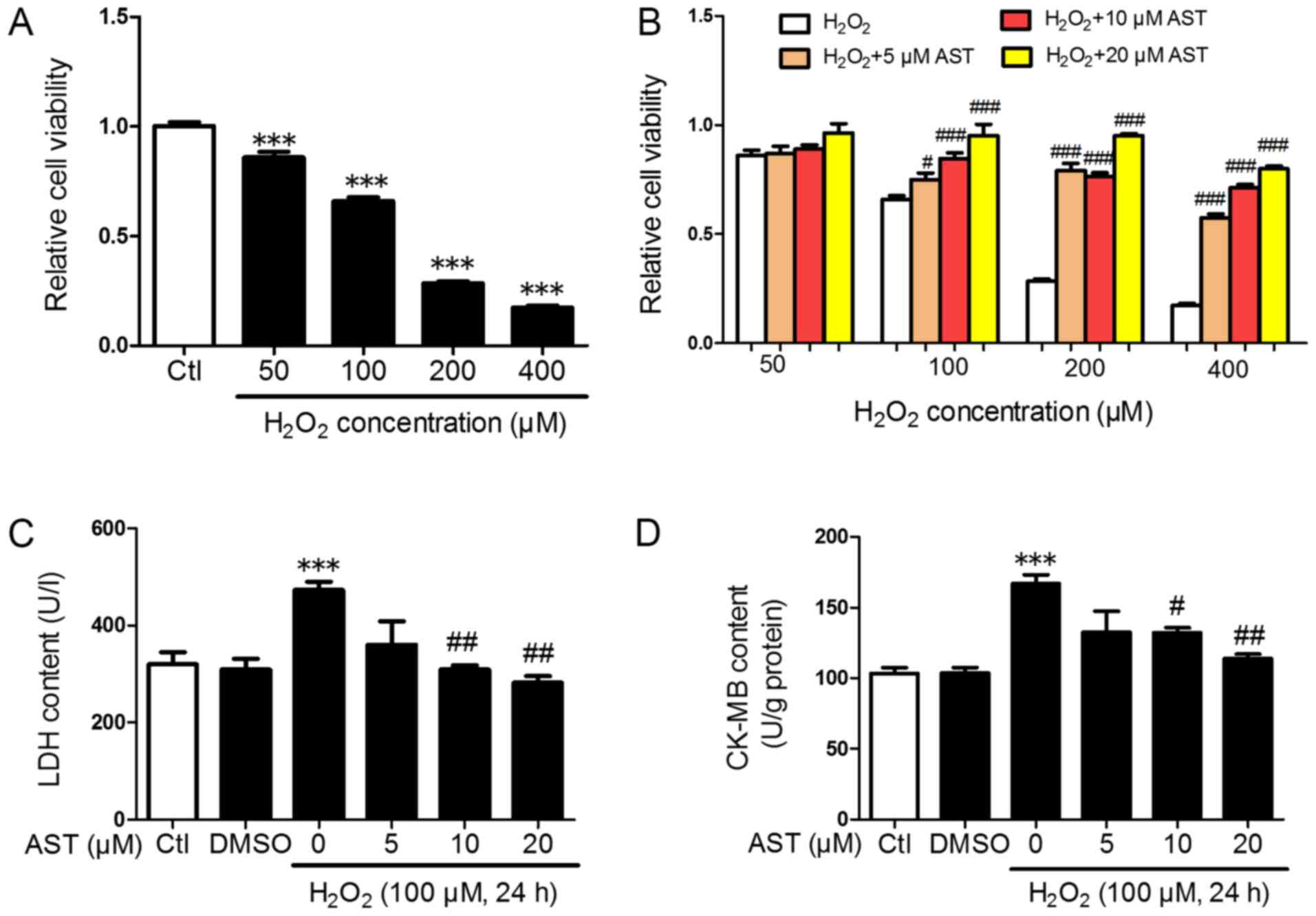
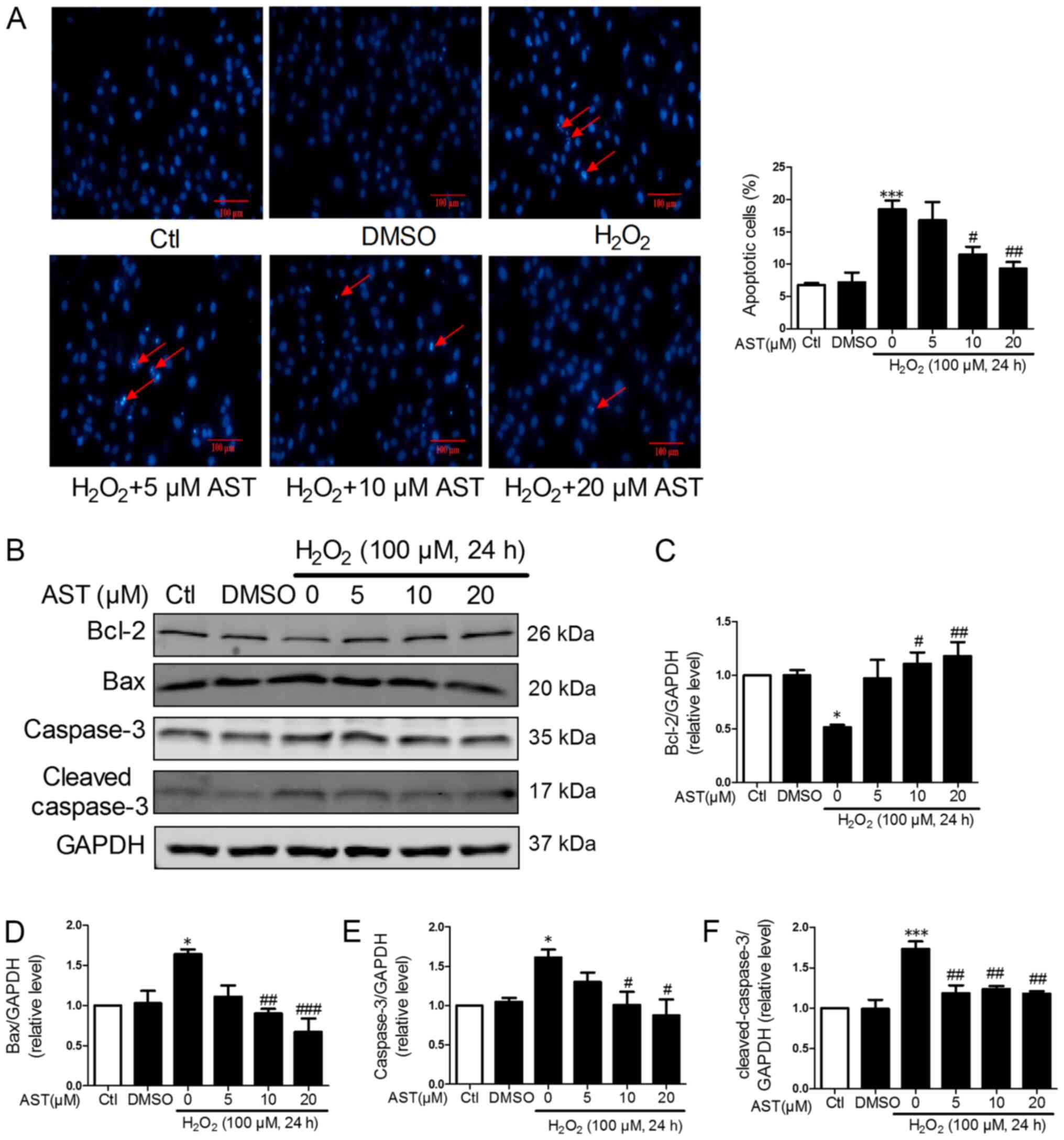
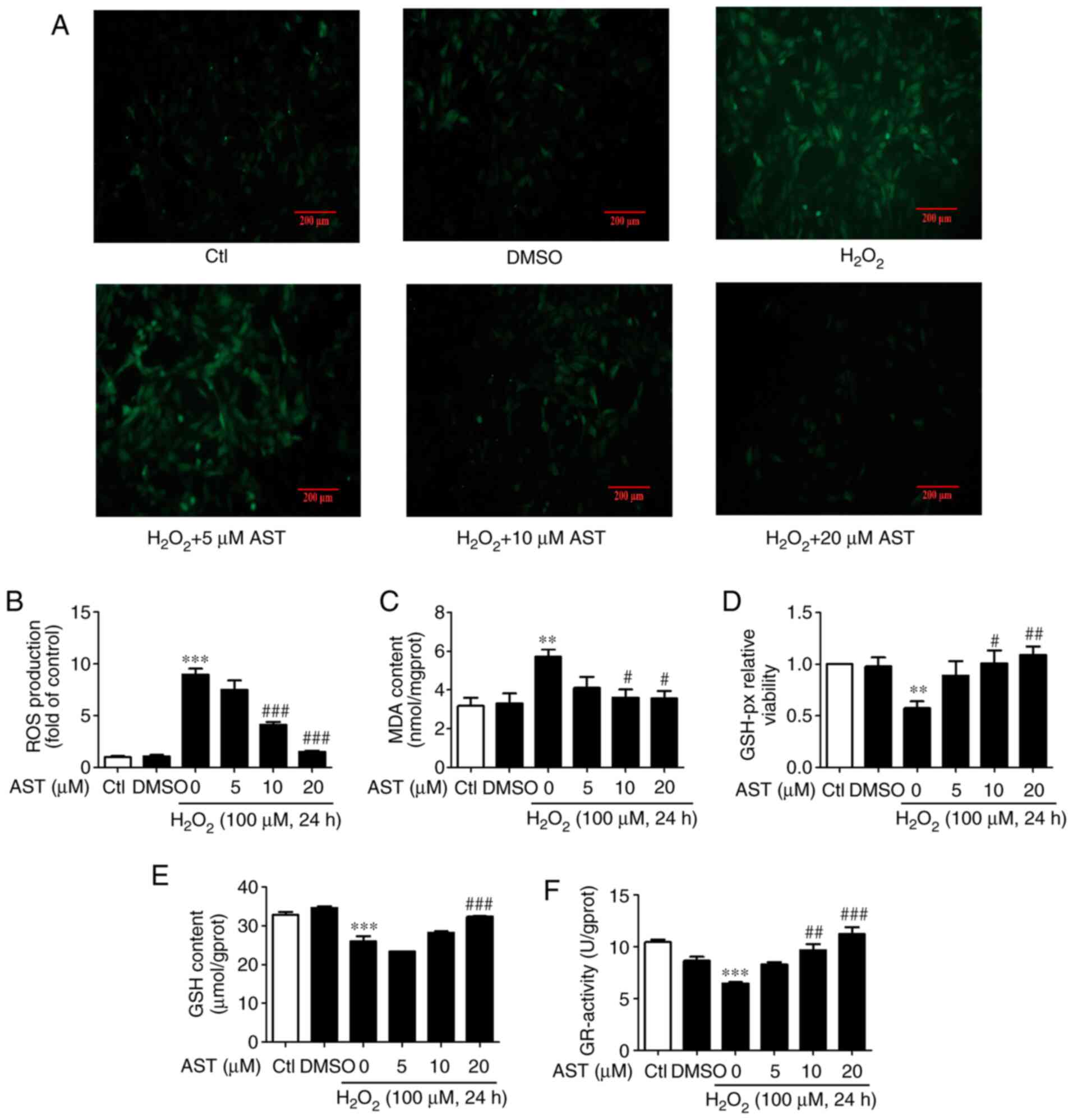
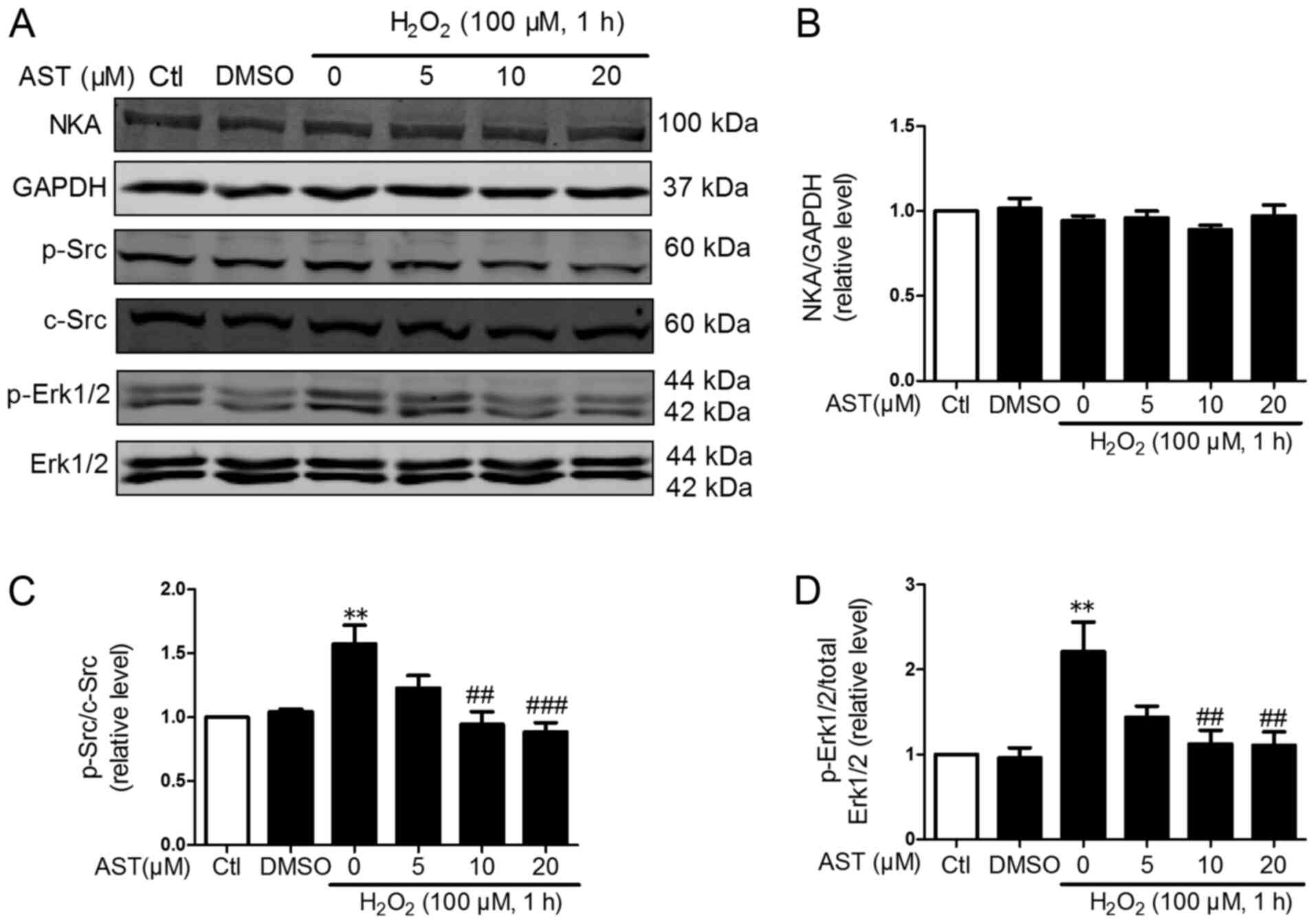
|
1
|
Ong SB, Hernández-Reséndiz S,
Crespo-Avilan GE, Mukhametshina RT, Kwek XY, Cabrera-Fuentes HA and
Hausenloy DJ: Inflammation following acute myocardial infarction:
Multiple players, dynamic roles, and novel therapeutic
opportunities. Pharmacol Ther. 186:73–87. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hausenloy DJ and Yellon DM: Myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury: A neglected therapeutic target. J Clin
Invest. 123:92–100. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xie B, Liu X, Yang J, Cheng J, Gu J and
Xue S: PIAS1 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury by stimulating PPARγ SUMOylation. BMC Cell Biol. 19:242018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sies H: Hydrogen peroxide as a central
redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress:
Oxidative eustress. Redox Biol. 11:613–619. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu D, Li M, Tian Y, Liu J and Shang J:
Luteolin inhibits ROS-activated MAPK pathway in myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Life Sci. 122:15–25. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guo J, Wang SB, Yuan TY, Wu YJ, Yan Y, Li
L, Xu XN, Gong LL, Qin HL, Fang LH and Du GH: Coptisine protects
rat heart against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by
suppressing myocardial apoptosis and inflammation. Atherosclerosis.
