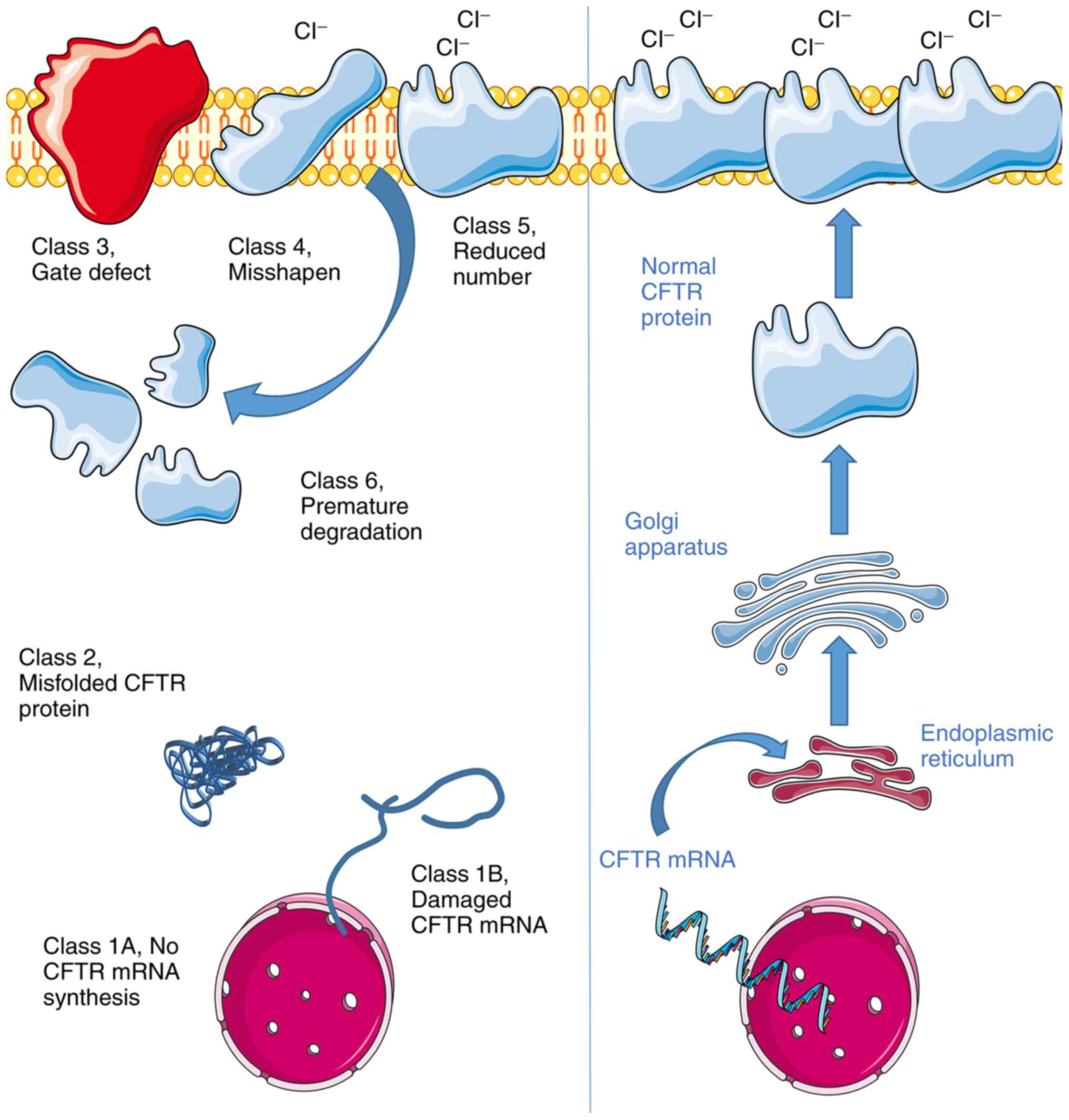
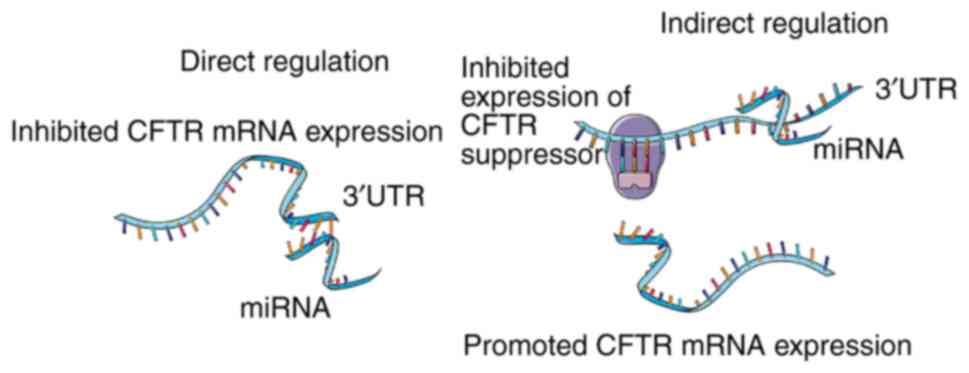
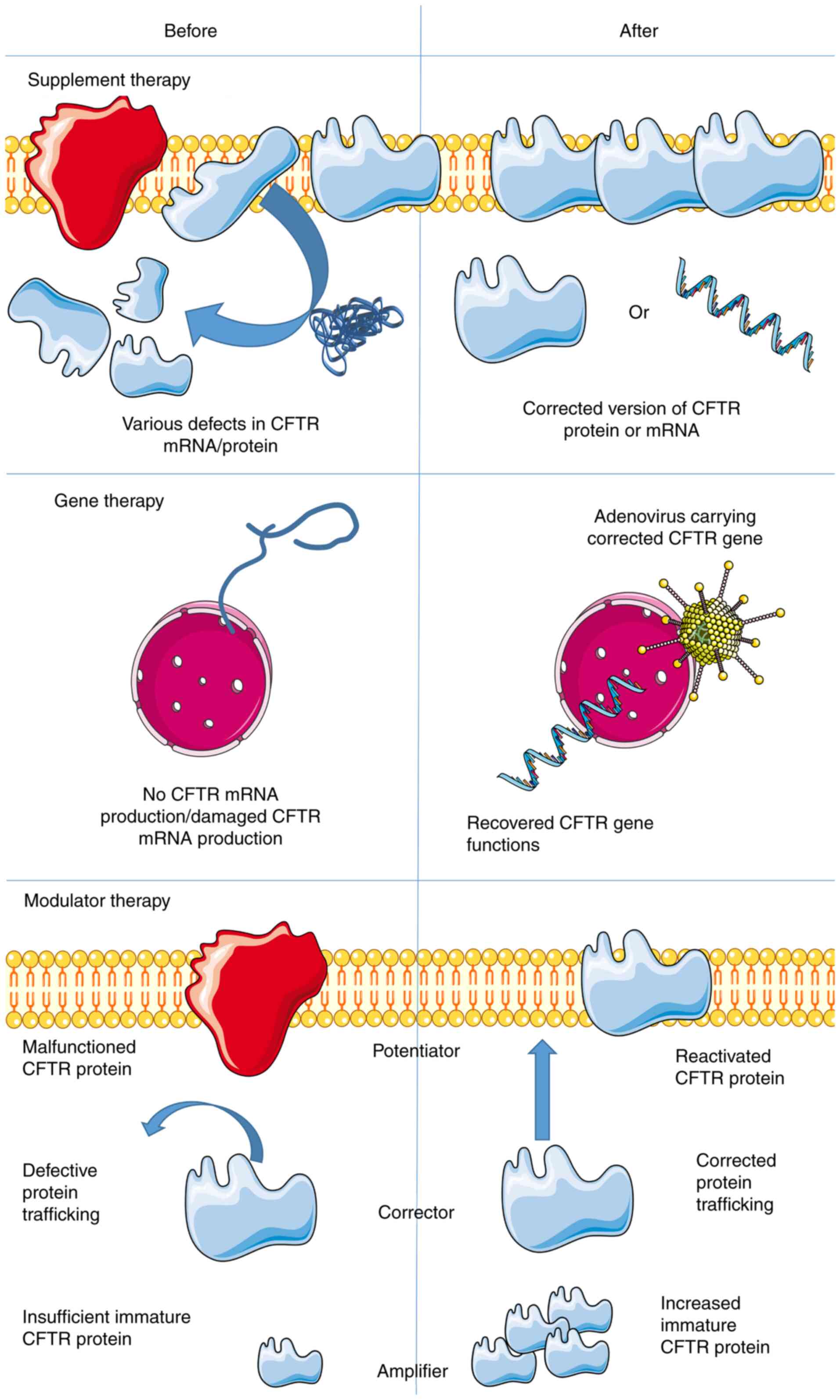
|
1
|
Klimova B, Kuca K, Novotny M and Maresova
P: Cystic fibrosis revisited-a review study. Med Chem. 13:102–109.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brewington JJ, Filbrandt ET, LaRosa FJ
III, Ostmann AJ, Strecker LM, Szczesniak RD and Clancy JP:
Detection of CFTR function and modulation in primary human nasal
cell spheroids. J Cyst Fibros. 17:26–33. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Keiser NW, Birket SE, Evans IA, Tyler SR,
Crooke AK, Sun X, Zhou W, Nellis JR, Stroebele EK, Chu KK, et al:
Defective innate immunity and hyperinflammation in newborn cystic
fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-knockout ferret lungs.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 52:683–694. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Santoro D, Postorino A, Lucanto C, Costa
S, Cristadoro S, Pellegrino S, Conti G, Buemi M, Magazzù G and
Bellinghieri G: Cystic fibrosis: A risk condition for renal
disease. J Ren Nutr. 27:470–473. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dekkers JF, Wiegerinck CL, de Jonge HR,
Bronsveld I, Janssens HM, de Winter-de Groot KM, Brandsma AM, de
Jong NW, Bijvelds MJ, Scholte BJ, et al: A functional CFTR assay
using primary cystic fibrosis intestinal organoids. Nat Med.
19:939–945. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Harutyunyan M, Huang Y, Mun KS, Yang F,
Arora K and Naren AP: Personalized medicine in CF: From modulator
development to therapy for cystic fibrosis patients with rare CFTR
