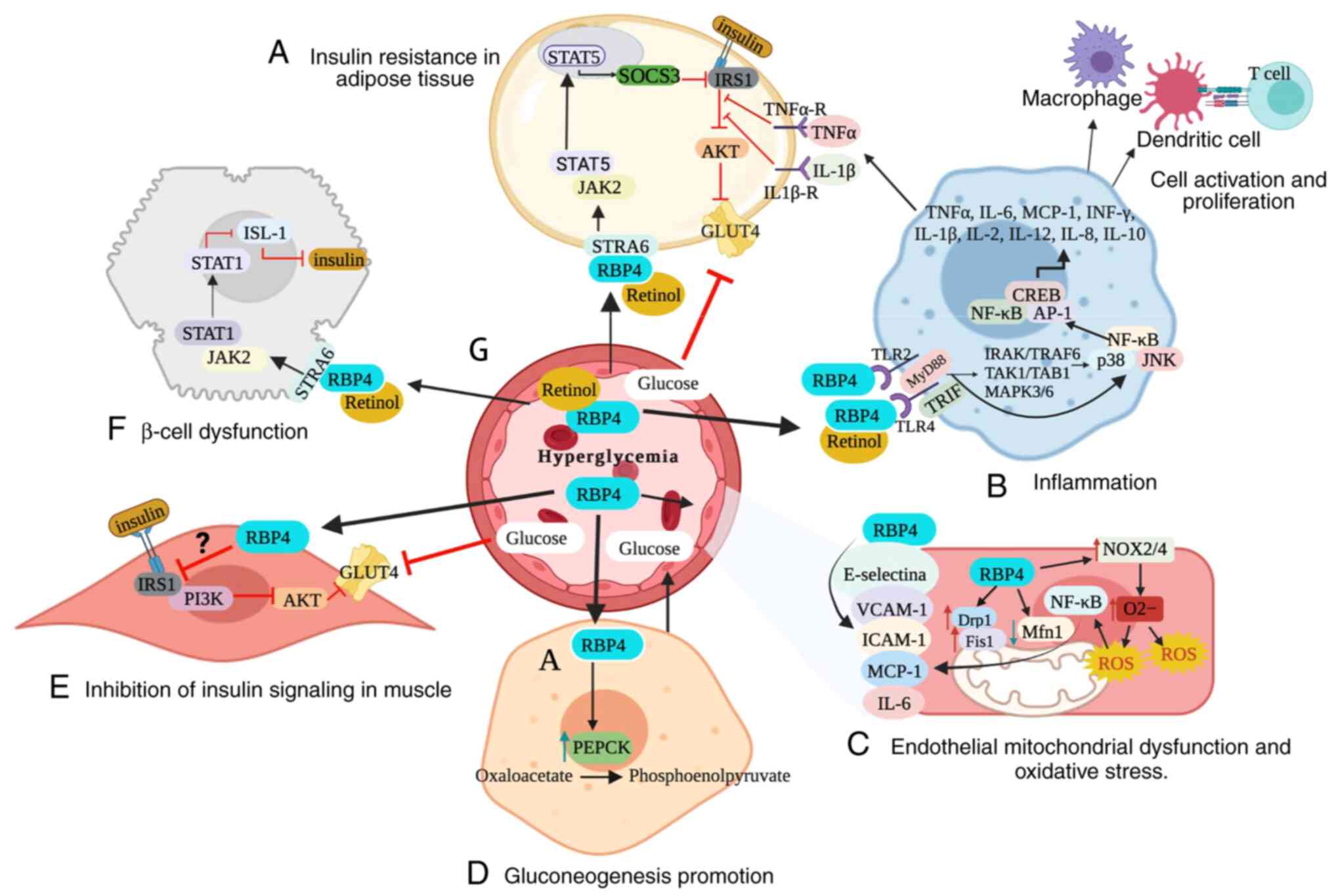
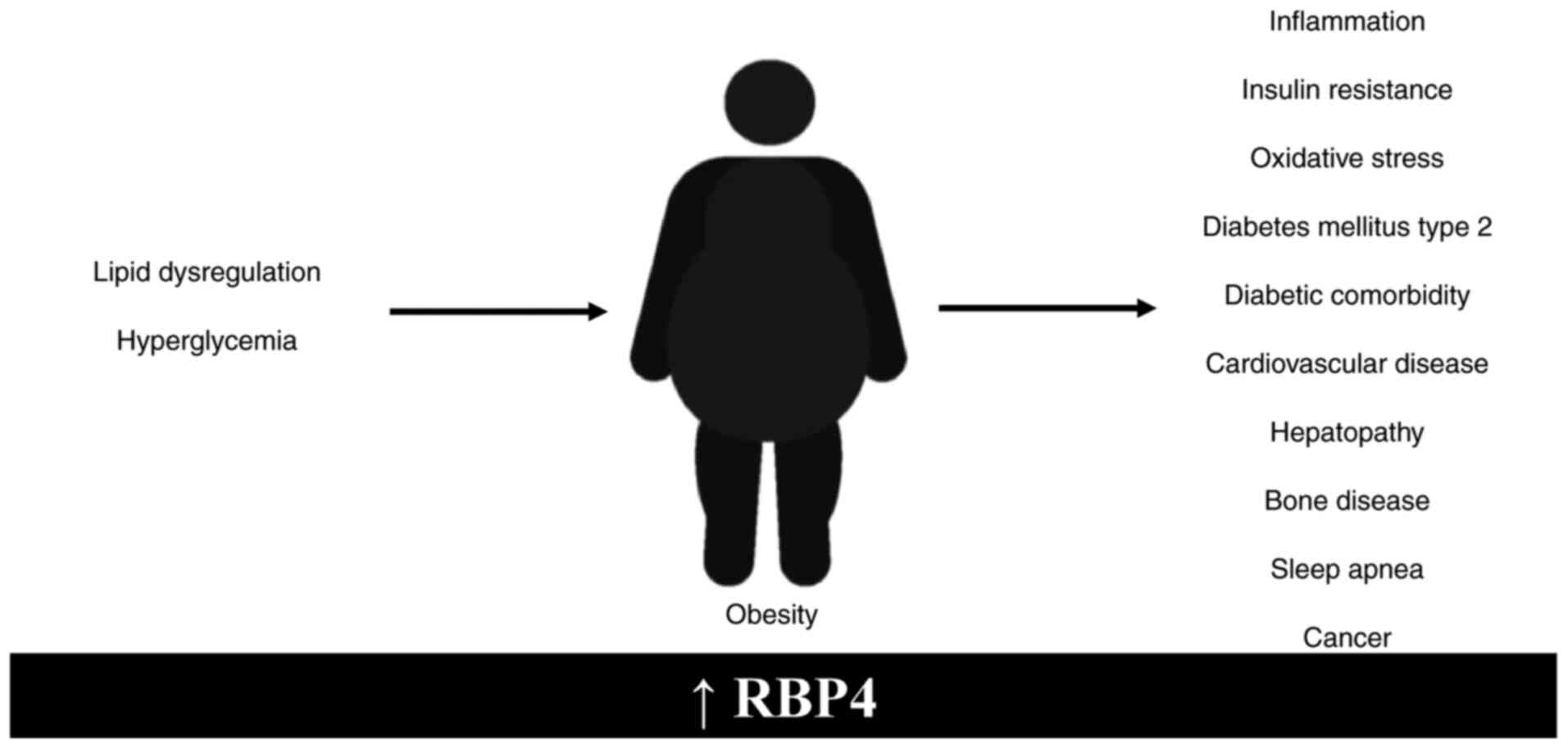
|
1
|
Piché ME, Tchernof A and Després JP:
Obesity phenotypes, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Circ
Res. 126:1477–1500. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
WHO: World Health Organization, . Obesity
and overweight. 2021 July 20;https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
|
|
3
|
Shamah-Levy T, Vielma-Orozco E,
Heredia-Hernández O, Romero-Martínez M, Mojica-Cuevas J,
Cuevas-Nasu L and Rivera-Dommarco J: Encuesta Nacional de Salud y
Nutrición 2018–19: Resultados Nacionales. Pública IN: Instituto
Nacional de Salud Pública; 2020
|
|
4
|
Wu H and Ballantyne CM: Metabolic
inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. Circ Res.
