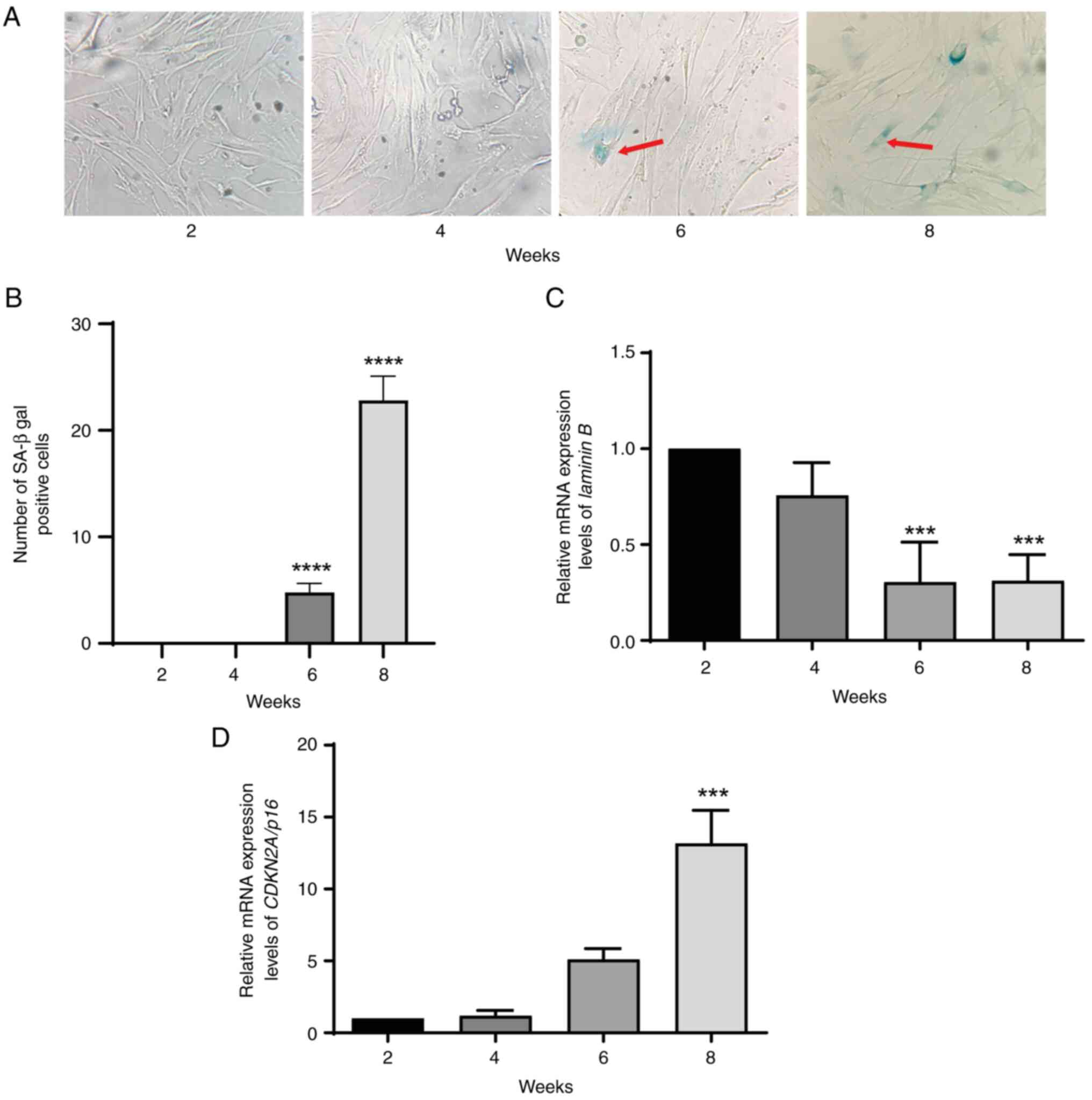
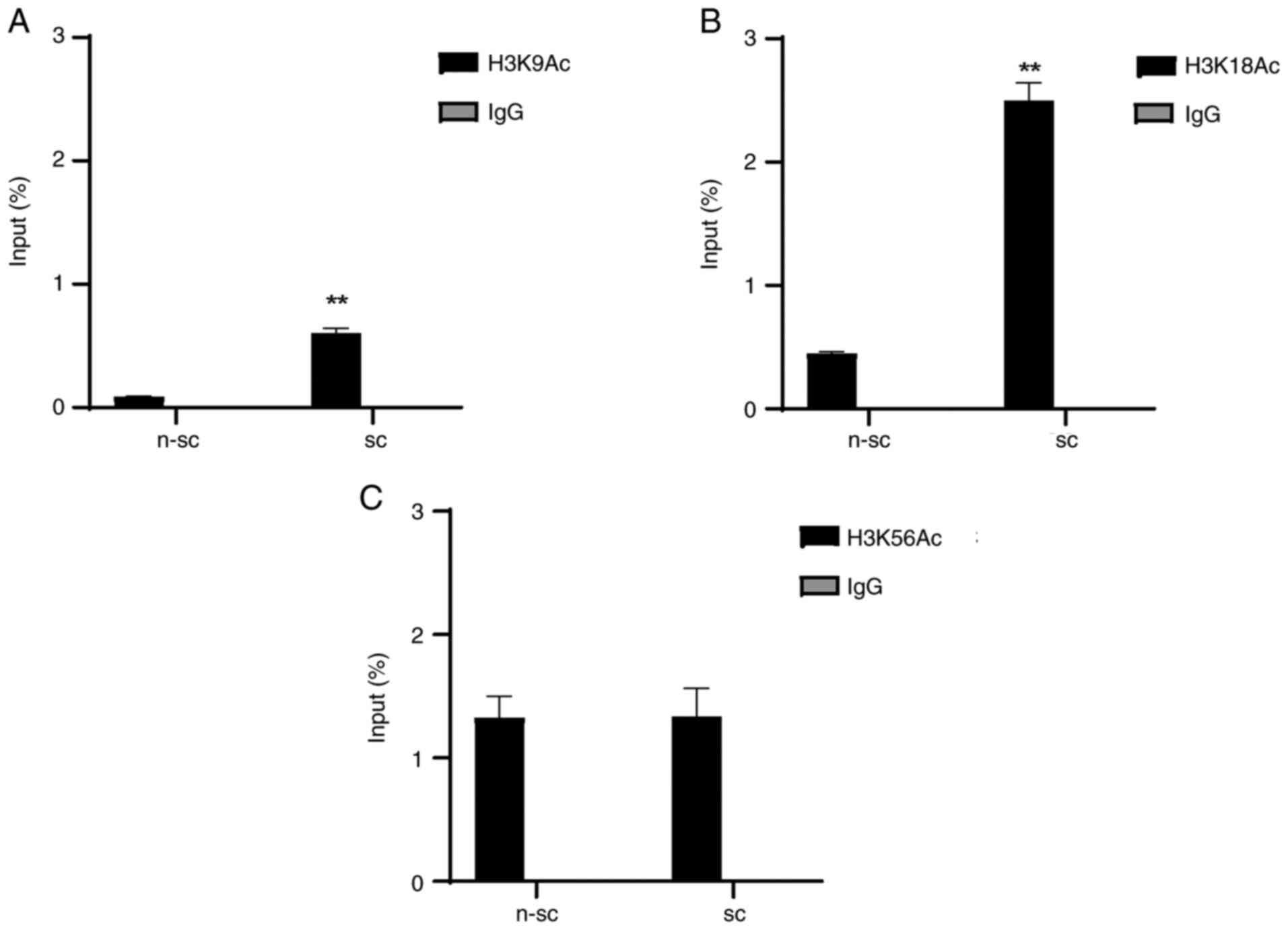
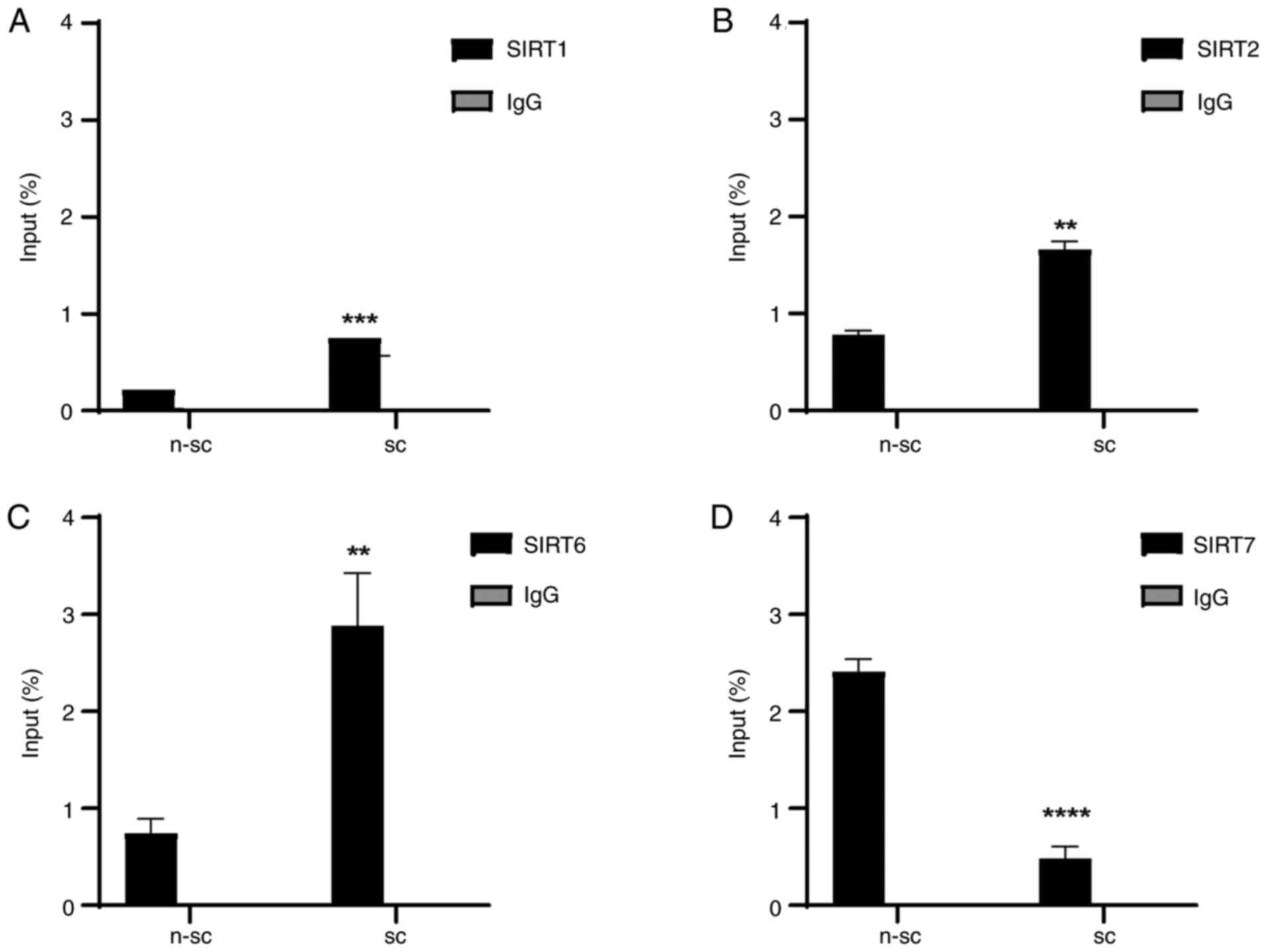
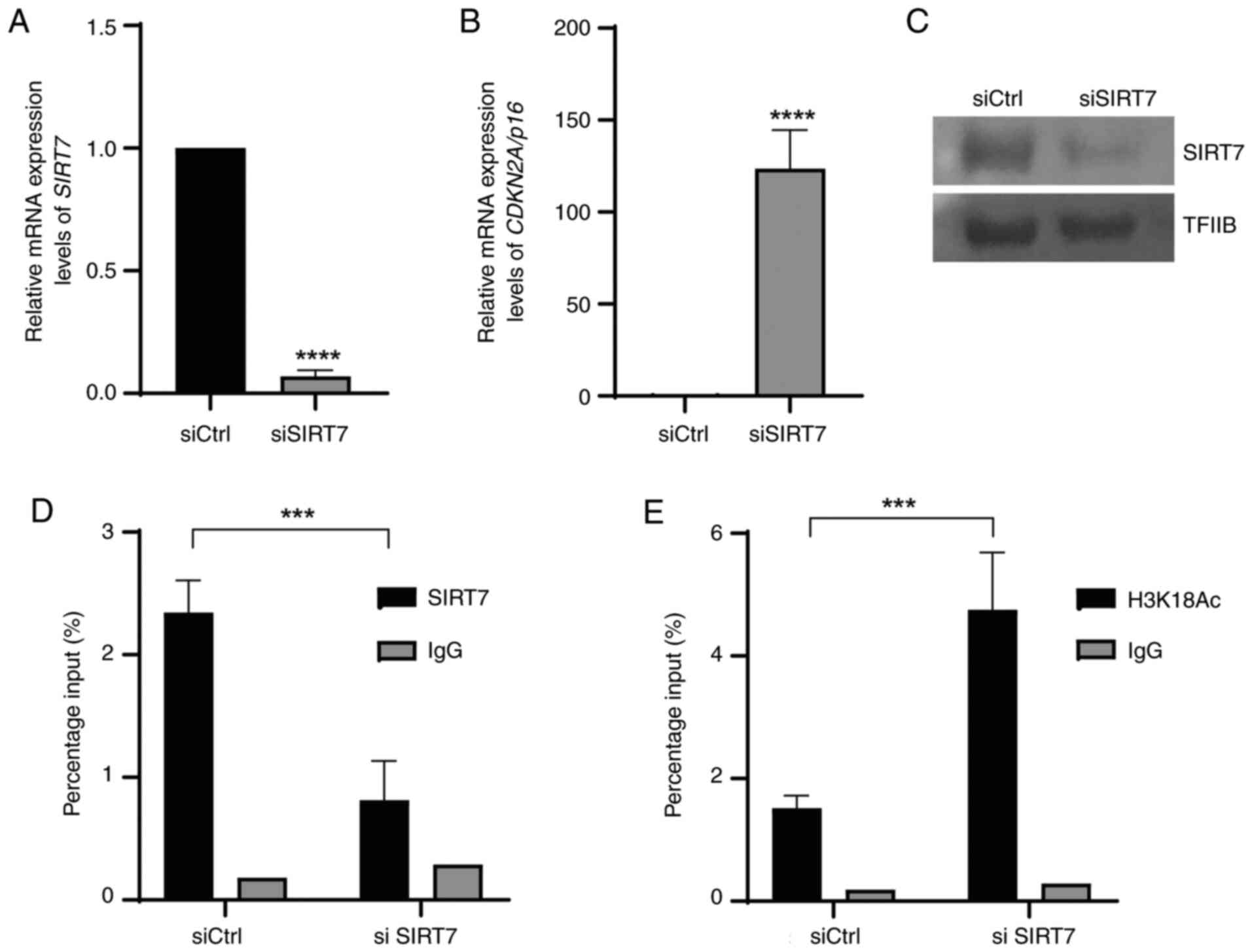
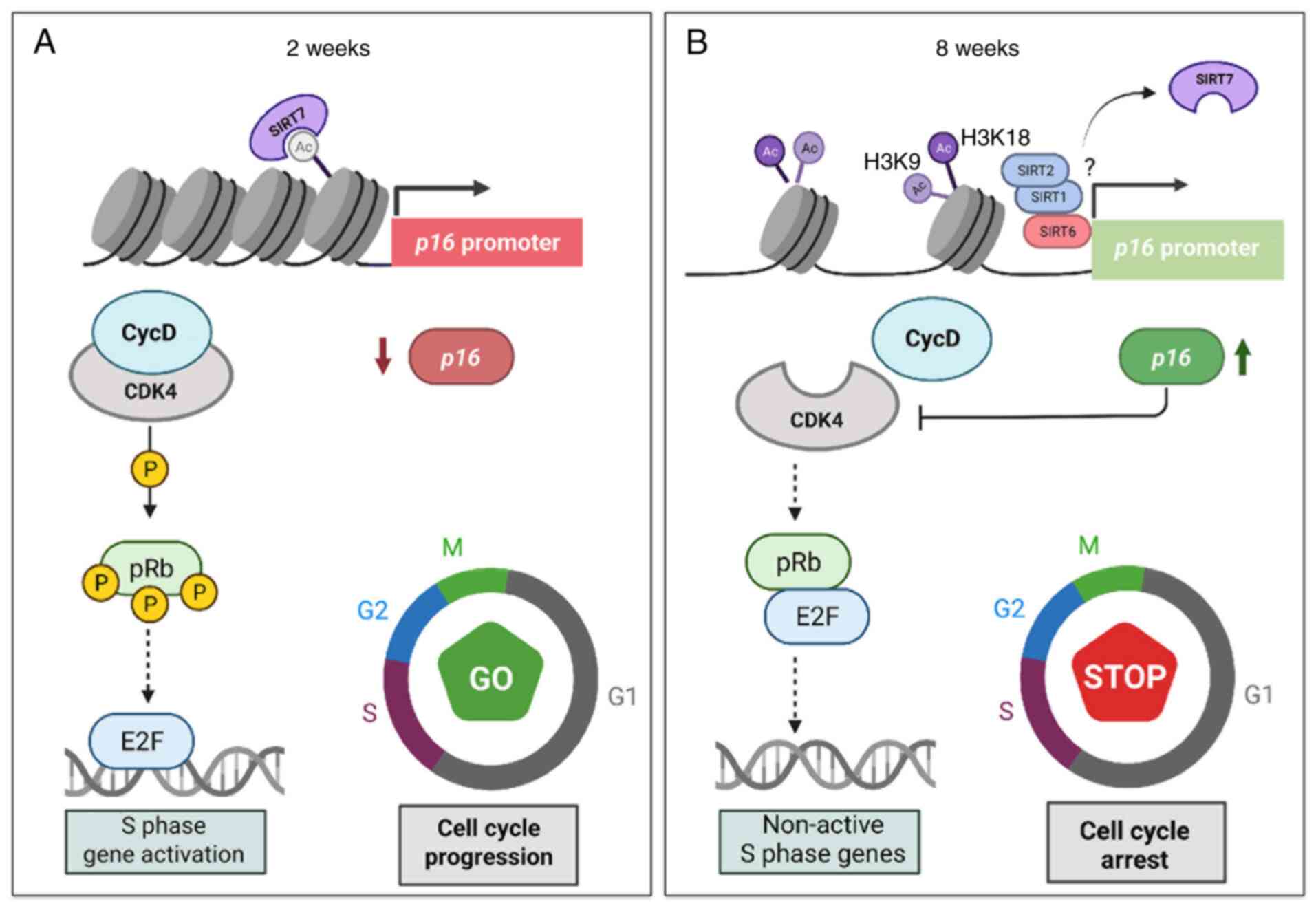
|
1
|
Kuilman T, Michaloglou C, Mooi WJ and
Peeper DS: The essence of senescence. Genes Dev. 24:2463–2479.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Muñoz-Espín D and Serrano M: Cellular
senescence: From physiology to pathology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:482–496. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hernandez-Segura A, Nehme J and Demaria M:
Hallmarks of Cellular Senescence. Trends Cell Biol. 28:436–453.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Childs BG, Baker DJ, Kirkland JL, Campisi
J and van Deursen JM: Senescence and apoptosis: Dueling or
complementary cell fates? EMBO Rep. 15:1139–1153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Coppé JP, Desprez PY, Krtolica A and
Campisi J: The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: The dark
side of tumor suppression. Annu Rev Pathol. 5:99–118. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pluquet O, Pourtier A and Abbadie C: The
unfolded protein response and cellular senescence. A review in the
theme: Cellular mechanisms of endoplasmic reticulum stress
signaling in health and disease. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
308:C415–C425. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gorgoulis V, Adams PD, Alimonti A, Bennett
DC, Bischof O, Bishop C, Campisi J, Collado M, Evangelou K,
Ferbeyre G, et al: Cellular senescence: Defining a path forward.
