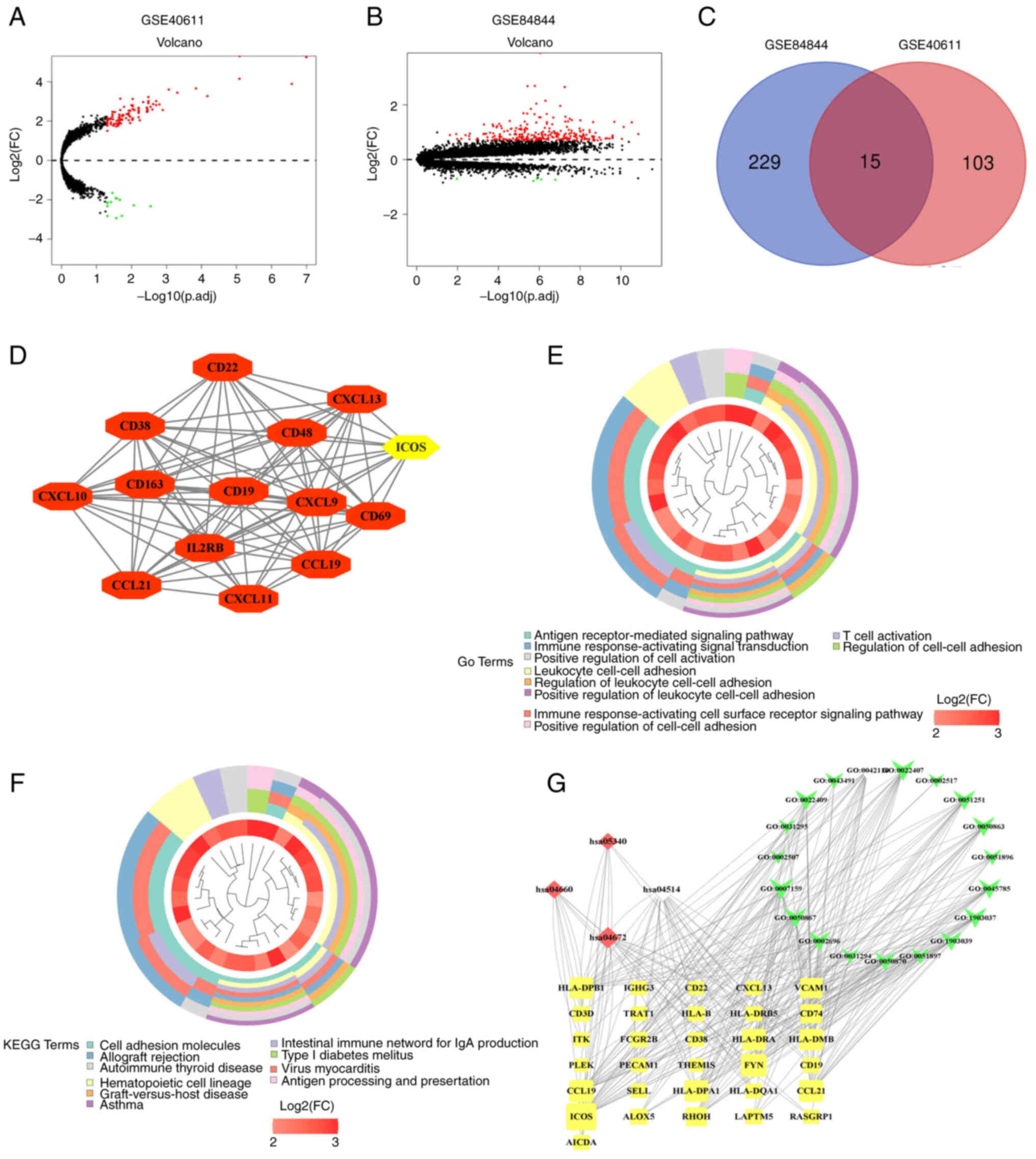
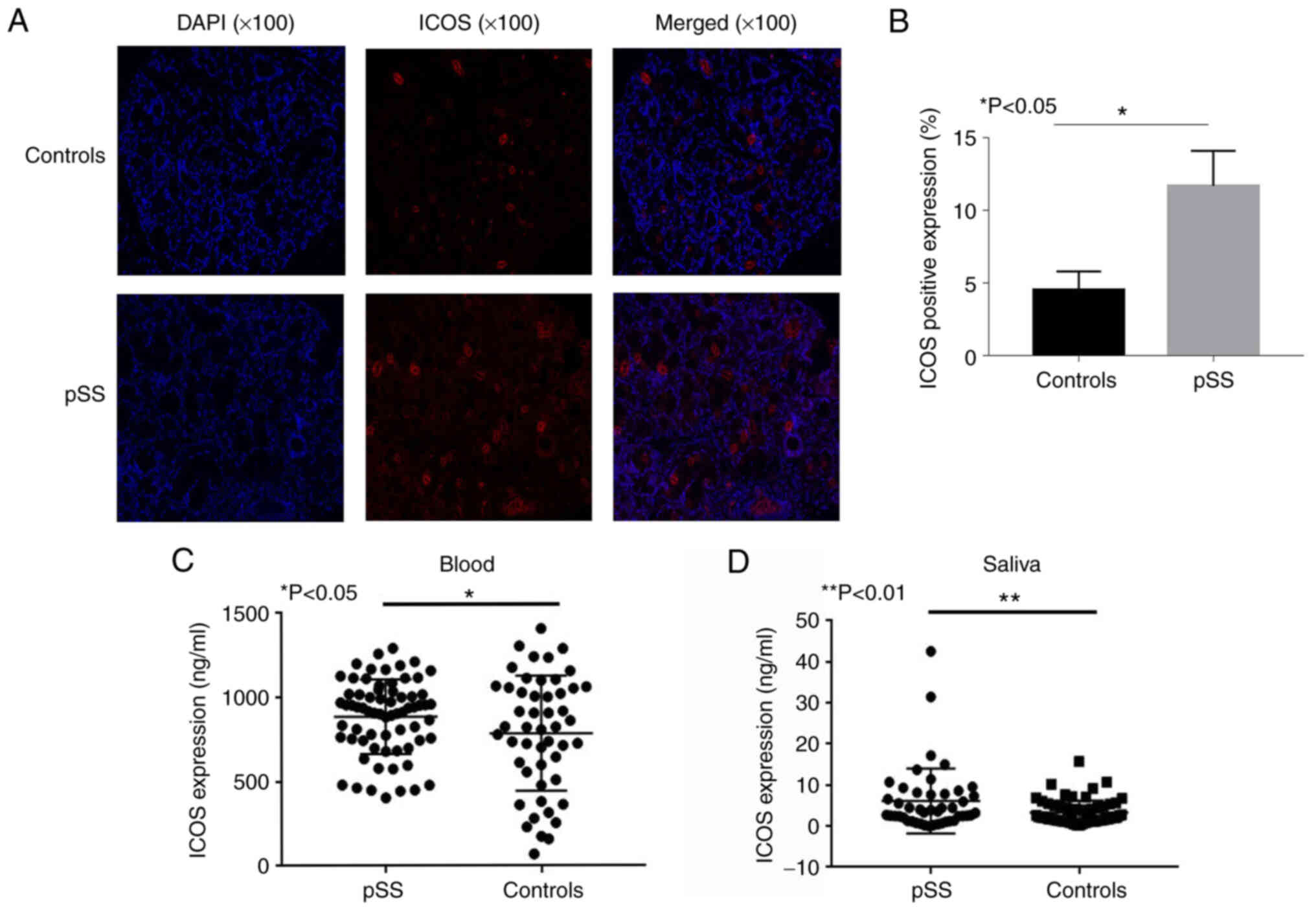
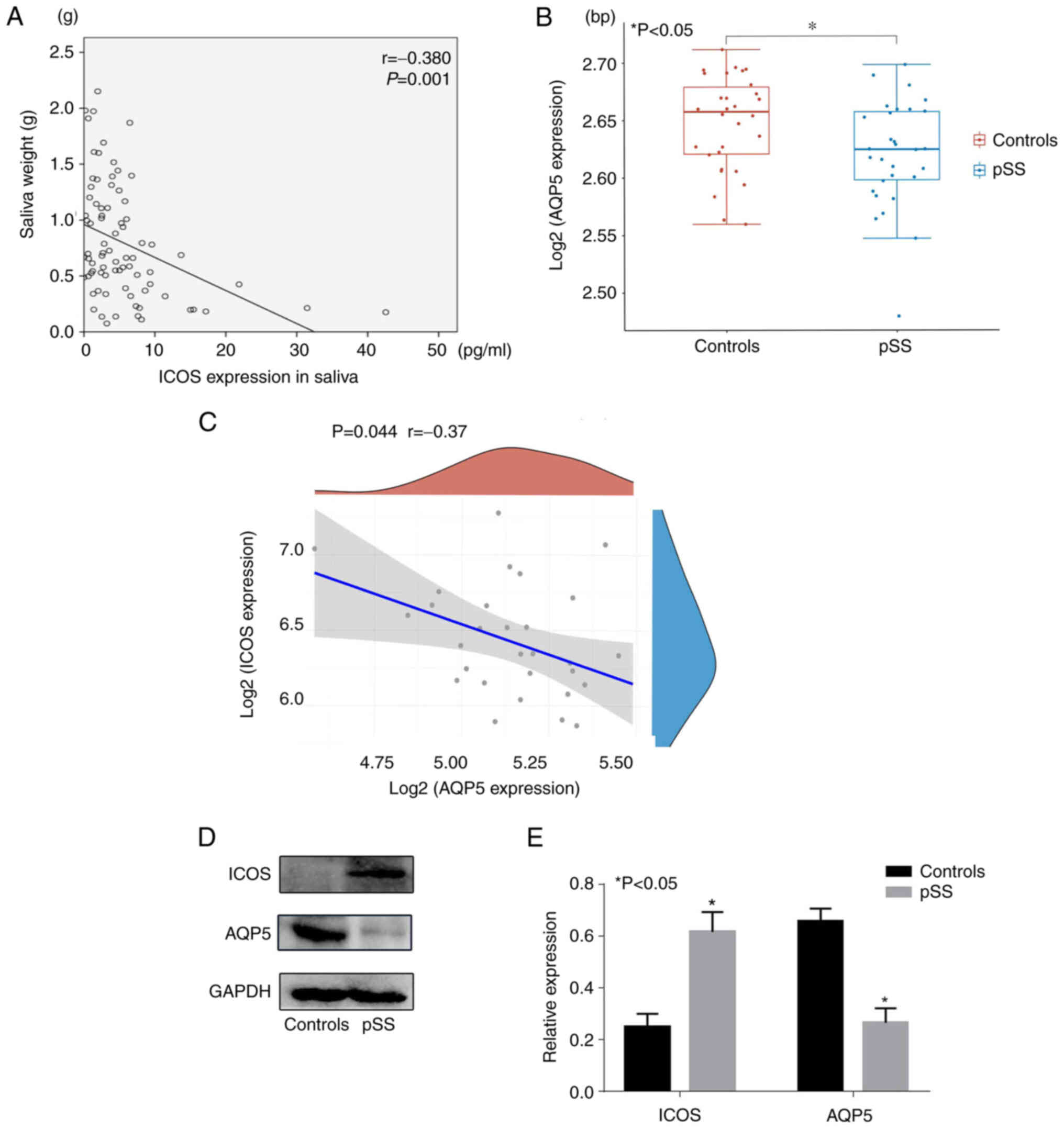
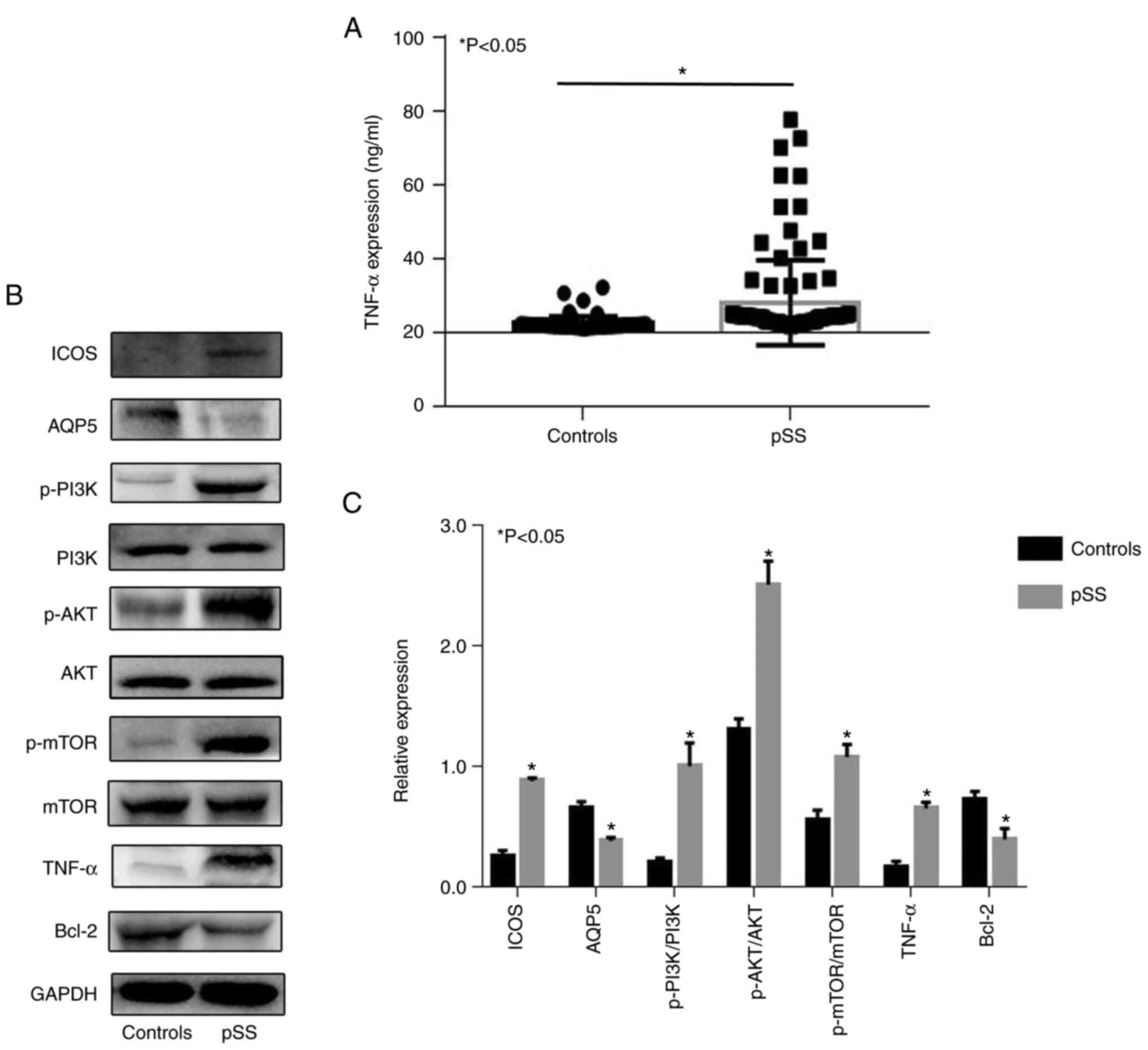
|
1
|
Manoussakis MN and Moutsopoulos HM:
Sjögren's syndrome: Autoimmune epithelitis. Baillieres Best Pract
Res Clin Rheumatol. 14:73–95. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Norcross MA: A synaptic basis for
T-lymphocyte activation. Ann Immunol (Paris). 135D:113–134.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Janeway CA Jr and Bottomly K: Signals and
signs for lymphocyte responses. Cell. 76:275–285. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jenkins MK: The ups and downs of T cell
costimulation. Immunity. 1:443–446. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li X, Yu D, Yu N, Wang X, Li X, Harris DCH
