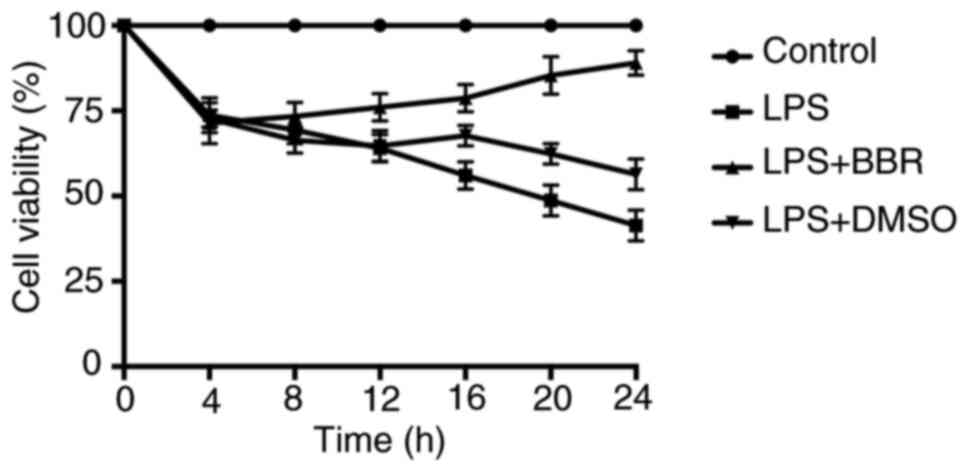
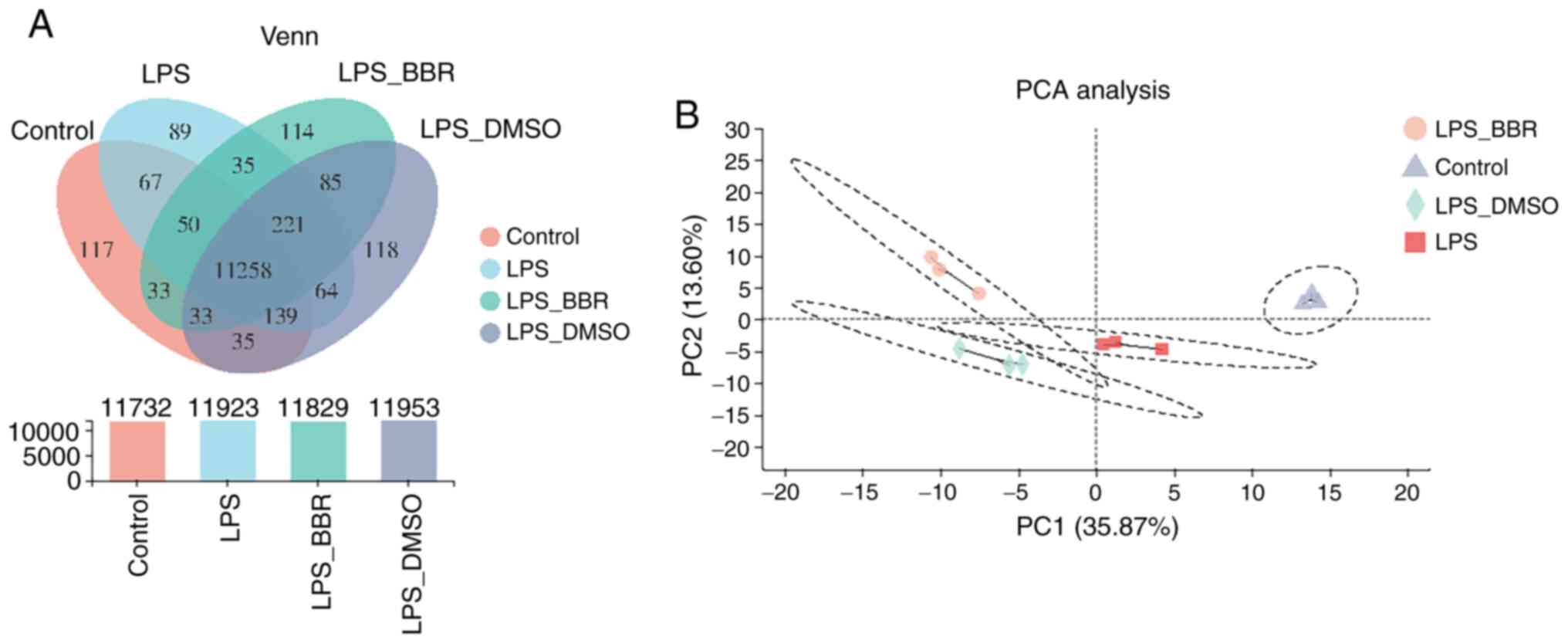
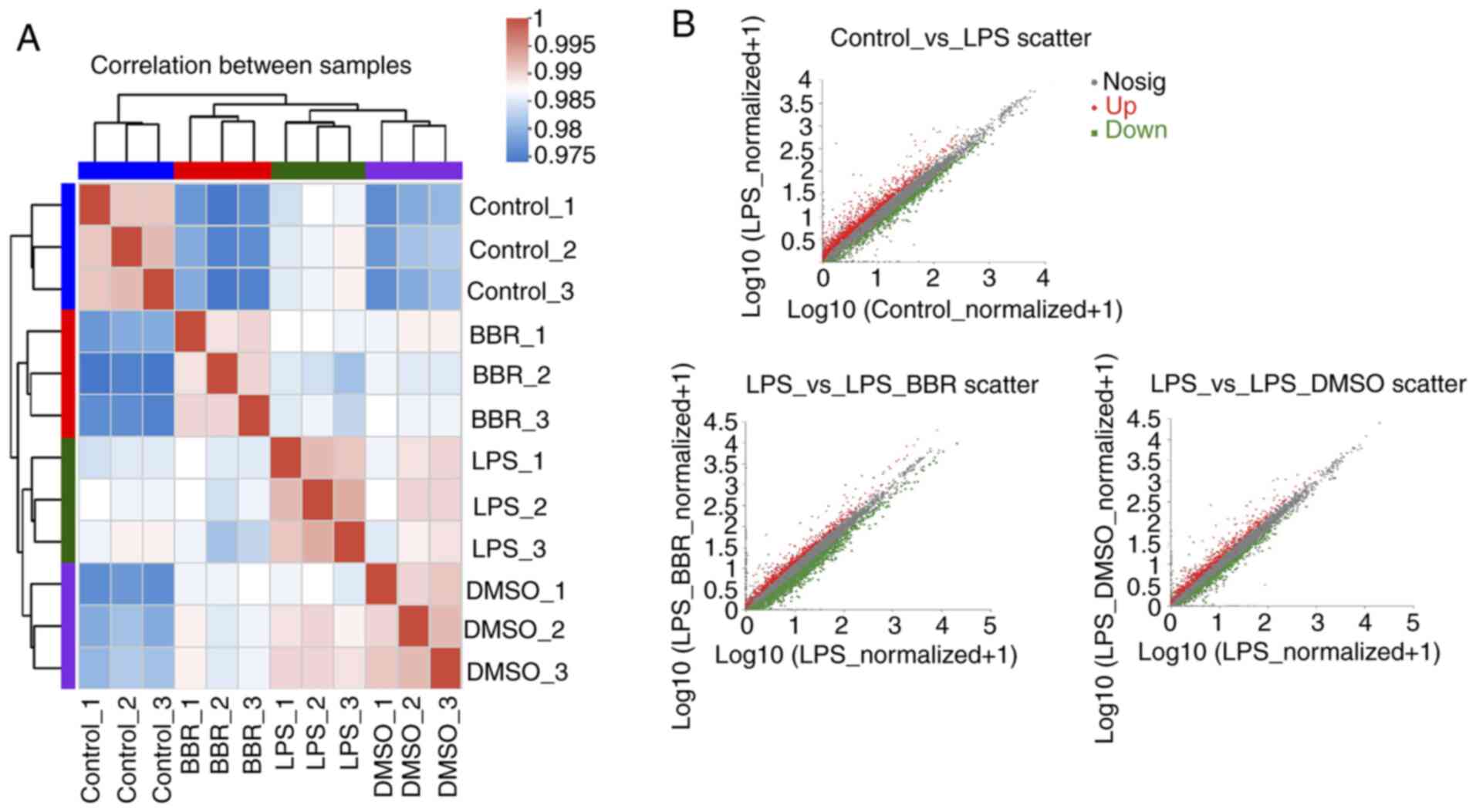
