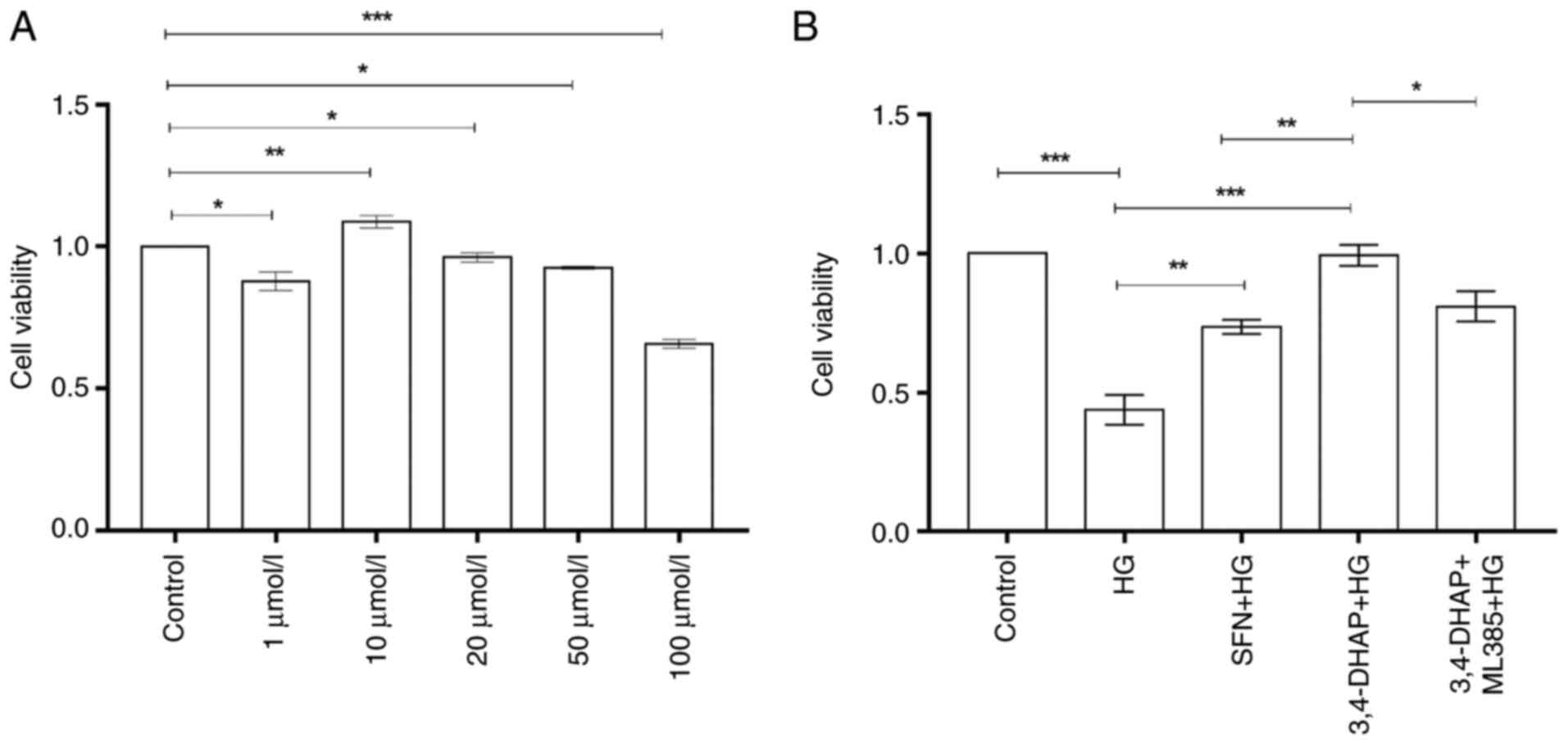
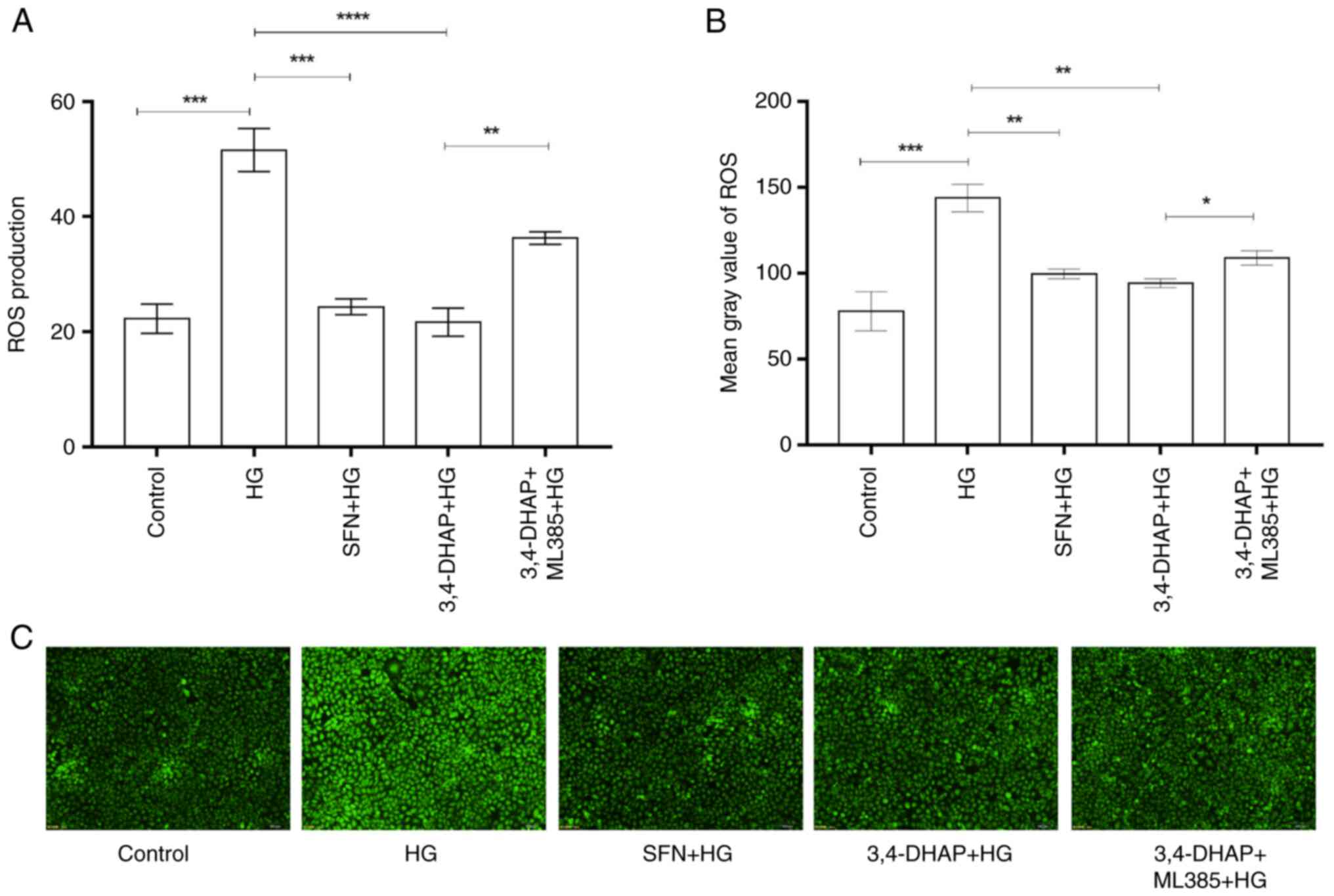
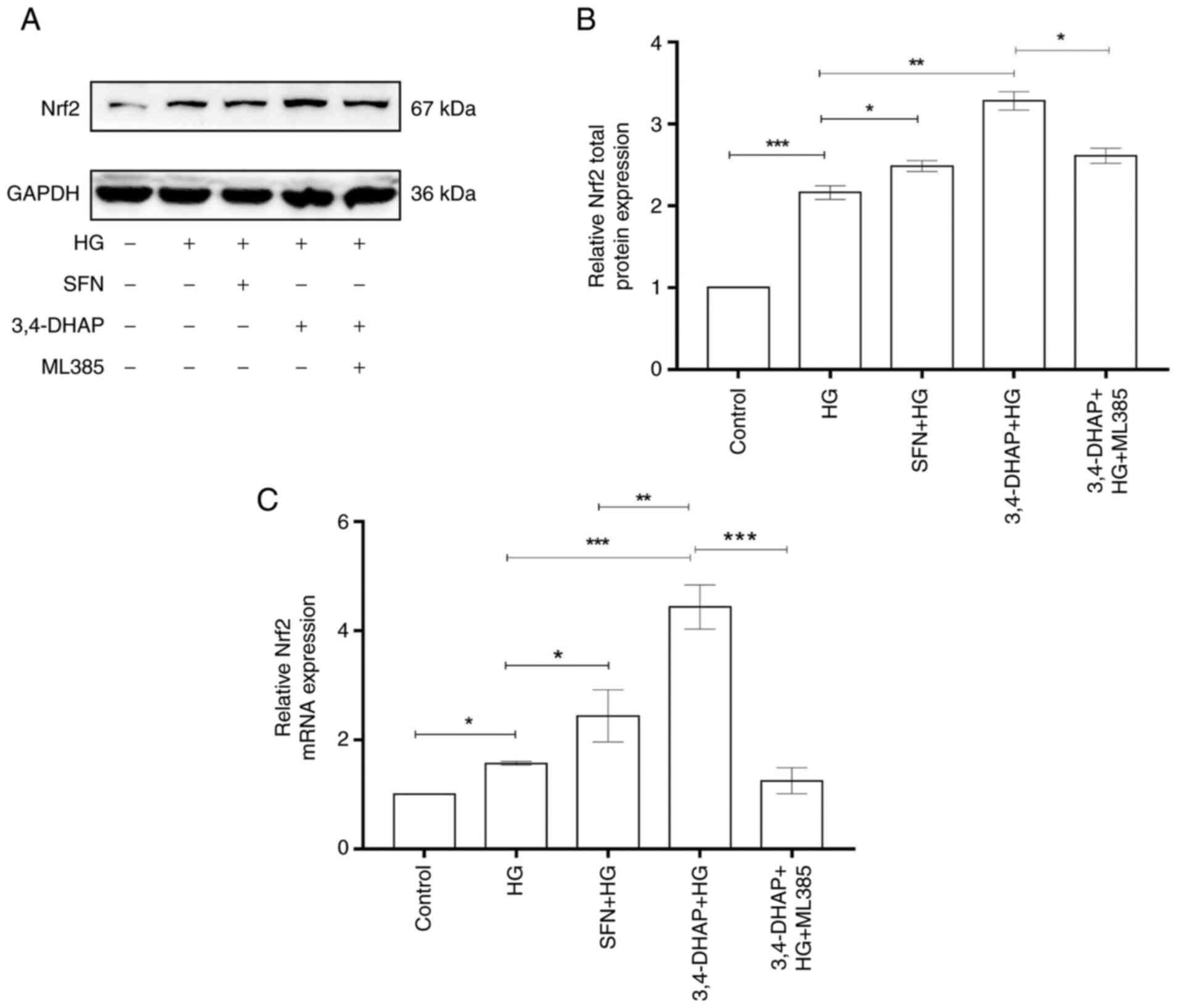
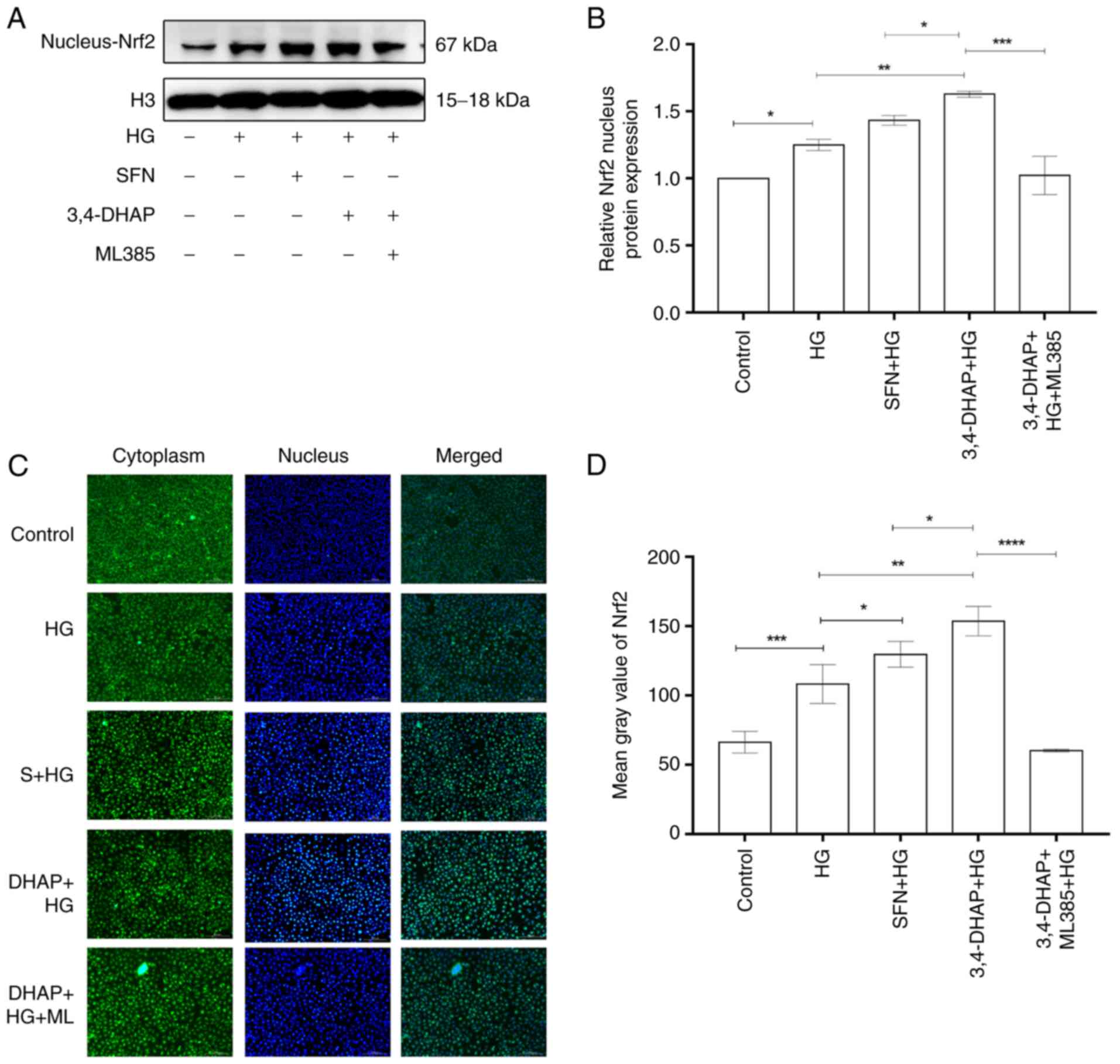
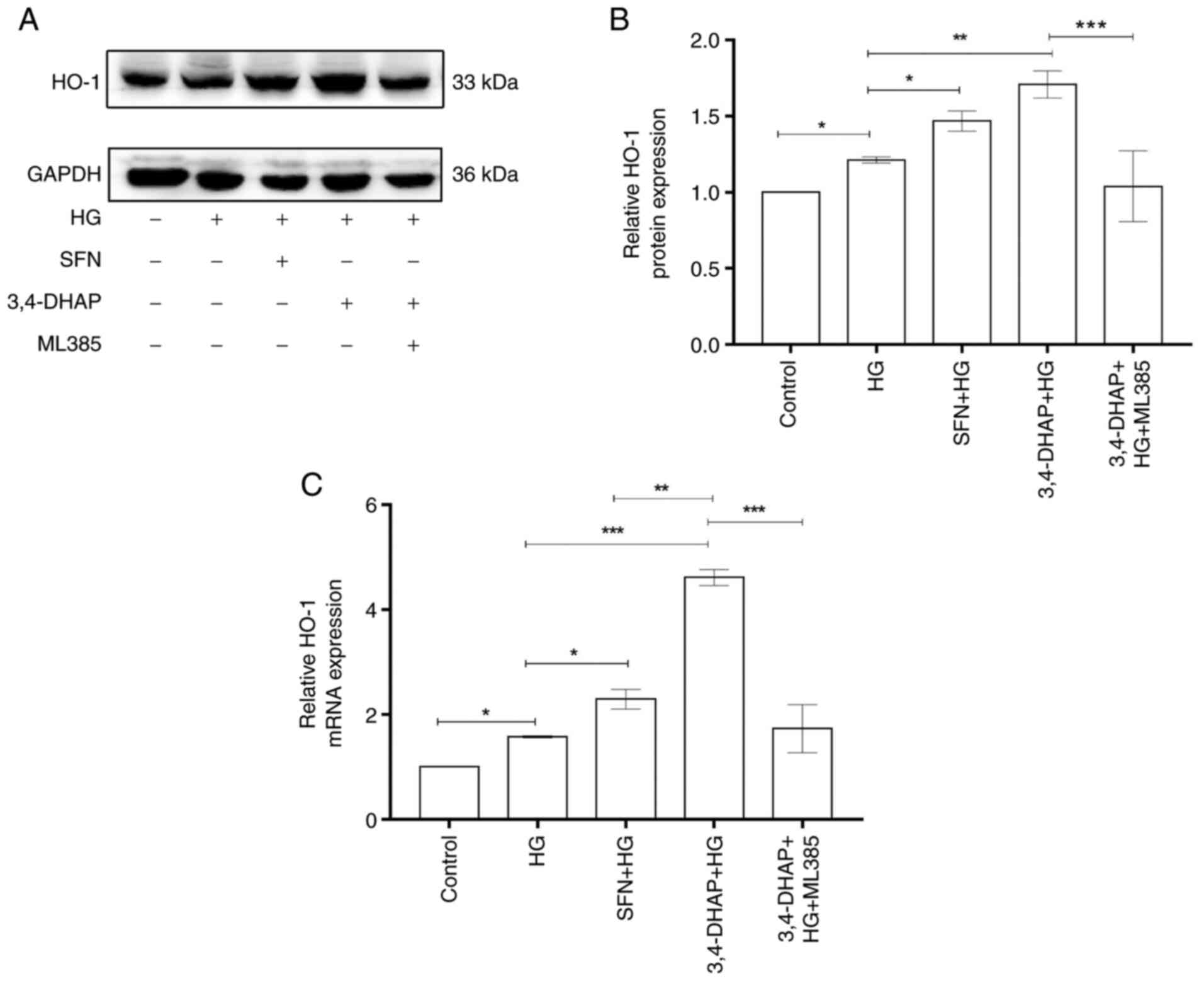
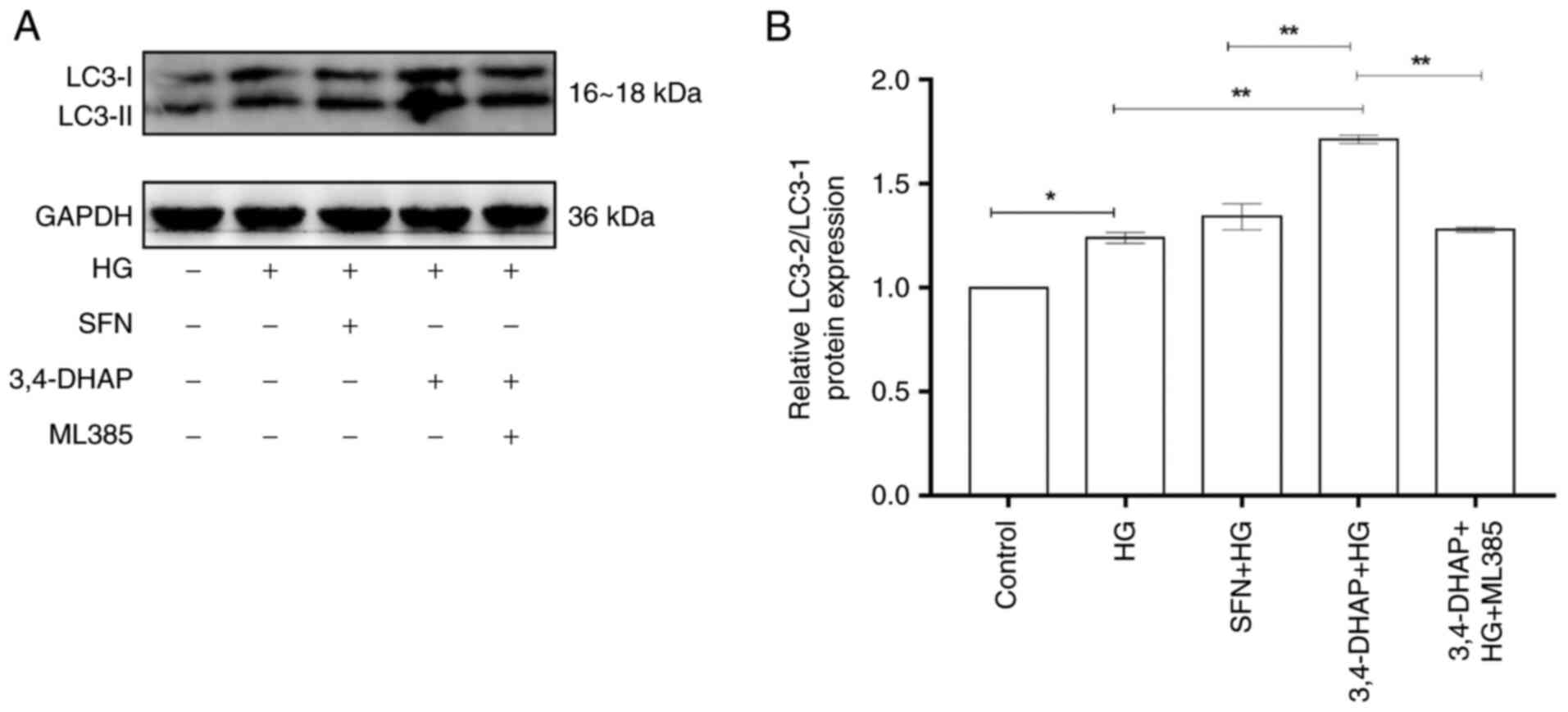
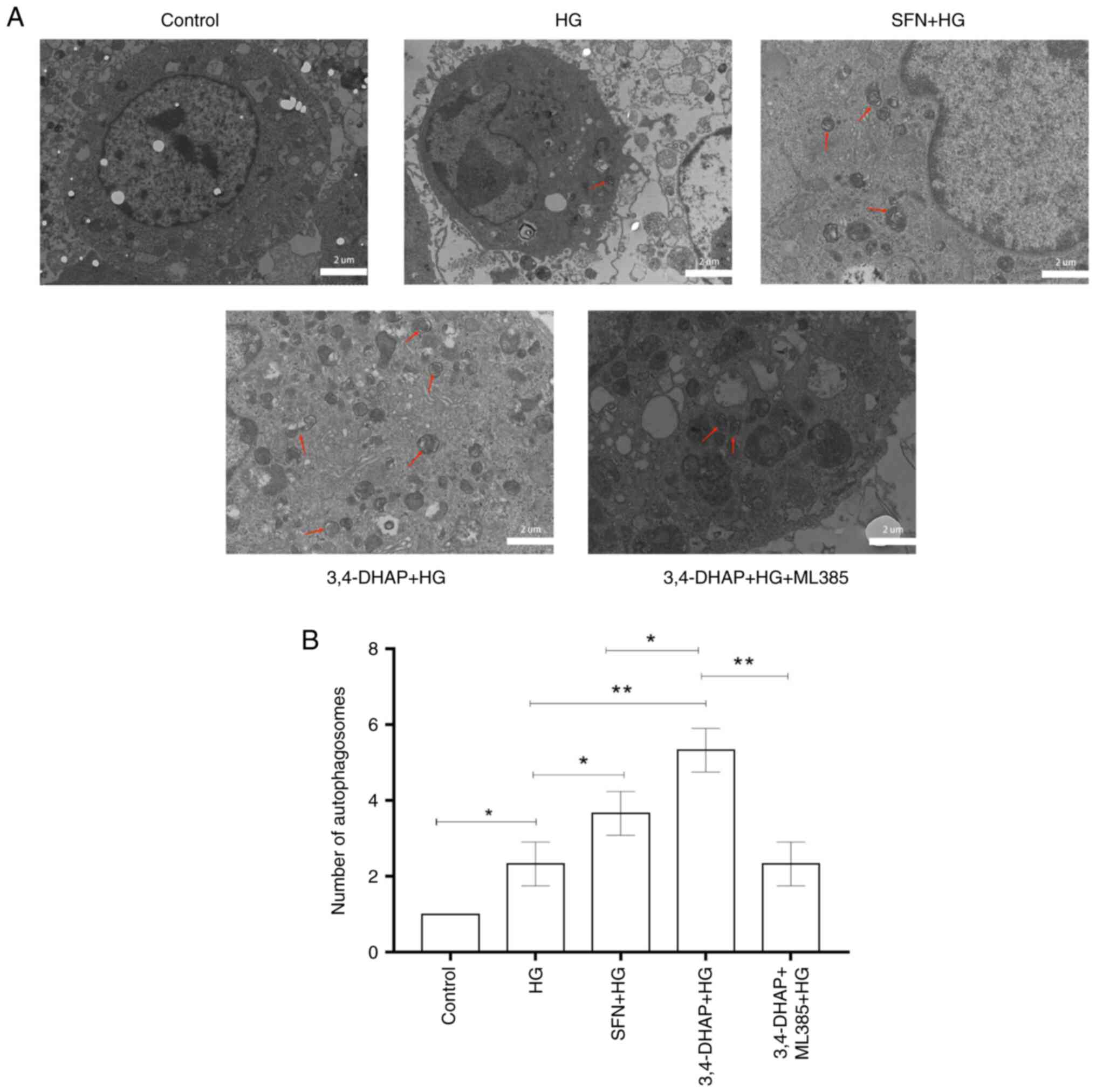
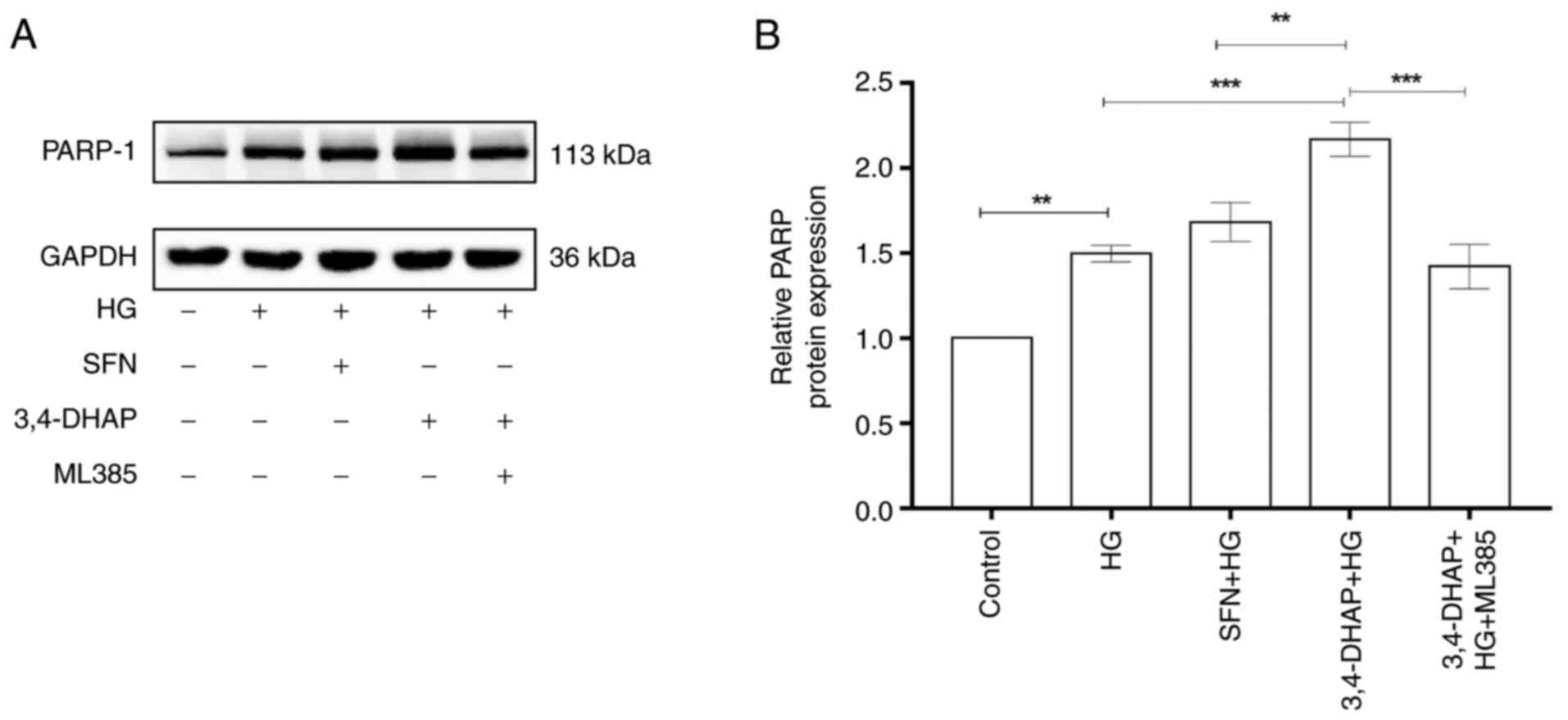
|
1
|
Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da
Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW and Malanda B: IDF diabetes atlas:
Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections
for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 138:271–281. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Newman JD, Schwartzbard AZ, Weintraub HS,
Goldberg IJ and Berger JS: Primary prevention of cardiovascular
disease in diabetes mellitus. J Am Coll Cardiol. 70:883–893. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sheng B, Truong K, Spitler H, Zhang L,
Tong X and Chen L: The long-term effects of bariatric surgery on
type 2 diabetes remission, microvascular and macrovascular
complications, and mortality: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Obes Surg. 27:2724–2732. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
GBD 2016 Causes of Death Collaborators, .
Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264
causes of death, 1980-2016: A systematic analysis for the Global
Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 390:1151–1210. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Luo JF, Shen XY, Lio CK, Dai Y, Cheng CS,
Liu JX, Yao YD, Yu Y, Xie Y, Luo P, et al: Activation of Nrf2/HO-1
pathway by nardochinoid C inhibits inflammation and oxidative
stress in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Front
Pharmacol. 9:9112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zuo L, Prather ER, Stetskiv M, Garrison
DE, Meade JR, Peace TI and Zhou T: Inflammaging and oxidative
stress in human diseases: From molecular mechanisms to novel
treatments. Int J Mol Sci. 20:44722019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Förstermann U, Xia N and Li H: Roles of
vascular oxidative stress and nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of
atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 120:713–735. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Costa JG, Saraiva N, Batinic-Haberle I,
Castro M, Oliveira NG and Fernandes AS: The SOD Mimic
MnTnHex-2-PyP5+ reduces the viability and migration of
786-O human renal cancer cells. Antioxidants (Basel). 8:4902019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ge C, Tan J, Zhong S, Lai L, Chen G, Zhao
J, Yi C, Wang L, Zhou L, Tang T, et al: Nrf2 mitigates prolonged
PM2.5 exposure-triggered liver inflammation by positively
regulating SIKE activity: Protection by Juglanin. Redox Biol.