Cell. 179:813–827. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
James EL, Michalek RD, Pitiyage GN, de
Castro AM, Vignola KS, Jones J, Mohney RP, Karoly ED, Prime SS and
Parkinson EK: Senescent human fibroblasts show increased glycolysis
and redox homeostasis with extracellular metabolomes that overlap
with those of irreparable DNA damage, aging, and disease. J
Proteome Res. 14:1854–1871. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schmeer C, Kretz A, Wengerodt D,
Stojiljkovic M and Witte OW: Dissecting aging and
senescence-current concepts and open lessons. Cells. 8:14462019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ferrari S and Pesce M: Stiffness and aging
in cardiovascular diseases: The dangerous relationship between
force and senescence. Int J Mol Sci. 22:34042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Otto T and Sicinski P: Cell cycle proteins
as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:93–115.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rayess H, Wang MB and Srivatsan ES:
Cellular senescence and tumor suppressor gene p16. Int J Cancer.
130:1715–1725. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sterner DE and Berger SL: Acetylation of
histones and transcription-related factors. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev.
64:435–459. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen HP, Zhao YT and Zhao TC: Histone
deacetylases and mechanisms of regulation of gene expression. Crit
Rev Oncog. 20:35–47. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Langley B and Sauve A: Sirtuin
deacetylases as therapeutic targets in the nervous system.
Neurotherapeutics. 10:605–620. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Allis D, Caparros ML, Jenuwein T, Reinberg
D and Lachner M: Epigenetics. 2nd edition. Cold Spring Harbor
Laboratory Press; New York, NY: 2015
|
|
17
|
Elibol B and Kilic U: High levels of SIRT1
expression as a protective mechanism against disease-related
conditions. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:6142018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakagawa T and Guarente L: SnapShot:
Sirtuins, NAD, and aging. Cell Metab. 20:192–192.e1. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wątroba M, Dudek I, Skoda M, Stangret A,
Rzodkiewicz P and Szukiewicz D: Sirtuins, epigenetics and
longevity. Ageing Res Rev. 40:11–19. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Criscione SW, Teo YV and Neretti N: The
chromatin landscape of cellular senescence. Trends Genet.
32:751–761. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen C, Zhou M, Ge Y and Wang X: SIRT1 and
aging related signaling pathways. Mech Ageing Dev. 187:1112152020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nacarelli T and Sell C: Targeting
metabolism in cellular senescence, a role for intervention. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 455:83–92. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jing H and Lin H: Sirtuins in epigenetic
regulation. Chem Rev. 115:2350–2375. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang N and Sen P: The senescent cell
epigenome. Aging (Albany NY). 10:3590–3609. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Carey MF, Peterson CL and Smale ST: Dignam
and roeder nuclear extract preparation. Cold Spring Harb Protoc.
2009.pdb.prot5330, 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
He F: Bradford Protein Assay. Bio.
101:e452011.
|
|
28
|
Rojas A, Aguilar R, Henriquez B, Lian JB,
Stein JL, Stein GS, van Wijnen AJ, van Zundert B, Allende ML and
Montecino M: Epigenetic control of the bone-master Runx2 gene
during osteoblast-lineage commitment by the histone demethylase
JARID1B/KDM5B. J Biol Chem. 290:28329–28342. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee BY, Han JA, Im JS, Morrone A, Johung
K, Goodwin EC, Kleijer WJ, DiMaio D and Hwang ES:
Senescence-associated beta-galactosidase is lysosomal
beta-galactosidase. Aging Cell. 5:187–195. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Davan-Wetton CSA, Pessolano E, Perretti M
and Montero-Melendez T: Senescence under appraisal: Hopes and
challenges revisited. Cell Mol Life Sci. 78:3333–3354. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ropero S and Esteller M: The role of
histone deacetylases (HDACs) in human cancer. Mol Oncol. 1:19–25.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huang J, Gan Q, Han L, Li J, Zhang H, Sun
Y, Zhang Z and Tong T: SIRT1 overexpression antagonizes cellular
senescence with activated ERK/S6k1 signaling in human diploid
fibroblasts. PLoS One. 3:e17102008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee SH, Lee JH, Lee HY and Min KJ: Sirtuin
signaling in cellular senescence and aging. BMB Rep. 52:24–34.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sadaie M, Salama R, Carroll T, Tomimatsu
K, Chandra T, Young AR, Narita M, Pérez-Mancera PA, Bennett DC,
Chong H, et al: Redistribution of the Lamin B1 genomic binding
profile affects rearrangement of heterochromatic domains and SAHF
formation during senescence. Genes Dev. 27:1800–1808. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Perrigue PM, Rakoczy M, Pawlicka KP,
Belter A, Giel-Pietraszuk M, Naskręt-Barciszewska M, Barciszewski J
and Figlerowicz M: Cancer stem cell-inducing media activates
senescence reprogramming in fibroblasts. Cancers (Basel).