mutations. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 314:L529–L543. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pankow S, Bamberger C, Calzolari D,
Martínez-Bartolomé S, Lavallée-Adam M, Balch WE and Yates JR III:
∆F508 CFTR interactome remodelling promotes rescue of cystic
fibrosis. Nature. 528:510–516. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gadsby DC, Vergani P and Csanady L: The
ABC protein turned chloride channel whose failure causes cystic
fibrosis. Nature. 440:477–483. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rommens JM, Iannuzzi MC, Kerem B, Drumm
ML, Melmer G, Dean M, Rozmahel R, Cole JL, Kennedy D, Hidaka N, et
al: Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: Chromosome walking
and jumping. Science. 245:1059–1065. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Saint-Criq V and Gray MA: Role of CFTR in
epithelial physiology. Cell Mol Life Sci. 74:93–115. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cuthbert AW: New horizons in the treatment
of cystic fibrosis. Br J Pharmacol. 163:173–183. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Z and Chen J: Atomic structure of
the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. Cell.
167:1586–1597.e9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xue X, Mutyam V, Thakerar A, Mobley J,
Bridges RJ, Rowe SM, Keeling KM and Bedwell DM: Identification of
the amino acids inserted during suppression of CFTR nonsense
mutations and determination of their functional consequences. Hum
Mol Genet. 26:3116–3129. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dodge JA: A millennial view of cystic
