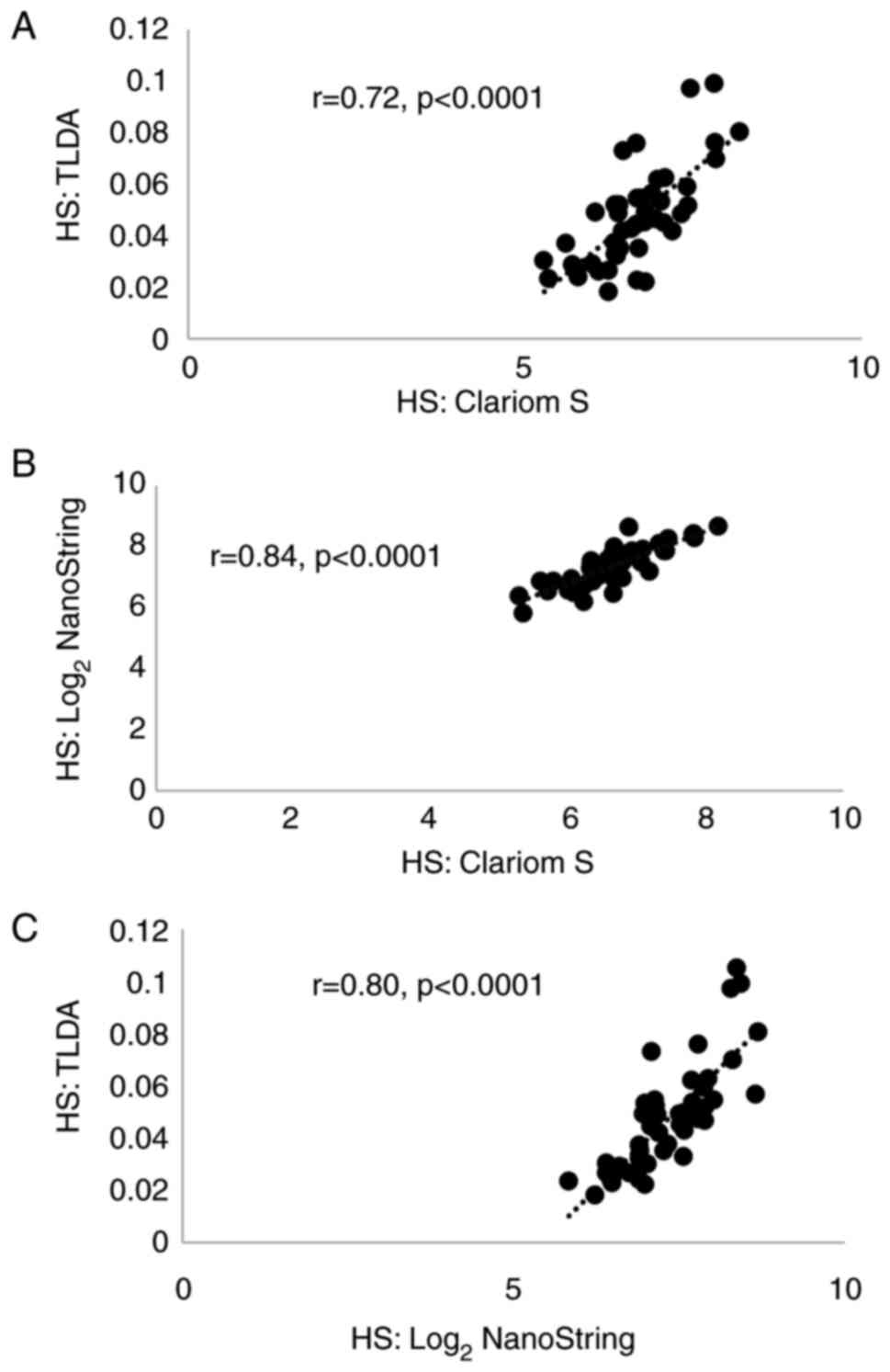
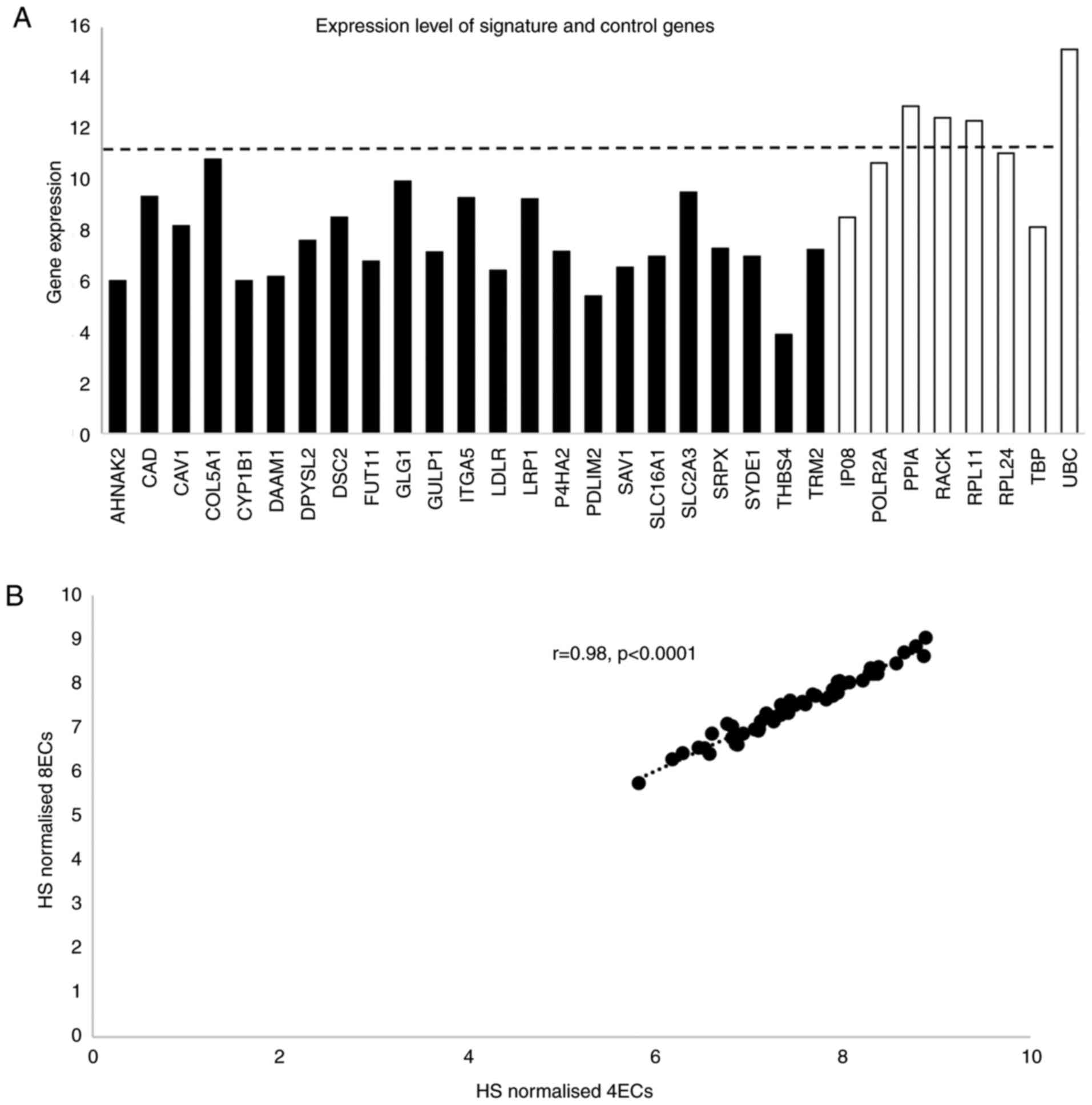
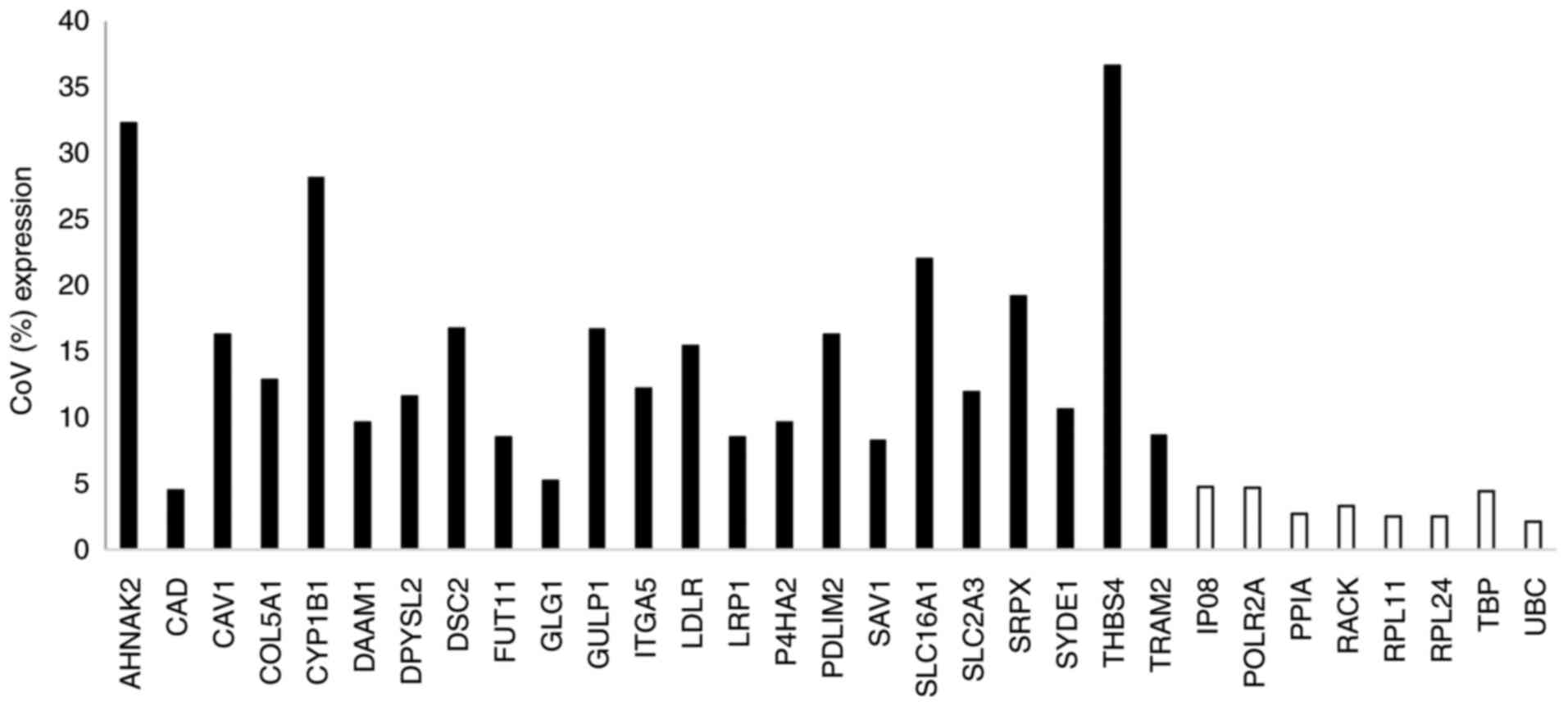
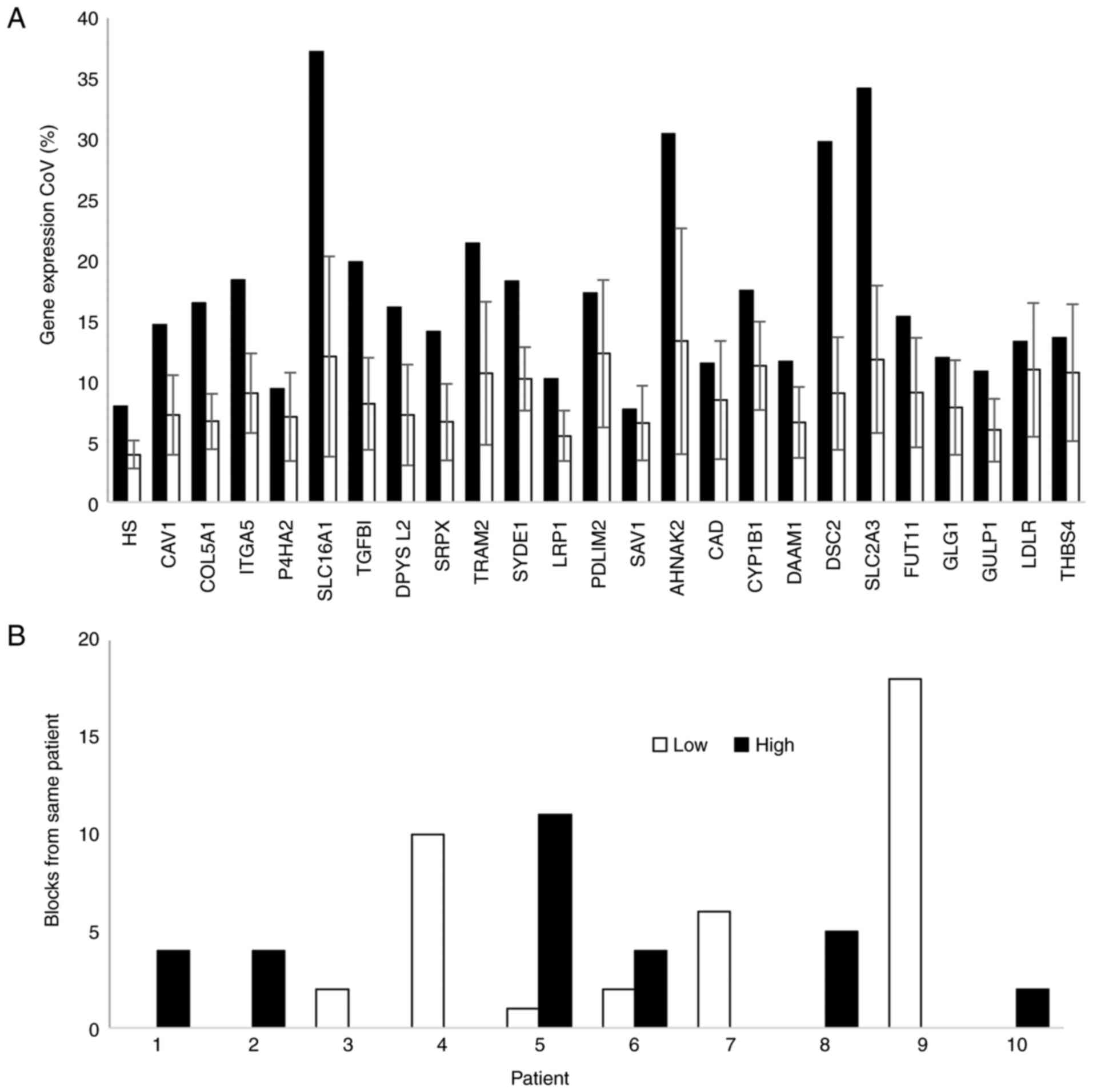
|
1
|
Huddart RA, Hall E, Lewis R, Porta N,
Crundwell M, Jenkins PJ, Rawlings C, Tremlett J, Campani L, Hendron
C, et al: Patient-reported quality of life outcomes in patients
treated for muscle-invasive bladder cancer with radiotherapy ±
chemotherapy in the BC2001 phase III randomised controlled trial.
Eur Urol. 77:260–268. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rammant E, Van Wilder L, Van Hemelrijck M,
Pauwels NS, Decaestecker K, Van Praet C, Bultijnck R, Ost P, Van