126:1549–1564. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang L, Hu J and Zhou H: Macrophage and
adipocyte mitochondrial dysfunction in obesity-induced metabolic
diseases. World J Mens Health. 39:606–614. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moraes-Vieira PM, Yore MM, Dwyer PM, Syed
I, Aryal P and Kahn BB: RBP4 activates antigen-presenting cells,
leading to adipose tissue inflammation and systemic insulin
resistance. Cell Metab. 19:512–526. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nono Nankam PA and Blüher M:
Retinol-binding protein 4 in obesity and metabolic dysfunctions.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 531:1113122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsutsumi C, Okuno M, Tannous L, Piantedosi
R, Allan M, Goodman DS and Blaner WS: Retinoids and
retinoid-binding protein expression in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem.
267:1805–1810. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fan J, Yin S, Lin D, Liu Y, Chen N, Bai X,
Ke Q, Shen J, You L, Lin X, et al: Association of serum
retinol-binding protein 4 Levels and the risk of incident type 2
diabetes in subjects with prediabetes. Diabetes Care. 42:1574–1581.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Grosjean F, Esposito P, Maccarrone R,
Libetta C, Dal Canton A and Rampino T: RBP4: A culprit for insulin
resistance in end stage renal disease that can be cleared by
hemodiafiltration. BioMed Res Int. Nov 23–2017.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li G, Esangbedo IC, Xu L, Fu J, Li L, Feng
D, Han L, Xiao X, Li M, Mi J, et al: Childhood retinol-binding
protein 4 (RBP4) levels predicting the 10-year risk of insulin
resistance and metabolic syndrome: The BCAMS study. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 17:692018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grzegorczyk EA, Harasim-Symbor E, Lukaszuk
B, Harasiuk D, Choromanska B, Mysliwiec P, Zendzian-Piotrowska M
and Chabowski A: Lack of pronounced changes in the expression of
fatty acid handling proteins in adipose tissue and plasma of
morbidly obese humans. Nutr Diabetes. 8:32018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen Y, Lv P, Du M, Liang Z, Zhou M and
Chen D: Increased retinol-free RBP4 contributes to insulin
resistance in gestational diabetes mellitus. Arch Gynecol Obstet.
296:53–61. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Abbas NAT and El Salem A: Metformin,
sitagliptin, and liraglutide modulate serum retinol-binding
protein-4 level and adipocytokine production in type 2 diabetes
mellitus rat model. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 96:1226–1231. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Steinhoff JS, Lass A and Schupp M:
Biological functions of RBP4 and its relevance for human diseases.
Front Physiol. 12:6599772021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fairulnizal Md, Noh M, Devi Nair
Gunasegavan R and Mustar S: Vitamin A in health and disease.
Vitamin A. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Olsen T and Blomhoff R: Retinol, retinoic
acid, and retinol-binding protein 4 are differentially associated
with cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and obesity: An
overview of human studies. Adv Nutr. 11:644–666. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zabetian-Targhi F, Mahmoudi MJ, Rezaei N
and Mahmoudi M: Retinol binding protein 4 in relation to diet,
inflammation, immunity, and cardiovascular diseases. Adv Nutr.
