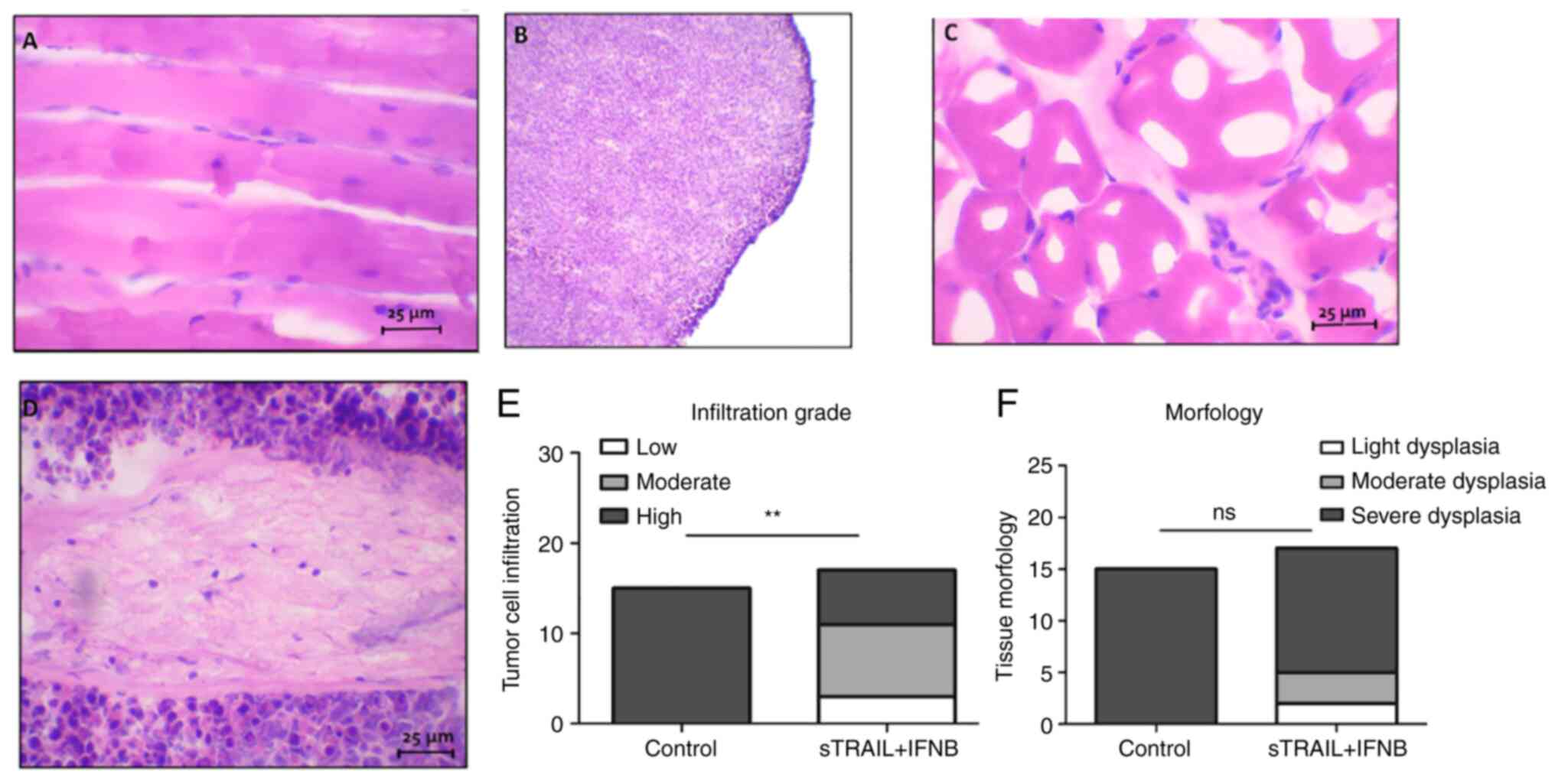
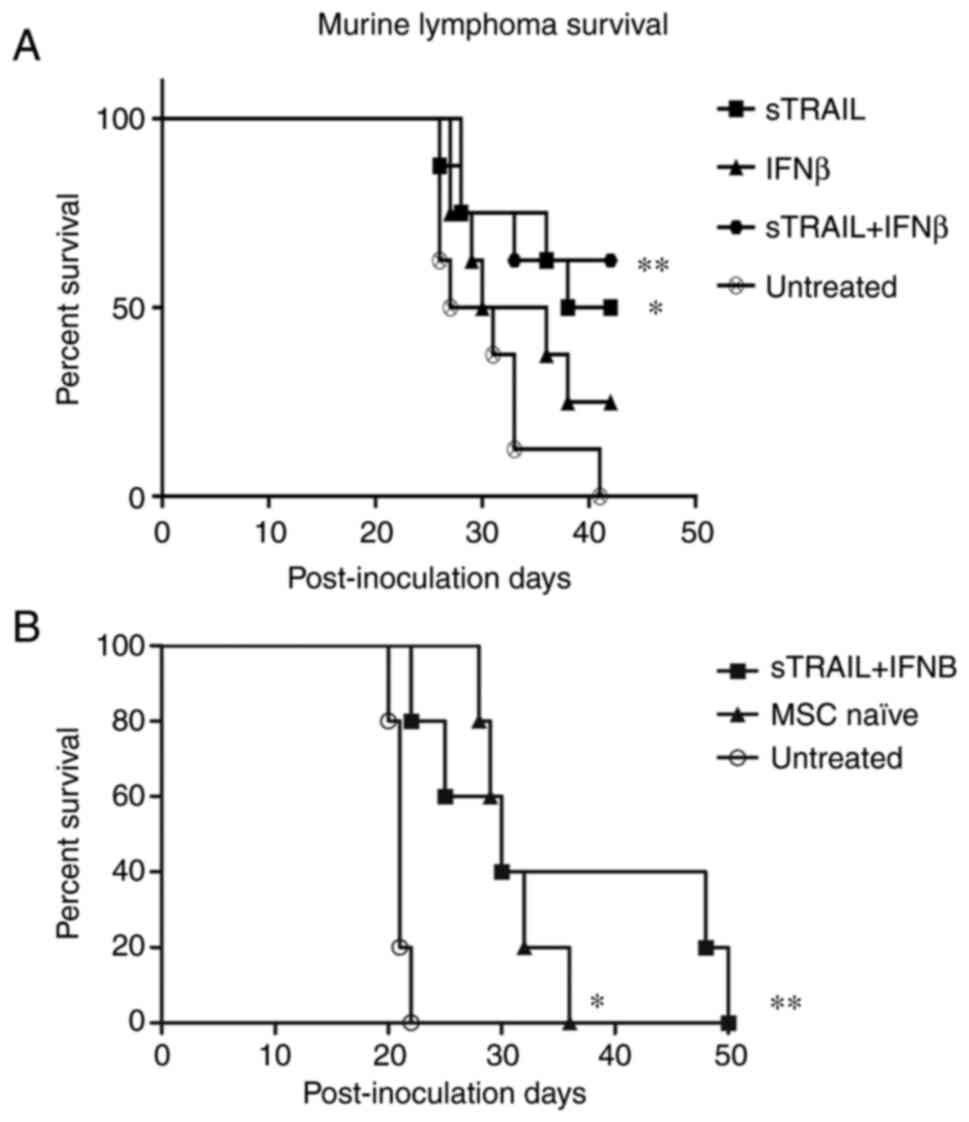
|
1
|
Urrutiocoechea A, Alemany R, Balart J,
Villanueva A, Viñals F and Capellá G: Recent advances in cancer: An
Overview. Curr Pharm Des. 16:3–10. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Herskovic A, Martz K, Al-Sarraf M,
Leichman L, Brindle J, Vaitkevicius V, Cooper J, Byhardt R, Davis L
and Emami B: Combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy compared with
radiotherapy alone in patients with cancer of the esophagus. N Engl
J Med. 326:1593–1598. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Singh P, Pandit S, Mokkapati VRSS, Garg A,
Ravikumar V and Mijakovic I: Gold nanoparticles in diagnostics and
therapeutics for human cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 19:19792018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Baetke SC, Lammers T and Kiessling F:
Applications of nanoparticles for diagnosis and therapy of cancer.