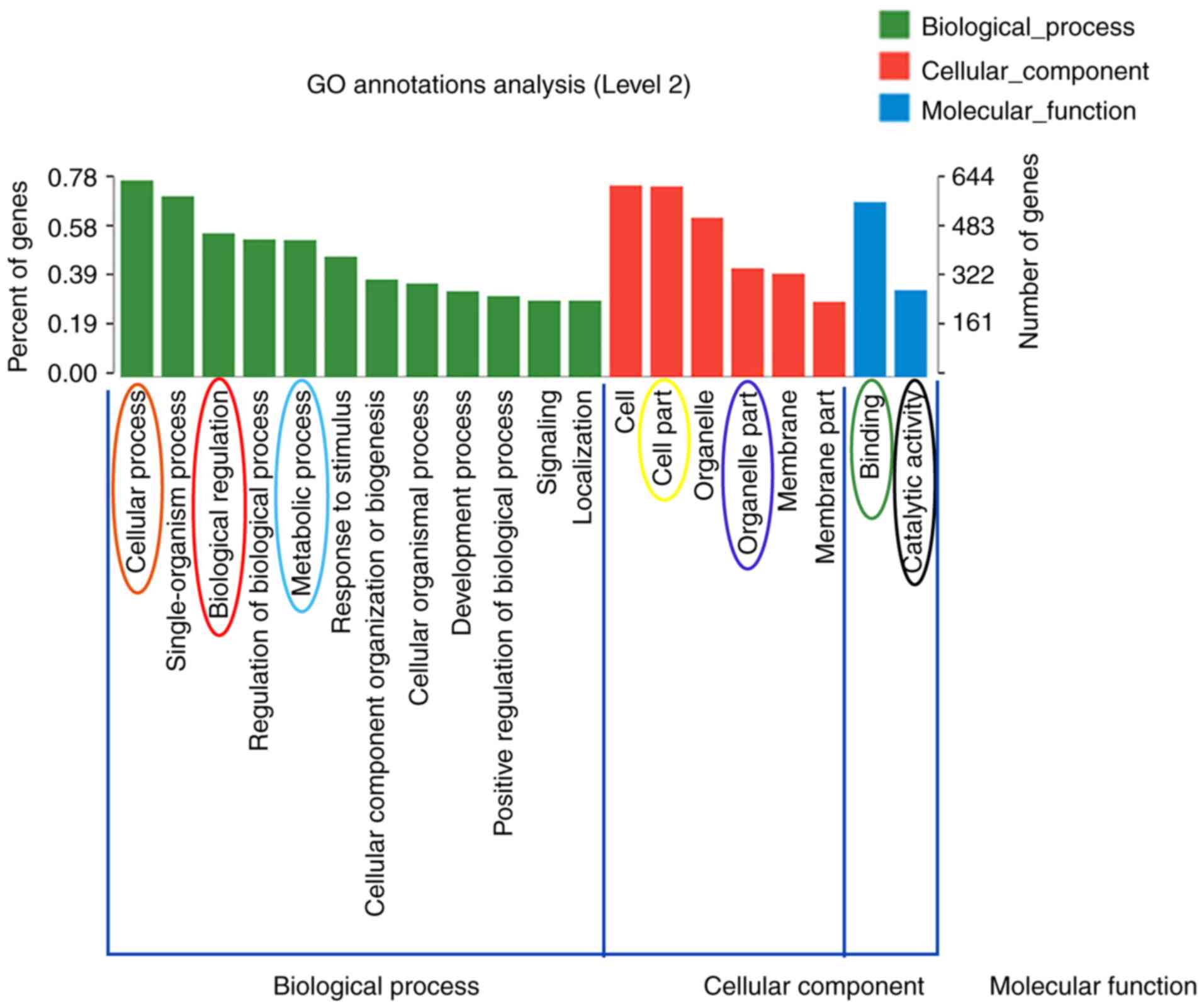
|
1
|
Fest J, Ruiter R, Mulder M, Groot Koerkamp
B, Ikram MA, Stricker BH and van Eijck CHJ: The systemic
immune-inflammation index is associated with an increased risk of
incident cancer-A population-based cohort study. Int J Cancer.