6:748–762. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Noy N: Vitamin A in regulation of insulin
responsiveness: Mini review. Proc Nutr Soc. 75:212–215. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kawaguchi R, Yu J, Honda J, Hu J,
Whitelegge J, Ping P, Wiita P, Bok D and Sun H: A membrane receptor
for retinol binding protein mediates cellular uptake of vitamin A.
Science. 315:820–825. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Napoli JL: Functions of intracellular
retinoid binding-proteins. Subcell Biochem. 81:21–76. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saari JC: Vitamin A metabolism in rod and
cone visual cycles. Annu Rev Nutr. 32:125–145. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dowling JE: Vitamin A: Its many roles-from
vision and synaptic plasticity to infant mortality. J Comp Physiol
A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 206:389–399. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chelstowska S, Widjaja-Adhi MA, Silvaroli
JA and Golczak M: Molecular basis for vitamin A uptake and storage
in vertebrates. Nutrients. 8:6762016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wright CB, Redmond TM and Nickerson JM: A
history of the classical visual cycle. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci.
134:433–448. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang FC, Xu F, Wang TN and Chen GX: Roles
of vitamin A in the regulation of fatty acid synthesis. World J
Clin Cases. 9:4506–4519. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iskakova M, Karbyshev M, Piskunov A and
Rochette-Egly C: Nuclear and extranuclear effects of vitamin A. Can
J Physiol Pharmacol. 93:1065–1075. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ghyselinck NB and Duester G: Retinoic acid
signaling pathways. Development. 146:dev1675022019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Balmer JE and Blomhoff R: Gene expression
regulation by retinoic acid. J Lipid Res. 43:1773–1808. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Smith JE, Borek C, Gawinowicz MA and
Goodman DS: Structure-function relationships of retinoids in their
effects on retinol-binding protein metabolism in cultured H4II EC3
liver cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 238:1–9. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bellovino D, Lanyau Y, Garaguso I, Amicone
L, Cavallari C, Tripodi M and Gaetani S: MMH cells: An in vitro
model for the study of retinol-binding protein secretion regulated
by retinol. J Cell Physiol. 181:24–32. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Boaghi A, Pop RM, Vasilache SL, Banescu C,
Hutanu A, Marginean OC and Pascanu IM: Plasma RBP4 level in
association with body composition, metabolic profile, STRA6 and
RBP4 gene polymorphisms in obese Romanian children. Diabetes Metab
Syndr Obes. 13:4643–4650. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F,
Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM, Kotani K, Quadro L and Kahn BB: Serum
retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in
obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 436:356–362. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Codoñer-Franch P, Mora-Herranz A,
Simó-Jordá R, Pérez-Rambla C, Boix-García L and Faus-Pérez A:
Retinol-binding protein 4 levels are associated with measures of
liver and renal function and oxidant/antioxidant status in obese
children. J Pediatr. 163:593–595. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wessel H, Saeed A, Heegsma J, Connelly MA,
Faber KN and Dullaart RPF: Plasma levels of retinol binding protein
4 relate to large VLDL and small LDL particles in subjects with and
without type 2 diabetes. J Clin Med. 8:17922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Korek E, Gibas-Dorna M,
Chęcińska-Maciejewska Z, Krauss H, Łagiedo-Żelazowska M,
Kołodziejczak B and Bogdański P: Serum RBP4 positively correlates
with triglyceride level but not with BMI, fat mass and insulin
resistance in healthy obese and non-obese individuals. Biomarkers.