fibrosis. Dev Period Med. 19:9–13. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Singh M, Rebordosa C, Bernholz J and
Sharma N: Epidemiology and genetics of cystic fibrosis in Asia: In
preparation for the next-generation treatments. Respirology.
20:1172–1181. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Alibakhshi R and Zamani M: Mutation
analysis of CFTR gene in 70 Iranian cystic fibrosis patients. Iran
J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 5:3–8. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zeitlin PL: Cystic fibrosis and estrogens:
A perfect storm. J Clin Invest. 118:3841–3844. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lui JK, Kilch J, Fridlyand S, Dheyab A and
Bielick Kotkowski C: Non-classic cystic fibrosis: The value in
family history. Am J Med. 130:e333–e334. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thomas JM, Durack A, Sterling A, Todd PM
and Tomson N: Aquagenic wrinkling of the palms: A diagnostic clue
to cystic fibrosis carrier status and non-classic disease. Lancet.
389:8462017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Severiche-Bueno D, Gamboa E, Reyes LF and
Chotirmall SH: Hot topics and current controversies in non-cystic
fibrosis bronchiectasis. Breathe (Sheff). 15:286–295. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Andersen DH: Cystic fibrosis of the
pancreas and its relation to celiac disease. Am J Dis Child.
56:1938. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bell SC, Mall MA, Gutierrez H, Macek M,
Madge S, Davies JC, Burgel PR, Tullis E, Castaños C, Castellani C,
et al: The future of cystic fibrosis care: A global perspective.
