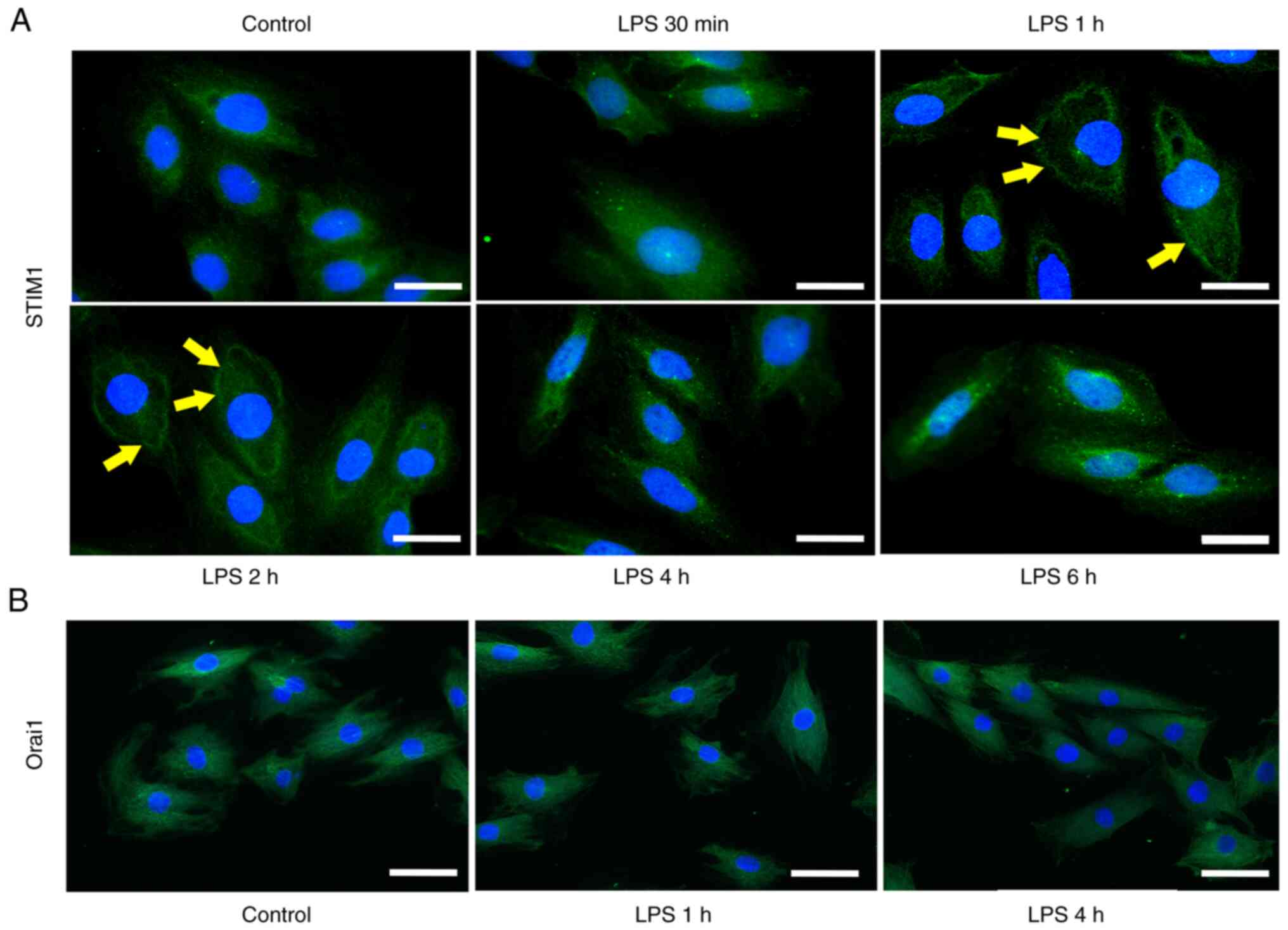
|
1
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The Third International consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Landesberg G, Gilon D, Meroz Y, Georgieva
M, Levin PD, Goodman S, Avidan A, Beeri R, Weissman C, Jaffe AS and
Sprung CL: Diastolic dysfunction and mortality in severe sepsis and
septic shock. Eur Heart J. 33:895–903. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jeong HS, Lee TH, Bang CH, Kim JH and Hong
SJ: Risk factors and outcomes of sepsis-induced myocardial
dysfunction and stressinduced cardiomyopathy in sepsis or septic
shock: A comparative retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore).
