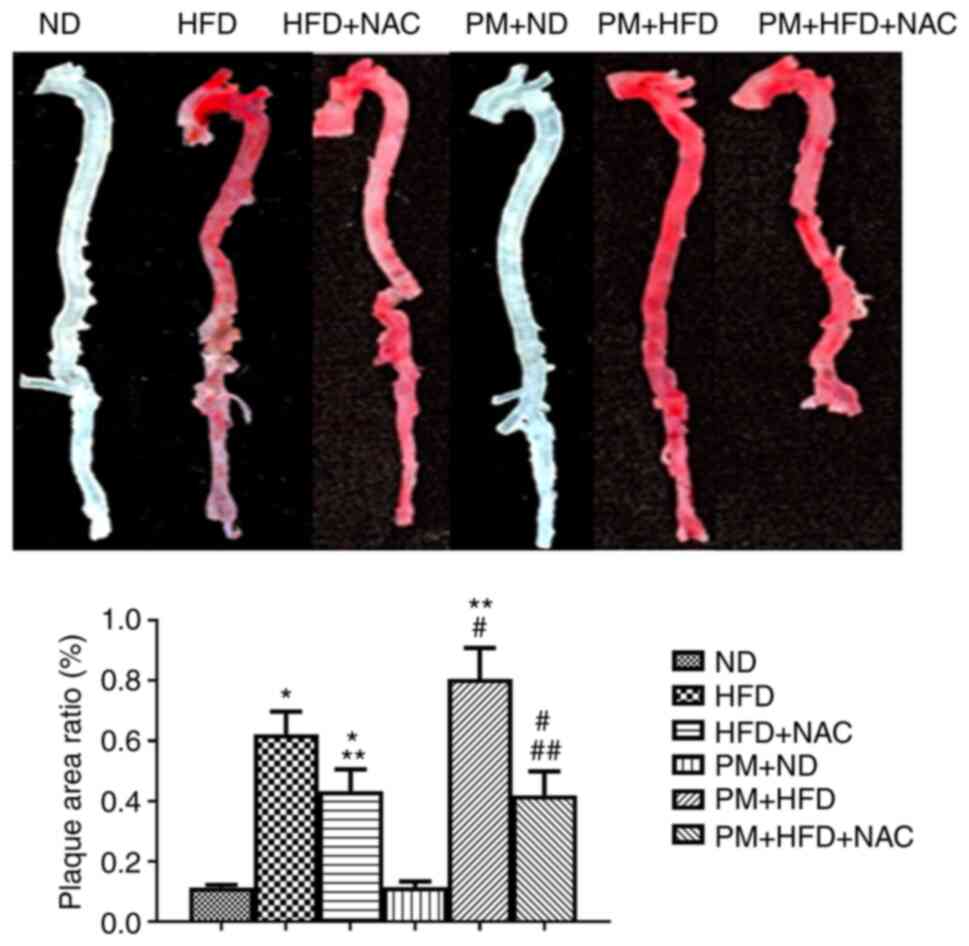
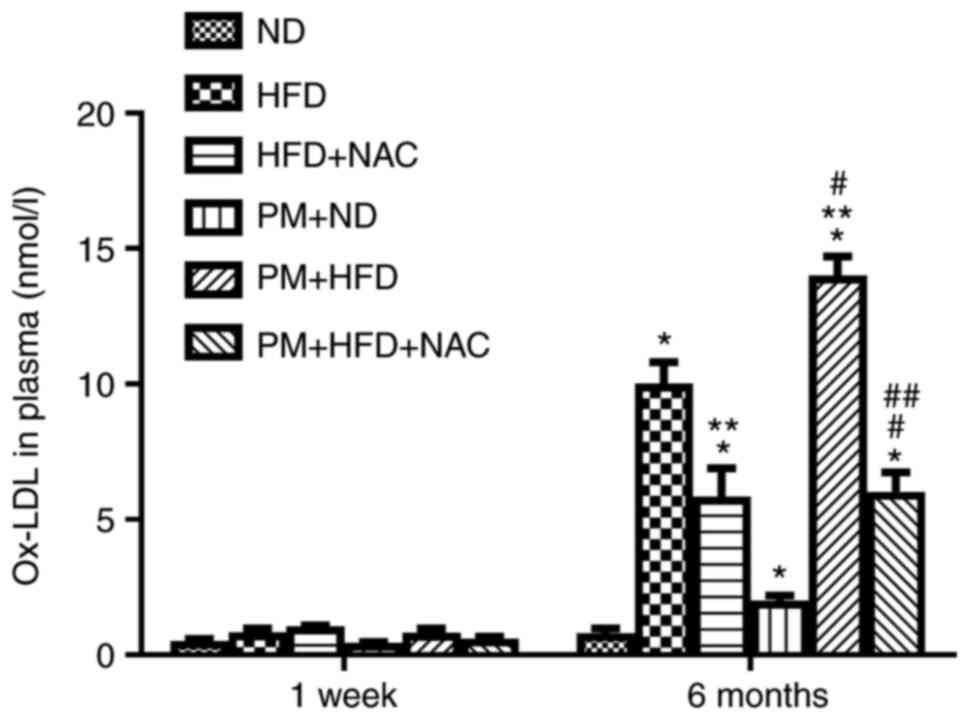
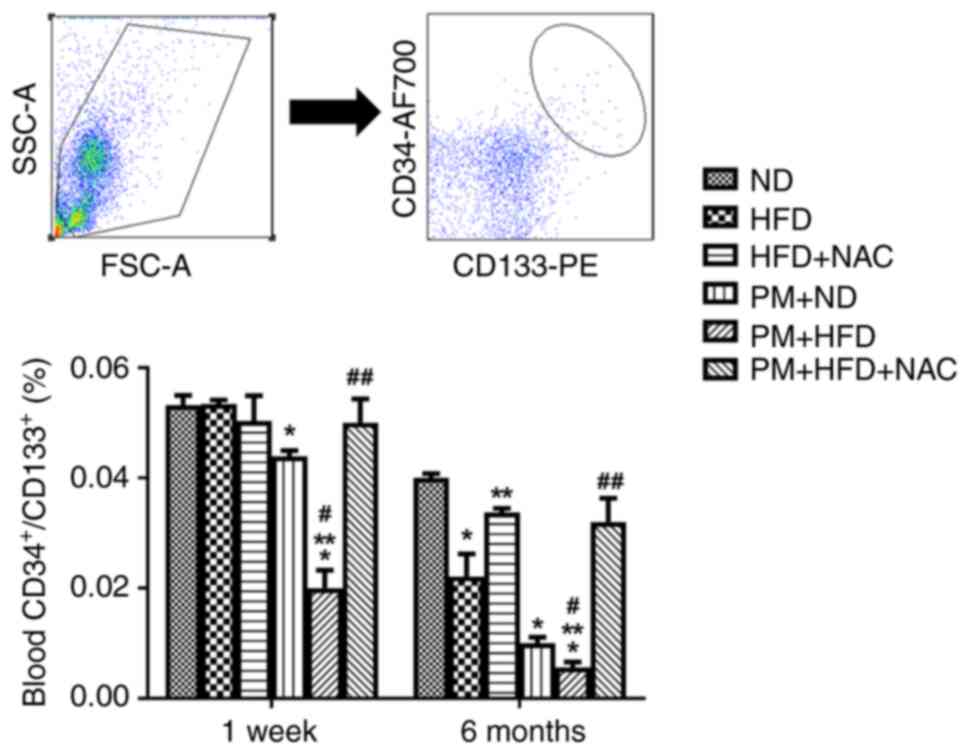
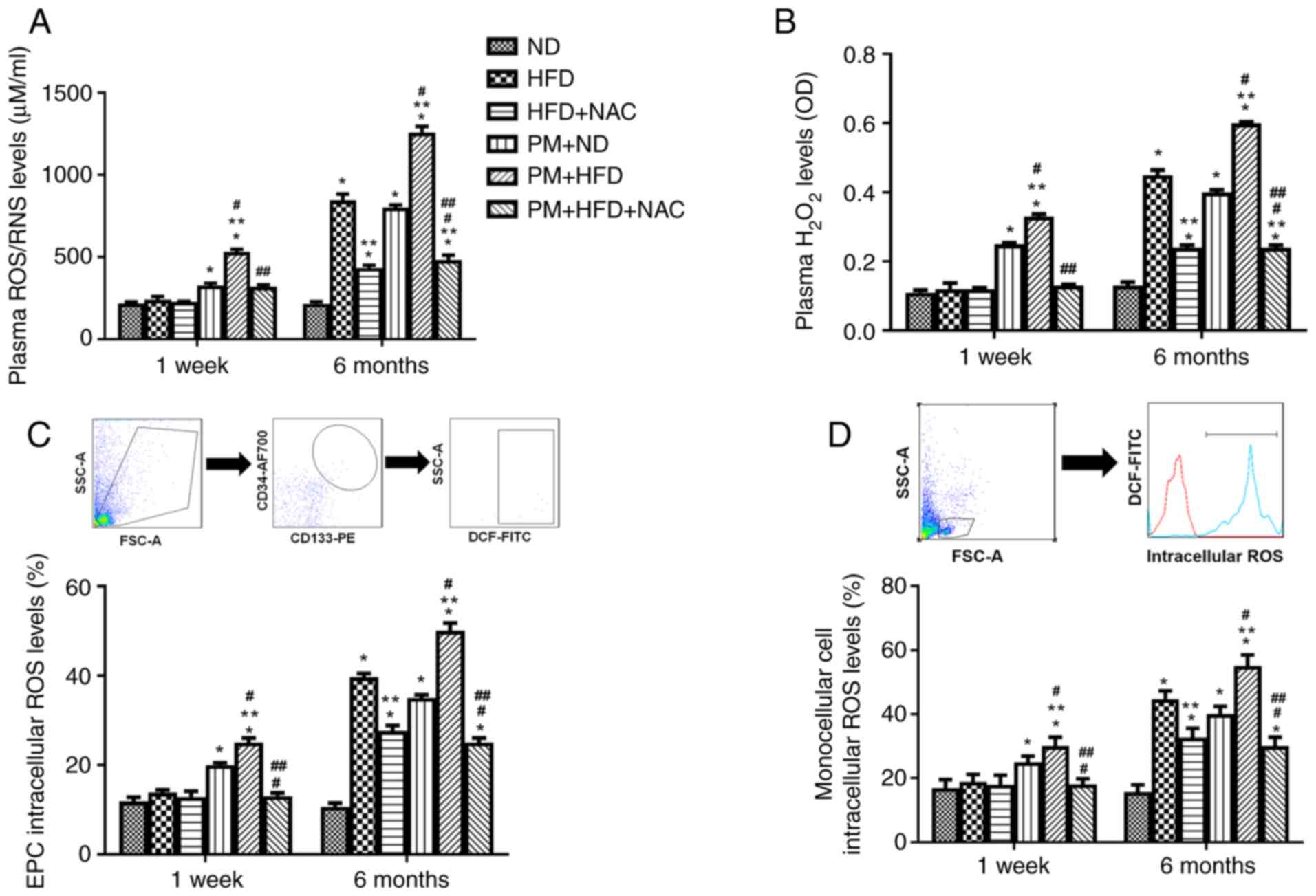
|
1
|
Cui Y, Sun Q and Liu Z: Ambient
particulate matter exposure and cardiovascular diseases: A focus on
progenitor and stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 20:782–793. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu Y, Pan J, Fan C, Xu R, Wang Y, Xu C,
Xie S, Zhang H, Cui X, Peng Z, et al: Short-term exposure to
ambient air pollution and mortality from myocardial infarction. J
Am Coll Cardiol. 77:271–281. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shah AS, Lee KK, McAllister DA, Hunter A,
Nair H, Whiteley W, Langrish JP, Newby DE and Mills NL: Short term
exposure to air pollution and stroke: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. BMJ. 350:h12952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rajagopalan S, Al-Kindi SG and Brook RD:
Air pollution and cardiovascular disease: JACC state-of-the-art
review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 72:2054–2070. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun Q, Wang A, Jin X, Natanzon A, Duquaine
D, Brook RD, Aguinaldo JG, Fayad ZA, Fuster V, Lippmann M, et al:
Long-term air pollution exposure and acceleration of
atherosclerosis and vascular inflammation in an animal model. JAMA.