146:692–698. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Das S, Reddy MA, Senapati P, Stapleton K,
Lanting L, Wang M, Amaram V, Ganguly R, Zhang L, Devaraj S, et al:
Diabetes mellitus-induced long noncoding RNA Dnm3os regulates
macrophage functions and inflammation via nuclear mechanisms.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 38:1806–1820. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sorriento D and Iaccarino G: Inflammation
and cardiovascular diseases: The most recent findings. Int J Mol
Sci. 20:38792019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dragasevic S, Stankovic B, Kotur N,
Sokic-Milutinovic A, Milovanovic T, Lukic S, Milosavljevic T,
Srzentic Drazilov S, Klaassen K, Pavlovic S and Popovic D:
Metabolic syndrome in inflammatory bowel disease: Association with
genetic markers of obesity and inflammation. Metab Syndr Relat
Disord. 18:31–38. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bian Y, Dong Y, Sun J, Sun M, Hou Q, Lai Y
and Zhang B: Protective effect of kaempferol on LPS-induced
inflammation and barrier dysfunction in a coculture model of
intestinal epithelial cells and intestinal microvascular
endothelial cells. J Agric Food Chem. 68:160–167. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huttenhower C, Kostic AD and Xavier RJ:
Inflammatory bowel disease as a model for translating the
microbiome. Immunity. 40:843–854. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vong LB, Mo J, Abrahamsson B and Nagasaki
Y: Specific accumulation of orally administered redox
nanotherapeutics in the inflamed colon reducing inflammation with
dose-response efficacy. J Control Release. 210:19–25. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aziz DA, Moin M, Majeed A, Sadiq K and
Biloo AG: Paediatric inflammatory bowel disease: Clinical
presentation and disease location. Pak J Med Sci. 33:793–797.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peterson LW and Artis D: Intestinal
epithelial cells: Regulators of barrier function and immune
homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:141–153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Allaire JM, Crowley SM, Law HT, Chang SY,
Ko HJ and Vallance BA: The intestinal epithelium: Central
coordinator of mucosal immunity. Trends Immunol. 39:677–696. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zeng XZ, Zhang YY, Yang Q, Wang S, Zou BH,
Tan YH, Zou M, Liu SW and Li XJ: Artesunate attenuates LPS-induced
osteoclastogenesis by suppressing TLR4/TRAF6 and PLCγ1-Ca
2+-NFATc1 signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
41:229–236. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fang F and Jiang D: IL-1β/HMGB1 signalling
promotes the inflammatory cytokines release via TLR signalling in
human intervertebral disc cells. Biosci Rep. 36:e003792016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yeh M, Granger DN and Glass J: Increases
in IKK-A activity, IKB-A phosphorylation and degradation and p50
subunit production precede nfkb activation in the intestine of rats
after LPS administration. Gastroenterology. 118:PA8192000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shirwaikar A, Shirwaikar A, Rajendran K
and Punitha IS: In vitro antioxidant studies on the benzyl tetra
isoquinoline alkaloid berberine. Biol Pharm Bull. 29:1906–1910.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tang J, Feng Y, Tsao S, Wang N, Curtain R
and Wang Y: Berberine and Coptidis rhizoma as novel antineoplastic
agents: A review of traditional use and biomedical investigations.
J Ethnopharmacol. 126:5–17. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Germoush MO and Mahmoud AM: Berberine
mitigates cyclophosphamide-induced hepatotoxicity by modulating
antioxidant status and inflammatory cytokines. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 140:1103–1109. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu YF, Wen CY, Chen Z, Wang Y, Huang Y
and Tu SH: Effects of berberine on NLRP3 and IL-1β expressions in
monocytic THP-1 cells with monosodium urate crystals-induced
inflammation. Biomed Res Int. 2016:25037032016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kuo CL, Chi CW and Liu TY: The
anti-inflammatory potential of berberine in vitro and in vivo.