231:384–391. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mokhtari-Zaer A, Marefati N, Atkin SL,
Butler AE and Sahebkar A: The protective role of curcumin in
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Cell Physiol.
234:214–222. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Faraone I, Sinisgalli C, Ostuni A,
Armentano MF, Carmosino M, Milella L, Russo D, Labanca F and Khan
H: Astaxanthin anticancer effects are mediated through multiple
molecular mechanisms: A systematic review. Pharmacol Res.
155:1046892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Alam MN, Hossain MM, Rahman MM, Subhan N,
Mamun MAA, Ulla A, Reza HM and Alam MA: Astaxanthin prevented
oxidative stress in heart and kidneys of isoproterenol-administered
aged rats. J Diet Suppl. 15:42–54. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fang Q, Guo S, Zhou H, Han R, Wu P and Han
C: Astaxanthin protects against early burn-wound progression in
rats by attenuating oxidative stress-induced inflammation and
mitochondria-related apoptosis. Sci Rep. 7:414402017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Coombes JS, Sharman JE and Fassett RG:
Astaxanthin has no effect on arterial stiffness, oxidative stress,
or inflammation in renal transplant recipients: A randomized
controlled trial (the XANTHIN trial). Am J Clin Nutr. 103:283–289.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu L, Zhu J, Yin W and Ding X: Astaxanthin
improves cognitive deficits from oxidative stress, nitric oxide
synthase and inflammation through upregulation of PI3K/Akt in
diabetes rat. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:6083–6094. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim YJ, Kim YA and Yokozawa T: Protection
against oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis of
high-glucose-exposed proximal tubular epithelial cells by
astaxanthin. J Agric Food Chem. 57:8793–8797. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ambati RR, Phang SM, Ravi S and
Aswathanarayana RG: Astaxanthin: Sources, extraction, stability,
biological activities and its commercial applications-a review. Mar
Drugs. 12:128–152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kishimoto Y, Yoshida H and Kondo K:
Potential anti-atherosclerotic properties of astaxanthin. Mar
Drugs. 14:352016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang ZW, Xu XC, Liu T and Yuan S:
Mitochondrion-permeable antioxidants to treat ROS-burst-mediated
acute diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:68595232016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shi Y, Lin P, Wang X, Zou G and Li K:
Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 1 (SMPD1) mediates the attenuation
of myocardial infarction-induced cardiac fibrosis by astaxanthin.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 503:637–643. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Belliard A, Sottejeau Y, Duan Q, Karabin
JL and Pierre SV: Modulation of cardiac
Na+,K+-ATPase cell surface abundance by
simulated ischemia-reperfusion and ouabain preconditioning. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 304:H94–H103. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li Z and Xie Z: The Na/K-ATPase/Src
complex and cardiotonic steroid-activated protein kinase cascades.
Pflugers Arch. 457:635–644. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yan Y, Shapiro AP, Haller S, Katragadda V,
Liu L, Tian J, Basrus V, Malhotra D, Xie Z, Abraham NG, et al:
Involvement of reactive oxygen species in a feed-forward mechanism
of Na/K-ATPase-mediated signaling transduction. J Biol Chem.