294:3003–3010. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Davignon J and Ganz P: Role of endothelial
dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation. 109 (23 Suppl
1):III27–III32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Heitzer T, Schlinzig T, Krohn K, Meinertz
T and Munzel T: Endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and risk
of cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease.
Circulation. 104:2673–2678. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rauscher FM, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ,
Davis BH, Wang T, Gregg D, Ramaswami P, Pippen AM, Annex BH, Dong C
and Taylor DA: Aging, progenitor cell exhaustion, and
atherosclerosis. Circulation. 108:457–463. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Strehlow K, Werner N, Berweiler J, Link A,
Dirnagl U, Priller J, Laufs K, Ghaeni L, Milosevic M, Böhm M and
Nickenig G: Estrogen increases bone marrow-derived endothelial
progenitor cell production and diminishes neointima formation.
Circulation. 107:3059–3065. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Urbich C and Dimmeler S: Endothelial
progenitor cells: Characterization and role in vascular biology.
Circ Res. 95:343–353. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Werner N, Junk S, Laufs U, Link A, Walenta
K, Bohm M and Nickenig G: Intravenous transfusion of endothelial
progenitor cells reduces neointima formation after vascular injury.
Circ Res. 93:e17–e24. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen JZ, Zhang FR, Tao QM, Wang XX and Zhu
JH and Zhu JH: Number and activity of endothelial progenitor cells
from peripheral blood in patients with hypercholesterolaemia. Clin
Sci (Lond). 107:273–280. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vasa M, Fichtlscherer S, Aicher A, Adler
K, Urbich C, Martin H, Zeiher AM and Dimmeler S: Number and
migratory activity of circulating endothelial progenitor cells
inversely correlate with risk factors for coronary artery disease.
Circ Res. 89:E1–E7. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kattoor AJ, Pothineni NVK, Palagiri D and
Mehta JL: Oxidative stress in atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler
Rep. 19:422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cui Y, Narasimhulu CA, Liu L, Li X, Xiao
Y, Zhang J, Xie X, Hao H, Liu JZ, He G, et al: Oxidized low-density
lipoprotein alters endothelial progenitor cell populations. Front
Biosci (Landmark Ed). 20:975–988. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Auten RL and Davis JM: Oxygen toxicity and
reactive oxygen species: The devil is in the details. Pediatr Res.
66:121–127. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ogasawara MA and Zhang H: Redox regulation
and its emerging roles in stem cells and stem-like cancer cells.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 11:1107–1122. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pervaiz S, Taneja R and Ghaffari S:
Oxidative stress regulation of stem and progenitor cells. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 11:2777–2789. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cominacini L, Garbin U, Pasini AF, Davoli
A, Campagnola M, Pastorino AM, Gaviraghi G and Lo Cascio V:
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein increases the production of
intracellular reactive oxygen species in endothelial cells:
Inhibitory effect of lacidipine. J Hypertens. 16:1913–1919. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vasconcelos EM, Degasperi GR, de Oliveira
HC, Vercesi AE, de Faria EC and Castilho LN: Reactive oxygen
species generation in peripheral blood monocytes and oxidized LDL
are increased in hyperlipidemic patients. Clin Biochem.