Cancer Lett. 203:127–137. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bae YA and Cheon HG: Activating
transcription factor-3 induction is involved in the
anti-inflammatory action of berberine in RAW264.7 murine
macrophages. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 20:415–424. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang H, Shan Y, Wu Y, Xu C, Yu X, Zhao J,
Yan J and Shang W: Berberine suppresses LPS-induced inflammation
through modulating Sirt1/NF-κB signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells.
Int Immunopharmacol. 52:93–100. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li H, Fan C, Lu H, Feng C, He P, Yang X,
Xiang C, Zuo J and Tang W: Protective role of berberine on
ulcerative colitis through modulating enteric glial
cells-intestinal epithelial cells-immune cells interactions. Acta
Pharm Sin B. 10:447–461. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jing W, Safarpour Y, Zhang T, Guo P, Chen
G, Wu X, Fu Q and Wang Y: Berberine upregulates P-Glycoprotein in
human caco-2 cells and in an experimental model of colitis in the
rat via activation of Nrf2-dependent mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 366:332–340. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li C, Xi Y, Li S, Zhao Q, Cheng W, Wang Z,
Zhong J, Niu X and Chen G: Berberine ameliorates TNBS induced
colitis by inhibiting inflammatory responses and Th1/Th17
differentiation. Mol Immunol. 67:444–454. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pengyu Z, Yan Y, Xiying F, Maoguang Y, Mo
L, Yan C, Hong S, Lijuan W, Xiujuan Z and Hanqing C: The
differential expression of long noncoding RNAs in type 2 diabetes
mellitus and latent autoimmune diabetes in adults. Int J
Endocrinol. 2020:92353292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
The Gene Ontology Consortium: The gene
ontology resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids
Res. 47:D330–D338. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ogata H, Goto S, Sato K, Fujibuchi W, Bono
H and Kanehisa M: KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes.
Nucleic Acids Res. 27:29–34. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chang S, Chen W and Yang J: Another
formula for calculating the gene change rate in real-time RT-PCR.
Mol Biol Rep. 36:2165–2168. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Y, Zhao L, Li X, Wang Y, Yao J, Wang
H, Li F, Li Z and Guo Q: V8, a newly synthetic flavonoid, induces
apoptosis through ROS-mediated ER stress pathway in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Arch Toxicol. 88:97–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 65:55–63. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Loeb LA and Monnat RJ Jr: DNA polymerases
and human disease. Nature Rev Genet. 9:594–604. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zeman MK and Cimprich KA: Causes and
consequences of replication stress. Nat Cell Biol. 16:2–9. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Blow JJ and Gillespie PJ: Replication
licensing and cancer-a fatal entanglement? Nat Rev Cancer.
