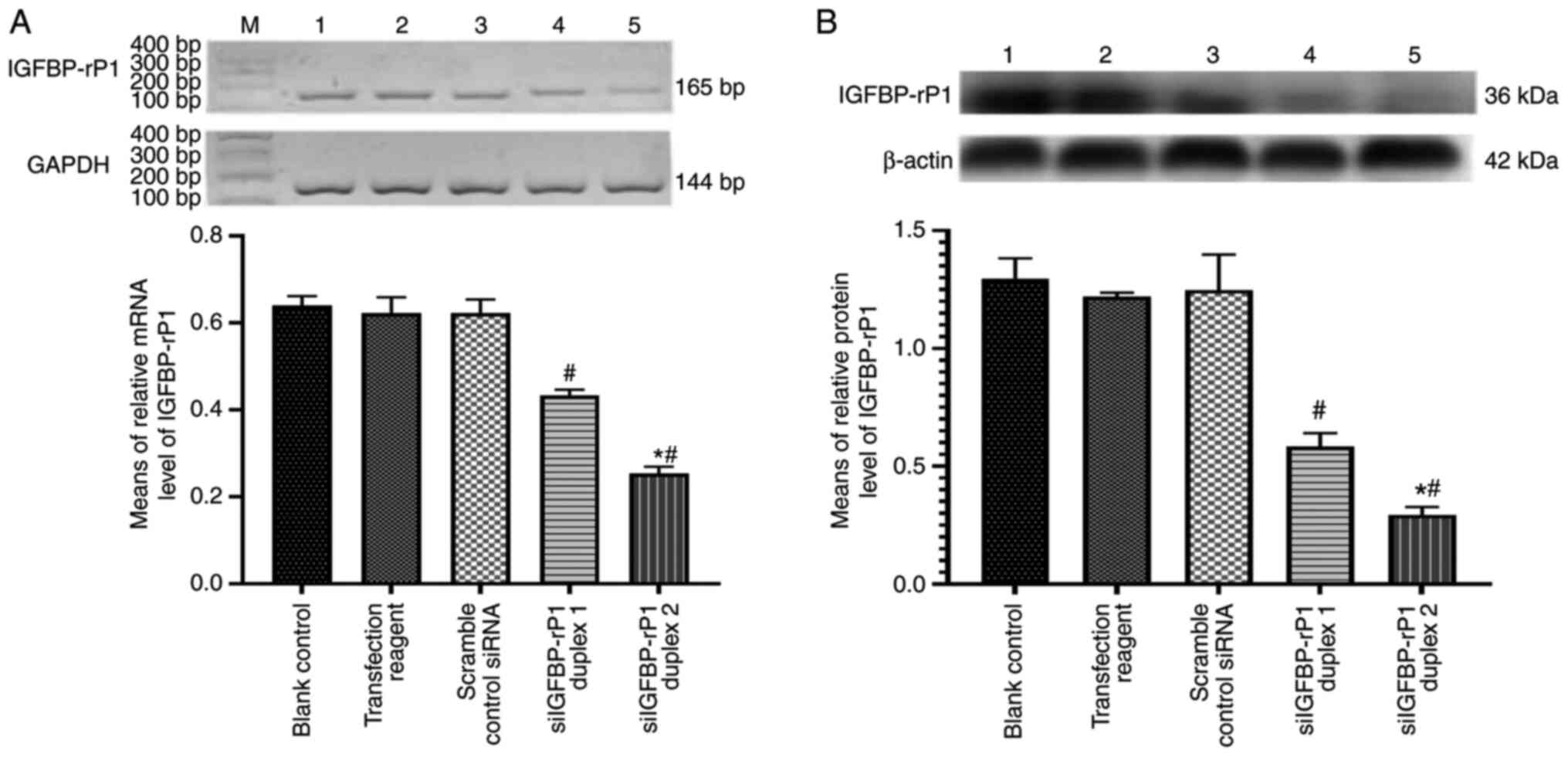
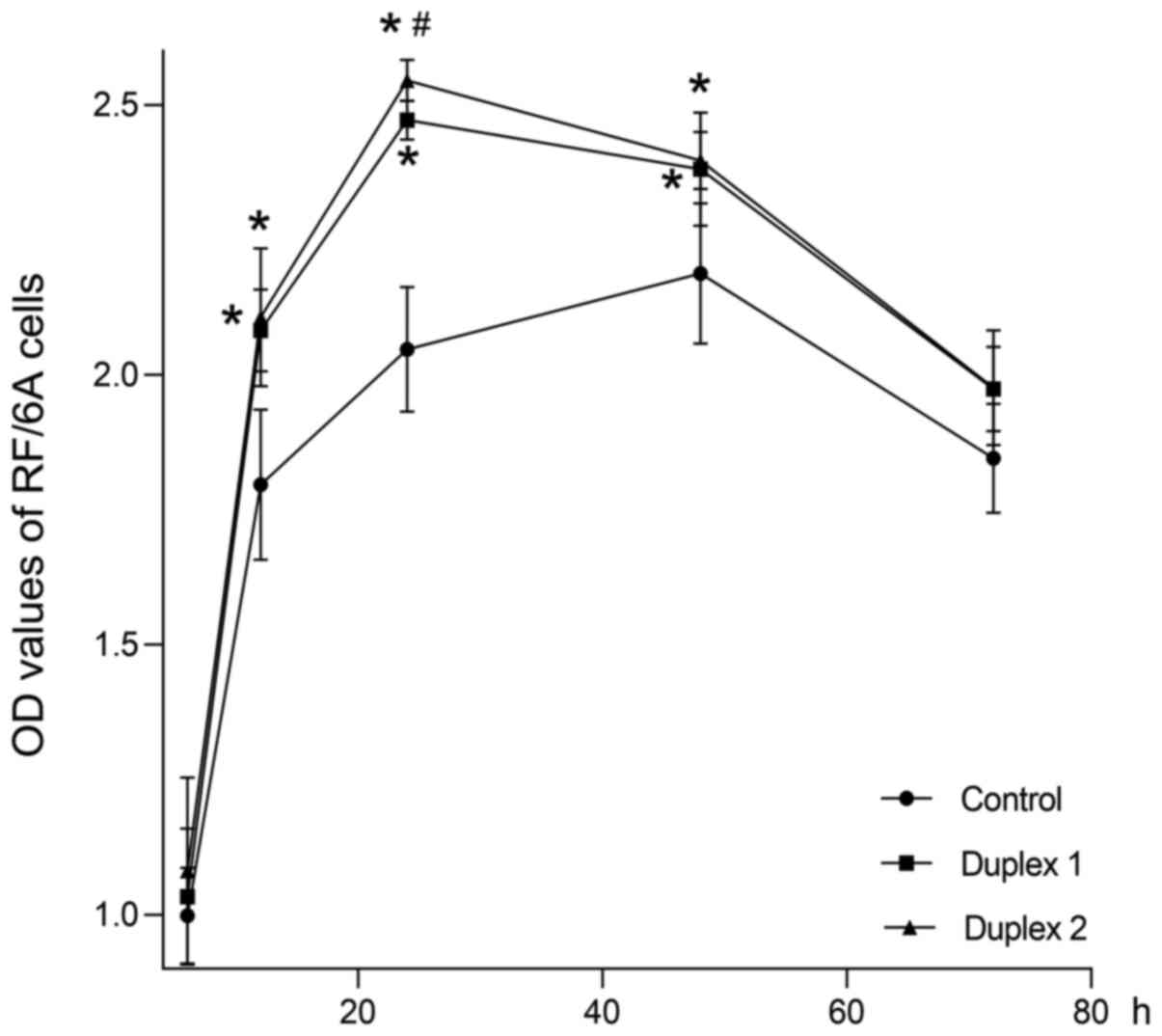
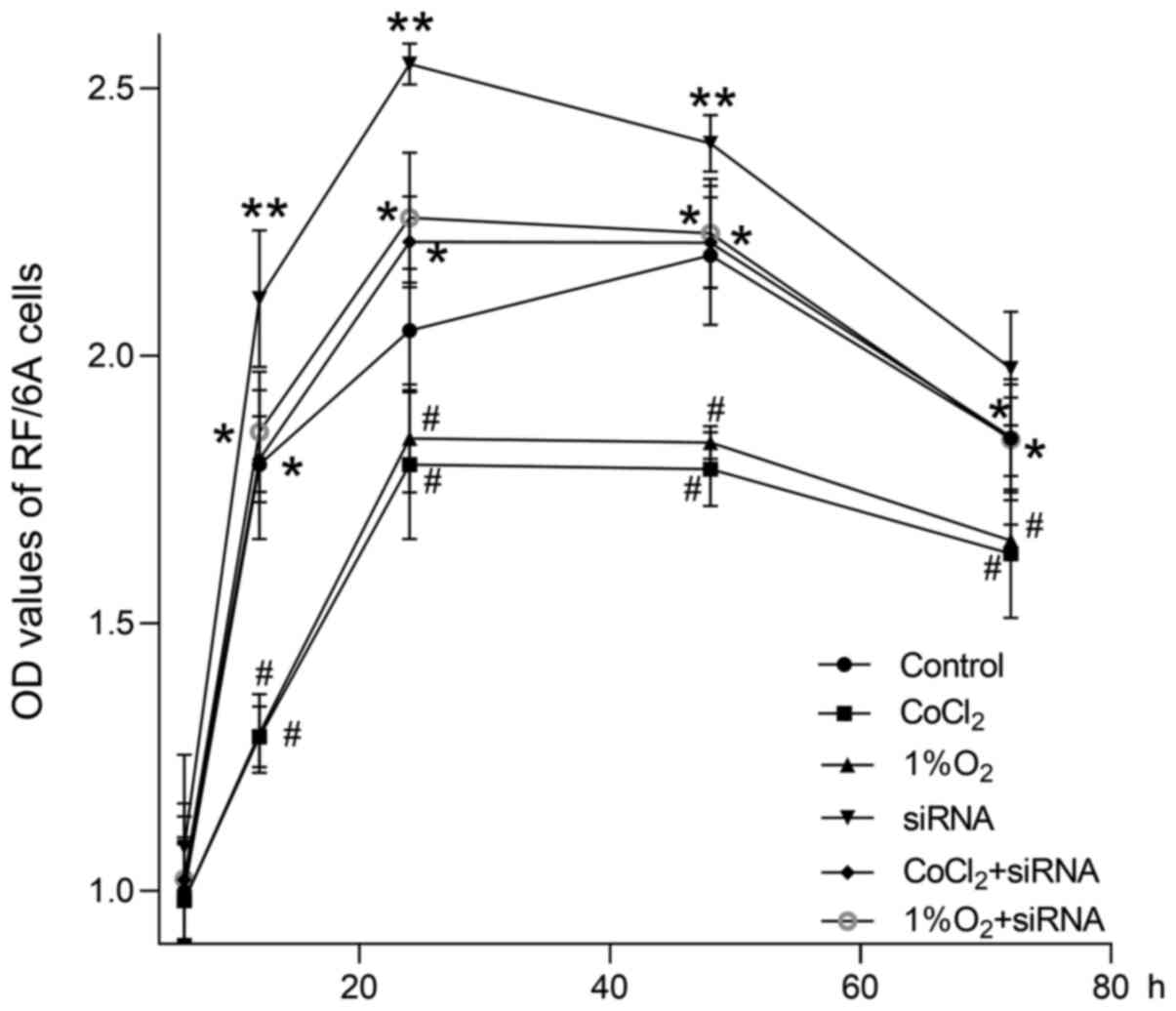
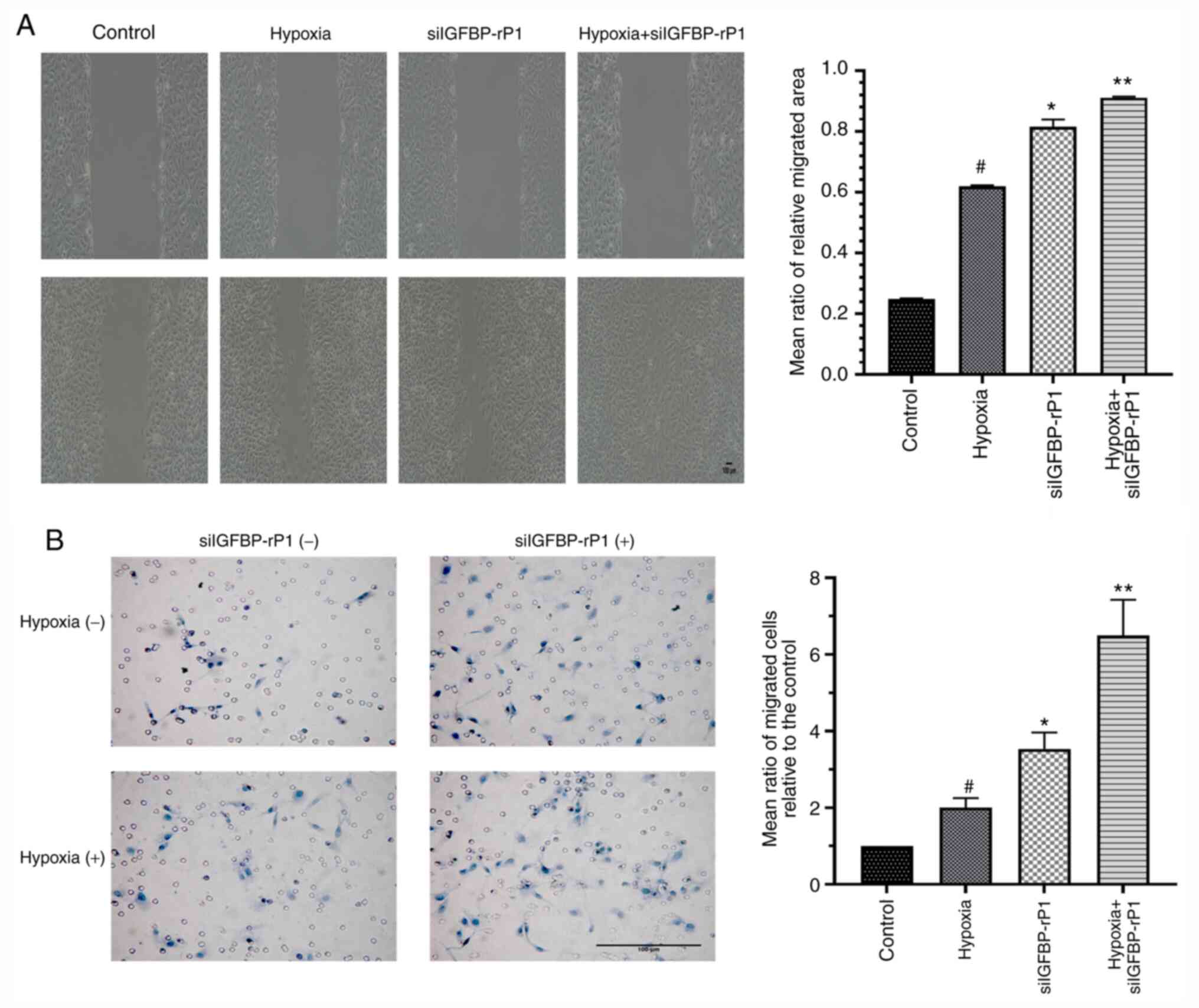
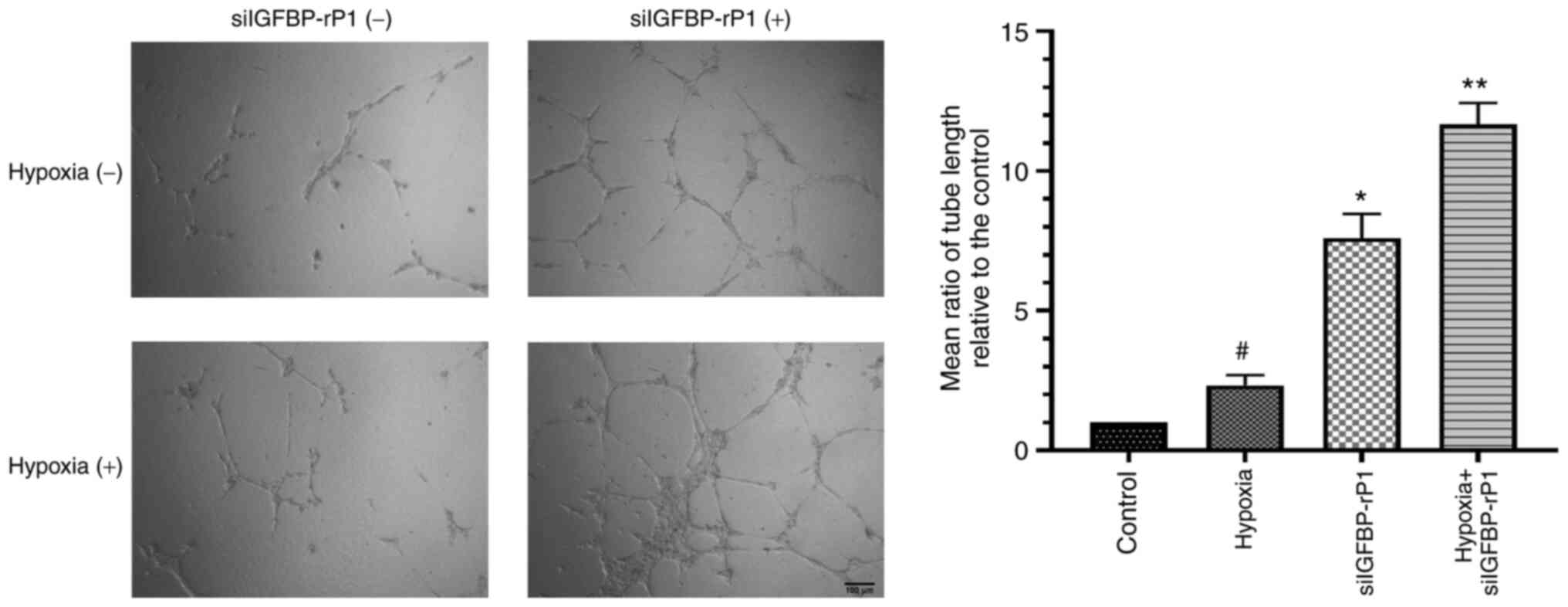
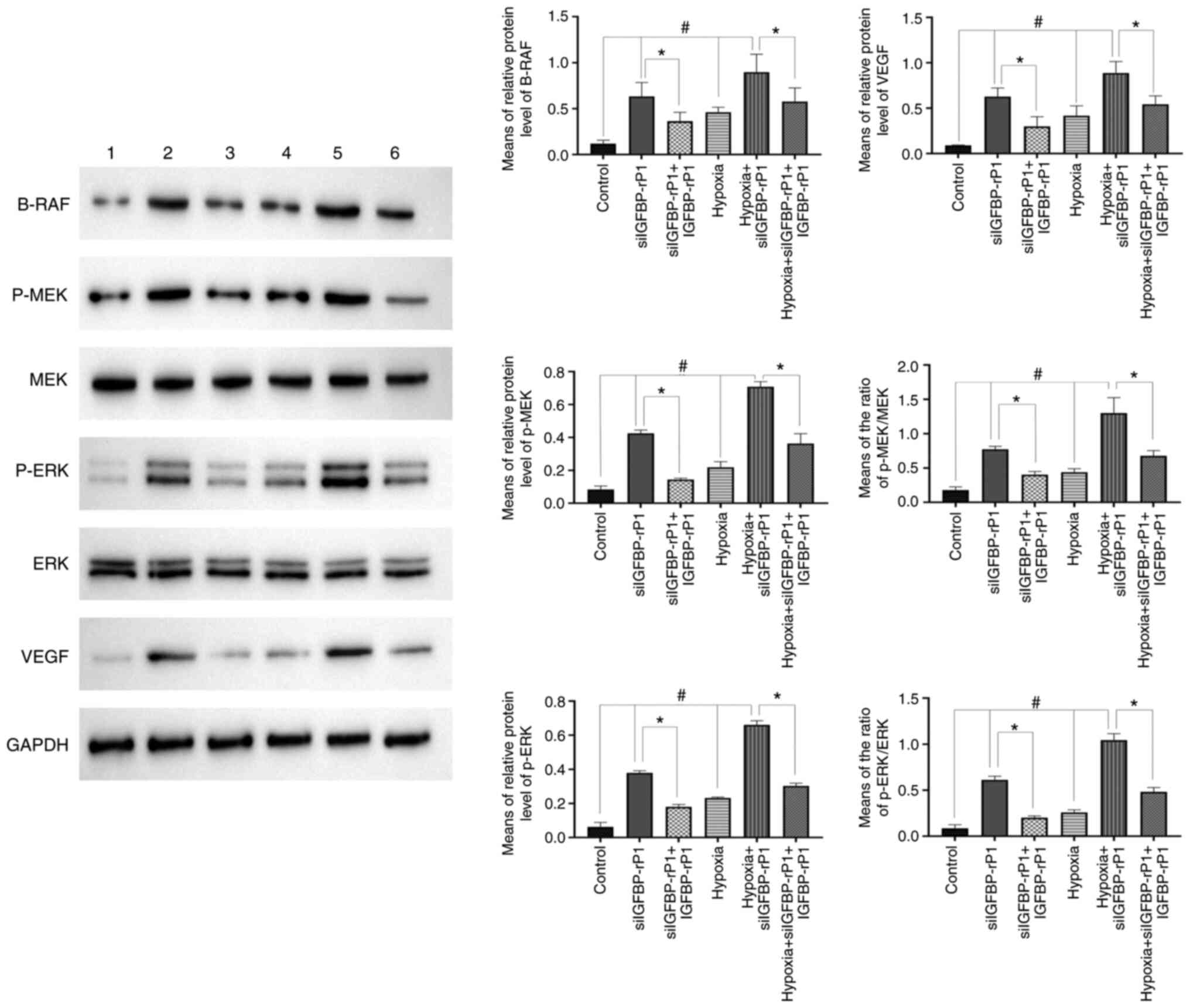
|
1
|
Yancopoulos GD, Davis S, Gale NW, Rudge
JS, Wiegand SJ and Holash J: Vascular-specific growth factors and
blood vessel formation. Nature. 407:242–248. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Daien V, Eldem BM, Talks JS, Korobelnik
JF, Mitchell P, Finger RP, Sakamoto T, Wong TY, Evuarherhe O,