Vaerenbergh T, Verhaeghe S, et al: Health-related quality of life
overview after different curative treatment options in
muscle-invasive bladder cancer: An umbrella review. Qual Life Res.
29:2887–2910. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mak RH, Hunt D, Shipley WU, Efstathiou JA,
Tester WJ, Hagan MP, Kaufman DS, Heney NM and Zietman AL: Long-term
outcomes in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer after
selective bladder-preserving combined-modality therapy: A pooled
analysis of radiation therapy oncology group protocols 8802, 8903,
9506, 9706, 9906, and 0233. J Clin Oncol. 32:3801–3809. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Larionova I, Rakina M, Ivanyuk E,
Trushchuk Y, Chernyshova A and Denisov E: Radiotherapy resistance:
Identifying universal biomarkers for various human cancers. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 148:1015–1031. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hoskin PJ, Rojas AM, Bentzen SM and
Saunders MI: Radiotherapy with concurrent carbogen and nicotinamide
in bladder carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 28:4912–4918. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Song YP, Mistry H, Irlam J, Valentine H,
Yang LJ, Lane B, West C, Choudhury A and Hoskin PJ: Long-term
outcomes of radical radiation therapy with hypoxia modification
with biomarker discovery for stratification: 10-year update of the
BCON (bladder carbogen nicotinamide) phase 3 randomized trial
(ISRCTN45938399). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Physics. 110:1407–1415.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang LJ, Taylor J, Eustace A, Irlam JJ,
Denley H, Hoskin PJ, Alsner J, Buffa FM, Harris AL, Choudhury A and
West CML: A gene signature for selecting benefit from hypoxia
modification of radiotherapy for high-risk bladder cancer patients.