8:799–806. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mendez J and Stillman B: Perpetuating the
double helix: Molecular machines at eukaryotic DNA replication
origins. Bioessays. 25:1158–1167. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Blow JJ and Dutta A: Preventing
re-replication of chromosomal DNA. Nature reviews. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 6:476–486. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Arias EE and Walter JC: Strength in
numbers: Preventing rereplication via multiple mechanisms in
eukaryotic cells. Genes Dev. 21:497–518. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Moyer SE, Lewis PW and Botchan MR:
Isolation of the Cdc45/Mcm2-7/GINS (CMG) complex, a candidate for
the eukaryotic DNA replication fork helicase. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:10236–10241. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ilves I, Petojevic T, Pesavento JJ and
Botchan MR: Activation of the MCM2-7 helicase by association with
Cdc45 and GINS proteins. Mol Cell. 37:247–258. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Moldovan GL, Pfander B and Jentsch S:
PCNA, the maestro of the replication fork. Cell. 129:665–679. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cernak I, Stoica B, Byrnes KR, Di Giovanni
S and Faden AI: Role of the cell cycle in the pathobiology of
central nervous system trauma. Cell Cycle. 4:1286–1293. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Stoica BA, Byrnes KR and Faden AI: Cell
cycle activation and CNS injury. Neurotox Res. 16:221–237. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li L, Wang X, Sharvan R, Gao J and Qu S:
Berberine could inhibit thyroid carcinoma cells by inducing
mitochondrial apoptosis, G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and suppressing
migration via PI3K-AKT and MAPK signaling pathways. Biomed
Pharmacother. 95:1225–1231. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chong SJ, Low IC and Pervaiz S:
Mitochondrial ROS and involvement of Bcl-2 as a mitochondrial ROS
regulator. Mitochondrion. 19:39–48. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hashemi-Niasari F, Rabbani-Chadegani A,
Razmi M and Fallah S: Synergy of theophylline reduces necrotic
effect of berberine, induces cell cycle arrest and PARP, HMGB1,
Bcl-2 family mediated apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 106:858–867. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
PLOS ONE Editors: Retraction: Bak
compensated for bax in p53-null cells to release cytochrome c for
the initiation of mitochondrial signaling during withanolide
D-induced apoptosis. PLoS One. 15:e02288392020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Neame SJ, Rubin LL and Philpott KL:
Blocking cytochrome c activity within intact neurons inhibits
apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 142:1583–1593. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chauhan D, Pandey P, Ogata A, Teoh G,
Krett N, Halgren R, Rosen S, Kufe D, Kharbanda S and Anderson K:
Cytochrome c-dependent and -independent induction of apoptosis in
multiple myeloma cells. J Biol Chem. 272:29995–29997. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Campisi L, Cummings RJ and Blander JM:
Death-defining immune responses after apoptosis. Am J Transplant.
14:1488–1498. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Song Z and Steller H: Death by design:
Mechanism and control of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 9:M49–M52.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Stanford A, Chen Y, Zhang XR, Hoffman R,
Zamora R and Ford HR: Nitric oxide mediates dendritic cell
apoptosis by downregulating inhibitors of apoptosis proteins and
upregulating effector caspase activity. Surgery. 130:326–332. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Fu L, Chen W, Guo W, Wang J, Tian Y, Shi
D, Zhang X, Qiu H, Xiao X, Kang T, et al: Berberine targets
AP-2/hTERT, NF-κB/COX-2, HIF-1α/VEGF and Cytochrome-c/Caspase
signaling to suppress human cancer cell growth. PLoS One.
8:e692402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kalaiarasi A, Anusha C, Sankar R,
Rajasekaran S, John Marshal J, Muthusamy K and Ravikumar V: Plant
isoquinoline alkaloid berberine exhibits chromatin remodeling by
modulation of histone deacetylase to induce growth arrest and
apoptosis in the A549 cell line. J Agric Food Chem. 64:9542–9550.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhao C, Wang Y, Yuan X, Sun G, Shen B, Xu
F, Fan G, Jin M, Li X and Liu G: Berberine inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines by
suppressing TLR4-mediated NF-ĸB and MAPK signaling pathways in
rumen epithelial cells of Holstein calves. J Dairy Res. 86:171–176.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kim S, Choi JH, Kim JB, Nam SJ, Yang JH,
Kim JH and Lee JE: Berberine suppresses TNF-alpha-induced MMP-9 and
cell invasion through inhibition of AP-1 activity in MDA-MB-231
human breast cancer cells. Molecules. 13:2975–2985. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Güney Eskiler G, Deveci Özkan A, Kaleli S
and Bilir C: Inhibition of TLR4/TRIF/IRF3 signaling pathway by
curcumin in breast cancer cells. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 22:281–291.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Muroi M and Tanamoto K: TRAF6
distinctively mediates MyD88- and IRAK-1-induced activation of
NF-kappaB. J Leukoc Biol. 83:702–707. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang J, Macartney T, Peggie M and Cohen
P: Interleukin-1 and TRAF6-dependent activation of TAK1 in the
absence of TAB2 and TAB3. Biochem J. 474:2235–2248. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Jang JH, Kim H and Cho JH: Molecular
cloning and functional characterization of TRAF6 and TAK1 in
rainbow trout, oncorhynchus mykiss. Fish Shellfish Immunol.