288:34249–34258. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu J, Tian J, Haas M, Shapiro JI, Askari
A and Xie Z: Ouabain interaction with cardiac
Na+/K+-ATPase initiates signal cascades
independent of changes in intracellular Na+ and
Ca2+ concentrations. J Biol Chem. 275:27838–27844.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Y, Ye Q, Liu C, Xie JX, Yan Y, Lai F,
Duan Q, Li X, Tian J and Xie Z: Involvement of Na/K-ATPase in
hydrogen peroxide-induced activation of the Src/ERK pathway in
LLC-PK1 cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 71:415–426. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li H, Yin A, Cheng Z, Feng M, Zhang H, Xu
J, Wang F and Qian L: Attenuation of Na/K-ATPase/Src/ROS
amplification signal pathway with pNaktide ameliorates myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Biol Macromol. 118:1142–1148.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ding S, Liu D, Wang L, Wang G and Zhu Y:
Inhibiting MicroRNA-29a protects myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury by targeting SIRT1 and suppressing oxidative stress and
NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis pathway. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
372:128–135. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Karu I, Tähepõld P, Ruusalepp A and
Starkopf J: Pretreatment by hyperoxia-a tool to reduce
ischaemia-reperfusion injury in the myocardium. Curr Clin
Pharmacol. 5:125–132. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cadenas S: ROS and redox signaling in
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection. Free
Radic Biol Med. 117:76–89. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang L, Lin R, Guo L and Hong M:
Rosuvastatin relieves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by
upregulating PPAR-γ and UCP2. Mol Med Rep. 18:789–798.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hoffman JJ Jr, Gilbert TB, Poston RS and
Silldorff EP: Myocardial reperfusion injury: Etiology, mechanisms,
and therapies. J Extra Corpor Technol. 36:391–411. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Visioli F and Artaria C: Astaxanthin in
cardiovascular health and disease: Mechanisms of action,
therapeutic merits, and knowledge gaps. Food Funct. 8:39–63. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lauver DA, Lockwood SF and Lucchesi BR:
Disodium Disuccinate Astaxanthin (Cardax) attenuates complement
activation and reduces myocardial injury following
ischemia/reperfusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 314:686–692. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shah MM, Liang Y, Cheng JJ and Daroch M:
Astaxanthin-producing green microalga Haematococcus pluvialis: From
single cell to high value commercial products. Front Plant Sci.
7:5312016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products Nutrition
and Allergies (NDA), . Scientific opinion on the safety of
astaxanthin-rich ingredients (AstaREAL A1010 and AstaREAL L10) as
novel food ingredients. EFSA J. 15–July;2014.(Epub ahead of print).
doi: org/10.2903/j.efsa.2014.3757. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Iwamoto T, Hosoda K, Hirano R, Kurata H,
Matsumoto A, Miki W, Kamiyama M, Itakura H, Yamamoto S and Kondo K:
Inhibition of low-density lipoprotein oxidation by astaxanthin. J
Atheroscler Thromb. 7:216–222. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yoshida H, Yanai H, Ito K, Tomono Y,
Koikeda T, Tsukahara H and Tada N: Administration of natural
astaxanthin increases serum HDL-cholesterol and adiponectin in
subjects with mild hyperlipidemia. Atherosclerosis. 209:520–523.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ruen-Ngam D, Shotipruk A and Pavasant P:
Comparison of extraction methods for recovery of astaxanthin from
Haematococcus pluvialis. Sep Sci Technol. 46:64–70. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhu S, Wang T, Luo F, Li H, Jia Q, He T,
Wu H and Zou T: Astaxanthin inhibits proliferation and induces
apoptosis of LX2 cells by regulating the miR29b/Bcl2 pathway. Mol
Med Rep. 19:3537–3547. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fan CD, Sun JY, Fu XT, Hou YJ, Li Y, Yang
MF, Fu XY and Sun BL: Astaxanthin attenuates homocysteine-induced
cardiotoxicity in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting mitochondrial
dysfunction and oxidative damage. Front Physiol. 8:10412017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Okada Y, Ishikura M and Maoka T:
Bioavailability of astaxanthin in Haematococcus algal
extract: The effects of timing of diet and smoking habits. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 73:1928–1932. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Qiao X, Yang L, Zhang T, Zhou Q, Wang Y,
Xu J and Xue C: Synthesis, stability and bioavailability of
astaxanthin succinate diester. J Sci Food Agric. 98:3182–3189.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mercke OJ, Lignell A, Pettersson A and
Hoglund P: Oral bioavailability of the antioxidant astaxanthin in
humans is enhanced by incorporation of lipid based formulations.