23:683–688. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mateo-Gallego R, Lamiquiz-Moneo I,
Perez-Calahorra S, Marco-Benedí V, Bea AM, Baila-Rueda L,
Laclaustra M, Peñalvo JL, Civeira F and Cenarro A: Different
protein composition of low-calorie diet differently impacts
adipokine profile irrespective of weight loss in overweight and
obese women. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 28:133–142. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Comerford KB, Buchan W and Karakas SE: The
effects of weight loss on FABP4 and RBP4 in obese women with
metabolic syndrome. Horm Metab Res. 46:224–231. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Numao S, Sasai H, Nomata Y, Matsuo T, Eto
M, Tsujimoto T and Tanaka K: Effects of exercise training on
circulating retinol-binding protein 4 and cardiovascular disease
risk factors in obese men. Obes Facts. 5:845–855. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
López-Domènech S, Abad-Jiménez Z,
Iannantuoni F, de Marañón AM, Rovira-Llopis S, Morillas C, Bañuls
C, Víctor VM and Rocha M: Moderate weight loss attenuates chronic
endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in human
obesity. Mol Metab. 19:24–33. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kwanbunjan K, Panprathip P, Phosat C,
Chumpathat N, Wechjakwen N, Puduang S, Auyyuenyong R, Henkel I and
Schweigert FJ: Association of retinol binding protein 4 and
transthyretin with triglyceride levels and insulin resistance in
rural thais with high type 2 diabetes risk. BMC Endocr Disord.
18:262018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhou W, Ye SD, Chen C and Wang W:
Involvement of RBP4 in diabetic atherosclerosis and the role of
vitamin D intervention. J Diabetes Res. 2018:73298612018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Weiss K, Mihály J, Liebisch G, Marosvölgyi
T, Schmitz G, Decsi T and Rühl R: Effect of synthetic ligands of
PPAR α, β/δ, γ, RAR, RXR and LXR on the fatty acid composition of
phospholipids in mice. Lipids. 46:1013–1020. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rosell M, Hondares E, Iwamoto S, Gonzalez
FJ, Wabitsch M, Staels B, Olmos Y, Monsalve M, Giralt M, Iglesias R
and Villarroya F: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors-α and
-γ, and cAMP-mediated pathways, control retinol-binding protein-4
gene expression in brown adipose tissue. Endocrinology.
153:1162–1173. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Moraes-Vieira PM, Yore MM,
Sontheimer-Phelps A, Castoldi A, Norseen J, Aryal P, Simonyté
Sjödin K and Kahn BB: Retinol binding protein 4 primes the NLRP3
inflammasome by signaling through Toll-like receptors 2 and 4. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 117:31309–31318. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yesudhas D, Gosu V, Anwar MA and Choi S:
Multiple roles of toll-like receptor 4 in colorectal cancer. Front
Immunol. 5:3342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kilicarslan M, de Weijer BA, Simonyté
Sjödin K, Aryal P, Ter Horst KW, Cakir H, Romijn JA, Ackermans MT,
Janssen IM, Berends FJ, et al: RBP4 increases lipolysis in human
adipocytes and is associated with increased lipolysis and hepatic
insulin resistance in obese women. FASEB J. 34:6099–6110. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Grant RW and Stephens JM: Fat in flames:
Influence of cytokines and pattern recognition receptors on
adipocyte lipolysis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 309:E205–E213.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Morigny P, Houssier M, Mouisel E and
Langin D: Adipocyte lipolysis and insulin resistance. Biochimie.
125:259–266. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Farjo KM, Farjo RA, Halsey S, Moiseyev G
and Ma JX: Retinol-binding protein 4 induces inflammation in human
endothelial cells by an NADPH oxidase- and nuclear factor kappa
B-dependent and retinol-independent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol.
32:5103–5115. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Norseen J, Hosooka T, Hammarstedt A, Yore
MM, Kant S, Aryal P, Kiernan UA, Phillips DA, Maruyama H, Kraus BJ,
et al: Retinol-binding protein 4 inhibits insulin signaling in
adipocytes by inducing proinflammatory cytokines in macrophages
through a c-Jun N-terminal kinase- and toll-like receptor
4-dependent and retinol-independent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol.
32:2010–2019. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Pandey GK, Balasubramanyam J, Balakumar M,
Deepa M, Anjana RM, Abhijit S, Kaviya A, Velmurugan K, Miranda P,
Balasubramanyam M, et al: Altered circulating levels of retinol
binding protein 4 and transthyretin in relation to insulin
resistance, obesity, and glucose intolerance in Asian Indians.