Carter G and Carrasco J: Real-world data in retinal diseases
treated with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF)
therapy-a systematic approach to identify and characterize data
sources. BMC Ophthalmol. 19:2062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Campbell M and Doyle SL: Current
perspectives on established and novel therapies for pathological
neovascularization in retinal disease. Biochem Pharmacol.
164:321–325. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Campochiaro PA: Molecular pathogenesis of
retinal and choroidal vascular diseases. Prog Retin Eye Res.
49:67–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang H, Chai Z, Hu D, Ji Q, Xin J, Zhang C
and Zhong J: A global analysis of CNVs in diverse yak populations
using whole-genome resequencing. BMC Genomics. 20:612019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Park SM, Lee K, Huh M, Eom S, Park B, Kim
KH, Park DH, Kim DS and Kim HK: Development of an in vitro 3D
choroidal neovascularization model using chemically induced hypoxia
through an ultra-thin, free-standing nanofiber membrane. Mater Sci
Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 104:1099642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Alivand MR, Sabouni F and Soheili ZS:
Probable chemical hypoxia effects on progress of CNV through
induction of promoter CpG demethylation and overexpression of
IL17RC in human RPE cells. Curr Eye Res. 41:1245–1254. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Andre H, Tunik S, Aronsson M and Kvanta A:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is associated with sprouting
angiogenesis in the murine laser-induced choroidal
neovascularization model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 56:6591–6604.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Penn JS, Madan A, Caldwell RB, Bartoli M,
Caldwell RW and Hartnett ME: Vascular endothelial growth factor in
eye disease. Prog Retin Eye Res. 27:331–371. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hwa V, Oh Y and Rosenfeld RG: The
insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) superfamily.