Br J Radiol. 88:201502072015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ: MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–221. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNA
dysregulation in cancer: Diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics.
A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med. 4:143–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ling H, Fabbri M and Calin GA: MicroRNAs
and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug
development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 176:139–148. 2013.
|
|
8
|
Loebinger M, Sage E, Davies D and Janes S:
TRAIL-expressing mesenchymal stem cells kill the putative cancer
stem cell population. Br J Cancer. 103:1692–1697. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu X, Hu J, Li Y, Cao W, Wang Y, Ma Z and
Li F: Mesenchymal stem cells expressing interleukin-18 inhibit
breast cancer in a mouse model. Oncol Lett. 15:6265–6274. 2018.
|
|
10
|
Matosevic S: Viral and nonviral
engineering of natural killer cells as emerging adoptive cancer
immunotherapies. J Immunol Res. 2018:40548152018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Friedenstein AJ, Gorskaja JF and Kulagina
NN: Fibroblast precursors in normal and irradiated mouse
hematopoietic organs. Exp Hematol. 4:267–274. 1976.
|
|
12
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Igura K, Zhang X, Takahashi K, Mitsuru A,
Yamaguchi S and Takahashi TA: Isolation and characterization of
mesenchymal progenitor cells from chorionic villi of human
placenta. Cytotherapy. 6:543–553. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Karp JM and Leng Teo GS: Mesenchymal stem
cell homing: The devil is in the details. Cell Stem Cell.
4:206–216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Karnoub AE, Dash AB, Vo AP, Sullivan A,
Brooks MW, Bell GW, Richardson AL, Polyak K, Tubo R and Weinberg
RA: Mesenchymal stem cells within tumour stroma promote breast
cancer metastasis. Nature. 449:557–563. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shinagawa K, Kitadai Y, Tanaka M, Sumida
T, Kodama M, Higashi Y, Tanaka S, Yasui W and Chayama K:
Mesenchymal stem cells enhance growth and metastasis of colon
cancer. Int J Cancer. 127:2323–2333. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu JM, Jun ES, Bae YC and Jung JS:
Mesenchymal stem cells derived from human adipose tissues favor
tumor cell growth in vivo. Stem Cells Dev. 17:463–473. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pan G, O'Rourke K, Chinnaiyan A, Gentz R,
Ebner R, Ni J and Dixit V: The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand
TRAIL. Science. 276:111–113. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wong SHM, Kong WY, Fang CM, Loh HS, Chuah
LH, Abdullah S and Ngai SC: The TRAIL to cancer therapy: Hindrances
and potential solutions. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 143:81–94. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Nicolini A, Carpi A and Rossi G: Cytokines
in breast cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17:325–337. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Studeny M, Marini FC, Champlin RE,
Zompetta C, Fidler IJ and Andreeff M: Bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells as vehicles for interferon-β delivery into
tumors. Cancer Res. 62:3603–3608. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gonzalez-Villarreal C, Rodriguez M and
Said-Fernández S: How desirable and undesirable features of naïve
or genetically reengineered mesenchymal stem cells are being
considered in preclinical or clinical assays. J BUON. 22:812–830.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qin JY, Zhang L, Clift KL, Hulur I, Xiang
AP, Ren BZ and Lahn BT: Systematic comparison of constitutive
promoters and the doxycycline-inducible promoter. PLoS One. 5:3–6.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kim MH, Billiar TR and Seol DW: The
secretable form of trimeric TRAIL, a potent inducer of apoptosis.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 321:930–935. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yan C, Li S, Li Z, Peng H, Yuan X, Jiang
L, Zhang Y, Fan D, Hu X, Yang M and Xiong D: Human umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells as vehicles of CD20-specific TRAIL fusion
protein delivery: A double-target therapy against non-Hodgkin's
lymphoma. Mol Pharm. 10:142–151. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stern B, Olsen LC, Tröße C, Ravneberg H
and Pryme IF: Improving mammalian cell factories: The selection of
signal peptide has a major impact on recombinant protein synthesis
and secretion in mammalian cells. Trends Cell Mol Biol. 10:19–24.