42:1222–1227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cui Y, Xie X, Jia F, He J, Li Z, Fu M, Hao
H, Liu Y, Liu JZ, Cowan PJ, et al: Ambient fine particulate matter
induces apoptosis of endothelial progenitor cells through reactive
oxygen species formation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:353–363. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dludla PV, Dias SC, Obonye N, Johnson R,
Louw J and Nkambule BB: A systematic review on the protective
effect of N-Acetyl cysteine against diabetes-associated
cardiovascular complications. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 18:283–298.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cui Y, Narasimhulu CA, Liu L, Zhang Q, Liu
PZ, Li X, Xiao Y, Zhang J, Hao H, Xie X, et al: N-acetylcysteine
inhibits in vivo oxidation of native low-density lipoprotein. Sci
Rep. 5:163392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mutlu GM, Green D, Bellmeyer A, Baker CM,
Burgess Z, Rajamannan N, Christman JW, Foiles N, Kamp DW, Ghio AJ,
et al: Ambient particulate matter accelerates coagulation via an
IL-6-dependent pathway. J Clin Invest. 117:2952–2961. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gavett SH, Haykal-Coates N, Highfill JW,
Ledbetter AD, Chen LC, Cohen MD, Harkema JR, Wagner JG and Costa
DL: World Trade Center fine particulate matter causes respiratory
tract hyperresponsiveness in mice. Environ Health Perspect.
111:981–991. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shadie AM, Herbert C and Kumar RK: Ambient
particulate matter induces an exacerbation of airway inflammation
in experimental asthma: Role of interleukin-33. Clin Exp Immunol.
177:491–499. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Holt GR: Effects of air pollution on the
upper aerodigestive tract. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 114:201–204.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Aggarwal DJ, Kathariya MG and Verma DPK:
LDL-C, NON-HDL-C and APO-B for cardiovascular risk assessment:
Looking for the ideal marker. Indian Heart J. 73:544–548. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhuo X, Bu H, Hu K, Si Z, Chen L, Chen Y,
Yang L, Jiang Y, Xu Y, Zhao P, et al: Differences in the reaction
of hyperlipidemia on different endothelial progenitor cells based
on sex. Biomed Rep. 15:642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cui Y, Liu L, Xiao Y, Li X, Zhang J, Xie
X, Tian J, Sen CK, He X, Hao H and Liu Z: N-acetylcysteine
differentially regulates the populations of bone marrow and
circulating endothelial progenitor cells in mice with limb
ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol. 881:1732332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rosenkranz AR, Schmaldienst S, Stuhlmeier
KM, Chen W, Knapp W and Zlabinger GJ: A microplate assay for the
detection of oxidative products using
2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin-diacetate. J Immunol Methods. 156:39–45.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Eggermann J, Kliche S, Jarmy G, Hoffmann
K, Mayr-Beyrle U, Debatin KM, Waltenberger J and Beltinger C:
Endothelial progenitor cell culture and differentiation in vitro: A
methodological comparison using human umbilical cord blood.
Cardiovasc Res. 58:478–486. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ii M, Takenaka H, Asai J, Ibusuki K,
Mizukami Y, Maruyama K, Yoon YS, Wecker A, Luedemann C, Eaton E, et
al: Endothelial progenitor thrombospondin-1 mediates
diabetes-induced delay in reendothelialization following arterial
injury. Circ Res. 98:697–704. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kinnaird T, Stabile E, Zbinden S, Burnett
MS and Epstein SE: Cardiovascular risk factors impair native
collateral development and may impair efficacy of therapeutic
interventions. Cardiovasc Res. 78:257–264. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sodha NR, Clements RT, Boodhwani M, Xu SH,
Laham RJ, Bianchi C and Sellke FW: Endostatin and angiostatin are
increased in diabetic patients with coronary artery disease and
associated with impaired coronary collateral formation. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 296:H428–H434. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Panahi Y, Ahmadi Y, Teymouri M, Johnston
TP and Sahebkar A: Curcumin as a potential candidate for treating
hyperlipidemia: A review of cellular and metabolic mechanisms. J
Cell Physiol. 233:141–152. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Krauzova E, Kracmerova J, Rossmeislova L,
Mališová L, Tencerová M, Koc M, Štich V and Šiklová M: Acute
hyperlipidemia initiates proinflammatory and proatherogenic changes
in circulation and adipose tissue in obese women. Atherosclerosis.