Lancet Respir Med. 8:65–124. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gibson LE and Cooke RE: A test for
concentration of electrolytes in sweat in cystic fibrosis of the
pancreas utilizing pilocarpine by iontophoresis. Pediatrics.
23:545–549. 1959.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Di Sant'agnese PA, Darling RC, Perera GA
and Shea E: Abnormal electrolyte composition of sweat in cystic
fibrosis of the pancreas; clinical significance and relationship to
the disease. Pediatrics. 12:549–563. 1953.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Davis PB: Cystic fibrosis since 1938. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 173:475–482. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yamada A, Komaki Y, Komaki F, Micic D,
Zullow S and Sakuraba A: Risk of gastrointestinal cancers in
patients with cystic fibrosis: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 19:758–767. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Goetz D and Ren CL: Review of cystic
fibrosis. Pediatr Ann. 48:e154–e161. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fanen P, Wohlhuter-Haddad A and Hinzpeter
A: Genetics of cystic fibrosis: CFTR mutation classifications
toward genotype-based CF therapies. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
52:94–102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Linsdell P: Cystic fibrosis transmembrane
conductance regulator (CFTR): Making an ion channel out of an
active transporter structure. Channels (Austin). 12:284–290. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Moran O: The gating of the CFTR channel.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 74:85–92. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mall MA and Galietta LJ: Targeting ion
channels in cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros. 14:561–570. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gentzsch M and Mall MA: Ion channel
modulators in cystic fibrosis. Chest. 154:383–393. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shah VS, Meyerholz DK, Tang XX, Reznikov
L, Abou Alaiwa M, Ernst SE, Karp PH, Wohlford-Lenane CL, Heilmann
KP, Leidinger MR, et al: Airway acidification initiates host
defense abnormalities in cystic fibrosis mice. Science.
351:503–507. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu F, Zhang Z, Csanády L, Gadsby DC and
Chen J: Molecular structure of the human CFTR ion channel. Cell.
169:85–95.e8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cook DP, Rector MV, Bouzek DC, Michalski
AS, Gansemer ND, Reznikov LR, Li X, Stroik MR, Ostedgaard LS, Abou
Alaiwa MH, et al: Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance
regulator in sarcoplasmic reticulum of airway smooth muscle.
Implications for airway contractility. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
193:417–426. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Iitiä A, Høgdall E, Dahlen P, Hurskainen
P, Vuust J and Siitari H: Detection of mutation delta F508 in the
cystic fibrosis gene using allele-specific PCR primers and
time-resolved fluorometry. PCR Methods Appl. 2:157–162. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xia E, Zhang Y, Cao H, Li J, Duan R and Hu
J: TALEN-mediated gene targeting for cystic fibrosis-gene therapy.
Genes (Basel). 10:392019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Costa C, Pruliere-Escabasse V, de
Becdelievre A, Gameiro C, Golmard L, Guittard C, Bassinet L,
Bienvenu T, Georges MD, Epaud R, et al: A recurrent deep-intronic
splicing CF mutation emphasizes the importance of mRNA studies in
clinical practice. J Cyst Fibros. 10:479–482. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Brandt C, Roehmel J, Rickerts V, Melichar
V, Niemann N and Schwarz C: Aspergillus bronchitis in patients with
cystic fibrosis. Mycopathologia. 183:61–69. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Strom CM, Ginsberg N, Rechitsky S, Cieslak
J, Ivakhenko V, Wolf G, Lifchez A, Moise J, Valle J, Kaplan B, et
al: Three births after preimplantation genetic diagnosis for cystic
fibrosis with sequential first and second polar body analysis. Am J
Obstet Gynecol. 178:1298–1306. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Girardet A, Viart V, Plaza S, Daina G, De
Rycke M, Des Georges M, Fiorentino F, Harton G, Ishmukhametova A,
Navarro J, et al: The improvement of the best practice guidelines
for preimplantation genetic diagnosis of cystic fibrosis: Toward an
international consensus. Eur J Hum Genet. 24:469–478. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Brennan ML and Schrijver I: Cystic
fibrosis: A review of associated phenotypes, use of molecular
diagnostic approaches, genetic characteristics, progress, and
dilemmas. J Mol Diagn. 18:3–14. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bell CJ, Dinwiddie DL, Miller NA, Hateley
SL, Ganusova EE, Mudge J, Langley RJ, Zhang L, Lee CC, Schilkey FD,
et al: Carrier testing for severe childhood recessive diseases by
next-generation sequencing. Sci Transl Med. 3:65ra42011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rengaraju B, Thana K, La A, Pavithra K,
Durairaj V, Challapalli SH and Das A: Inquest of the SNP in cystic
fibrosis-A bioinformatic approach. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci.