36:1016452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rojo de la Vega M, Chapman E and Zhang DD:
NRF2 and the hallmarks of cancer. Cancer Cell. 34:21–43. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Suzuki T, Motohashi H and Yamamoto M:
Toward clinical application of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 34:340–346. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Leinonen HM, Kansanen E, Pölönen P,
Heinäniemi M and Levonen AL: Role of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in
cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 122:281–320. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cuadrado A, Rojo AI, Wells G, Hayes JD,
Cousin SP, Rumsey WL, Attucks OC, Franklin S, Levonen AL, Kensler
TW and Dinkova-Kostova AT: Therapeutic targeting of the NRF2 and
KEAP1 partnership in chronic diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
18:295–317. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kobayashi A, Kang MI, Okawa H, Ohtsuji M,
Zenke Y, Chiba T, Igarashi K and Yamamoto M: Oxidative stress
sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to
regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol Cell Biol.
24:7130–7139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Warabi E, Takabe W, Minami T, Inoue K,
Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Ishii T, Kodama T and Noguchi N: Shear stress
stabilizes NF-E2-related factor 2 and induces antioxidant genes in
endothelial cells: Role of reactive oxygen/nitrogen species. Free
Radic Biol Med. 42:260–269. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Farkhondeh T, Pourbagher-Shahri AM,
Azimi-Nezhad M, Forouzanfar F, Brockmueller A, Ashrafizadeh M,
Talebi M, Shakibaei M and Samarghandian S: Roles of Nrf2 in gastric
cancer: Targeting for therapeutic strategies. Molecules.
26:31572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Su L, Cao P and Wang H: Tetrandrine
mediates renal function and redox homeostasis in a
streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy rat model through
Nrf2/HO-1 reactivation. Ann Transl Med. 8:9902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang S, Li T, Zhang L, Wang X, Dong H, Li
L, Fu D, Li Y, Zi X, Liu HM, et al: A novel chalcone derivative S17
induces apoptosis through ROS dependent DR5 up-regulation in
gastric cancer cells. Sci Rep. 7:98732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ci X, Lv H, Wang L, Wang X, Peng L, Qin FX
and Cheng G: The antioxidative potential of farrerol occurs via the
activation of Nrf2 mediated HO-1 signaling in RAW 264.7 cells. Chem
Biol Interact. 239:192–199. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mohammad J, Singh RR, Riggle C, Haugrud B,
Abdalla MY and Reindl KM: JNK inhibition blocks
piperlongumine-induced cell death and transcriptional activation of
heme oxygenase-1 in pancreatic cancer cells. Apoptosis. 24:730–744.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu B, Zhang Y, Jia L, Wu H, Fan C, Sun Y,
Ye C, Liao M and Zhou J: Binding of the pathogen receptor HSP90AA1
to avibirnavirus VP2 induces autophagy by inactivating the AKT-MTOR
pathway. Autophagy. 11:503–515. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao YG, Codogno P and Zhang H: Machinery,
regulation and pathophysiological implications of autophagosome
maturation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 22:733–750. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Laverdure S, Wang Z, Yang J, Yamamoto T,
Thomas T, Sato T, Nagashima K and Imamichi T: Interleukin-27
promotes autophagy in human serum-induced primary macrophages via
an mTOR- and LC3-independent pathway. Sci Rep. 11:148982021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rakovic A, Shurkewitsch K, Seibler P,
Grünewald A, Zanon A, Hagenah J, Krainc D and Klein C: Phosphatase
and tensin homolog (PTEN)-induced putative kinase 1
(PINK1)-dependent ubiquitination of endogenous Parkin attenuates
mitophagy: Study in human primary fibroblasts and induced
pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons. J Biol Chem. 288:2223–2237.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang A, Pantoom S and Wu YW: Elucidation
of the anti-autophagy mechanism of the Legionella effector RavZ
using semisynthetic LC3 proteins. Elife. 6:e239052017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Han X, Liu JX and Li XZ: Salvianolic acid
B inhibits autophagy and protects starving cardiac myocytes. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 32:38–44. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mikolaskova B, Jurcik M, Cipakova I,
Kretova M, Chovanec M and Cipak L: Maintenance of genome stability:
The unifying role of interconnections between the DNA damage
response and RNA-processing pathways. Curr Genet. 64:971–983. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Y, Luo W and Wang Y: PARP-1 and its
associated nucleases in DNA damage response. DNA Repair (Amst).
81:1026512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou Y, Tang S, Chen T and Niu MM:
Structure-based pharmacophore modeling, virtual screening,
molecular docking and biological evaluation for identification of
potential poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-1 (PARP-1) Inhibitors.
Molecules. 24:42582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schiewer MJ, Mandigo AC, Gordon N, Huang
F, Gaur S, de Leeuw R, Zhao SG, Evans J, Han S, Parsons T, et al:
PARP-1 regulates DNA repair factor availability. EMBO Mol Med.
10:e88162018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pazzaglia S and Pioli C: Multifaceted Role
of PARP-1 in DNA repair and inflammation: Pathological and
therapeutic implications in cancer and non-cancer diseases. Cells.
9:412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu Y, Song H, Song H, Feng X, Zhou C and
Huo Z: Targeting autophagy potentiates the anti-tumor effect of
PARP inhibitor in pediatric chronic myeloid leukemia. AMB Express.
9:1082019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang L, Wei W, Xiao Q, Yang H and Ci X:
Farrerol Ameliorates APAP-induced hepatotoxicity via activation of
Nrf2 and autophagy. Int J Biol Sci. 15:788–799. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fan SF, Zhou NH, Hu SL and Xu SG: Effects
of 3,4-dihydroxyacetophenone in shortening of action potential
duration of cardiac cells (author's transl). Zhongguo Yao Li Xue
Bao. 2:107–110. 1981.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim YJ, No JK, Lee JS, Kim MS and Chung
HY: Antimelanogenic activity of 3,4-dihydroxyacetophenone:
Inhibition of tyrosinase and MITF. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
70:532–534. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lu XY and Chen WC: Effect of 3,
4-dihydroxyacetophenone on Na+, K+-ATPase
activity of injured mitochondria and the oxygen consumption of
brain cells of rat. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 40:13–16. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang D, Liu J, Wang L, Wang J, Li W,
Zhuang B, Hou J and Liu T: Effects of 3,4-dihydroxyacetophenone on
the hypercholesterolemia-induced atherosclerotic rabbits. Biol
Pharm Bull. 36:733–740. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Aranda A, Sequedo L, Tolosa L, Quintas G,
Burello E, Castell JV and Gombau L: Dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein
diacetate (DCFH-DA) assay: A quantitative method for oxidative
stress assessment of nanoparticle-treated cells. Toxicol In Vitro.
