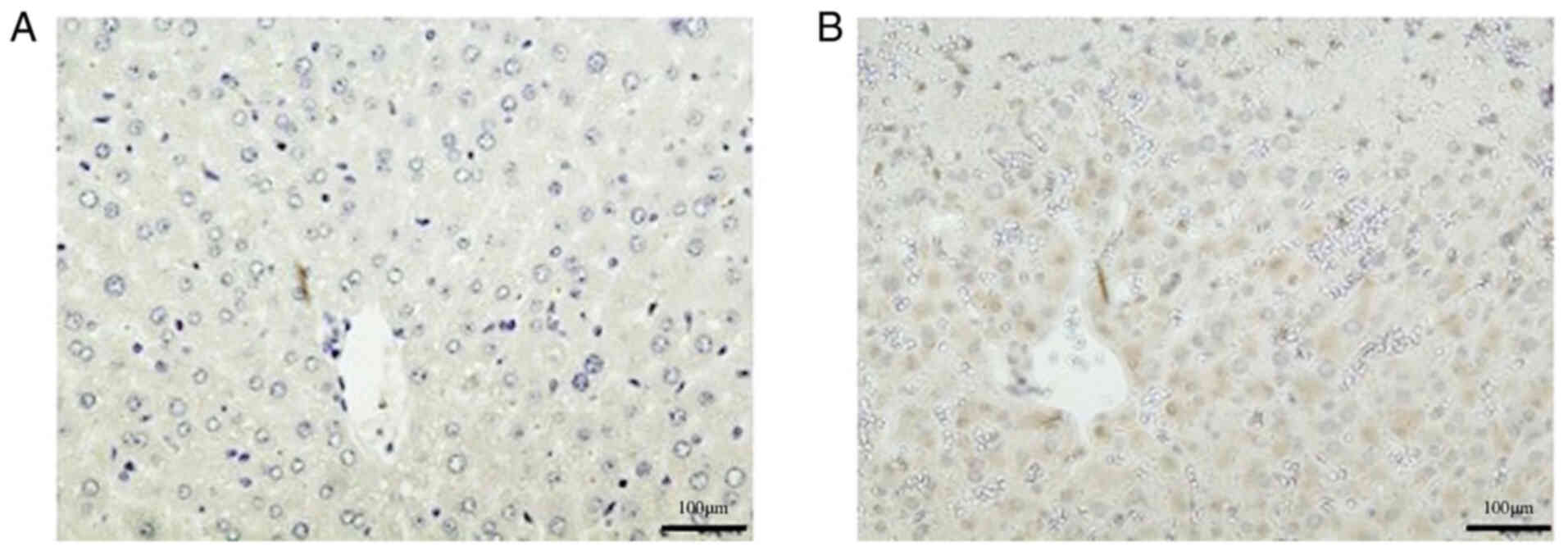
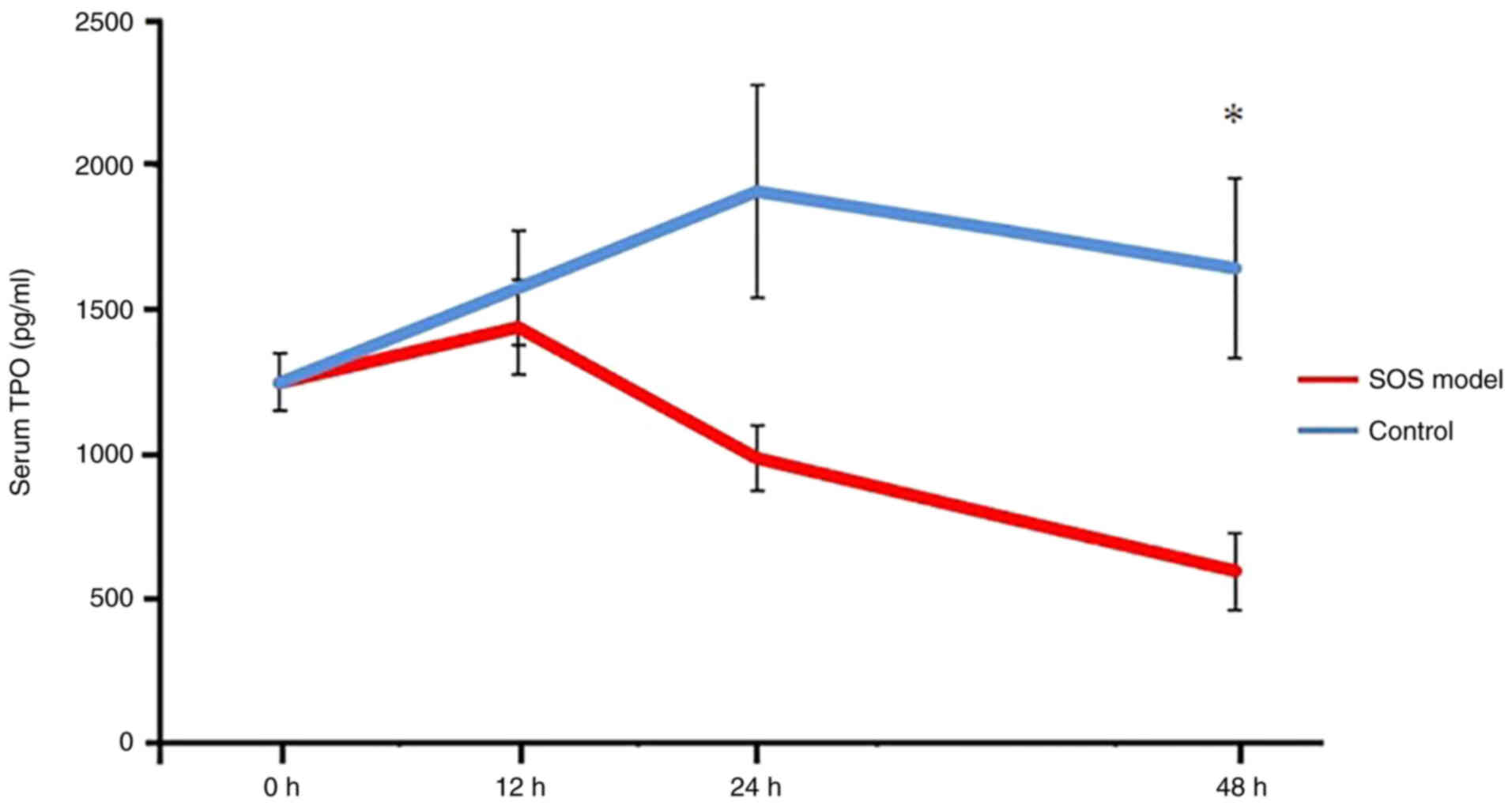
|
1
|
Takamura H, Nakanuma S, Hayashi H, Tajima
H, Kakinoki K, Kitahara M, Sakai S, Makino I, Nakagawara H,
Miyashita T, et al: Severe veno-occlusive disease/sinusoidal
obstruction syndrome after deceased-donor and living-donor liver
transplantation. Transplant Proc. 46:3523–3535. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nakanuma S, Miyashita T, Hayashi H, Tajima
H, Takamura H, Tsukada T, Okamoto K, Sakai S, Makino I, Kinoshita
J, et al: Extravasated platelet aggregation in liver zone 3 may
correlate with the progression of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome
following living donor liver transplantation: A case report. Exp
Ther Med. 9:1119–1124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tajima H, Ohta T, Miyashita T, Nakanuma S,
Matoba M, Miyata T, Sakai S, Okamoto K, Makino I, Kinoshita J, et
al: Oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy induces extravasated platelet
aggregation in the liver. Mol Clin Oncol. 3:555–558. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dignan FL, Wynn RF, Hadzic N, Karani J,
Quaglia A, Pagliuca A, Veys P and Potter MN; Haemato-oncology Task
Force of British Committee for Standards in Haematology, ; British
Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation, : BCSH/BSBMT
guideline: Diagnosis and management of veno-occlusive disease
(sinusoidal obstruction syndrome) following haematopoietic stem
cell transplantation. Br J Haematol. 163:444–457. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tamandl D, Klinger M, Eipeldauer S,
Herberger B, Kaczirek K, Gruenberger B and Gruenberger T: Sinusoid
obstruction syndrome impairs long-term outcome of colorectal liver
metas- tases treated with resection after neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Ann Surg Oncol. 18:421–430. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Duret-Aupy N, Lagarce L, Blouet A, Kettani
S, Conte C, Bourneau-Martin D, Drablier G, Umlil A and Briet M:
Liver sinusoidal obstruction syndrome associated with trastuzumab
emtansine treatment for breast cancer. Therapie. 74:675–677. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bornhäuser M, Illmer T, Oelschlaegel U,
Schetelig J, Ordemann R, Schaich M, Hänel M, Schuler U, Thiede C,
Kiani A, et al: Gemtuzumab ozogamicin as part of reduced-intensity
conditioning for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in
patients with relapsed acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res.