Endocr Pract. 21:861–869. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Grundy SM: Hypertriglyceridemia, insulin
resistance, and the metabolic syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 83:25F–29F.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yousefi MR and TaheriChadorneshin H: The
effect of moderate endurance training on gastrocnemius
retinol-binding protein 4 and insulin resistance in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Interv Med Appl Sci.
10:59–63. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Marschner RA, Pinto G, Borges J, Markoski
MM, Schaan BD and Lehnen AM: Short-term detraining does not change
insulin sensitivity and RBP4 in rodents previously submitted to
aerobic exercise. Horm Metab Res. 49:58–63. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sapra A and Bhandari P: Diabetes mellitus.
StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL: 2022
|
|
57
|
Huang R, Bai X, Li X, Wang X and Zhao L:
Retinol-binding protein 4 activates STRA6, provoking pancreatic
β-cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 70:449–463. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ediger BN, Du A, Liu J, Hunter CS, Walp
ER, Schug J, Kaestner KH, Stein R, Stoffers DA and May CL: Islet-1
Is essential for pancreatic β-cell function. Diabetes.
63:4206–4217. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li JY, Chen XX, Lu XH, Zhang CB, Shi QP
and Feng L: Elevated RBP4 plasma levels were associated with
diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes. Biosci Rep.
38:BSR201811002018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Han W, Wei H, Kong W, Wang J, Yang L and
Wu H: Association between retinol binding protein 4 and diabetic
retinopathy among type 2 diabetic patients: A meta-analysis. Acta
Diabetol. 57:1203–1218. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Behl T, Kaur I and Kotwani A: Implication
of oxidative stress in progression of diabetic retinopathy. Surv
Ophthalmol. 61:187–196. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang L, Cheng YL, Xue S and Xu ZG: The
role of circulating RBP4 in the type 2 diabetes patients with
kidney diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dis
Markers. 2020:88304712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Mahfouz MH, Assiri AM and Mukhtar MH:
Assessment of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and
retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4) in type 2 diabetic patients with
nephropathy. Biomark Insights. 11:31–40. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zachariah JP, Hwang S, Hamburg NM,
Benjamin EJ, Larson MG, Levy D, Vita JA, Sullivan LM, Mitchell GF
and Vasan RS: Circulating adipokines and vascular function:
Cross-sectional associations in a community-based cohort.
Hypertension. 67:294–300. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhang JX, Zhu GP, Zhang BL and Cheng YY:
Elevated serum retinol-binding protein 4 levels are correlated with
blood pressure in prehypertensive Chinese. J Hum Hypertens.
31:611–615. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Liu G, Ding M, Chiuve SE, Rimm EB, Franks
PW, Meigs JB, Hu FB and Sun Q: Plasma levels of fatty acid-binding
protein 4, retinol-binding protein 4, high-molecular-weight
adiponectin, and cardiovascular mortality among men with type 2
diabetes: A 22-year prospective study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 36:2259–2267. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Liu Y, Zhong Y, Chen H, Wang D, Wang M, Ou
JS and Xia M: Retinol-binding protein-dependent cholesterol uptake
regulates macrophage foam cell formation and promotes
atherosclerosis. Circulation. 135:1339–1354. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Rychter AM, Skrzypczak-Zielińska M,
Zielińska A, Eder P, Souto EB, Zawada A, Ratajczak AE, Dobrowolska
A and Krela-Kaźmierczak I: Is the retinol-binding protein 4 a
possible risk factor for cardiovascular diseases in obesity? Int J
Mol Sci. 21:52292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yaribeygi H, Sathyapalan T, Atkin SL and
Sahebkar A: Molecular mechanisms linking oxidative stress and
diabetes mellitus. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020:86092132020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Papachristoforou E, Lambadiari V, Maratou
E and Makrilakis K: Association of glycemic indices (hyperglycemia,
glucose variability, and hypoglycemia) with oxidative stress and
diabetic complications. J Diabetes Res. 2020:74897952020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Daneshzad E, Farsad-Naeimi A, Heshmati J,
Mirzaei K, Maghbooli Z and Keshavarz SA: The association between
dietary antioxidants and adipokines level among obese women.
