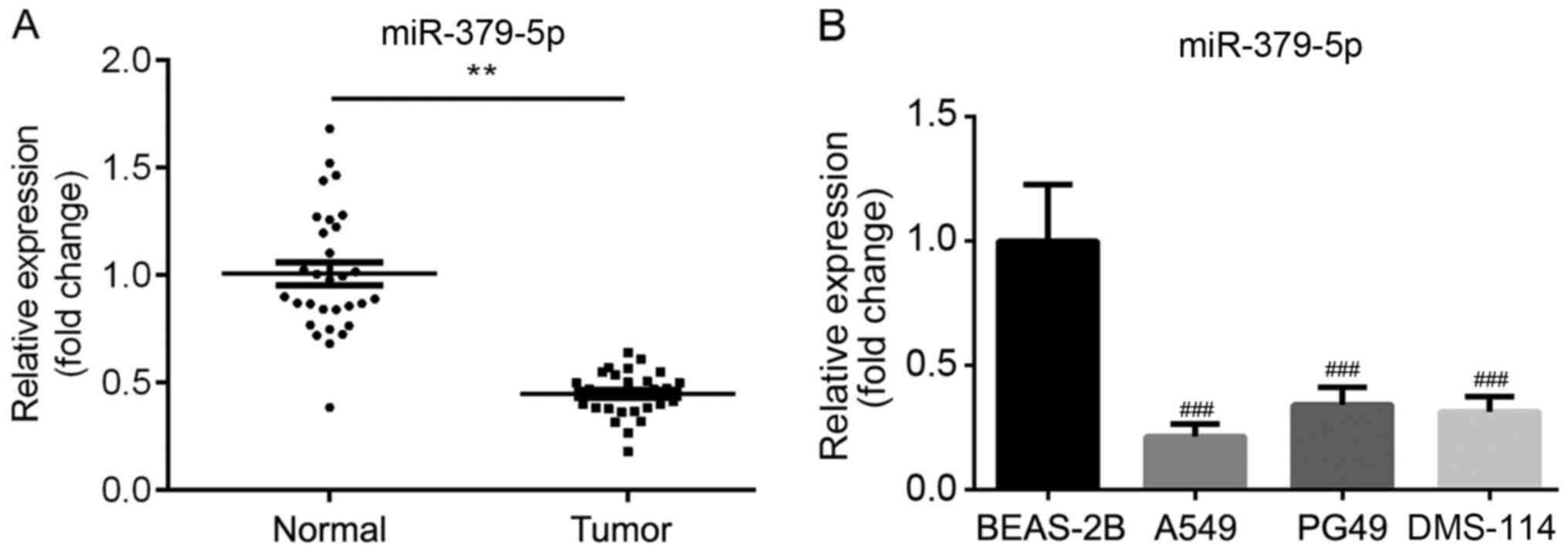
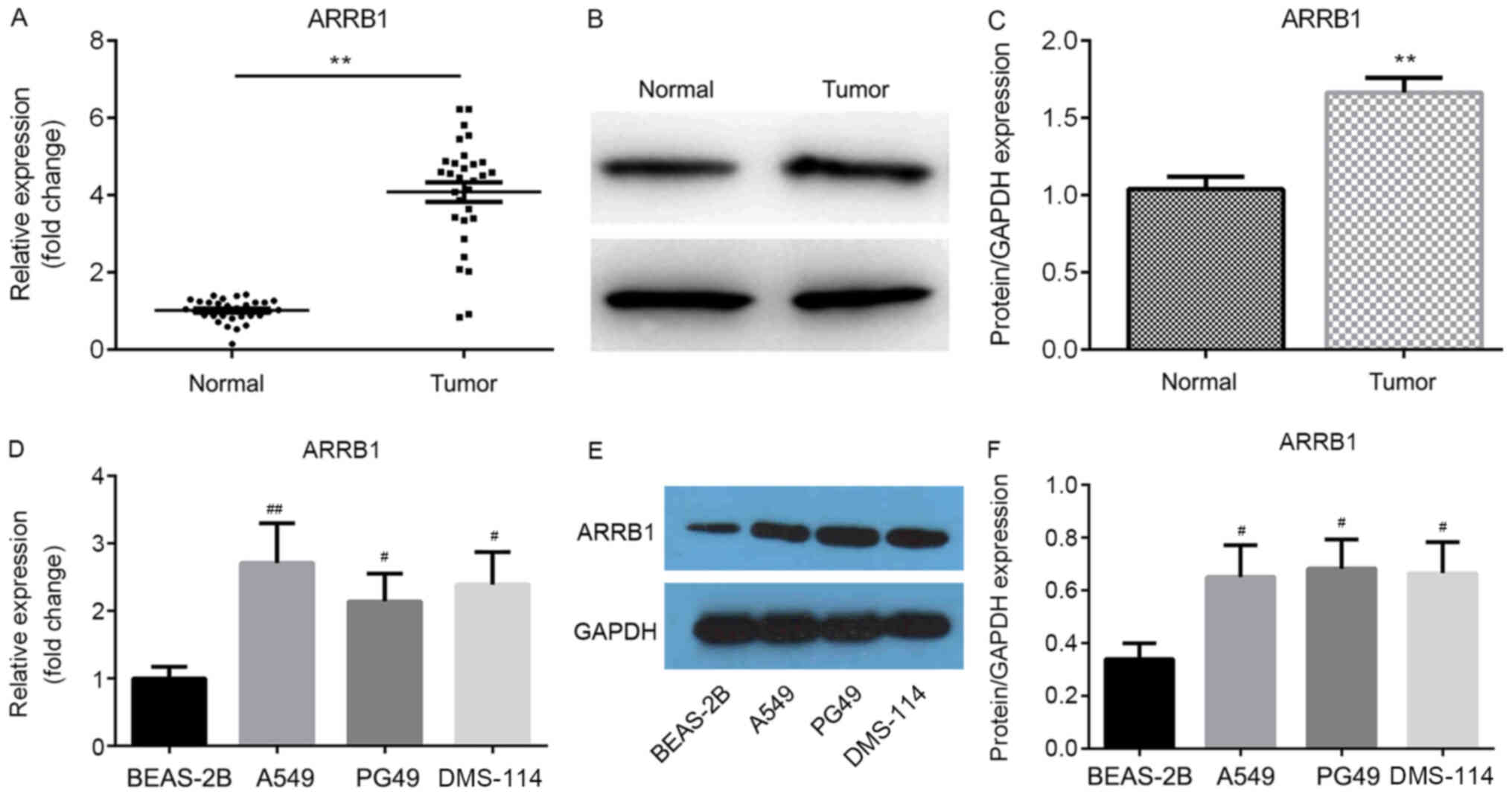
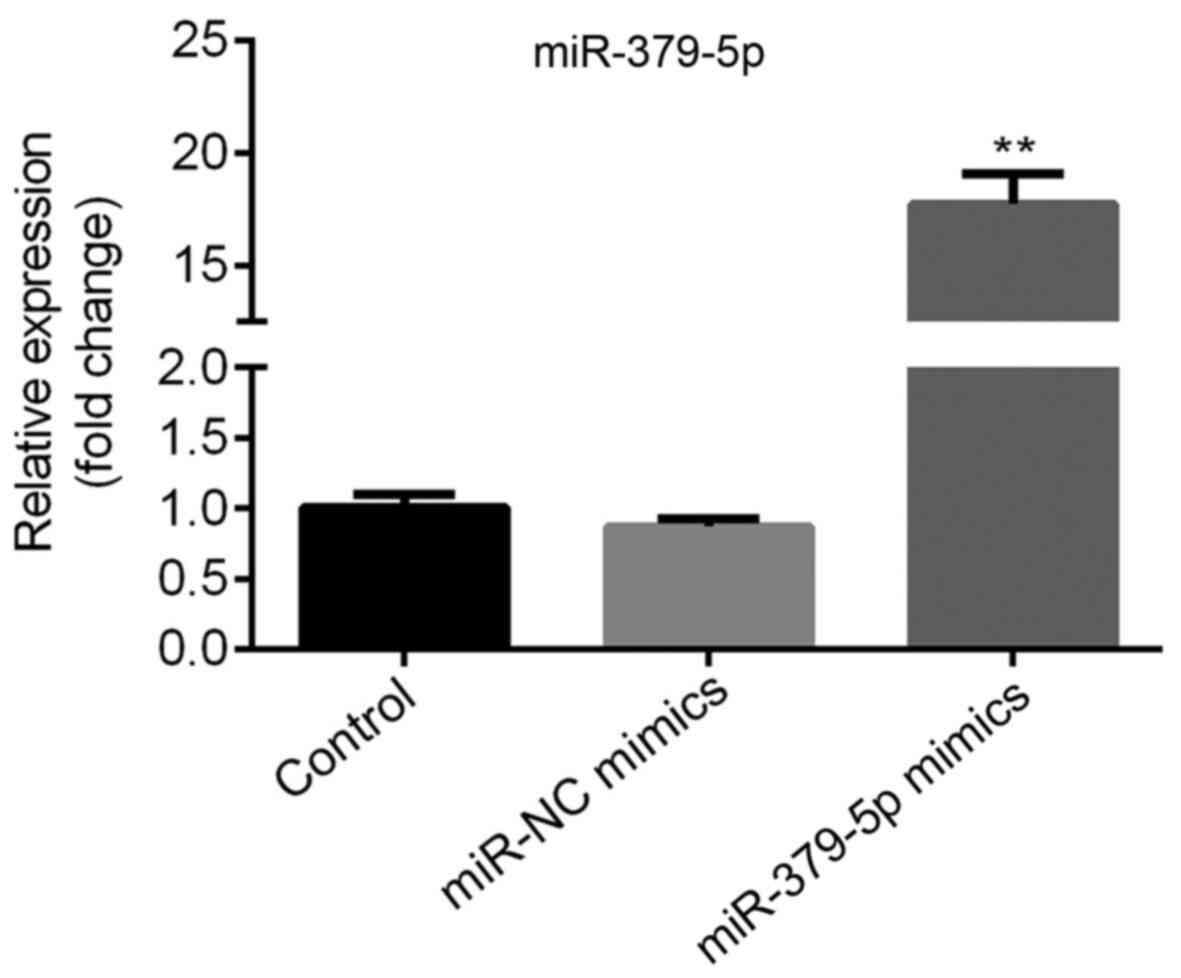
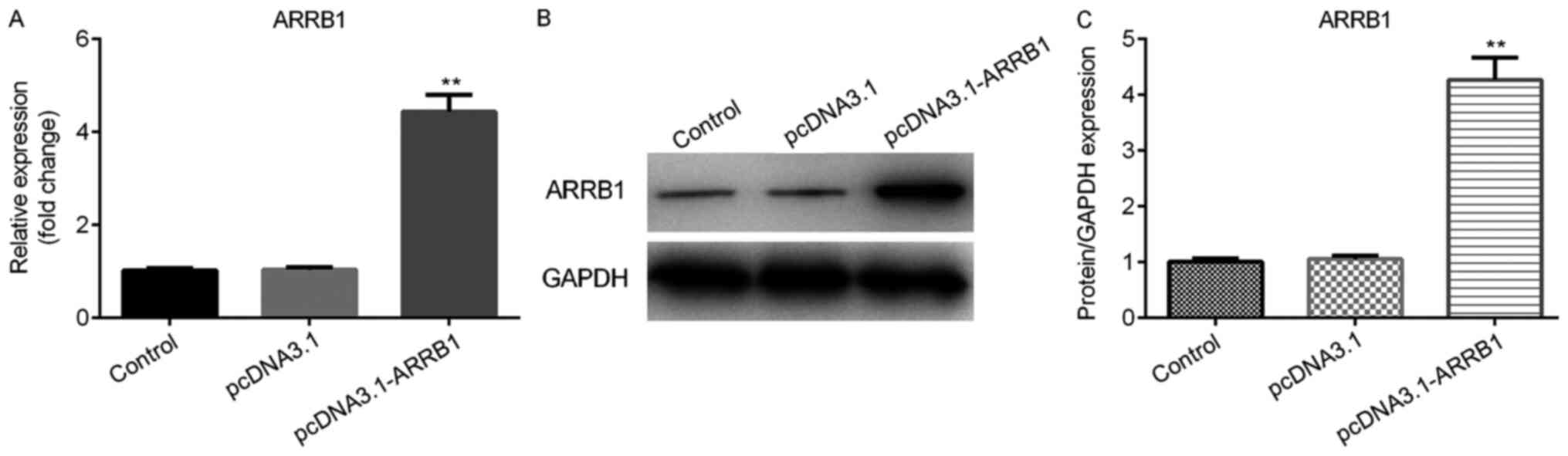
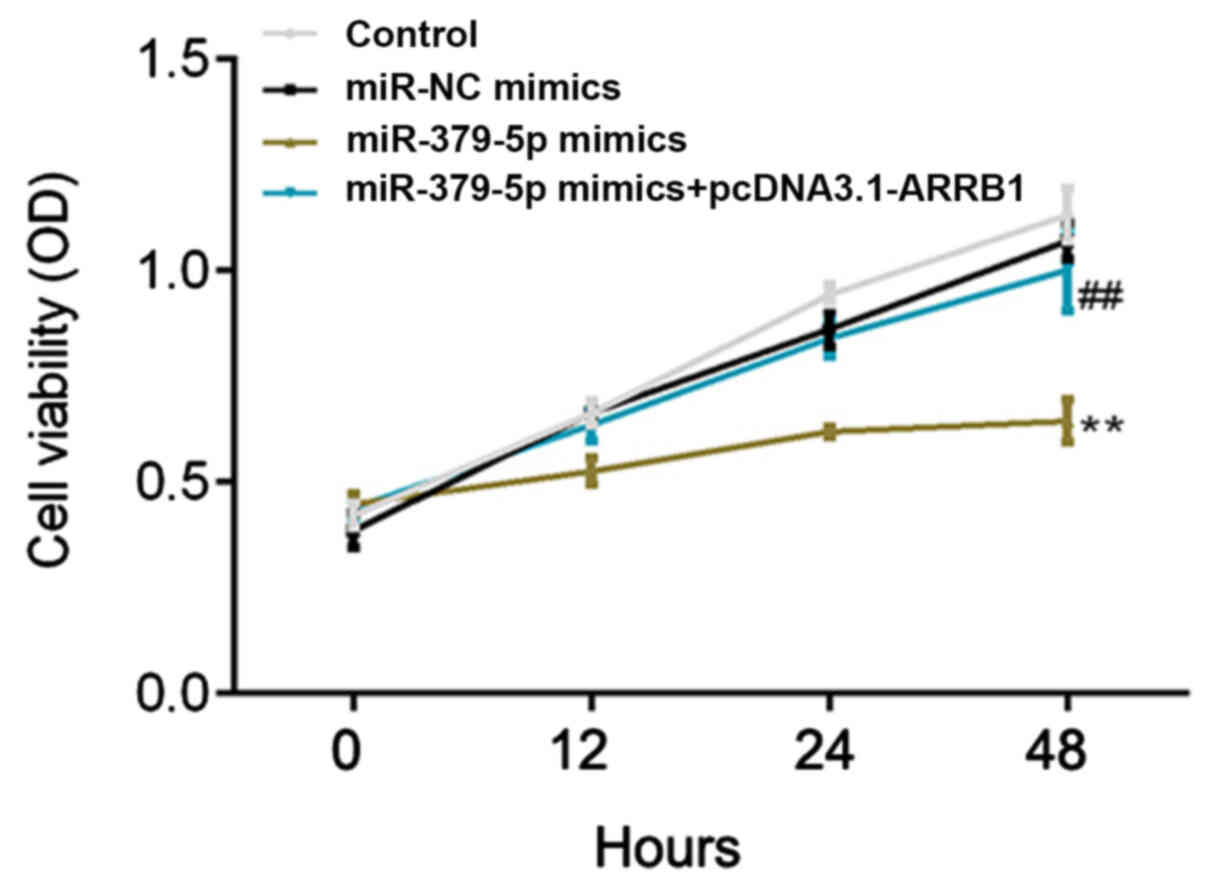
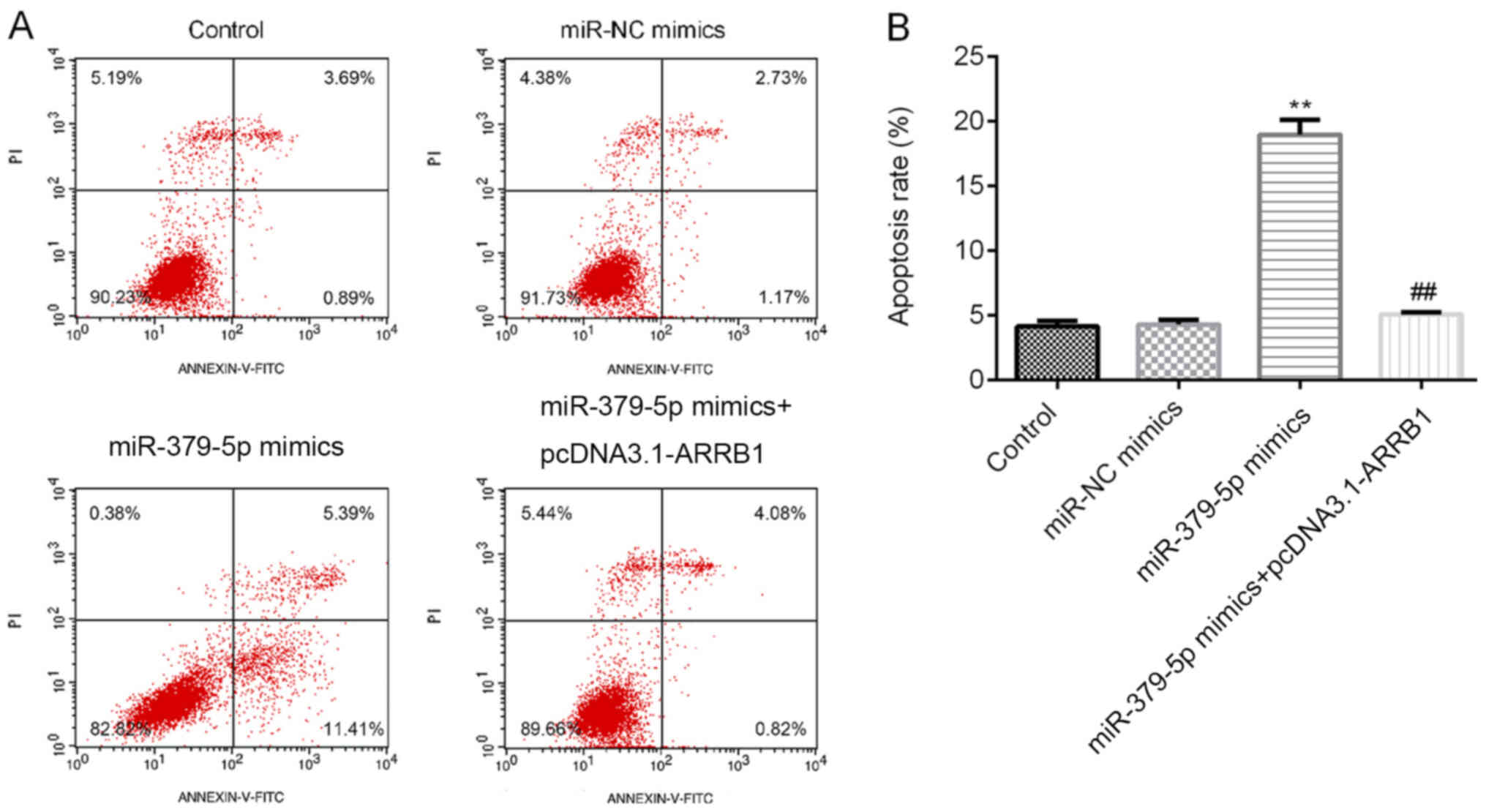
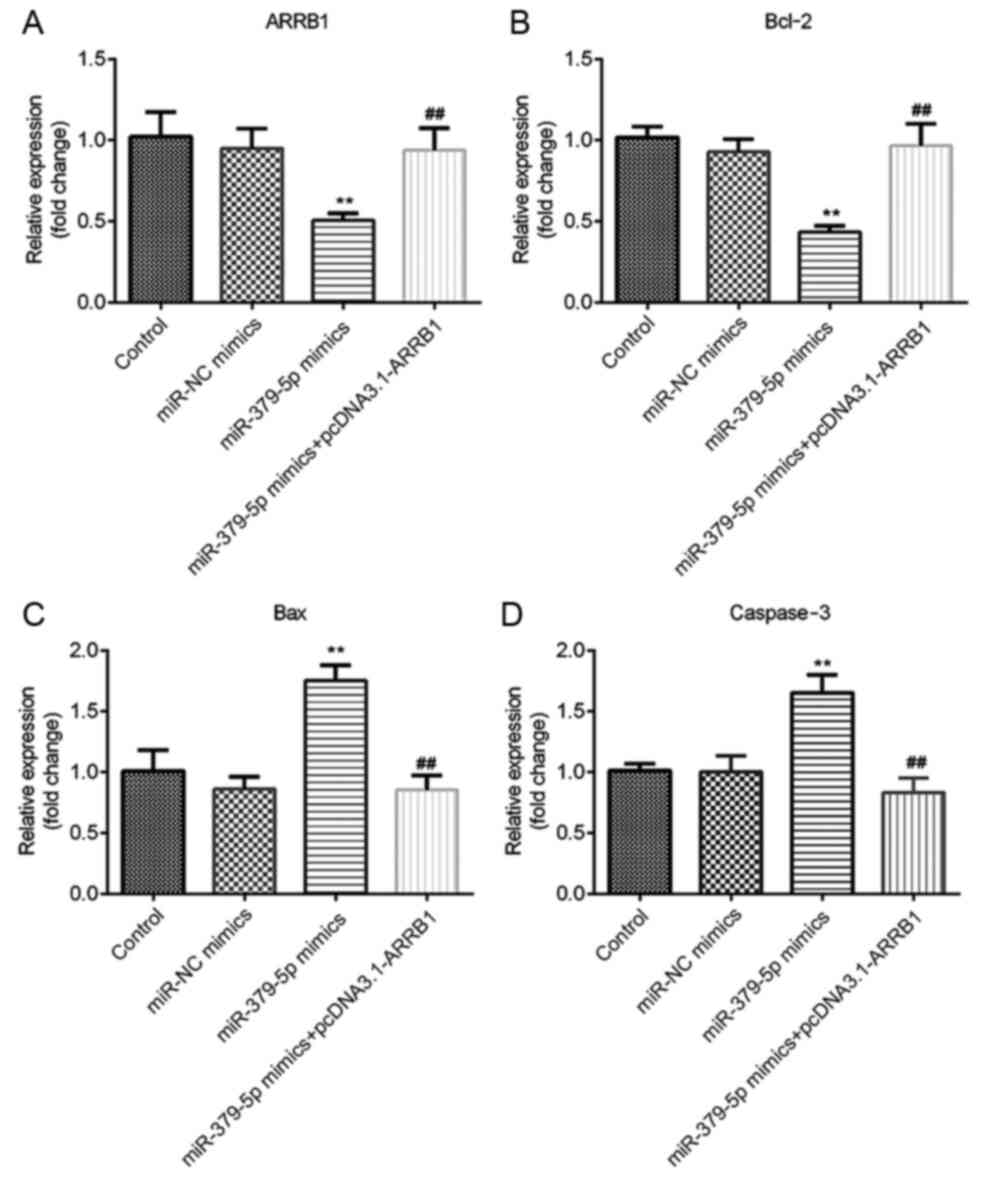
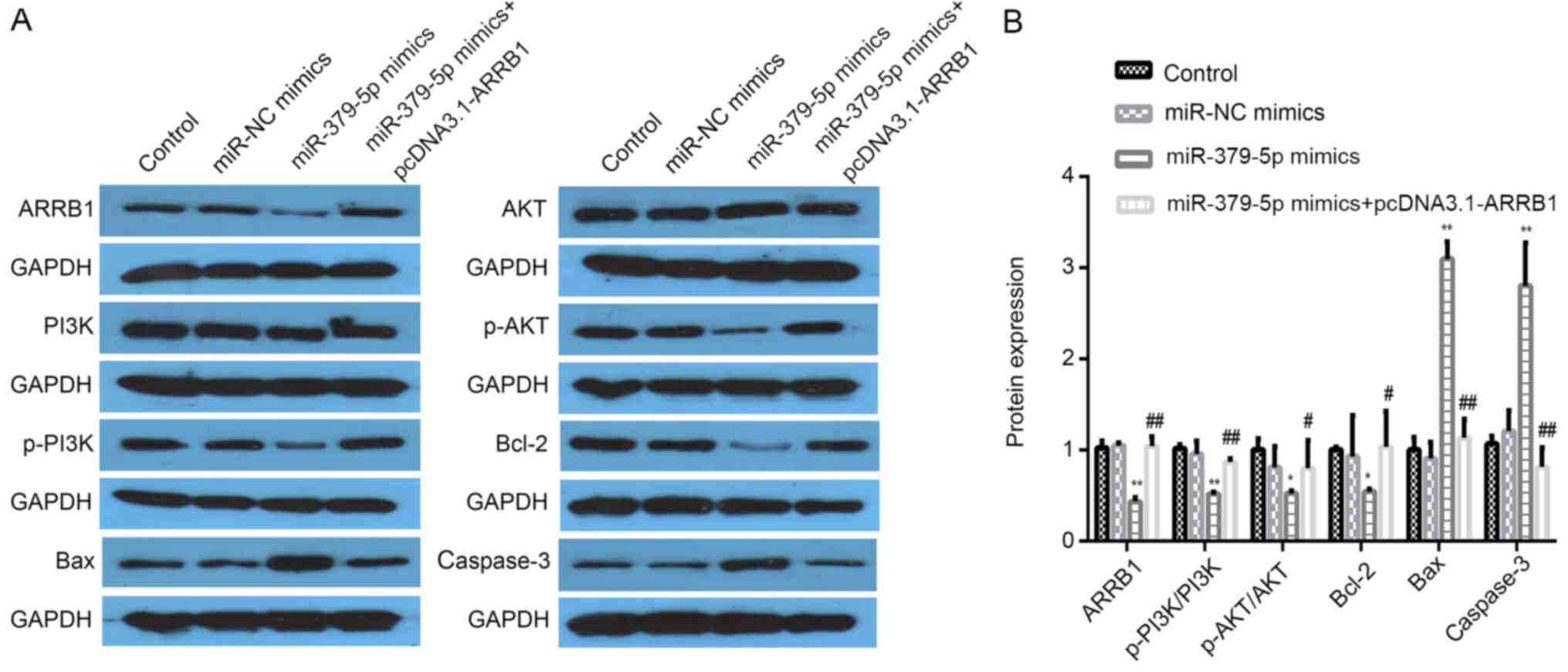
|
1
|
Chen R, Xia W, Wang S, Xu Y, Ma Z, Xu W,
Zhang E, Wang J, Fang T, Zhang Q, et al: Long noncoding RNA