Clin Cancer Res. 23:4761–4768. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kong H, Zhu MG, Cui FY, Wang SY, Gao X, Lu
SH, Wu Y and Zhu HG: Quantitative assessment of short amplicons in
FFPE-derived long-chain RNA. Sci Rep. 4:72462009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Smith TAD, AbdelKarem OA, Irlam-Jones JJ,
Lane B, Valentine H, Bibby BAS, Denley H, Choudhury A and West CML:
Selection of endogenous control genes for normalising gene
expression data derived from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded
tumour tissue. Sci Rep. 10:172582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dehne N, Hintereder G and Brüne B: High
glucose concentrations attenuate hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha
expression and signaling in non-tumor cells. Exp Cell Res.
316:1179–89. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Z, Jia X, Duan Y, Xiao H, Sundqvist
KG, Permert J and Wang F: Excess glucose induces hypoxia-inducible
factor-1α in pancreatic cancer cells and stimulates glucose
metabolism and cell migration. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:428–435. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang P, Cheng CL, Chang YH, Liu CH, Hsu
YC, Chen JS, Chang GC, Ho BC, Su KY, Chen HY and Yu SL: Molecular
gene signature and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:51898–51907. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li JY, Xue Y, Wenger A, Sun YY, Wang Z,
Zhang CB, Zhang YQ, Fekete B, Rydenhag B, Jakola AS, et al:
Individual assignment of adult diffuse gliomas into the EM/PM
molecular subtypes using a TaqMan low-density array. Clin Cancer
Res. 25:7068–7077. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Betts GNJ, Eustace A, Patia S, Valentine
HR, Irlam J, Ramachandran A, Merve A, Homer JJ, Möller-Levet C,
Buffa FM, et al: Prospective technical validation and assessment of
intra-tumour heterogeneity of a low density array hypoxia gene
profile in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer.
49:156–165. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thomson D, Yang H, Baines H, Miles E,
Bolton S, West C and Slevin N: NIMRAD-a phase III trial to
investigate the use of nimorazole hypoxia modification with
intensity-modulated radiotherapy in head and neck cancer. Clin
Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 26:344–347. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schmidt S, Linge A, Grosser M, Lohaus F,
Gudziol V, Nowak A, Tinhofer I, Budach V, Sak A, Stuschke M, et al:
Comparison of GeneChip, nCounter, and real-time PCR-based gene
expressions predicting locoregional tumor control after primary and
postoperative radiochemotherapy in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. J Mol Diag. 22:801–810. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Geiss GK, Bumgarner RE, Birditt B, Dahl T,
Dowidar N, Dunaway DL, Fell HP, Ferree S, George RD, Grogan T, et
al: Direct multiplexed measurement of gene expression with
color-coded probe pairs. Nat Biotech. 26:317–325. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Reis PP, Waldron L, Goswami RS, Xu W, Xuan
Y, Perez-Ordonez B, Gullane P, Irish J, Jurisica I and Kamel-Reid
S: mRNA transcript quantification in archival samples using
multiplexed, color-coded probes. BMC Biotechnol. 11:462011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pintilie M, Iakovlev V, Fyles A, Hedley D,
Milosevic M and Hill RP: Heterogeneity and power in clinical
biomarker studies. J Clin Oncol. 27:1517–1521. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li Y and Ryan L: Survival analysis with
heterogeneous covariate measurement error. J Am Stat Assoc.
99:724–735. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dibben SM, Holt RJ, Davison TS, Wilson CL,
Taylor J, Paul I, McManus K, Kelly PJ, Proutski V, Harkin DP, et
al: Implications for powering biomarker discovery studies. J Mol
Diag. 14:130–139. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang LJ and West CML: Hypoxia gene
expression signatures as predictive biomarkers for personalising
radiotherapy. Br J Radiol. 92:201800362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang LJ, Forker L, Irlam JJ, Pillay N,
Choudhury A and West CML: Validation of a hypoxia related gene
signature in multiple soft tissue sarcoma cohorts. Oncotarget.
9:3946–3955. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang LJ, Roberts D, Takhar M, Erho N,
Bibby BAS, Thiruthaneeswaran N, Bhandari V, Cheng WC, Haider S,
McCorry AMB, et al: Development and validation of a 28-gene
hypoxia-related prognostic signature for localized prostate cancer.
EBioMedicine. 31:182–189. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|