2007.
|
|
27
|
Yuan Z, Kolluri KK, Sage EK, Gowers KH and
Janes SM: Mesenchymal stromal cell delivery of full-length tumor
necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand is superior to
soluble type for cancer therapy. Cytotherapy. 17:885–896. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Langford DJ, Bailey AL, Chanda ML, Clarke
SE, Drummond TE, Echols S, Glick S, Ingrao J, Klassen-Ross T,
Lacroix-Fralish ML, et al: Coding of facial expressions of pain in
the laboratory mouse. Nat Methods. 7:447–449. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Committee on Rodents, Institute of
Laboratory Animal Resources, Commission on Life Sciences and the
National Research Council, . Laboratory Animal Managent Rodents.
National Academies Press; Washington, D.C., USA: pp. 991996
|
|
30
|
Bankert RB, Egilmez NK and Hess SD:
Human-SCID mouse chimeric models for the evaluation of anti-cancer
therapies. Trends Immunol. 22:386–393. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Haouzi P: Murine models in critical care
research. Crit Care Med. 39:2290–2293. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Frese K and Tuveson D: Maximizing mouse
cancer models. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:654–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Boxall SA and Jones E: Markers for
characterization of bone marrow multipotential stromal cells. Stem
Cells Int. 2012:9758712012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Darzi S, Werkmeister JA, Deane JA and
Gargett CE: Identification and characterization of human
endometrial mesenchymal stem/stromal cells and their potential for
cellular therapy. Stem Cells Transl Med. 5:1127–1132. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li Q, Hou H, Li M, Yu X, Zuo H, Gao J,
Zhang M, Li Z and Guo Z: CD73+ Mesenchymal stem cells
ameliorate myocardial infarction by promoting angiogenesis. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 9:6372392021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Song N, Gao L, Qiu H, Huang C, Cheng H,
Zhou H, Lv S, Chen L and Wang J: Mouse bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells inhibit leukemia/lymphoma cell proliferation
in vitro and in a mouse model of allogeneic bone marrow
transplant. Int J Mol Med. 36:139–149. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Secchiero P, Zorzet S, Tripodo C,
Corallini F, Melloni E, Caruso L, Bosco R, Ingrao S, Zavan B and
Zauli G: Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells display
anti-cancer activity in SCID mice bearing disseminated
non-hodgkin's lymphoma xenografts. PLoS One. 5:e111402010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tu E, Chia PZC and Chen W: TGFβ in T cell
biology and tumor immunity: Angel or devil? Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 25:423–435. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yuen GJ, Demissie E, Pillai S and Burnet
M: B lymphocytes and cancer: A love-hate relationship. Trends
Cancer. 2:747–757. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Soussi T: p53 Antibodies in the sera of
patients with various types of cancer: A review. Cancer Res.
60:1777–1788. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sharonov GV, Serebrovskaya EO, Yuzhakova
DV, Britanova OV and Chudakov DM: B cells, plasma cells and
antibody repertoires in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev
Immunol. 20:294–307. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Lei H, Furlong PJ, Jin HR, Mullins D,
Cantor R, Fraker DL and Spitz FR: AKT activation and response to
interferon-β in human cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:709–715.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ren C, Kumar S, Chanda D, Kallman L, Chen
J, Mountz JD and Ponnazhagan S: Cancer gene therapy using
mesenchymal stem cells expressing interferon-β in a mouse prostate
cancer lung metastasis model. Gene Ther. 15:1446–1453. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dong Z, Greene G, Pettaway C, Dinney CP,
Eue I, Lu W, Bucana CD, Balbay MD, Bielenberg D and Fidler IJ:
Suppression of angiogenesis, tumorigenicity, and metastasis by
human prostate cancer cells engineered to produce interferon-beta.