SBF2-AS1 is critical for tumorigenesis of early-stage lung
adenocarcinoma. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 16:543–553. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nanavaty P, Alvarez MS and Alberts WM:
Lung cancer screening: Advantages, controversies, and applications.
Cancer Control. 21:9–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Richtmann S, Wilkens D, Warth A,
Lasitschka F, Winter H, Christopoulos P, Herth FJF, Muley T,
Meister M and Schneider MA: FAM83A and FAM83B as prognostic
biomarkers and potential new therapeutic targets in NSCLC. Cancers
(Basel). 11:6522019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lemjabbar-Alaoui H, Hassan OU, Yang YW and
Buchanan P: Lung Cancer: Biology and treatment options. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1856:189–210. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang T, Song X, Liao X, Wang X, Zhu G,
Yang C and Xie X: Distinct prognostic values of phospholipase C
beta family members for non-small cell lung carcinoma. Biomed Res
Int. 2019:42565242019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Castellanos-Rizaldos E, Zhang X, Tadigotla
VR, Grimm DG, Karlovich C, Raez LE and Skog JK: Exosome-based
detection of activating and resistance EGFR mutations from plasma
of non-small cell lung cancer patients. Oncotarget. 10:2911–2920.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu C, Hu Q, Xu B, Hu X, Su H, Li Q, Zhang
X, Yue J and Yu J: Peripheral memory and naïve T cells in non-small
cell lung cancer patients with lung metastases undergoing
stereotactic body radiotherapy: Predictors of early tumor response.
Cancer. Cell Int. 19:1212019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hammond SM: An overview of microRNAs. Adv
Drug Deliv Rev. 87:3–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Di Leva G, Garofalo M and Croce CM:
MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 9:287–314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gebert LFR and MacRae IJ: Regulation of
microRNA function in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:21–37.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu B, Li J and Cairns MJ: Identifying
miRNAs, targets and functions. Brief Bioinform. 15:1–19. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cazzoli R, Buttitta F, Nicola MD,
Malatesta S, Marchetti A, Rom WN and Pass HI: Micrornas derived
from circulating exosomes as noninvasive biomarkers for screening
and diagnosing lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 8:1156–1162. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang S, Wang Z, Wang Q, Cui Y and Luo S:
Clinical significance of the expression of miRNA-21, miRNA-31 and
miRNA-let7 in patients with lung cancer. Saudi J Biol Sci.
