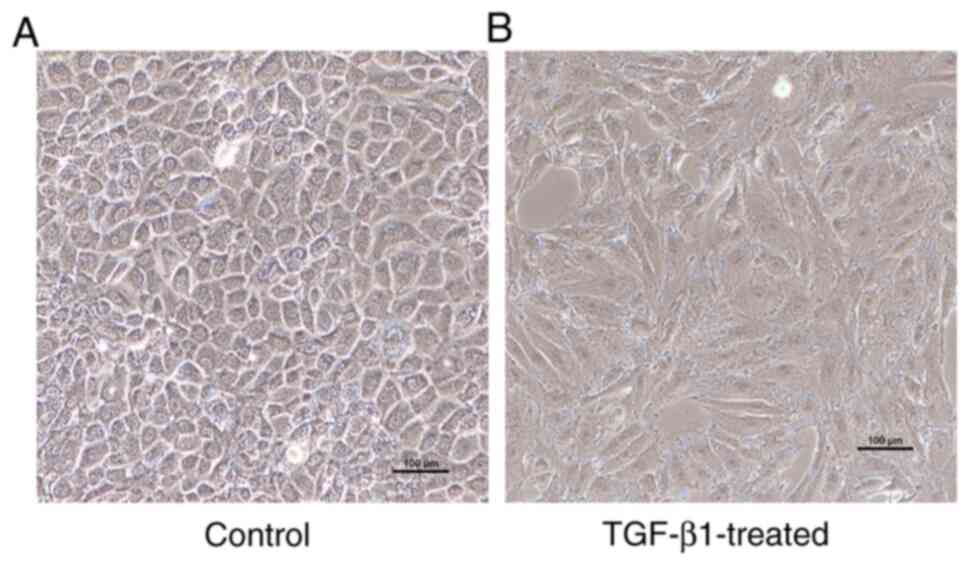
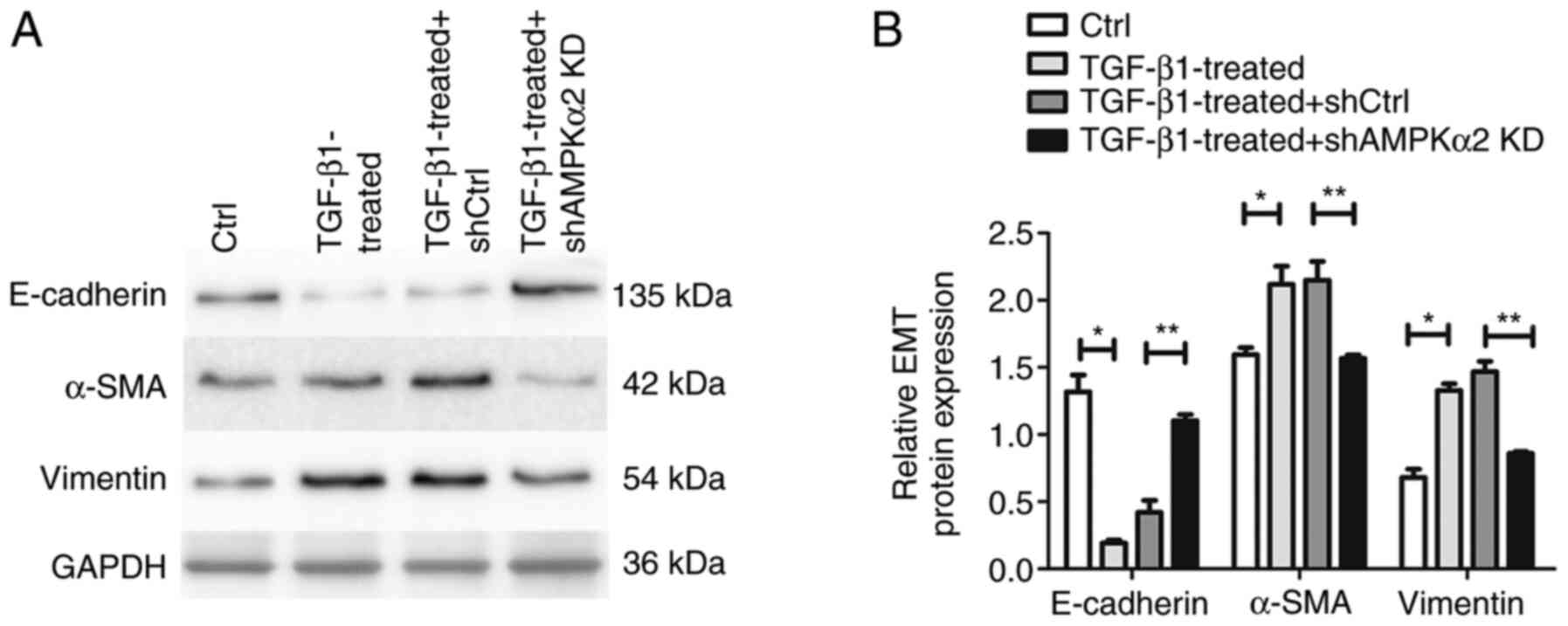
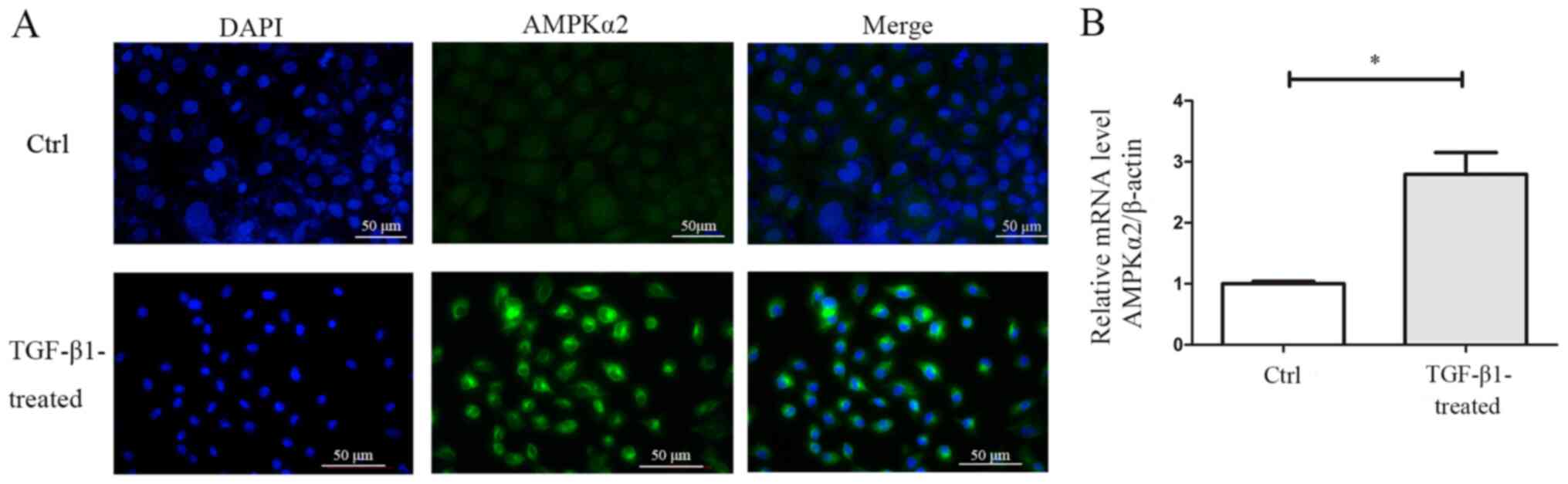
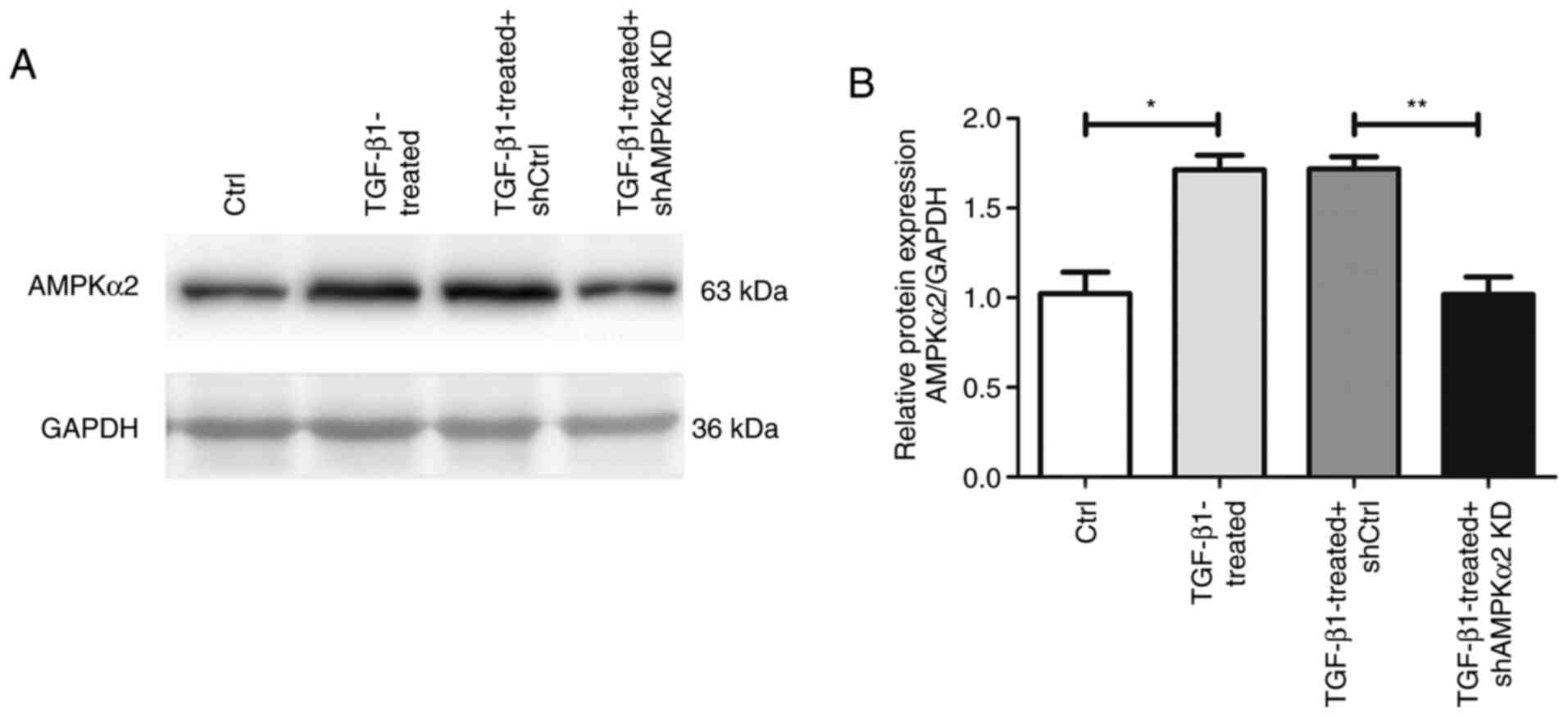
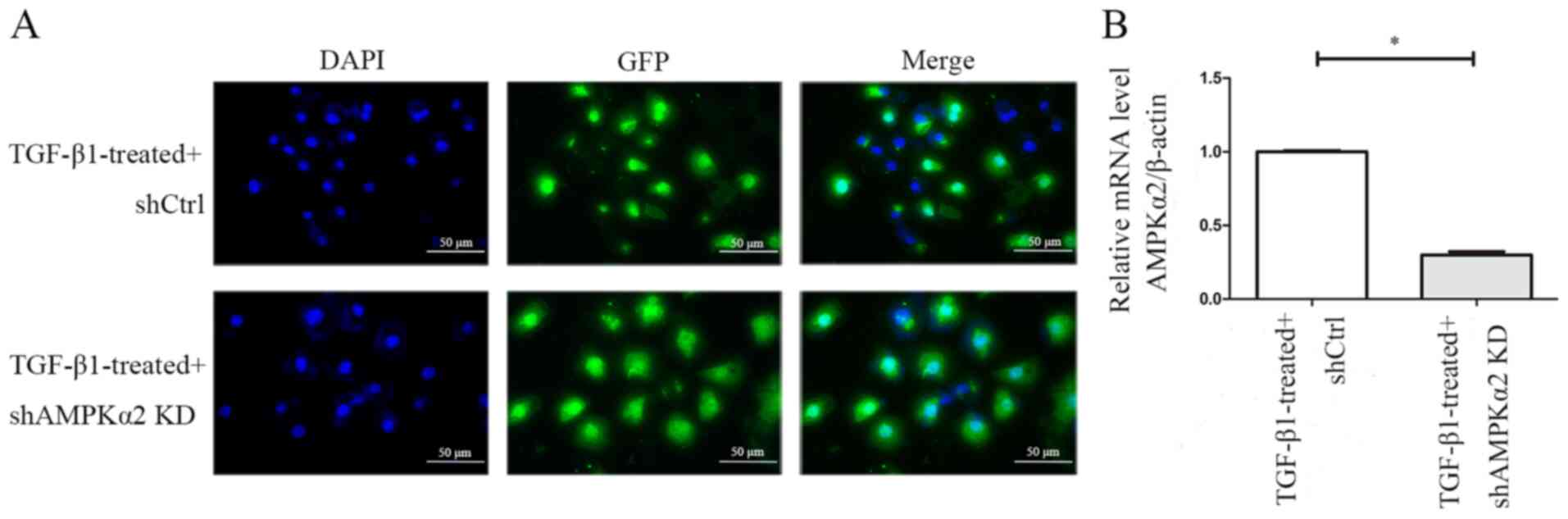
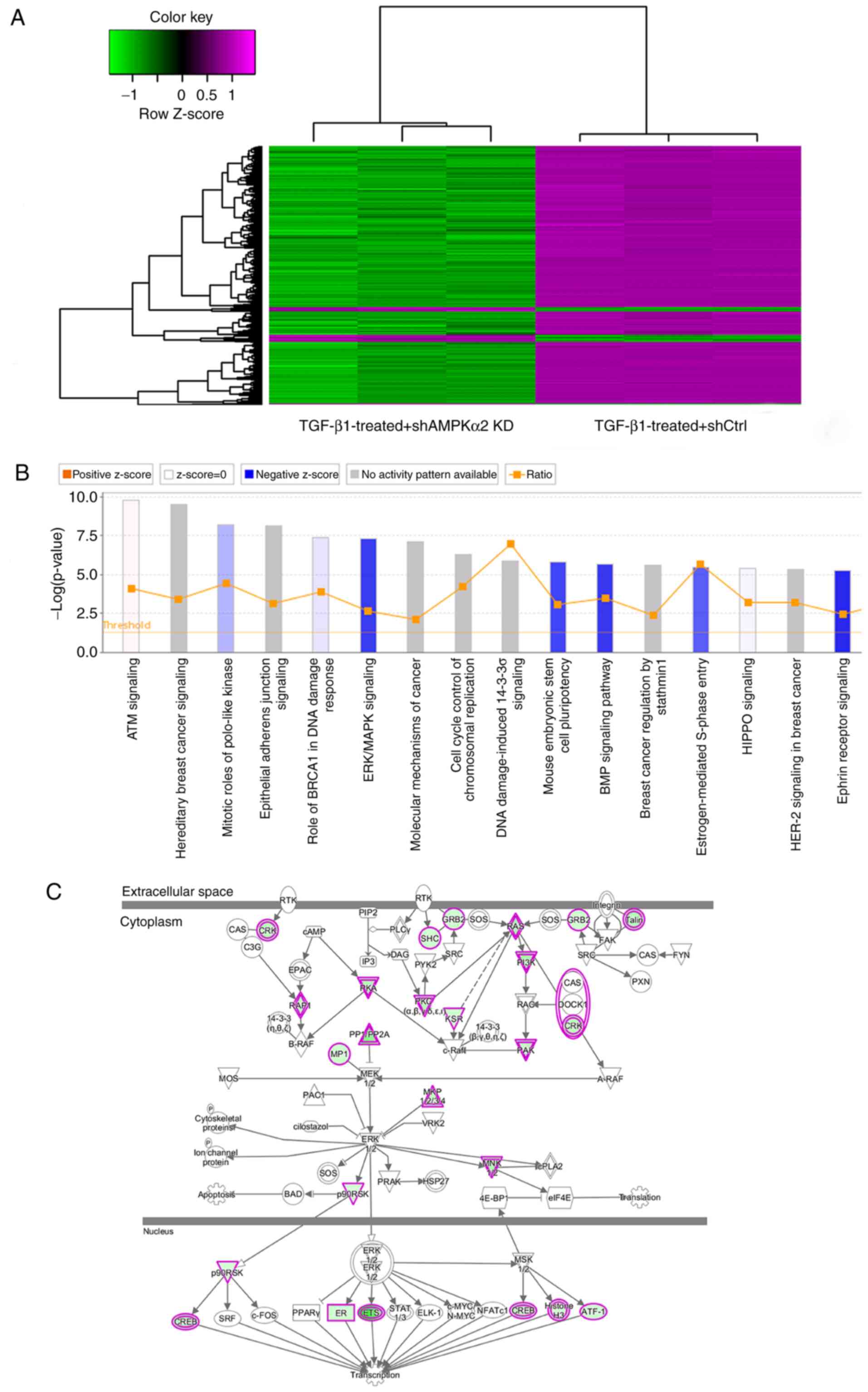
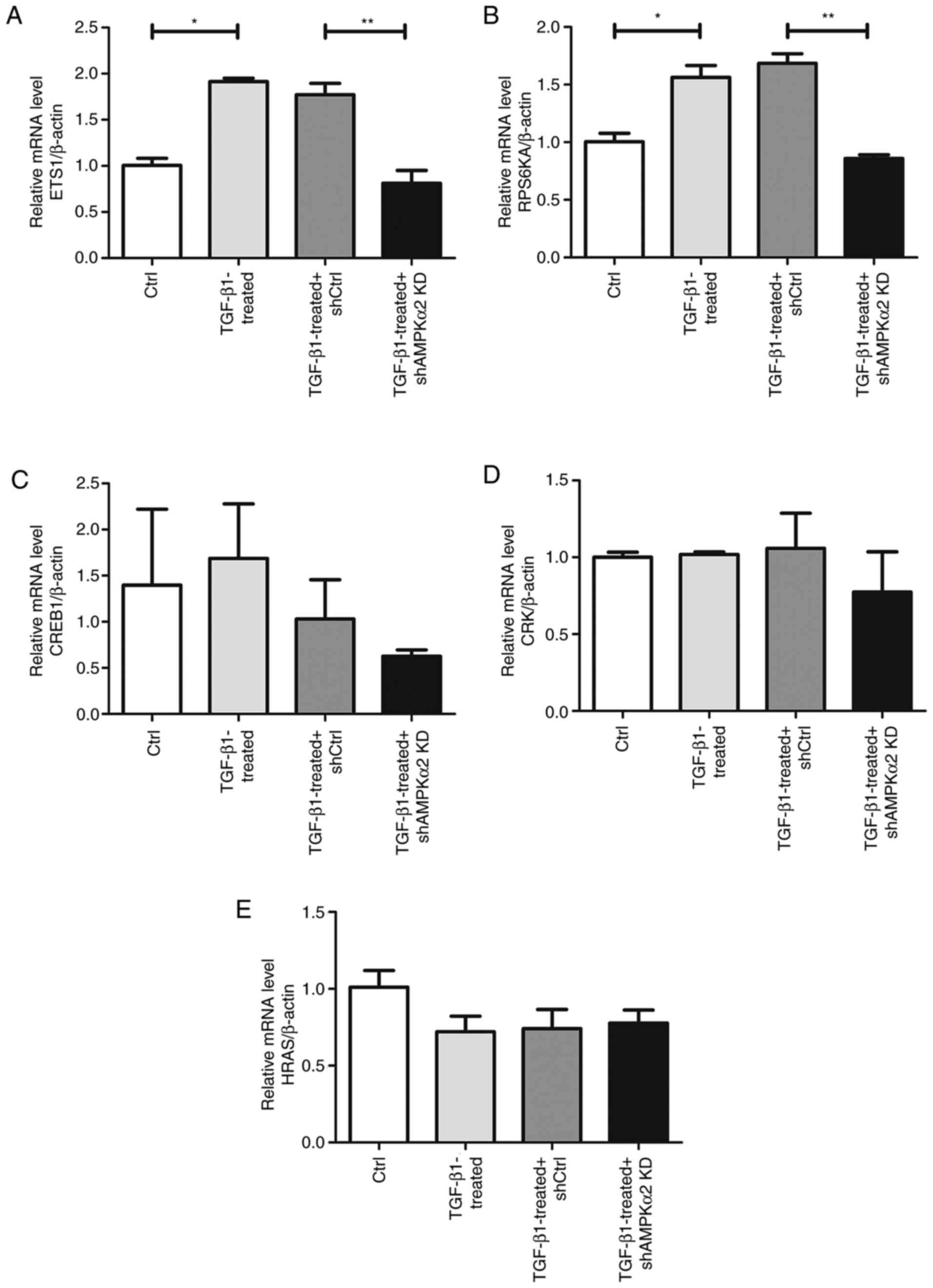
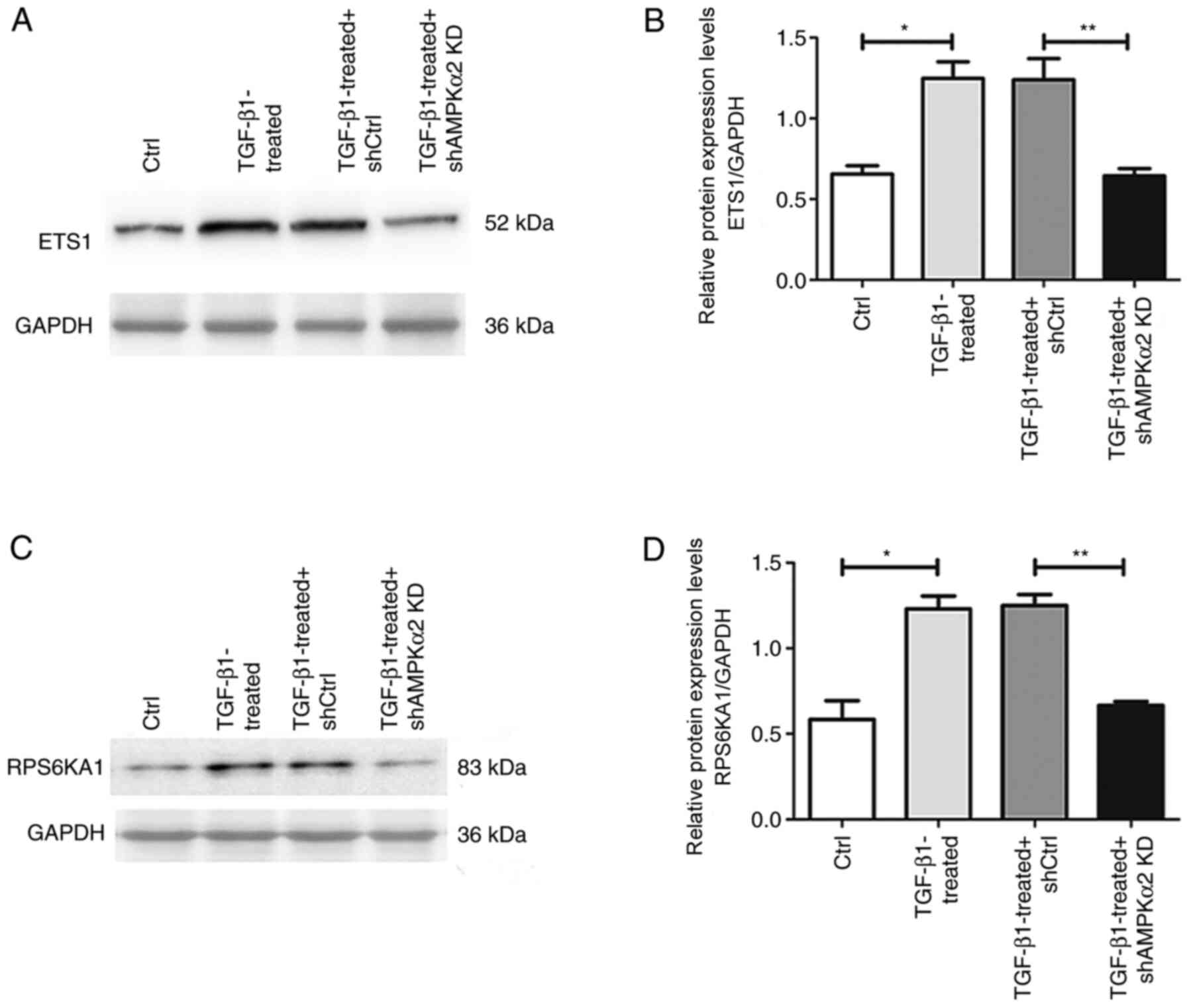
|
1
|
Weitz M, Portz S, Laube GF, Meerpohl JJ
and Bassler D: Surgery versus non-surgical management for
unilateral ureteric-pelvic junction obstruction in newborns and
infants less than two years of age. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
7:CD0107162016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Klahr S: Obstructive nephropathy. Intern