Endocr Rev. 20:761–787. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Forbes BE, McCarthy P and Norton RS:
Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins: A structural
perspective. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 3:382012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun T, Cao H, Xu L, Zhu B, Gu Q and Xu X:
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1
mediates VEGF-induced proliferation, migration and tube formation
of retinal endothelial cells. Curr Eye Res. 36:341–349. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang P, Wang H, Cao H, Xu X and Sun T:
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1
inhibit retinal neovascularization in the mouse model of
oxygen-induced retinopathy. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 33:459–465.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sung HJ, Han JI, Lee JW, Uhm KB and Heo K:
TCCR/WSX-1 is a novel angiogenic factor in age-related macular
degeneration. Mol Vis. 18:234–240. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu M, Liu X, Wang S, Miao J, Wu L, Yang
X, Wang Y, Kang L, Li W, Cui C, et al: PKR promotes choroidal
neovascularization via upregulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
in VEGF expression. Mol Vis. 22:1361–1374. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Feng Y, Wang J, Yuan Y, Zhang X, Shen M
and Yuan F: miR-539-5p inhibits experimental choroidal
neovascularization by targeting CXCR7. Faseb J. 32:1626–1639. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chan C, Hsiao C, Li H, Fang J, Chang D and
Hung C: The inhibitory effects of gold nanoparticles on
VEGF-A-induced cell migration in choroid-retina endothelial cells.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:1092019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu Z, Liu H, Fang W, Yang Y, Wang H and
Peng J: Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 modulates
estrogen-induced trophoblast proliferation and invasion in HTR-8
and JEG-3 cells. Cell Biochem Biophys. 63:73–84. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tamura K, Yoshie M, Hashimoto K and
Tachikawa E: Inhibitory effect of insulin-like growth
factor-binding protein-7 (IGFBP7) on in vitro angiogenesis of
vascular endothelial cells in the rat corpus luteum. J Reprod Dev.
60:447–453. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Verhagen HJMP, van Gils N, Martiañez T,
van Rhenen A, Rutten A, Denkers F, de Leeuw DC, Smit MA, Tsui M, de
Vos Klootwijk LLE, et al: IGFBP7 induces differentiation and loss
of survival of human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells without
affecting normal hematopoiesis. Cell Rep. 25:3021–3035. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rozing MP, Durhuus JA, Krogh NM, Subhi Y,
Kirkwood TB, Westendorp RG and Sørensen TL: Age-related macular
degeneration: A two-level model hypothesis. Prog Retin Eye Res.
100825:2019.
|
|
22
|
Wong WL, Su X, Li X, Cheung CM, Klein R,
Cheng CY and Wong TY: Global prevalence of age-related macular
degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health.
2:e106–e116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pascolini D and Mariotti SP: Global
estimates of visual impairment: 2010. Br J Ophthalmol. 96:614–618.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lipecz A, Miller L, Kovacs I, Czako C,
Csipo T, Baffi J, Csiszar A, Tarantini S, Ungvari Z, Yabluchanskiy
A and Conley S: Microvascular contributions to age-related macular
degeneration (AMD): From mechanisms of choriocapillaris aging to
novel interventions. Geroscience. 41:813–845. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lambert NG, ElShelmani H, Singh MK,
Mansergh FC, Wride MA, Padilla M, Keegan D, Hogg RE and Ambati BK:
Risk factors and biomarkers of age-related macular degeneration.
Prog Retin Eye Res. 54:64–102. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pan H and Finkel T: Key proteins and
pathways that regulate lifespan. J Biol Chem. 292:6452–6460. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jesko H, Stepien A, Lukiw WJ and
Strosznajder RP: The cross-talk between sphingolipids and
insulin-like growth factor signaling: Significance for aging and
neurodegeneration. Mol Neurobiol. 56:3501–3521. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Haywood NJ, Slater TA, Matthews CJ and
Wheatcroft SB: The insulin like growth factor and binding protein
family: Novel therapeutic targets in obesity & diabetes. Mol
Metab. 19:86–96. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Slater T, Haywood NJ, Matthews C, Cheema H
and Wheatcroft SB: Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and
angiogenesis: From cancer to cardiovascular disease. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 46:28–35. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bach LA: Endothelial cells and the IGF
system. J Mol Endocrinol. 54:R1–R13. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cha DM, Woo SJ, Kim HJ, Lee C and Park KH:
Comparative analysis of aqueous humor cytokine levels between
patients with exudative age-related macular degeneration and normal
controls. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 54:7038–7044. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu S, Xu F, Zhang J, Ruan W and Lai M:
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 and
cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 431:23–32. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wilson HM, Birnbaum RS, Poot M, Quinn LS
and Swisshelm K: Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related
protein 1 inhibits proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells via a
senescence-like mechanism. Cell Growth Differ. 13:205–213.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mutaguchi K, Yasumoto H, Mita K, Matsubara
A, Shiina H, Igawa M, Dahiya R and Usui T: Restoration of
insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 has a
tumor-suppressive activity through induction of apoptosis in human
prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 63:7717–7723. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hu S, Chen R, Man X, Feng X, Cen J, Gu W,
He H, Li J, Chai Y and Chen Z: Function and expression of
insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) gene in
childhood acute myeloid leukemia. Pediatr Hematol Oncol.