97:e02632018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Eisner DA, Caldwell JL, Kistamás K and
Trafford AW: Calcium and excitation-contraction coupling in the
heart. Circ Res. 121:181–195. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang HG, Pathan N, Ethell IM, Krajewski S,
Yamaguchi Y, Shibasaki F, McKeon F, Bobo T, Franke TF and Reed JC:
Ca2+-induced apoptosis through calcineurin dephosphorylation of
BAD. Science. 284:339–343. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Winslow RL, Walker MA and Greenstein JL:
Modeling calcium regulation of contraction, energetics, signaling,
and transcription in the cardiac myocyte. Wiley Interdiscip Rev
Syst Biol Med. 8:37–67. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thompson M, Kliewer A, Maass D, Becker L,
White DJ, Bryant D, Arteaga G, Horton J and Giroir BP: Increased
cardiomyocyte intracellular calcium during endotoxin-induced
cardiac dysfunction in guinea pigs. Pediatr Res. 47:669–676. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Celes MR, Malvestio LM, Suadicani SO,
Prado CM, Figueiredo MJ, Campos EC, Freitas AC, Spray DC, Tanowitz
HB, da Silva JS and Rossi MA: Disruption of calcium homeostasis in
cardiomyocytes underlies cardiac structural and functional changes
in severe sepsis. PLoS One. 8:e688092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Suzuki J, Bayna E, Li HL, Molle ED and Lew
WY: Lipopolysaccharide activates calcineurin in ventricular
myocytes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 49:491–499. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bers DM: Calcium fluxes involved in
control of cardiac myocyte contraction. Circ Res. 87:275–281. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bers DM: Calcium cycling and signaling in
cardiac myocytes. Annu Rev Physiol. 70:23–49. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Feske S, Gwack Y, Prakriya M, Srikanth S,
Puppel SH, Tanasa B, Hogan PG, Lewis RS, Daly M and Rao A: A
mutation in Orai1 causes immune deficiency by abrogating CRAC
channel function. Nature. 441:179–185. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zitt C, Strauss B, Schwarz EC, Spaeth N,
Rast G, Hatzelmann A and Hoth M: Potent inhibition of Ca2+
release-activated Ca2+ channels and T-lymphocyte activation by the
pyrazole derivative BTP2. J Biol Chem. 279:12427–12437. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hauser CJ, Fekete Z, Adams JM, Garced M,
Livingston DH and Deitch EA: PAF-mediated Ca2+ influx in human
neutrophils occurs via store-operated mechanisms. J Leukoc Biol.
69:63–68. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hunton DL, Lucchesi PA, Pang Y, Cheng X,
Dell'Italia LJ and Marchase RB: Capacitative calcium entry
contributes to nuclear factor of activated T-cells nuclear
translocation and hypertrophy in cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem.
277:14266–14273. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Uehara A, Yasukochi M, Imanaga I, Nishi M
and Takeshima H: Store-operated Ca2+ entry uncoupled with ryanodine
receptor and junctional membrane complex in heart muscle cells.
Cell Calcium. 31:89–96. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shen Y, Thillaiappan NB and Taylor CW: The
store-operated Ca2+ entry complex comprises a small
cluster of STIM1 associated with one Orai1 channel. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 118:e20107891182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Luo X, Hojayev B, Jiang N, Wang ZV, Tandan
S, Rakalin A, Rothermel BA, Gillette TG and Hill JA:
STIM1-dependent store-operated Ca2+ entry is required
for pathological cardiac hypertrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
52:136–147. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hulot JS, Fauconnier J, Ramanujam D,
Chaanine A, Aubart F, Sassi Y, Merkle S, Cazorla O, Ouillé A,
Dupuis M, et al: Critical role for stromal interaction molecule 1
in cardiac hypertrophy. Circulation. 124:796–805. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Voelkers M, Salz M, Herzog N, Frank D,
Dolatabadi N, Frey N, Gude N, Friedrich O, Koch WJ, Katus HA, et
al: Orai1 and Stim1 regulate normal and hypertrophic growth in
cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 48:1329–1334. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Prakriya M, Feske S, Gwack Y, Srikanth S,
Rao A and Hogan PG: Orai1 is an essential pore subunit of the CRAC
channel. Nature. 443:230–233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang SL, Yu Y, Roos J, Kozak JA, Deerinck
TJ, Ellisman MH, Stauderman KA and Cahalan MD: STIM1 is a Ca2+
sensor that activates CRAC channels and migrates from the Ca2+
store to the plasma membrane. Nature. 437:902–905. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Luo R, Gomez AM, Benitah JP and Sabourin
J: Targeting Orai1-mediated store-operated Ca2+ entry in
heart failure. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:5861092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cacheux M, Strauss B, Raad N, Ilkan Z, Hu
J, Benard L, Feske S, Hulot JS and Akar FG: Cardiomyocyte-Specific
STIM1 (Stromal Interaction Molecule 1) depletion in the adult heart
promotes the development of arrhythmogenic discordant alternans.
Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 12:e0073822019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Correll RN, Goonasekera SA, van Berlo JH,
Burr AR, Accornero F, Zhang H, Makarewich CA, York AJ, Sargent MA,
Chen X, et al: STIM1 elevation in the heart results in aberrant
Ca2+ handling and cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
87:38–47. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shiou YL, Lin HT, Ke LY, Wu BN, Shin SJ,
Chen CH, Tsai WC, Chu CS and Lee HC: Very Low-density lipoproteins
of metabolic syndrome modulates STIM1, suppresses store-operated
calcium entry, and deranges myofilament proteins in atrial
myocytes. J Clin Med. 8:8812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Troupes CD, Wallner M, Borghetti G, Zhang
C, Mohsin S, von Lewinski D, Berretta RM, Kubo H, Chen X, Soboloff
J and Houser S: Role of STIM1 (Stromal Interaction Molecule 1) in
hypertrophy-related contractile dysfunction. Circ Res. 121:125–136.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zheng C, Lo CY, Meng Z, Li Z, Zhong M,
Zhang P, Lu J, Yang Z, Yan F, Zhang Y, et al: Gastrodin inhibits
store-operated Ca2+ entry and alleviates cardiac
hypertrophy. Front Pharmacol. 8:2222017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hobai IA, Edgecomb J, LaBarge K and
Colucci WS: Dysregulation of intracellular calcium transporters in
animal models of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Shock. 43:3–15.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals, . Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. 8th
edition. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
31
|
Rumienczyk I, Kulecka M, Ostrowski J, Mar
D, Bomsztyk K, Standage SW and Mikula M: Multi-Organ transcriptome
dynamics in a mouse model of cecal ligation and puncture-induced
polymicrobial sepsis. J Inflamm Res. 14:2377–2388. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gao M, Ha T, Zhang X, Liu L, Wang X,
Kelley J, Singh K, Kao R, Gao X, Williams D and Li C: Toll-like
receptor 3 plays a central role in cardiac dysfunction during
polymicrobial sepsis. Crit Care Med. 40:2390–2399. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li M, Ye J, Zhao G, Hong G, Hu X, Cao K,
Wu Y and Lu Z: Gas6 attenuates lipopolysaccharideinduced TNF-α
expression and apoptosis in H9C2 cells through NF-κB and MAPK
inhibition via the Axl/PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Med. 44:982–994.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Merx MW and Weber C: Sepsis and the heart.