6:1255–1263. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Beauchamp KA, Johansen Taber KA, Grauman
PV, Spurka L, Lim-Harashima J, Svenson A, Goldberg JD and Muzzey D:
Sequencing as a first-line methodology for cystic fibrosis carrier
screening. Genet Med. 21:2569–2576. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Baker MW, Atkins AE, Cordovado SK, Hendrix
M, Earley MC and Farrell PM: Improving newborn screening for cystic
fibrosis using next-generation sequencing technology: A technical
feasibility study. Genet Med. 18:231–238. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Marangi M and Pistritto G: Innovative
therapeutic strategies for cystic fibrosis: Moving forward to
CRISPR technique. Front Pharmacol. 9:3962018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hodges CA and Conlon RA: Delivering on the
promise of gene editing for cystic fibrosis. Genes Dis. 6:97–108.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Park S and Beal PA: Off-target editing by
CRISPR-guided DNA base editors. Biochemistry. 58:3727–3734. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Schwank G, Koo BK, Sasselli V, Dekkers JF,
Heo I, Demircan T, Sasaki N, Boymans S, Cuppen E, van der Ent CK,
et al: Functional repair of CFTR by CRISPR/Cas9 in intestinal stem
cell organoids of cystic fibrosis patients. Cell Stem Cell.
13:653–658. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Crane AM, Kramer P, Bui JH, Chung WJ, Li
XS, Gonzalez-Garay ML, Hawkins F, Liao W, Mora D, Choi S, et al:
Targeted correction and restored function of the CFTR gene in
cystic fibrosis induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Reports.
4:569–577. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liang P, Xu Y, Zhang X, Ding C, Huang R,
Zhang Z, Lv J, Xie X, Chen Y, Li Y, et al: CRISPR/Cas9-mediated
gene editing in human tripronuclear zygotes. Protein Cell.
6:363–372. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Saayman SM, Ackley A, Burdach J, Clemson
M, Gruenert DC, Tachikawa K, Chivukula P, Weinberg MS and Morris
KV: Long non-coding RNA BGas regulates the cystic fibrosis
transmembrane conductance regulator. Mol Ther. 24:1351–1357. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Dimartino D, Colantoni A, Ballarino M,
Martone J, Mariani D, Danner J, Bruckmann A, Meister G, Morlando M
and Bozzoni I: The long non-coding RNA lnc-31 interacts with Rock1
mRNA and mediates its YB-1-dependent translation. Cell Rep.
23:733–740. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kishore S and Stamm S: The snoRNA HBII-52
regulates alternative splicing of the serotonin receptor 2C.
Science. 311:230–232. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Gil N and Ulitsky I: Regulation of gene
expression by cis-acting long non-coding RNAs. Nat Rev Genet.
21:102–117. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Fabbri E, Tamanini A, Jakova T, Gasparello
J, Manicardi A, Corradini R, Sabbioni G, Finotti A, Borgatti M,
Lampronti I, et al: A peptide nucleic acid against MicroRNA
miR-145-5p enhances the expression of the cystic fibrosis
transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) in Calu-3 cells.
Molecules. 23:712017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Megiorni F, Cialfi S, Dominici C,
Quattrucci S and Pizzuti A: Synergistic post-transcriptional
regulation of the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane conductance
Regulator (CFTR) by miR-101 and miR-494 specific binding. PLoS One.
6:e266012011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li Z, Yao JN, Huang WT, He RQ, Ma J, Chen
G and Wei QJ: Expression of miR-542-3p in osteosarcoma with miRNA
microarray data, and its potential signaling pathways. Mol Med Rep.
19:974–983. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hassan F, Nuovo GJ, Crawford M, Boyaka PN,
Kirkby S, Nana-Sinkam SP and Cormet-Boyaka E: MiR-101 and miR-144
regulate the expression of the CFTR chloride channel in the lung.
PLoS One. 7:e508372012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ramachandran S, Karp PH, Jiang P,
Ostedgaard LS, Walz AE, Fisher JT, Keshavjee S, Lennox KA, Jacobi
AM, Rose SD, et al: A microRNA network regulates expression and
biosynthesis of wild-type and DeltaF508 mutant cystic fibrosis
transmembrane conductance regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:13362–13367. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Fesen K, Silveyra P, Fuentes N, Nicoleau
M, Rivera L, Kitch D, Graff GR and Siddaiah R: The role of
microRNAs in chronic pseudomonas lung infection in Cystic fibrosis.