Diabetes Metab Syndr. 13:1369–1373. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Liu Y, Wang D, Li D, Sun R and Xia M:
Associations of retinol-binding protein 4 with oxidative stress,
inflammatory markers, and metabolic syndrome in a middle-aged and
elderly Chinese population. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 6:252014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wang J, Chen H, Liu Y, Zhou W, Sun R and
Xia M: Retinol binding protein 4 induces mitochondrial dysfunction
and vascular oxidative damage. Atherosclerosis. 240:335–344. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Umeno A, Sakashita M, Sugino S, Murotomi
K, Okuzawa T, Morita N, Tomii K, Tsuchiya Y, Yamasaki K, Horie M,
et al: Comprehensive analysis of PPARγ agonist activities of
stereo-, regio-, and enantio-isomers of hydroxyoctadecadienoic
acids. Biosci Rep. 40:BSR201937672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Makino S, Fujiwara M, Suzukawa K, Handa H,
Fujie T, Ohtaka Y, Komatsu Y, Aoki Y, Maruyama H, Terada Y, et al:
Visceral obesity is associated with the metabolic syndrome and
elevated plasma retinol binding protein-4 level in obstructive
sleep apnea syndrome. Horm Metab Res. 41:221–226. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Nena E, Steiropoulos P, Tzouvelekis A,
Tsara V, Hatzizisi O, Kyriazis G, Froudarakis M, Trakada G, Papanas
N and Bouros D: Reduction of serum retinol-binding protein-4 levels
in nondiabetic obstructive sleep apnea patients under continuous
positive airway pressure treatment. Respiration. 80:517–523. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Karamfilova V, Gateva A, Alexiev A,
Zheleva N, Velikova T, Ivanova-Boyanova R, Ivanova R, Cherkezov N,
Kamenov Z and Mateva L: The association between retinol-binding
protein 4 and prediabetes in obese patients with nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Arch Physiol Biochem. 128:217–222. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Saeed A, Bartuzi P, Heegsma J, Dekker D,
Kloosterhuis N, de Bruin A, Jonker JW, van de Sluis B and Faber KN:
Impaired hepatic vitamin A metabolism in NAFLD mice leading to
vitamin A accumulation in hepatocytes. Cell Mol Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 11:309–325.e3. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wang X, Chen X, Zhang H, Pang J, Lin J, Xu
X, Yang L, Ma J, Ling W and Chen Y: Circulating retinol-binding
protein 4 is associated with the development and regression of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Metab. 46:119–128.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Tsai YL, Liu CW, Huang SF, Yang YY, Lin
MW, Huang CC, Li TH, Huang YH, Hou MC and Lin HC: Urinary fatty
acid and retinol binding protein-4 predict CKD progression in
severe NAFLD patients with hypertension: 4-Year study with clinical
and experimental approaches. Medicine (Baltimore). 99:e186262020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Toussirot E, Aubin F, Desmarets M,
Wendling D, Augé B, Gillard J, Messica O, Guillot X, Laheurte C,
Monnet E and Dumoulin G: Visceral adiposity in patients with
psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis alone and its relationship with
metabolic and cardiovascular risk. Rheumatology (Oxford).