28:279–287. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Laranjeira AB, de Vasconcellos JF, Sodek
L, Spago MC, Fornazim MC, Tone LG, Brandalise SR, Nowill AE and
Yunes JA: IGFBP7 participates in the reciprocal interaction between
acute lymphoblastic leukemia and BM stromal cells and in leukemia
resistance to asparaginase. Leukemia. 26:1001–1011. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Burger AM, Leyland-Jones B, Banerjee K,
Spyropoulos DD and Seth AK: Essential roles of IGFBP-3 and
IGFBP-rP1 in breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 41:1515–1527. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhu S, Zhang J, Xu F, Xu E, Ruan W, Ma Y,
Huang Q and Lai M: IGFBP-rP1 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis.
6:e16952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Seki M, Teishima J, Mochizuki H, Mutaguchi
K, Yasumoto H, Oka K, Nagamatsu H, Shoji K and Matsubara A:
Restoration of IGFBP-rP1 increases radiosensitivity and
chemosensitivity in hormone-refractory human prostate cancer.
Hiroshima J Med Sci. 62:13–19. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Akiel M, Guo C, Li X, Rajasekaran D,
Mendoza RG, Robertson CL, Jariwala N, Yuan F, Subler MA, Windle J,
et al: IGFBP7 deletion promotes hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer
Res. 77:4014–4025. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jiang H, Wu M, Liu Y, Song L, Li S, Wang
X, Zhang YF, Fang J and Wu S: Serine racemase deficiency attenuates
choroidal neovascularization and reduces nitric oxide and VEGF
levels by retinal pigment epithelial cells. J Neurochem.
143:375–388. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen S, Zhou Y, Zhou L, Guan Y, Zhang Y
and Han X: Anti-neovascularization effects of DMBT in age-related
macular degeneration by inhibition of VEGF secretion through
ROS-dependent signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 448:225–235.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Milhavet O, Gary DS and Mattson MP: RNA
interference in biology and medicine. Pharmacol Rev. 55:629–648.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tam C, Wong JH, Cheung R, Zuo T and Ng TB:
Therapeutic potentials of short interfering RNAs. Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 101:7091–7111. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ramachandran PS, Keiser MS and Davidson
BL: Recent advances in RNA interference therapeutics for CNS
diseases. Neurotherapeutics. 10:473–485. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Corydon TJ: Antiangiogenic eye gene
therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 26:525–537. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Moore NA, Bracha P, Hussain RM, Morral N
and Ciulla TA: Gene therapy for age-related macular degeneration.
Expert Opin Biol Ther. 17:1235–1244. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Moore SM, Skowronska-Krawczyk D and Chao
DL: Emerging concepts for RNA therapeutics for inherited retinal
disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1185:85–89. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yang XM, Wang YS, Zhang J, Li Y, Xu JF,
Zhu J, Zhao W, Chu DK and Wiedemann P: Role of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK
in mediating hypoxia-induced expression of HIF-1alpha and VEGF in
laser-induced rat choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 50:1873–1879. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lee CS, Choi EY, Lee SC, Koh HJ, Lee JH
and Chung JH: Resveratrol inhibits hypoxia-induced vascular
endothelial growth factor expression and pathological
neovascularization. Yonsei Med J. 56:1678–1685. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Biswal MR, Prentice HM, Smith GW, Zhu P,
Tong Y, Dorey CK, Lewin AS and Blanks JC: Cell-specific gene
therapy driven by an optimized hypoxia-regulated vector reduces
choroidal neovascularization. J Mol Med (Berl). 96:1107–1118. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang T, Li X, Yu W, Yan Z, Zou H and He
X: Overexpression of thymosin beta-10 inhibits VEGF mRNA
expression, autocrine VEGF protein production, and tube formation
in hypoxia-induced monkey choroid-retinal endothelial cells.
Ophthalmic Res. 41:36–43. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jin J, Yuan F, Shen MQ, Feng YF and He QL:
Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates primate
choroid-retinal endothelial cell proliferation and tube formation
through PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK dependent signaling. Mol Cell Biochem.
381:267–272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li R, Du J and Chang Y: Role of autophagy
in hypoxia-induced angiogenesis of RF/6A cells in vitro. Curr Eye
Res. 41:1566–1570. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Cui K, Zhang S, Liu X, Yan Z, Huang L,
Yang X, Zhu R and Sang A: Inhibition of TBK1 reduces choroidal
neovascularization in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Bioph Res Co.