Circulation. 116:793–802. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Martin L, Derwall M, Al Zoubi S,
Zechendorf E, Reuter DA, Thiemermann C and Schuerholz T: The septic
heart: Current understanding of molecular mechanisms and clinical
implications. Chest. 155:427–437. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Munt B, Jue J, Gin K, Fenwick J and
Tweeddale M: Diastolic filling in human severe sepsis: An
echocardiographic study. Crit Care Med. 26:1829–1833. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ren J, Ren BH and Sharma AC:
Sepsis-induced depressed contractile function of isolated
ventricular myocytes is due to altered calcium transient
properties. Shock. 18:285–288. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Merx MW, Liehn EA, Janssens U, Lütticken
R, Schrader J, Hanrath P and Weber C: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor
simvastatin profoundly improves survival in a murine model of
sepsis. Circulation. 109:2560–2565. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang H, Bei Y, Shen S, Huang P, Shi J,
Zhang J, Sun Q, Chen Y, Yang Y, Xu T, et al: MiR-21-3p controls
sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction via regulating SORBS2. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 94:43–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
McDonald TE, Grinman MN, Carthy CM and
Walley KR: Endotoxin infusion in rats induces apoptotic and
survival pathways in hearts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
279:H2053–H2061. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lancel S, Petillot P, Favory R, Stebach N,
Lahorte C, Danze PM, Vallet B, Marchetti P and Neviere R:
Expression of apoptosis regulatory factors during myocardial
dysfunction in endotoxemic rats. Crit Care Med. 33:492–496. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li Z, Yi N, Chen R, Meng Y, Wang Y, Liu H,
Cao W, Hu Y, Gu Y, Tong C, et al: miR-29b-3p protects
cardiomyocytes against endotoxin-induced apoptosis and inflammatory
response through targeting FOXO3A. Cell Signal. 74:1097162020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu L, Yan M, Yang R, Qin X, Chen L, Li L,
Si J, Li X and Ma K: Adiponectin attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis by regulating the
Cx43/PI3K/AKT pathway. Front Pharmacol. 12:6442252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Su ZD, Wei XB, Fu YB, Xu J, Wang ZH, Wang
Y, Cao JF, Huang JL and Yu DQ: Melatonin alleviates
lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting
inflammation and pyroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Ann Transl Med.
9:4132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ravikumar N, Sayed MA, Poonsuph CJ, Sehgal
R, Shirke MM and Harky A: Septic cardiomyopathy: From basics to
management choices. Curr Probl Cardiol. 46:1007672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu YC, Yu MM, Shou ST and Chai YF:
Sepsis-Induced cardiomyopathy: Mechanisms and treatments. Front
Immunol. 8:10212017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dal-Secco D, DalBó S, Lautherbach NES,
Gava FN, Celes MRN, Benedet PO, Souza AH, Akinaga J, Lima V, Silva
KP, et al: Cardiac hyporesponsiveness in severe sepsis is
associated with nitric oxide-dependent activation of G protein
receptor kinase. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 313:H149–H163.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang Y, Wang Y, Yang D, Yu X, Li H, Lv X,
Lu D and Wang H: β1-adrenoceptor stimulation promotes
LPS-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis through activating PKA and
enhancing CaMKII and IκBα phosphorylation. Crit Care. 19:762015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gavali JT, Carrillo ED, García MC and
Sánchez JA: The mitochondrial K-ATP channel opener diazoxide
upregulates STIM1 and Orai1 via ROS and the MAPK pathway in adult
rat cardiomyocytes. Cell Biosci. 10:962020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Numaga-Tomita T and Nishida M: TRPC
channels in cardiac plasticity. Cells. 9:4542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Johnson MT, Gudlur A, Zhang X, Xin P,
Emrich SM, Yoast RE, Courjaret R, Nwokonko RM, Li W, Hempel N, et
al: L-type Ca2+ channel blockers promote vascular
remodeling through activation of STIM proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 117:17369–17380. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Collins HE, Zhu-Mauldin X, Marchase RB and
Chatham JC: STIM1/Orai1-mediated SOCE: Current perspectives and
potential roles in cardiac function and pathology. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 305:H446–H458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lewis RS: Store-Operated calcium channels:
From function to structure and back again. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 12:a0350552020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Putney JW Jr: A model for
receptor-regulated calcium entry. Cell Calcium. 7:1–12. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Climent B, Santiago E, Sánchez A,
Muñoz-Picos M, Pérez-Vizcaíno F, García-Sacristán A, Rivera L and
Prieto D: Metabolic syndrome inhibits store-operated
Ca2+ entry and calcium-induced calcium-release mechanism
in coronary artery smooth muscle. Biochem Pharmacol.
182:1142222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Segin S, Berlin M, Richter C, Flockerzi
RMV, Worley P, Freichel M and Londoño JEC: cardiomyocyte-specific
deletion of orai1 reveals its protective role in
angiotensin-II-induced pathological cardiac remodeling. Cells.
9:10922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kappel S, Borgström A, Stokłosa P, Dörr K
and Peinelt C: Store-operated calcium entry in disease: Beyond
STIM/Orai expression levels. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 94:66–73. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|