Respir Med. 151:133–138. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Balloy V, Koshy R, Perra L, Corvol H,
Chignard M, Guillot L and Scaria V: Bronchial epithelial cells from
cystic fibrosis patients express a specific long non-coding RNA
signature upon Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Front Cell
Infect Microbiol. 7:2182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
McKiernan PJ, Molloy K, Cryan SA,
McElvaney NG and Greene CM: Long noncoding RNA are aberrantly
expressed in vivo in the cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelium. Int
J Biochem Cell Biol. 52:184–191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kumar P, Sen C, Peters K, Frizzell RA and
Biswas R: Comparative analyses of long non-coding RNA profiles in
vivo in cystic fibrosis lung airway and parenchyma tissues. Respir
Res. 20:2842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
McKiernan PJ, Cunningham O, Greene CM and
Cryan SA: Targeting miRNA-based medicines to cystic fibrosis airway
epithelial cells using nanotechnology. Int J Nanomed. 8:3907–3915.
2013.
|
|
67
|
Lu Q, Liu T, Feng H, Yang R, Zhao X, Chen
W, Jiang B, Qin H, Guo X, Liu M, et al: Circular RNA circSLC8A1
acts as a sponge of miR-130b/miR-494 in suppressing bladder cancer
progression via regulating PTEN. Mol Cancer. 18:1112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yu CY, Li TC, Wu YY, Yeh CH, Chiang W,
Chuang CY and Kuo HC: The circular RNA circBIRC6 participates in
the molecular circuitry controlling human pluripotency. Nat Commun.
8:11492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Nowacka-Zawisza M and Wiśnik E: DNA
methylation and histone modifications as epigenetic regulation in
prostate cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 38:2587–2596. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Sirinupong N and Yang Z: Epigenetics in
cystic fibrosis: Epigenetic targeting of a genetic disease. Curr
Drug Targets. 16:976–987. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Morandini AC, Santos CF and Yilmaz Ö: Role
of epigenetics in modulation of immune response at the junction of
host-pathogen interaction and danger molecule signaling. Pathog
Dis. 74:ftw0822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Chen Y, Armstrong DA, Salas LA, Hazlett
HF, Nymon AB, Dessaint JA, Aridgides DS, Mellinger DL, Liu X,
Christensen BC and Ashare A: Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling
shows a distinct epigenetic signature associated with lung
macrophages in cystic fibrosis. Clin Epigenetics. 10:1522018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Magalhães M, Tost J, Pineau F, Rivals I,
Busato F, Alary N, Mely L, Leroy S, Murris M, Caimmi D, et al:
Dynamic changes of DNA methylation and lung disease in cystic
fibrosis: Lessons from a monogenic disease. Epigenomics.
10:1131–1145. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Scott M and De Sario A: DNA methylation
changes in cystic fibrosis: Cause or consequence? Clin Genet.
98:3–9. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hutt DM, Herman D, Rodrigues AP, Noel S,
Pilewski JM, Matteson J, Hoch B, Kellner W, Kelly JW, Schmidt A, et
al: Reduced histone deacetylase 7 activity restores function to
misfolded CFTR in cystic fibrosis. Nat Chem Biol. 6:25–33. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Bartling TR and Drumm ML: Loss of CFTR
results in reduction of histone deacetylase 2 in airway epithelial
cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 297:L35–L43. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Rymut SM, Harker A, Corey DA, Burgess JD,
Sun H, Clancy JP and Kelley TJ: Reduced microtubule acetylation in
cystic fibrosis epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 305:L419–L431. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Bergougnoux A, Rivals I, Liquori A, Raynal
C, Varilh J, Magalhães M, Perez MJ, Bigi N, Des Georges M, Chiron
R, et al: A balance between activating and repressive histone
modifications regulates cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance
regulator (CFTR) expression in vivo. Epigenetics. 9:1007–1017.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Cutting GR: Cystic fibrosis genetics: From
molecular understanding to clinical application. Nat Rev Genet.