26:777–781. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao X and Chu J: MicroRNA-379 suppresses
cell proliferation, migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma by targeting tumor protein D52. Exp Ther Med.
16:1232–1240. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu D, Niu X, Tao J, Li P, Lu Q, Xu A, Chen
W and Wang Z: MicroRNA-379-5p plays a tumor-suppressive role in
human bladder cancer growth and metastasis by directly targeting
MDM2. Oncol Rep. 37:3502–3508. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie X, Li YS, Xiao WF, Deng ZH, He HB, Liu
Q and Luo W: MicroRNA-379 inhibits the proliferation, migration and
invasion of human osteosarcoma cells by targetting EIF4G2. Biosci
Rep. 37:BSR201605422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hao GJ, Hao HJ, Ding YH, Wen H, Li XF,
Wang QR and Zhang BB: Suppression of EIF4G2 by miR-379 potentiates
the cisplatin chemosensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer cells.
FEBS Lett. 591:636–645. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun JC, Liu B, Zhang RW, Jiao PL, Tan X,
Wang YK and Wang WZ: Overexpression of ß-arrestin1 in the rostral
ventrolateral medulla downregulates angiotensin receptor and lowers
blood pressure in hypertension. Front Physiol. 9:2972018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim J, Grotegut CA, Wisler JW, Li T, Mao
L, Chen M, Chen W, Rosenberg PB, Rockman HA and Lefkowitz RJ:
β-Arrestin 1 regulates β2-adrenergic receptor-mediated skeletal
muscle hypertrophy and contractility. Skelet Muscle. 8:392018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rosanò L and Bagnato A: β-arrestin1 at the
cross-road of endothelin-1 signaling in cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 35:1212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lan T, Wang H, Zhang Z, Zhang M, Qu Y,
Zhao Z, Fan X, Zhan Q, Song Y and Yu C: Downregulation of
β-arrestin 1 suppresses glioblastoma cell malignant progression via
inhibition of src signaling. Exp Cell Res. 357:51–58. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dasgupta P, Rizwani W, Pillai S, Davis R,
Banerjee S, Hug K, Lloyd M, Coppola D, Haura E and Chellappan SP:
ARRB1-mediated regulation of E2F target genes in nicotine-induced
growth of lung tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 103:317–333. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shen H, Wang L, Zhang J, Dong W, Zhang T,
Ni Y, Cao H, Wang K, Li Y, Wang Y and Du J: ARRB1 enhances the
chemosensitivity of lung cancer through the mediation of DNA damage
response. Oncol Rep. 37:761–767. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao X and Chu J: MicroRNA-379 suppresses
cell proliferation, migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma by targeting tumor protein D52. Exp Ther Med.
16:1232–1240. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma Z, Yu YR, Badea CT, Kovacs JJ, Xiong X,
Comhair S, Piantadosi CA and Rajagopal S: Vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor 3 regulates endothelial function through
β-arrestin. Circulation. 139:1629–1642. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zecchini V, Madhu B, Russell R, Gomes NP,
Warren A, Gaude E, Borlido J, Stark R, Zecchini HI, Rao R, et al:
Nuclear ARRB1 induces pseudohypoxia and cellular metabolism
reprogramming in prostate cancer. EMBO J. 33:1365–1382. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Son D, Kim Y, Lim S, Kang HG, Kim DH, Park
JW, Cheong W, Kong HK, Han W, Park WY, et al: MiR-374a-5p promotes
tumor progression by targeting ARRB1 in triple negative breast
cancer. Cancer Lett. 454:224–233. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Z, Zhong X, Xiao Y and Chen C:
MicroRNA-296 inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth and enhances
apoptosis by targeting ARRB1-mediated AKT activation. Oncol Rep.
41:619–629. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhan Y, Xu C, Liu Z, Yang Y, Tan S, Yang
Y, Jiang J, Liu H, Chen J and Wu B: β-Arrestin1 inhibits
chemotherapy-induced intestinal stem cell apoptosis and mucositis.
Cell Death Dis. 7:e22292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|