250:151–157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
He L, Hao L, Fu X, Huang M and Li R:
Severe hypertriglyceridemia and hypercholesterolemia accelerating
renal injury: A novel model of type 1 diabetic hamsters induced by
short-term high-fat/high-cholesterol diet and low-dose
streptozotocin. BMC Nephrol. 16:512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Krysiak R, Zmuda W, Marek B and Okopien B:
Comparison of the effects of short-term hypolipidaemic treatment on
plasma adipokine levels in men and women with isolated
hypercholesterolaemia. Endokrynol Pol. 66:114–120. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bevan GH, Al-Kindi SG, Brook R and
Rajagopalan S: Ambient air pollution and atherosclerosis: Recent
updates. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 23:632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kander MC, Cui Y and Liu Z: Gender
difference in oxidative stress: A new look at the mechanisms for
cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 21:1024–1032. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu X, Xiao Y, Zhu Q, Cui Y, Hao H, Wang
M, Cowan PJ, Korthuis RJ, Li G, Sun Q and Liu Z: Circulating
endothelial progenitor cells are preserved in female mice exposed
to ambient fine particulate matter independent of estrogen. Int J
Mol Sci. 22:72002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu X, Wang A, Chen Z, Cui Y, Hao H,
Domeier TL, Sun Q and Liu Z: Tempol preserves endothelial
progenitor cells in male mice with ambient fine particulate matter
exposure. Biomedicines. 10:3272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zafarullah M, Li WQ, Sylvester J and Ahmad
M: Molecular mechanisms of N-acetylcysteine actions. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 60:6–20. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bartekova M, Barancik M, Ferenczyova K and
Dhalla NS: Beneficial effects of N-acetylcysteine and
N-mercaptopropionylglycine on ischemia reperfusion injury in the
heart. Curr Med Chem. 25:355–366. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Marian AJ: Experimental therapies in
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2:483–492.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Nikbakht M, Ahmadi F, Vaseghi G, Talasaz
AH, Eshraghi A, Naderi J and Daneshmehr MA: The role of
N-acetylcysteine in platelet aggregation and reperfusion injury in
recent years. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 12:83–91. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lin CP, Huang PH, Lai CF, Chen JW, Lin SJ
and Chen JS: Simvastatin attenuates oxidative stress, NF-κB
activation, and artery calcification in LDLR-/-mice fed with high
fat diet via down-regulation of tumor necrosis factor-α and TNF
receptor 1. PLoS One. 10:e01436862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Subrahmanian S, Varshney R, Subramani K,
Murphy B, Woolington S and Ahamed J: N-Acetylcysteine inhibits
aortic stenosis progression in a murine model by blocking
Shear-induced activation of platelet latent transforming growth
factor beta 1. Antioxid Redox Signal. Dec 7–2021.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Spartalis M, Siasos G, Mastrogeorgiou M,
Spartalis E, Kaminiotis VV, Mylonas KS, Kapelouzou A, Kontogiannis
C, Doulamis IP, Toutouzas K, et al: The effect of per os colchicine
administration in combination with fenofibrate and N-acetylcysteine
on triglyceride levels and the development of atherosclerotic
lesions in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
25:7765–7776. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Korou LM, Agrogiannis G, Pantopoulou A,
Vlachos IS, Iliopoulos D, Karatzas T and Perrea DN: Comparative
antilipidemic effect of N-acetylcysteine and sesame oil
administration in diet-induced hypercholesterolemic mice. Lipids
Health Dis. 9:232010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Meng XP, Yin CS, Cui JH, Li ZX, Wang L,
Wang YW and Li YL: Inhibitory effect of N-acetylcysteine upon
atherosclerotic processes in rabbit carotid. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 89:1850–1853. 2009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sung HJ, Kim J, Kim Y, Jang SW and Ko J:
N-acetyl cysteine suppresses the foam cell formation that is
induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein via regulation of gene
expression. Mol Biol Rep. 39:3001–3007. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Thiele H, Hildebrand L, Schirdewahn C,
Eitel I, Adams V, Fuernau G, Erbs S, Linke A, Diederich KW, Nowak
M, et al: Impact of high-dose N-acetylcysteine versus placebo on
contrast-induced nephropathy and myocardial reperfusion injury in
unselected patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. The
LIPSIA-N-ACC (Prospective, Single-Blind, Placebo-Controlled,
Randomized Leipzig Immediate PercutaneouS Coronary Intervention
Acute Myocardial Infarction N-ACC) Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol.