Med. 39:355–361. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shihab FS: Do we have a pill for renal
fibrosis? Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2:876–878. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Iwano M: EMT and TGF-beta in renal
fibrosis. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2:229–238. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rastaldi MP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and its implications for the development of renal
tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J Nephrol. 19:407–412. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Puisieux A, Brabletz T and Caramel J:
Oncogenic roles of EMT-inducing transcription factors. Nat Cell
Biol. 16:488–494. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Martin-Belmonte F and Perez-Moreno M:
Epithelial cell polarity, stem cells and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
12:23–38. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Y: Cellular and molecular mechanisms
of renal fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 7:684–696. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bronsert P, Enderle-Ammour K, Bader M,
Timme S, Kuehs M, Csanadi A, Kayser G, Kohler I, Bausch D, Hoeppner
J, et al: Cancer cell invasion and EMT marker expression: A
three-dimensional study of the human cancer-host interface. J
Pathol. 234:410–422. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim SI and Choi ME: TGF-β-activated
kinase-1: New insights into the mechanism of TGF-β signaling and
kidney disease. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 31:94–105. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang D, Sun L, Xian W, Liu F, Ling G,
Xiao L, Liu Y, Peng Y, Haruna Y and Kanwar YS: Low-dose paclitaxel
ameliorates renal fibrosis in rat UUO model by inhibition of
TGF-beta/Smad activity. Lab Invest. 90:436–447. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao Q, Yang Y, Wang CL, Hou Y and Chen H:
Screening and identification of the differential proteins in kidney
with complete unilateral ureteral obstruction. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:2615–2626. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hardie DG, Schaffer BE and Brunet A: AMPK:
An energy-sensing pathway with multiple inputs and outputs. Trends
Cell Biol. 26:190–201. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jeon SM: Regulation and function of AMPK
in physiology and diseases. Exp Mol Med. 48:e2452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Carling D: AMPK signalling in health and
disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 45:31–37. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hawley SA, Boudeau J, Reid JL, Mustard KJ,
Udd L, Mäkelä TP, Alessi DR and Hardie DG: Complexes between the
LKB1 tumor suppressor, STRAD alpha/beta and MO25 alpha/beta are
upstream kinases in the AMP-activated protein kinase cascade. J
Biol. 2:282003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang X, Pan X and Song J: AMP-activated
protein kinase is required for induction of apoptosis and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cell Signal. 22:1790–1797.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang M, Weng X, Guo J, Chen Z, Jiang G and
Liu X: Metformin alleviated EMT and fibrosis after renal
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Ren Fail. 38:614–621. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qiu S, Xiao Z, Piao C, Zhang J, Dong Y,
Cui W, Liu X, Zhang Y and Du J: AMPKα2 reduces renal epithelial
transdifferentiation and inflammation after injury through
interaction with CK2β. J Pathol. 237:330–342. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Saxena M, Balaji SA, Deshpande N,
Ranganathan S, Pillai DM, Hindupur SK and Rangarajan A:
AMP-activated protein kinase promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cancer cells through Twist1 upregulation. J Cell Sci.