503:202–208. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Borcar A, Menze MA, Toner M and Hand SC:
Metabolic preconditioning of mammalian cells: Mimetic agents for
hypoxia lack fidelity in promoting phosphorylation of pyruvate
dehydrogenase. Cell Tissue Res. 351:99–106. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cabral T, Mello L, Lima LH, Polido J,
Regatieri CV, Belfort RJ and Mahajan VB: Retinal and choroidal
angiogenesis: A review of new targets. Int J Retina Vitreous.
3:312017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Farnoodian M, Sorenson CM and Sheibani N:
Negative regulators of angiogenesis, ocular vascular homeostasis,
and pathogenesis and treatment of exudative AMD. J Ophthalmic Vis
Res. 13:470–486. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Farnoodian M, Wang S, Dietz J, Nickells
RW, Sorenson CM and Sheibani N: Negative regulators of
angiogenesis: Important targets for treatment of exudative AMD.
Clin Sci (Lond). 131:1763–1780. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Farnoodian M, Sorenson CM and Sheibani N:
PEDF expression affects the oxidative and inflammatory state of
choroidal endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
314:C456–C472. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Housset M and Sennlaub F: Thrombospondin-1
and pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. J Ocul
Pharmacol Ther. 31:406–412. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Terao N, Koizumi H, Kojima K, Yamagishi T,
Yamamoto Y, Yoshii K, Kitazawa K, Hiraga A, Toda M, Kinoshita S, et
al: Distinct aqueous humour cytokine profiles of patients with
pachychoroid neovasculopathy and neovascular age-related macular
degeneration. Sci Rep. 8:105202018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Gehart H, Kumpf S, Ittner A and Ricci R:
MAPK signalling in cellular metabolism: Stress or wellness? EMBO
Rep. 11:834–840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sun Y, Liu W, Liu T, Feng X, Yang N and
Zhou H: Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation,
differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept
Signal Transduct Res. 35:600–604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Rezatabar S, Karimian A, Rameshknia V,
Parsian H, Majidinia M, Kopi TA, Bishayee A, Sadeghinia A, Yousefi
M, Monirialamdari M and Yousefi B: RAS/MAPK signaling functions in
oxidative stress, DNA damage response and cancer progression. J
Cell Physiol. 234:14951–14965. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Marampon F, Ciccarelli C and Zani BM:
Biological rationale for targeting MEK/ERK pathways in anti-cancer
therapy and to potentiate tumour responses to radiation. Int J Mol
Sci. 20:25302019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Khaliq M and Fallahi-Sichani M: Epigenetic
mechanisms of escape from BRAF oncogene dependency. Cancers
(Basel). 11:14802019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Degirmenci U, Wang M and Hu J: Targeting
aberrant RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling for cancer therapy. Cells.
9:1982020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Huang M, Huang B, Li G and Zeng S:
Apatinib affect VEGF-mediated cell proliferation, migration,
invasion via blocking VEGFR2/RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways in
cholangiocarcinoma cell. BMC Gastroenterol. 18:1692018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yamana S, Tokiyama A, Fujita H, Terao Y,
Horibe S, Sasaki N, Satomi-Kobayashi S, Hirata KI and Rikitake Y:
Necl-4 enhances the PLCγ-c-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway without affecting
internalization of VEGFR2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 490:169–175.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Gong J, Zhou S and Yang S: Vanillic acid
suppresses HIF-1α expression via inhibition of mTOR/p70S6K/4E-BP1
and Raf/MEK/ERK pathways in human colon cancer HCT116 cells. Int J
Mol Sci. 20:e4652019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Pachmayr E, Treese C and Stein U:
Underlying mechanisms for distant metastasis-molecular biology.
Visc Med. 33:11–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhang EY, Gao B, Shi HL, Huang LF, Yang L,
Wu XJ and Wang ZT: 20(S)-protopanaxadiol enhances angiogenesis via
HIF-1α-mediated VEGF secretion by activating p70S6 kinase and
benefits wound healing in genetically diabetic mice. Exp Mol Med.
49:e3872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ye X, Xu G, Chang Q, Fan J, Sun Z, Qin Y
and Jiang AC: ERK1/2 signaling pathways involved in VEGF release in
diabetic rat retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 51:5226–5233. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hou SY, Li YP, Wang JH, Yang SL, Wang Y,
Wang Y and Kuang Y: Aquaporin-3 inhibition reduces the growth of
NSCLC cells induced by hypoxia. Cell Physiol Biochem. 38:129–140.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Shen K, Ji L, Gong C, Ma Y, Yang L, Fan Y,
Hou M and Wang Z: Notoginsenoside Ft1 promotes angiogenesis via
HIF-1α mediated VEGF secretion and the regulation of PI3K/AKT and
Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Biochem Pharmacol. 84:784–792.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|