27:954–963. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Arakawa S, Honda S, Yamaguchi H and
Shimizu S: Molecular mechanisms and physiological roles of
Atg5/Atg7-independent alternative autophagy. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B
Phys Biol Sci. 93:378–385. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dunphy G, Flannery SM, Almine JF, Connolly
DJ, Paulus C, Jønsson KL, Jakobsen MR, Nevels MM, Bowie AG and
Unterholzner L: Non-canonical activation of the DNA sensing adaptor
STING by ATM and IFI16 mediates NF-κB signaling after nuclear DNA
damage. Mol Cell. 71:745–760.e5. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hemmingsen B, Gimenez-Perez G, Mauricio D,
Roqué IFM, Metzendorf MI and Richter B: Diet, physical activity or
both for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its
associated complications in people at increased risk of developing
type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. Dec
4–2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wu Y, Song F, Li Y, Li J, Cui Y, Hong Y,
Han W, Wu W, Lakhani I, Li G and Wang Y: Acacetin exerts
antioxidant potential against atherosclerosis through Nrf2 pathway
in apoE(−/-) Mice. J Cell Mol Med. 25:521–534. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kaur R, Kaur M and Singh J: Endothelial
dysfunction and platelet hyperactivity in type 2 diabetes mellitus:
Molecular insights and therapeutic strategies. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
17:1212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sena CM, Leandro A, Azul L, Seiça R and
Perry G: Vascular oxidative stress: Impact and therapeutic
approaches. Front Physiol. 9:16682018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Jiao B, Wang YS, Cheng YN, Gao JJ and
Zhang QZ: Valsartan attenuated oxidative stress, decreased MCP-1
and TGF-β1 expression in glomerular mesangial and epithelial cells
induced by high-glucose levels. Biosci Trends. 5:173–181. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang M, Sun X, Yu D, Xu J, Chung K and Li
H: Genomic and transcriptomic analyses of the tangerine pathotype
of Alternaria alternata in response to oxidative stress. Sci Rep.
6:324372016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Guo J, Zhao MH, Shin KT, Niu YJ, Ahn YD,
Kim NH and Cui XS: The possible molecular mechanisms of bisphenol A
action on porcine early embryonic development. Sci Rep. 7:86322017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
An J, Li Q, Yang J, Zhao Z, Wu Y, Wang Y
and Wang W: Wheat F-box protein TaFBA1 positively regulates plant
drought tolerance but negatively regulates stomatal closure. Front
Plant Sci. 10:12422019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang R, Liu B, Fan X, Wang W, Xu T, Wei
S, Zheng W, Yuan Q, Gao L, Yin X, et al: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2
protects against post-cardiac arrest myocardial dysfunction through
a novel mechanism of suppressing mitochondrial reactive oxygen
species production. Front Pharmacol. 11:3732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bazhin AV, Philippov PP and Karakhanova S:
Reactive oxygen species in cancer biology and anticancer therapy.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:41978152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Senoner T and Dichtl W: Oxidative stress
in cardiovascular diseases: Still a therapeutic target? Nutrients.
11:20902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kang Q and Yang C: Oxidative stress and
diabetic retinopathy: Molecular mechanisms, pathogenetic role and
therapeutic implications. Redox Biol. 37:1017992020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Shah MS and Brownlee M: Molecular and
cellular mechanisms of cardiovascular disorders in diabetes. Circ
Res. 118:1808–1829. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhong Z, Fu X, Li H, Chen J, Wang M, Gao
S, Zhang L, Cheng C, Zhang Y, Li P, et al: Citicoline protects
auditory hair cells against neomycin-induced damage. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 8:7122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Das SK, Prusty A, Samantaray D, Hasan M,
Jena S, Patra JK, Samanta L and Thatoi H: Effect of Xylocarpus
granatum bark extract on amelioration of hyperglycaemia and
oxidative stress associated complications in STZ-induced diabetic
mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019:84931902019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wang SX, Wen X, Bell C and Appiah S:
Liposome-delivered baicalein induction of myeloid leukemia K562
cell death via reactive oxygen species generation. Mol Med Rep.
17:4524–4530. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yang DS, Xi-Rui W and Ting-Yuan M: Effects
of 3,4-dihydroxyacetophenone on the biosynthesis of TXA2 and PGI2
in human placental villus and umbilical artery segments in vitro.
Prostaglandins. 38:497–504. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wu P, Ye D, Zhang D, Zhang L, Wan J and
Pan Q: Dual effect of 3,4-dihydroxyacetophenone on LPS-induced
apoptosis in RAW264.7 cells by modulating the production of
TNF-alpha. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 25:131–134. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Fan X, Wei W, Huang J, Liu X and Ci X:
Isoorientin attenuates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through the
inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis via activating the
SIRT1/SIRT6/Nrf-2 pathway. Front Pharmacol. 11:2642020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Qin JJ, Cheng XD, Zhang J and Zhang WD:
Dual roles and therapeutic potential of Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in
pancreatic cancer: A systematic review. Cell Commun Signal.
17:1212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li T, Chen B, Du M, Song J, Cheng X, Wang
X and Mao X: Casein glycomacropeptide hydrolysates exert
cytoprotective effect against cellular oxidative stress by
Up-Regulating HO-1 expression in HepG2 cells. Nutrients. 9:312017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Martinez RM, Fattori V, Saito P, Pinto IC,
Rodrigues CCA, Melo CPB, Bussmann AJC, Staurengo-Ferrari L, Bezerra
JR, Vignoli JA, et al: The lipoxin Receptor/FPR2 agonist BML-111
protects mouse skin against ultraviolet B radiation. Molecules.