12:17452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dalle Pezze P, Nelson G, Otten EG,
Korolchuk VI, Kirkwood TB, von Zglinicki T and Shanley DP: Dynamic
modelling of pathways to cellular senescence reveals strategies for
targeted interventions. PLoS Comput Biol. 10:e10037282014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen P, Zhang Q, Zhang H, Gao Y, Zhou Y,
Chen Y, Guan L, Jiao T, Zhao Y, Huang M and Bi H: Carnitine
palmitoyltransferase 1C reverses cellular senescence of MRC-5
fibroblasts via regulating lipid accumulation and mitochondrial
function. J Cell Physiol. 236:958–970. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen B, Chai Q, Xu S, Li Q, Wu T, Chen S
and Wu L: Silver nanoparticle-activated COX2/PGE2 axis involves
alteration of lung cellular senescence in vitro and in vivo.
Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 204:1110702020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sun L and Dang W: SIRT7 slows down stem
cell aging by preserving heterochromatin: A perspective on the new
discovery. Protein Cell. 11:469–471. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vazquez BN, Thackray JK, Simonet NG,
Kane-Goldsmith N, Martinez-Redondo P, Nguyen T, Bunting S, Vaquero
A, Tischfield JA and Serrano L: SIRT 7 promotes genome integrity
and modulates non-homologous end joining DNA repair. EMBO J.
35:1488–1503. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Paredes S, Angulo-Ibanez M, Tasselli L,
Carlson SM, Zheng W, Li TM and Chua KF: The epigenetic regulator
SIRT7 guards against mammalian cellular senescence induced by
ribosomal DNA instability. J Biol Chem. 293:11242–11250. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vakhrusheva O, Smolka C, Gajawada P,
Kostin S, Boettger T, Kubin T, Braun T and Bober E: Sirt7 increases
stress resistance of cardiomyocytes and prevents apoptosis and
inflammatory cardiomyopathy in mice. Circ Res. 102:703–710. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shin J, He M, Liu Y, Paredes S, Villanova
L, Brown K, Qiu X, Nabavi N, Mohrin M, Wojnoonski K, et al: SIRT7
represses Myc activity to suppress ER stress and prevent fatty
liver disease. Cell Rep. 5:654–665. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ryu D, Jo YS, Lo Sasso G, Stein S, Zhang
H, Perino A, Lee JU, Zeviani M, Romand R, Hottiger MO, et al: A
SIRT7-Dependent Acetylation Switch of GABPβ1 controls mitochondrial
function. Cell Metab. 20:856–869. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Adrados I, Larrasa-Alonso J, Galarreta A,
López-Antona I, Menéndez C, Abad M, Gil J, Moreno-Bueno G and
Palmero I: The homeoprotein SIX1 controls cellular senescence
through the regulation of p16INK4A and differentiation-related
genes. Oncogene. 35:3485–3494. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wronska A, Lawniczak A, Wierzbicki PM and
Kmiec Z: Age-Related Changes in Sirtuin 7 expression in
calorie-restricted and refed rats. Gerontology. 62:304–310. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhao R, Choi BY, Lee MH, Bode AM and Dong
Z: Implications of genetic and epigenetic alterations of CDKN2A
(p16INK4a) in cancer. EBioMedicine. 8:30–39. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sherr CJ: Ink4-Arf locus in cancer and
aging. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 1:731–741. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|