Cancer Res. 59:872–879. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pestka S and Langer JA: Interferons and
their actions. Ann Rev Biochem. 56:727–777. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Qin X, Runkel L, Deck C, Dedios C and
Barsoum J: Interferon-beta induces S phase accumulation selectively
in human transformed cells. J Interf Cytokine Res. 17:355–367.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kavrochorianou N, Markogiannaki M and
Haralambous S: IFN-β differentially regulates the function of T
cell subsets in MS and EAE. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 30:47–54.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Teige I, Liu Y and Issazadeh-Navikas S:
IFN-β Inhibits T cell activation capacity of central nervous system
APCs. J Immunol. 177:3542–3553. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Makowska A, Wahab L, Braunschweig T,
Kapetanakis NI, Vokuhl C, Denecke B, Shen L, Busson P and Kontny U:
Interferon beta induces apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
via the TRAIL-signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 9:14228–14250. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Vannucchi S, Chiantore MV, Fiorucci G,
Percario ZA, Leone S, Affabris E and Romeo G: TRAIL is a key target
in S-phase slowing-dependent apoptosis induced by interferon-β in
cervical carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 24:2536–2546. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang J, LeBlanc FR, Dighe SA, Hamele CE,
Olson TL, Feith DJ and Loughran TP: TRAIL mediates and sustains
constitutive NF-kB activation in LGL leukemia. Blood.
131:2803–2815. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Mühlenbeck F, Schneider P, Bodmer JL,
Schwenzer R, Hauser A, Schubert G, Scheurich P, Moosmayer D,
Tschopp J and Wajant H: The tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand receptors TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 have
distinct cross-linking requirements for initiation of apoptosis and
are non-redundant in JNK activation. J Biol Chem. 275:32208–32213.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Wang CY, Guttridge DC, Mayo MW and Baldwin
AS: NF-κB induces expression of the Bcl-2 homologue A1/Bfl-1 to
preferentially suppress chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell
Biol. 19:5923–5929. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Baetu TM, Kwon H, Sharma S, Grandvaux N
and Hiscott J: Disruption of NF-kappaB signaling reveals a novel
role for NF-kappaB in the regulation of TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand expression. J Immunol. 167:3164–3173.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Shetty S, Brown Gladden J, Henson ES, Hu
X, Villanueva J, Haney N and Gibson SB: Tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) up-regulates death
receptor 5 (DR5) mediated by NFkappaB activation in epithelial
derived cell lines. Apoptosis. 7:413–420. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sedger LM, Shows DM, Blanton RA, Peschon
JJ, Goodwin RG, Cosman D and Wiley SR: IFN-gamma mediates a novel
antiviral activity through dynamic modulation of TRAIL and TRAIL
receptor expression. J Immunol. 163:920–926. 1999.
|
|
57
|
Meng RD and El-Deiry WS: P53-independent
upregulation of KILLER/DR5 TRAIL receptor expression by
glucocorticoids and interferon-gamma. Exp Cell Res. 262:154–169.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Shigeno M, Nakao K, Ichikawa T, Suzuki K,
Kawakami A, Abiru S, Miyazoe S, Nakagawa Y, Ishikawa H, Hamasaki K,
et al: Interferon-alpha sensitizes human hepatoma cells to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis through DR5 upregulation and NF-kappa B
inactivation. Oncogene. 22:1653–1662. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Choi EA, Lei H, Maron DJ, Wilson JM,
Barsoum J, Fraker DL, El-Deiry WS and Spitz FR: Stat1-dependent
induction of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand and the cell-surface death signaling pathway by interferon
beta in human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 63:5299–5307.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bao Q, Zhao Y, Niess H, Conrad C, Schwarz
B, Jauch KW, Huss R, Nelson PJ and Bruns CJ: Mesenchymal stem
cell-based tumor-targeted gene therapy in gastrointestinal cancer.
Stem Cells Dev. 21:2355–2363. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Taraballi F, Pasto A, Bauza G and Varner
C: Immunomodulatory potential of mesenchymal stem cell role in
diseases and therapies: A bioengineering prospective. J Immunol
Regen Med. 4:1000172019.
|
|
62
|
Monteran L and Erez N: The Dark side of
fibroblasts: Cancer-Associated fibroblasts as mediators of
immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol.
10:18352019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Yu P and Fu YX: Tumor-infiltrating T
lymphocytes: Friends or foes? Lab Investig. 86:231–245. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Badalamenti G, Fanale D, Incorvaia L,
Barraco N, Listì A, Maragliano R, Vincenzi B, Calò V, Iovanna JL,
Bazan V and Russo A: Role of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in
patients with solid tumors: Can a drop dig a stone? Cell Immunol.
343:1037532019. View Article : Google Scholar
|