131:cs2083142018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J R Statist Soc B. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zeisberg M, Maeshima Y, Mosterman B and
Kalluri R: Renal fibrosis: Extracellular matrix microenvironment
regulates migratory behavior of activated tubular epithelial cells.
Am J Pathol. 160:2001–2008. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sato M, Muragaki Y, Saika S, Roberts AB
and Ooshima A: Targeted disruption of TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling
protects against renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis induced by
unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Clin Invest. 112:1486–1494.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stahl PJ and Felsen D: Transforming growth
factor-beta, basement membrane, and epithelial-mesenchymal
transdifferentiation: Implications for fibrosis in kidney disease.
Am J Pathol. 159:1187–1192. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Grande MT and Lopez-Novoa JM: Fibroblast
activation and myofibroblast generation in obstructive nephropathy.
Nat Rev Nephrol. 5:319–328. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Garcia D and Shaw RJ: AMPK: Mechanisms of
cellular energy sensing and restoration of metabolic balance. Mol
Cell. 66:789–800. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tain YL and Hsu CN: AMP-activated protein
kinase as a reprogramming strategy for hypertension and kidney
disease of developmental origin. Int J Mol sci. 19:17442018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
He K, Guo X, Liu Y, Li J, Hu Y, Wang D and
Song J: TUFM downregulation induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and invasion in lung cancer cells via a mechanism
involving AMPK-GSK3β signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:2105–2121.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mishra R, Cool BL, Laderoute KR, Foretz M,
Viollet B and Simonson MS: AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits
transforming growth factor-beta-induced Smad3-dependent
transcription and myofibroblast transdifferentiation. J Biol Chem.
283:10461–10469. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lim JY, Oh MA, Kim WH, Sohn HY and Park
SI: AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits TGF-β-induced fibrogenic
responses of hepatic stellate cells by targeting transcriptional
coactivator p300. J Cell Physiol. 227:1081–1089. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Anjum R and Blenis J: The RSK family of
kinases: Emerging roles in cellular signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 9:747–758. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Abe JI, Sandhu UG, Hoang NM, Thangam M,
Quintana-Quezada RA, Fujiwara K and Le NT: Coordination of cellular
localization-dependent effects of sumoylation in regulating
cardiovascular and neurological diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol.
963:337–358. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lin L, Shi C, Sun Z, Le NT, Abe JI and Hu
K: The Ser/Thr kinase p90RSK promotes kidney fibrosis by modulating
fibroblast-epithelial crosstalk. J Biol Chem. 294:9901–9910. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Plotnik JP, Budka JA, Ferris MW and
Hollenhorst PC: ETS1 is a genome-wide effector of RAS/ERK signaling
in epithelial cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:11928–11940. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lawrence MC, McGlynn K, Shao C, Duan L,
Naziruddin B, Levy MF and Cobb MH: Chromatin-bound
mitogen-activated protein kinases transmit dynamic signals in
transcription complexes in beta-cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:13315–13320. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Paumelle R, Tulasne D, Kherrouche Z, Plaza
S, Leroy C, Reveneau S, Vandenbunder B and Fafeur V: Hepatocyte
growth factor/scatter factor activates the ETS1 transcription
factor by a RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK signaling pathway. Oncogene.
21:2309–2319. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Darling NJ and Cook SJ: The role of MAPK
signalling pathways in the response to endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843:2150–2163. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|