55:2201–2209. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Poitevin S, Garnotel R, Antonicelli F,
Gillery P and Nguyen P: Type I collagen induces tissue factor
expression and matrix metalloproteinase 9 production in human
primary monocytes through a redox-sensitive pathway. J Thromb
Haemost. 6:1586–1594. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wiklund O, Fager G, Andersson A, Lundstam
U, Masson P and Hultberg B: N-acetylcysteine treatment lowers
plasma homocysteine but not serum lipoprotein(a) levels.
Atherosclerosis. 119:99–106. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhu Q, Hao H, Xu H, Fichman Y, Cui Y, Yang
C, Wang M, Mittler R, Hill MA, Cowan PJ, et al: Combination of
antioxidant enzyme overexpression and N-acetylcysteine treatment
enhances the survival of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells in
ischemic limb in mice with type 2 diabetes. Am Heart Assoc.
10:e0234912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Omara FO, Fournier M, Vincent R and
Blakley BR: Suppression of rat and mouse lymphocyte function by
urban air particulates (Ottawa dust) is reversed by
N-acetylcysteine. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 59:67–85. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Rhoden CR, Lawrence J, Godleski JJ and
Gonzalez-Flecha B: N-acetylcysteine prevents lung inflammation
after short-term inhalation exposure to concentrated ambient
particles. Toxicol Sci. 79:296–303. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang T, Wang L, Moreno-Vinasco L, Lang GD,
Siegler JH, Mathew B, Usatyuk PV, Samet JM, Geyh AS, Breysse PN, et
al: Particulate matter air pollution disrupts endothelial cell
barrier via calpain-mediated tight junction protein degradation.
Part Fibre Toxicol. 9:352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sharma K, Lee HH, Gong DS, Park SH, Yi E,
Schini-Kerth V and Oak MH: Fine air pollution particles induce
endothelial senescence via redox-sensitive activation of local
angiotensin system. Environ Pollut. 252((Pt A)): 317–329. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Reboul C, Boissiere J, Andre L, Meyer G,
Bideaux P, Fouret G, Feillet-Coudray C, Obert P, Lacampagne A,
Thireau J, et al: Carbon monoxide pollution aggravates ischemic
heart failure through oxidative stress pathway. Sci Rep.
7:397152017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kim JB, Kim C, Choi E, Park S, Park H, Pak
HN, Lee MH, Shin DC, Hwang KC and Joung B: Particulate air
pollution induces arrhythmia via oxidative stress and calcium
calmodulin kinase II activation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 259:66–73.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Tzeng HP, Yang RS, Ueng TH and Liu SH:
Upregulation of cyclooxygenase-2 by motorcycle exhaust
particulate-induced reactive oxygen species enhances rat vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferation. Chem Res Toxicol. 20:1170–1176.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Rhoden CR, Wellenius GA, Ghelfi E,
Lawrence J and Gonzalez-Flecha B: PM-induced cardiac oxidative
stress and dysfunction are mediated by autonomic stimulation.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1725:305–313. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Cui Y, Jia F, He J, Xie X, Li Z, Fu M, Hao
H, Liu Y, Liu DZ, Cowan PJ, et al: Ambient fine particulate matter
suppresses in vivo proliferation of bone marrow stem cells through
reactive oxygen species formation. PLoS One. 10:e01273092015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|