25:29532020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Piao CH, Fan YJ, Nguyen TV, Song CH and
Chai OH: Mangiferin alleviates ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis
via Nrf2/HO-1/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 21:34152020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Probst BL, McCauley L, Trevino I, Wigley
WC and Ferguson DA: Cancer cell growth is differentially affected
by constitutive activation of NRF2 by KEAP1 deletion and
pharmacological activation of NRF2 by the synthetic triterpenoid,
RTA 405. PLoS One. 10:e01352572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Singh A, Venkannagari S, Oh KH, Zhang YQ,
Rohde JM, Liu L, Nimmagadda S, Sudini K, Brimacombe KR, Gajghate S,
et al: Small molecule inhibitor of NRF2 selectively intervenes
therapeutic resistance in KEAP1-deficient NSCLC tumors. ACS Chem
Biol. 11:3214–3225. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liu X, Zhu Q, Zhang M, Yin T, Xu R, Xiao
W, Wu J, Deng B, Gao X, Gong W, et al: Isoliquiritigenin
ameliorates acute pancreatitis in mice via inhibition of oxidative
stress and modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2018:71615922018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhao Y, Sun Y, Wang G, Ge S and Liu H:
Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides protect against MNNG-Induced
PLGC in rats via activating the NRF2 and antioxidant enzymes HO-1
and NQO-1. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:93102452019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Gomes LR, Menck CFM and Leandro GS:
Autophagy roles in the modulation of DNA repair pathways. Int J Mol
Sci. 18:23512017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Liao SX, Sun PP, Gu YH, Rao XM, Zhang LY
and Ou-Yang Y: Autophagy and pulmonary disease. Ther Adv Respir
Dis. 13:17534666198905382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Xu F, Li X, Yan L, Yuan N, Fang Y, Cao Y,
Xu L, Zhang X, Xu L, Ge C, et al: Autophagy promotes the repair of
Radiation-Induced DNA damage in bone marrow hematopoietic cells via
enhanced STAT3 signaling. Radiat Res. 187:382–396. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Galati S, Boni C, Gerra MC, Lazzaretti M
and Buschini A: Autophagy: A player in response to oxidative stress
and DNA damage. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:56929582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Poluzzi C, Iozzo RV and Schaefer L:
Endostatin and endorepellin: A common route of action for similar
angiostatic cancer avengers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 97:156–173. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Nguyen TM, Subramanian IV, Xiao X, Ghosh
G, Nguyen P, Kelekar A and Ramakrishnan S: Endostatin induces
autophagy in endothelial cells by modulating Beclin 1 and
beta-catenin levels. J Cell Mol Med. 13:3687–3698. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Deng W, Long Q, Zeng J, Li P, Yang W, Chen
X and Xie J: Mycobacterium tuberculosis PE_PGRS41 enhances the
intracellular survival of M. smegmatis within macrophages via
blocking innate immunity and inhibition of host defense. Sci Rep.
7:467162017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Qiao X, Wang X, Shang Y, Li Y and Chen SZ:
Azithromycin enhances anticancer activity of TRAIL by inhibiting
autophagy and up-regulating the protein levels of DR4/5 in colon
cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Commun (Lond). 38:432018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Lee JH, Parveen A, Do MH, Kang MC, Yumnam
S and Kim SY: Molecular mechanisms of methylglyoxal-induced aortic
endothelial dysfunction in human vascular endothelial cells. Cell
Death Dis. 11:4032020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Liang C, Lee JS, Inn KS, Gack MU, Li Q,
Roberts EA, Vergne I, Deretic V, Feng P, Akazawa C and Jung JU:
Beclin1-binding UVRAG targets the class C Vps complex to coordinate
autophagosome maturation and endocytic trafficking. Nat Cell Biol.
10:776–787. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Shaltiel IA, Krenning L, Bruinsma W and
Medema RH: The same, only different-DNA damage checkpoints and
their reversal throughout the cell cycle. J Cell Sci. 128:607–620.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ivy SP, de Bono J and Kohn EC: The
‘Pushmi-Pullyu’ of DNA REPAIR: Clinical synthetic lethality. Trends
Cancer. 2:646–656. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
He G, Siddik ZH, Huang Z, Koomen J,
Kobayashi R, Khokhar AR and Kuang J: Induction of p21 by p53
following DNA damage inhibits both Cdk4 and Cdk2 activities.
Oncogene. 24:2929–2943. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Bartek J and Lukas J: Mammalian G1- and
S-phase checkpoints in response to DNA damage. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
13:738–747. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Eckert MA, Orozco C, Xiao J, Javellana M
and Lengyel E: The Effects of chemotherapeutics on the ovarian
cancer microenvironment. Cancers (Basel). 13:31362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Min X, Heng H, Yu HL, Dan M, Jie C, Zeng
Y, Ning H, Liu ZG, Wang ZY and Lin W: Anticancer effects of
10-hydroxycamptothecin induce apoptosis of human osteosarcoma
through activating caspase-3, p53 and cytochrome c pathways. Oncol
Lett. 15:2459–2464. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Isakoff SJ, Puhalla S, Domchek SM,
Friedlander M, Kaufman B, Robson M, Telli ML, Diéras V, Han HS,
Garber JE, et al: A randomized Phase II study of veliparib with
temozolomide or carboplatin/paclitaxel versus placebo with
carboplatin/paclitaxel in BRCA1/2 metastatic breast cancer: Design
and rationale. Future Oncol. 13:307–320. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Pajares M, Jiménez-Moreno N, García-Yagüe
ÁJ, Escoll M, de Ceballos ML, Van Leuven F, Rábano A, Yamamoto M,
Rojo AI and Cuadrado A: Transcription factor NFE2L2/NRF2 is a
regulator of macroautophagy genes. Autophagy. 12:1902–1916. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Feng LX, Zhao F, Liu Q, Peng JC, Duan XJ,
Yan P, Wu X, Wang HS, Deng YH and Duan SB: Role of Nrf2 in
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury: Protection by human
umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2020:61234592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Yang J, Yu J, Li D, Yu S, Ke J, Wang L,
Wang Y, Qiu Y, Gao X, Zhang J and Huang L: Store-operated calcium
entry-activated autophagy protects EPC proliferation via the
CAMKK2-MTOR pathway in ox-LDL exposure. Autophagy. 13:82–98. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Lin W, Yin CY, Yu Q, Zhou SH, Chai L, Fan
J and Wang WD: Expression of glucose transporter-1, hypoxia
inducible factor-1α and beclin-1 in head and neck cancer and their
implication. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 11:3708–3717. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Rodríguez-Vargas JM, Ruiz-Magaña MJ,
Ruiz-Ruiz C, Majuelos-Melguizo J, Peralta-Leal A, Rodríguez MI,
Muñoz-Gámez JA, de Almodóvar MR, Siles E, Rivas AL, et al:
ROS-induced DNA damage and PARP-1 are required for optimal
induction of starvation-induced autophagy. Cell Res. 22:1181–1198.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|