84:927–936. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yu-Wei D, Li ZS, Xiong SM, Huang G, Luo
YF, Huo TY, Zhou MH and Zheng YW: Paclitaxel induces apoptosis
through the TAK1-JNK activation pathway. FEBS Open Bio.
10:1655–1667. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Yuan Z, Liang Z, Yi J, Chen X, Li R, Wu J
and Sun Z: Koumine promotes ROS production to suppress
hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation via NF-κB and ERK/p38
MAPK signaling. Biomolecules. 9:5592019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Pan J, Jin R, Shen M, Wu R and Xu S:
Acamprosate protects against adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats via
blocking the ERK/MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway. Inflammation.
41:1194–1199. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kitanaka T, Nakano R, Kitanaka N, Kimura
T, Okabayashi K, Narita T and Sugiya H: JNK activation is essential
for activation of MEK/ERK signaling in IL-1β-induced COX-2
expression in synovial fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 7:399142017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Rossaint J, Margraf A and Zarbock A: Role
of platelets in leukocyte recruitment and resolution of
inflammation. Front Immunol. 9:27122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Trivedi PJ and Adams DH: Chemokines and
chemokine receptors as therapeutic targets in inflammatory bowel
disease; pitfalls and promise. J Crohns Colitis. 12 (Suppl
2):S641–S652. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kvedaraite E, Lourda M, Ideström M, Chen
P, Olsson-Åkefeldt S, Forkel M, Gavhed D, Lindforss U, Mjösberg J,
Henter JI and Svensson M: Tissue-infiltrating neutrophils represent
the main source of IL-23 in the colon of patients with IBD. Gut.
65:1632–1641. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Habas K and Shang L: Alterations in
intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell
adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) in human endothelial cells. Tissue
Cell. 54:139–143. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Weber CR, Nalle SC, Tretiakova M, Rubin DT
and Turner JR: Claudin-1 and claudin-2 expression is elevated in
inflammatory bowel disease and may contribute to early neoplastic
transformation. Lab Invest. 88:1110–1120. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhou J, Yu Y, Yang X, Wang Y, Song Y, Wang
Q, Chen Z, Zong S, Fan M, Meng X, et al: Berberine attenuates
arthritis in adjuvant-induced arthritic rats associated with
regulating polarization of macrophages through AMPK/NF-кB pathway.
Eur J Pharmacol. 852:179–188. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Li H, Li XL, Zhang M, Xu H, Wang CC, Wang
S and Duan RS: Berberine ameliorates experimental autoimmune
neuritis by suppressing both cellular and humoral immunity. Scand J
Immunol. 79:12–19. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wang Q, Qi J, Hu R, Chen Y, Kijlstra A and
Yang P: Effect of berberine on proinflammatory cytokine production
by ARPE-19 cells following stimulation with tumor necrosis
factor-α. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:2395–2402. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Boulangé CL, Neves AL, Chilloux J,
Nicholson JK and Dumas ME: Impact of the gut microbiota on
inflammation, obesity, and metabolic disease. Genome Med. 8:422008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Ali L, Schnitzler JG and Kroon J:
Metabolism: The road to inflammation and atherosclerosis. Curr Opin
Lipidol. 29:474–480. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Xu F, Yang J, Meng B, Zheng JW, Liao Q,
Chen JP and Chen XW: The effect of berberine on ameliorating
chronic inflammatory pain and depression. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.
98:1103–1108. 2018.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Da Silva MS, Bigo C, Barbier O and
Rudkowska I: Whey protein hydrolysate and branched-chain amino
acids downregulate inflammation-related genes in vascular
endothelial cells. Nutr Res. 38:43–51. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chen YX, Gao QY, Zou TH, Wang BM, Liu SD,
Sheng JQ, Ren JL, Zou XP, Liu ZJ, Song YY, et al: Berberine versus
placebo for the prevention of recurrence of colorectal adenoma: A
multicentre, double-blinded, randomised controlled study. Lancet
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 5:267–275. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|