60:2816–2825. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Scotece M, Koskinen-Kolasa A, Pemmari A,
Leppänen T, Hämäläinen M, Moilanen T, Moilanen E and Vuolteenaho K:
Novel adipokine associated with OA: Retinol binding protein 4
(RBP4) is produced by cartilage and is correlated with MMPs in
osteoarthritis patients. Inflamm Res. 69:415–421. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Fan J, Zhu J, Sun L and Li Y, Wang T and
Li Y: Causal association of adipokines with osteoarthritis: A
Mendelian randomization study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 60:2808–2815.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Li M, Wang Z, Zhu L, Shui Y, Zhang S and
Guo W: Down-regulation of RBP4 indicates a poor prognosis and
correlates with immune cell infiltration in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Biosci Rep. 41:BSR202103282021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Papiernik D, Urbaniak A, Kłopotowska D,
Nasulewicz-Goldeman A, Ekiert M, Nowak M, Jarosz J, Cuprych M,
Strzykalska A, Ugorski M, et al: Retinol-binding protein 4
accelerates metastatic spread and increases impairment of blood
flow in mouse mammary gland tumors. Cancers (Basel). 12:6232020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Wu M, Li Q and Wang H: Identification of
novel biomarkers associated with the prognosis and potential
pathogenesis of breast cancer via integrated bioinformatics
analysis. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 20:15330338219920812021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Tsakogiannis D, Kalogera E, Zagouri F,
Zografos E, Balalis D and Bletsa G: Determination of FABP4, RBP4
and the MMP-9/NGAL complex in the serum of women with breast
cancer. Oncol Lett. 21:852021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Hu X, Huang W, Wang F, Dai Y, Hu X, Yue D
and Wang S: Serum levels of retinol-binding protein 4 and the risk
of non-small cell lung cancer: A case-control study. Medicine
(Baltimore). 99:e212542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Komor MA, Bosch LJ, Coupé VM, Rausch C,
Pham TV, Piersma SR, Mongera S, Mulder CJ, Dekker E, Kuipers EJ, et
al: Proteins in stool as biomarkers for non-invasive detection of
colorectal adenomas with high risk of progression. J Pathol.
250:288–298. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Wang Y, Wang Y and Zhang Z: Adipokine RBP4
drives ovarian cancer cell migration. J Ovarian Res. 11:292018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Preitner F, Mody N, Graham TE, Peroni OD
and Kahn BB: Long-term Fenretinide treatment prevents high-fat
diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis. Am
J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 297:E1420–E1429. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Cioffi CL, Racz B, Varadi A, Freeman EE,
Conlon MP, Chen P, Zhu L, Kitchen DB, Barnes KD, Martin WH, et al:
Design, synthesis, and preclinical efficacy of novel nonretinoid
antagonists of retinol-binding protein 4 in the mouse model of
hepatic steatosis. J Med Chem. 62:5470–5500. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Kim N and Priefer R: Retinol binding
protein 4 antagonists and protein synthesis inhibitors: Potential
for therapeutic development. Eur J Med Chem. 226:1138562021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Zhu C, Xiao Y, Liu X, Han J, Zhang J, Wei
L and Jia W: Pioglitazone lowers serum retinol binding protein 4 by
suppressing its expression in adipose tissue of obese rats. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 35:778–788. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Hu H, Xu M, Qi R, Wang Y, Wang C, Liu J,
Luo L, Xia L and Fang Z: Sitagliptin downregulates retinol-binding
protein 4 and upregulates glucose transporter type 4 expression in
a type 2 diabetes mellitus rat model. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:17902–17911. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Miller AP, Black M and Amengual J:
Fenretinide inhibits vitamin A formation from β-carotene and
regulates carotenoid levels in mice. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell
Biol Lipids. 1867:1590702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Blaner WS: Vitamin A signaling and
homeostasis in obesity, diabetes, and metabolic disorders.
Pharmacol Ther. 197:153–178. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Racz B, Varadi A, Kong J, Allikmets R,
Pearson PG, Johnson G, Cioffi CL and Petrukhin K: A non-retinoid
antagonist of retinol-binding protein 4 rescues phenotype in a
model of Stargardt disease without inhibiting the visual cycle. J
Biol Chem. 293(29): 11574–11588. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|