Eur J Pharm Sci. 19:299–304. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Barros MP, Marin DP, Bolin AP, de Cássia
Santos Macedo R, Campoio TR, Fineto C Jr, Guerra BA, Polotow TG,
Vardaris C, Mattei R and Otton R: Combined astaxanthin and fish oil
supplementation improves glutathione-based redox balance in rat
plasma and neutrophils. Chem-Biol Interact. 197:58–67. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rao AR, Reddy RLR, Baskaran V, Sarada R
and Ravishankar GA: Characterization of microalgal carotenoids by
mass spectrometry and their bioavailability and antioxidant
properties elucidated in rat model. J Agr Food Chem. 58:8553–8559.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Satoh A, Tsuji S, Okada Y, Murakami N,
Urami M, Nakagawa K, Ishikura M, Katagiri M, Koga Y and Shirasawa
T: Preliminary clinical evaluation of toxicity and efficacy of a
new astaxanthin-rich Haematococcus pluvialis extract. J Clin
Biochem Nutr. 44:280–284. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Baburina Y, Krestinin R, Odinokova I,
Sotnikova L, Kruglov A and Krestinina O: Astaxanthin inhibits
mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening in rat heart
mitochondria. Antioxidants (Basel). 8:5762019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Nakao R, Nelson OL, Park JS, Mathison BD,
Thompson PA and Chew BP: Effect of astaxanthin supplementation on
inflammation and cardiac function in BALB/c mice. Anticancer Res.
30:2721–2725. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kalogeris T, Bao Y and Korthuis RJ:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species: A double edged sword in
ischemia/reperfusion vs preconditioning. Redox Biol. 2:702–714.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ma JJ, Yu YG, Yin SW, Tang CH and Yang XQ:
Cellular uptake and intracellular antioxidant activity of
Zein/Chitosan nanoparticles incorporated with quercetin. J Agric
Food Chem. 66:12783–12793. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Goc Z, Szaroma W, Kapusta E and Dziubek K:
Protective effects of melatonin on the activity of SOD, CAT, GSH-Px
and GSH content in organs of mice after administration of SNP. Chin
J Physiol. 60:1–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Couto N, Wood J and Barber J: The role of
glutathione reductase and related enzymes on cellular redox
homoeostasis network. Free Radic Biol Med. 95:27–42. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lopez-Neblina F, Toledo AH and
Toledo-Pereyra LH: Molecular biology of apoptosis in ischemia and
reperfusion. J Invest Surg. 18:335–350. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Eefting F, Rensing B, Wigman J, Pannekoek
WJ, Liu WM, Cramer MJ, Lips SJ and Doevendans PA: Role of apoptosis
in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 61:414–426. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Skou JC: The influence of some cations on
an adenosine triphosphatase from peripheral nerves. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 23:394–401. 1957. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Pierre SV and Xie Z: The Na,K-ATPase
receptor complex: Its organization and membership. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 46:303–316. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cui X and Xie Z: Protein interaction and
Na/K-ATPase-mediated signal transduction. Molecules. 22:9902017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Wu J, Akkuratov EE, Bai Y, Gaskill CM,
Askari A and Liu L: Cell signaling associated with
Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase: Activation of phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase
IA/Akt by ouabain is independent of Src. Biochemistry.
52:9059–9067. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Haas M, Wang H, Tian J and Xie Z:
Src-mediated inter-receptor cross-talk between the
Na+/K+-ATPase and the epidermal growth factor
receptor relays the signal from ouabain to mitogen-activated
protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 277:18694–18702. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|