16:45–56. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Davis PB, Drumm M and Konstan MW: Cystic
fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 154:1229–1256. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
De Boeck K, Vermeulen F and Dupont L: The
diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. Presse Med. 46:e97–e108. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Schwarzenberg SJ, Hempstead SE, McDonald
CM, Powers SW, Wooldridge J, Blair S, Freedman S, Harrington E,
Murphy PJ, Palmer L, et al: Enteral tube feeding for individuals
with cystic fibrosis: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation evidence-informed
guidelines. J Cyst Fibros. 15:724–735. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Guglani L, Moir D and Jain A: Sweat
chloride concentrations in children with Idiopathic Nephrotic
Syndrome. Pediatr Pulmonol. 51:49–52. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Brown A, Jenkins L, Reid A, Leavy A,
McDowell G, McIlroy C, Thompson A and McNaughten B: How to perform
and interpret the sweat test. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed.
105:230–235. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Solomon GM, Liu B, Sermet-Gaudelus I,
Fajac I, Wilschanski M, Vermeulen F and Rowe SM: A multiple reader
scoring system for Nasal Potential Difference parameters. J Cyst
Fibros. 16:573–578. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Solomon GM, Bronsveld I, Hayes K,
Wilschanski M, Melotti P, Rowe SM and Sermet-Gaudelus I:
Standardized measurement of nasal membrane transepithelial
potential difference (NPD). J Vis Exp. 570062018.
|
|
87
|
Beka M and Leal T: Nasal potential
difference to quantify trans-epithelial ion transport in mice. J
Vis Exp. 579342018.
|
|
88
|
Old RW, Bestwick JP and Wald NJ: Prenatal
maternal plasma DNA screening for cystic fibrosis: A computer
modelling study of screening performance. F1000Res. 6:18962017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Sugunaraj JP, Brosius HM, Murray MF,
Manickam K, Stamm JA, Carey DJ and Mirshahi UL: Predictive value of
genomic screening: Cross-sectional study of cystic fibrosis in
50,788 electronic health records. NPJ Genom Med. 4:212019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Ferlin A and Stuppia L: Diagnostics of
CFTR-negative patients with congenital bilateral absence of vas
deferens: Which mutations are of most interest? Expert Rev Mol
Diagn. 20:265–267. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Wagener JS, Sontag MK and Accurso FJ:
Newborn screening for cystic fibrosis. Curr Opin Pediatr.
15:309–315. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
O'Brien TJ and Welch M: Recapitulation of
polymicrobial communities associated with cystic fibrosis airway
infections: A perspective. Future Microbiol. 14:1437–1450. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Lyczak JB, Cannon CL and Pier GB: Lung
infections associated with cystic fibrosis. Clin Microbiol Rev.
15:194–222. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Savant AP and McColley SA: Cystic fibrosis
year in review 2016. Pediatr Pulmonol. 52:1092–1102. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wilson J: Treating genes and patients.
Gene Ther. 27:109–110. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Rafeeq MM and Murad HAS: Cystic fibrosis:
Current therapeutic targets and future approaches. J Transl Med.
15:842017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Moss RB, Flume PA, Elborn JS, Cooke J,
Rowe SM, McColley SA, Rubenstein RC and Higgins M; VX11-770-110
(KONDUCT) Study Group, : Efficacy and safety of ivacaftor in
patients with cystic fibrosis who have an Arg117His-CFTR mutation:
A double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med.
3:524–533. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Arjmand B, Larijani B, Sheikh Hosseini M,
Payab M, Gilany K, Goodarzi P, Parhizkar Roudsari P, Amanollahi
Baharvand M and Hoseini Mohammadi NS: The horizon of gene therapy
in modern medicine: Advances and challenges. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1247:33–64. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Yang Q, Soltis AR, Sukumar G, Zhang X,
Caohuy H, Freedy J, Dalgard CL, Wilkerson MD, Pollard HB and
Pollard BS: Gene therapy-emulating small molecule treatments in
cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells and patients. Respir Res.
20:2902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Eymery M, Morfin F, Doleans-Jordheim A,
Perceval M, Ohlmann C, Mainguy C and Reix P: Viral respiratory
tract infections in young children with cystic fibrosis: A
prospective full-year seasonal study. Virol J. 16:1112019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Tümmler B: Treatment of cystic fibrosis
with CFTR modulators. Pneumologie. 70:301–313. 2016.(In German).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Bessonova L, Volkova N, Higgins M,
Bengtsson L, Tian S, Simard C, Konstan MW, Sawicki GS, Sewall A,
Nyangoma S, et al: Data from the US and UK cystic fibrosis
registries support disease modification by CFTR modulation with
ivacaftor. Thorax. 73:731–740. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Faruqi S, Shiferaw D and Morice AH: Effect
of ivacaftor on objective and subjective measures of cough in
patients with cystic fibrosis. Open Respir Med J. 10:105–108. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Heltshe SL, Mayer-Hamblett N, Burns JL,
Khan U, Baines A, Ramsey BW and Rowe SM; GOAL (the G551D
Observation-AL) Investigators of the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation
Therapeutics Development Network, : Pseudomonas aeruginosa
in cystic fibrosis patients with G551D-CFTR treated with ivacaftor.