14:5585–5593. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Efrati E, Zuckerman T, Ben-Ami E and
Krivoy N: MTHFR C677T/A1298C genotype: A possible risk factor for
liver sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Bone Marrow Transplant.
49:726–727. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rubbia-Brandt L, Audard V, Sartoretti P,
Roth AD, Brezault C, Le Charpentier M, Dousset B, Morel P, Soubrane
O, Chaussade S, et al: Severe hepatic sinusoidal obstruction
associated with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with
metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 15:460–466. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Morine Y, Shimada M and Utsunomiya T:
Evaluation and management of hepatic injury induced by
oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with hepatic resection
for colorectal liver metastasis. Hepatol Res. 44:59–69. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
DeLeve LD and Wang X: Role of oxidative
stress and glutathione in busulfan toxicity in cultured murine
hepatocytes. Pharmacology. 60:143–154. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hirata M, Tajima H, Miyashita T, Miyata T,
Nakanuma S, Makino I, Hayashi H, Oyama K, Takamura H, Ninomiya I,
et al: Extravasated platelet aggregation in the livers of rats with
drug induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Mol Med Rep.
15:3147–3152. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miyata T, Tajima H, Hirata M, Nakanuma SI,
Makino I, Hayashi H, Oyama K, Miyashita T, Takamura H, Ninomiya I,
et al: Phosphodiesterase III inhibitor attenuates rat sinusoidal
obstruction syndrome through inhibition of platelet aggregation in
Disse's space. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 33:950–957. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Takada S, Miyashita T, Yamamoto Y, Kanou
S, Munesue S, Ohbatake Y, Nakanuma S, Okamoto K, Sakai S, Kinoshita
J, et al: Soluble thrombomodulin attenuates endothelial cell damage
in hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. In Vivo. 32:1409–1417.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kanou S, Miyashita T, Yamamoto Y, Takada
S, Nakura M, Okazaki M, Ohbatake Y, Nakanuma S, Makino I, Tajima H,
et al: Prophylactic effect of recombinant human soluble
thrombomodulin for hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome model
mice. In Vivo. 34:1037–1045. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Conotte R and Colet JM: A metabonomic
evaluation of the monocrotaline-induced sinusoidal obstruction
syndrome (SOS) in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 276:147–156. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Grozovsky R, Giannini S, Falet H and
Hoffmeister KM: Regulating billions of blood platelets: Glycans and
beyond. Blood. 126:1877–1884. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Grozovsky R, Begonja AJ, Liu K, Visner G,
Hartwig JH, Falet H and Hoffmeister KM: The Ashwell-Morell receptor
regulates hepatic thrombopoietin production via JAK2-STAT3
signaling. Nat Med. 21:47–54. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hitchcock IS and Kaushansky K:
Thrombopoietin from beginning to end. Br J Haematol. 165:259–268.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kuter DJ: New thrombopoietic growth
factors. Blood. 109:4607–4616. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Narita M, Hatano E, Ikai I,
Miyagawa-Hayashino A, Yanagida A, Nagata H, Asechi H, Taura K and
Uemoto S: A phosphodiesterase III inhibitor protects rat liver from
sinusoidal obstruction syndrome through heme oxygenase-1 induction.
Ann Surg. 249:806–813. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nakura M, Miyashita T, Yamamoto Y, Takada
S, Kanou S, Tajima H, Takamura H and Ohta T: Inhibitory effects of
beraprost sodium in murine hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome.
Anticancer Res. 40:5171–5180. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yakushijin K, Atsuta Y, Doki N, Yokota A,
Kanamori H, Miyamoto T, Ohwada C, Miyamura K, Nawa Y, Kurokawa M,
et al: Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome after allogeneic
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Incidence, risk factors
and outcomes. Bone Marrow Transplant. 51:403–409. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Narita M, Oussoultzoglou E, Chenard MP,
Fuchshuber P, Rather M, Rosso E, Addeo P, Jaeck D and Bachellier P:
Liver injury due to chemotherapy-induced sinusoidal obstruction
syndrome is associated with sinusoidal capillarization. Ann Surg
Oncol. 19:2230–2237. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hickey PL, McLean AJ, Angus PW, Choo EF
and Morgan DJ: Increased sensitivity of propranolol clearance to
reduced oxygen delivery in the isolated perfused cirrhotic rat
liver. Gastroenterology. 111:1039–1048. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schaffner F and Poper H: Capillarization
of hepatic sinusoids in man. Gastroenterology. 44:239–242. 1963.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|