Clin Infect Dis. 60:703–712. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Krainer G, Schenkel M, Hartmann A,
Ravamehr-Lake D, Deber CM and Schlierf M: CFTR transmembrane
segments are impaired in their conformational adaptability by a
pathogenic loop mutation and dynamically stabilized by Lumacaftor.
J Biol Chem. 295:1985–1991. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Wainwright CE, Elborn JS and Ramsey BW:
Lumacaftor-ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis homozygous
for Phe508del CFTR. N Engl J Med. 373:1783–1784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Konstan MW, McKone EF, Moss RB, Marigowda
G, Tian S, Waltz D, Huang X, Lubarsky B, Rubin J, Millar SJ, et al:
Assessment of safety and efficacy of long-term treatment with
combination lumacaftor and ivacaftor therapy in patients with
cystic fibrosis homozygous for the F508del-CFTR mutation
(PROGRESS): A phase 3, extension study. Lancet Respir Med.
5:107–118. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Sala MA and Jain M: Tezacaftor for the
treatment of cystic fibrosis. Expert Rev Respir Med. 12:725–732.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Rowe SM, Daines C, Ringshausen FC, Kerem
E, Wilson J, Tullis E, Nair N, Simard C, Han L, Ingenito EP, et al:
Tezacaftor-ivacaftor in residual-function heterozygotes with cystic
fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 377:2024–2035. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Donaldson SH, Pilewski JM, Griese M, Cooke
J, Viswanathan L, Tullis E, Davies JC, Lekstrom-Himes JA and Wang
LT; VX11-661-101 Study Group, : Tezacaftor/ivacaftor in subjects
with cystic fibrosis and F508del/F508del-CFTR or
F508del/G551D-CFTR. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 197:214–224. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Taylor-Cousar JL, Munck A, McKone EF, van
der Ent CK, Moeller A, Simard C, Wang LT, Ingenito EP, McKee C, Lu
Y, et al: Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis
Homozygous for Phe508del. N Engl J Med. 377:2013–2023. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Giuliano KA, Wachi S, Drew L, Dukovski D,
Green O, Bastos C, Cullen MD, Hauck S, Tait BD, Munoz B, et al: Use
of a high-throughput phenotypic screening strategy to identify
amplifiers, a novel pharmacological class of small molecules that
exhibit functional synergy with potentiators and correctors. SLAS
Discov. 23:111–121. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Gambari R, Breveglieri G, Salvatori F,
Finotti A and Borgatti M: Therapy for cystic fibrosis caused by
nonsense mutations. Cystic Fibrosis in the Light of New Research
Ch. 13:2015. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Wang G: Interplay between inhibitory
ferric and stimulatory curcumin regulates phosphorylation-dependent
human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and
DeltaF508 activity. Biochemistry. 54:1558–1566. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Chaudary N: Triplet CFTR modulators:
Future prospects for treatment of cystic fibrosis. Ther Clin Risk
Manag. 14:2375–2383. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Raynal C, Baux D, Theze C, Bareil C,
Taulan M, Roux AF, Claustres M, Tuffery-Giraud S and des Georges M:
A classification model relative to splicing for variants of unknown
clinical significance: Application to the CFTR gene. Hum Mutat.
34:774–784. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Mention K, Santos L and Harrison PT: Gene
and base editing as a therapeutic option for cystic
fibrosis-learning from other diseases. Genes (Basel). 10:3872019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Osman G, Rodriguez J, Chan SY, Chisholm J,
Duncan G, Kim N, Tatler AL, Shakesheff KM, Hanes J, Suk JS and
Dixon JE: PEGylated enhanced cell penetrating peptide nanoparticles
for lung gene therapy. J Control Release. 285:35–45. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Condren ME and Bradshaw MD: Ivacaftor: A
novel gene-based therapeutic approach for cystic fibrosis. J
Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 18:8–13. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|