and Wang Y: B7-H4 deficiency in salivary gland of patients with
primary Sjögren's syndrome impairs the regulatory effect on T
cells. Int J Rheum Dis. 20:474–480. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mozaffarian N, Wiedeman AE and Stevens AM:
Active systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with failure of
antigen-presenting cells to express programmed death ligand-1.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 47:1335–1341. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Greenfield EA, Nguyen KA and Kuchroo VK:
CD28/B7 costimulation: A review. Crit Rev Immunol. 18:389–418.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hutloff A, Dittrich AM, Beier KC,
Eljaschewitsch B, Kraft R, Anagnostopoulos I and Kroczek RA: ICOS
is an inducible T-cell co-stimulator structurally and functionally
related to CD28. Nature. 397:263–266. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sharpe AH and Freeman GJ: The B7-CD28
superfamily. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:116–126. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Crotty S: T follicular helper cell
differentiation, function, and roles in disease. Immunity.
41:529–542. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Suh WK: Life of T follicular helper cells.
Mol Cells. 38:195–201. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu D, Xu H, Shih C, Wan Z, Ma X, Ma W,
Luo D and Qi H: T-B-cell entanglement and ICOSL-driven feed-forward
regulation of germinal centre reaction. Nature. 517:214–218. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu H, Li X, Liu D, Li J, Zhang X, Chen X,
Hou S, Peng L, Xu C, Liu W, et al: Follicular T-helper cell
recruitment governed by bystander B cells and ICOS-driven motility.
Nature. 496:523–527. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Grimbacher B, Hutloff A, Schlesier M,
Glocker E, Warnatz K, Dräger R, Eibel H, Fischer B, Schäffer AA,
Mages HW, et al: Homozygous loss of ICOS is associated with
adult-onset common variable immunodeficiency. Nat Immunol.
4:261–268. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tafuri A, Shahinian A, Bladt F, Yoshinaga
SK, Jordana M, Wakeham A, Boucher LM, Bouchard D, Chan VS, Duncan
G, et al: ICOS is essential for effective T-helper-cell responses.
Nature. 409:105–109. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dong C, Juedes AE, Temann UA, Shresta S,
Allison JP, Ruddle NH and Flavell RA: ICOS co-stimulatory receptor
is essential for T-cell activation and function. Nature.
409:97–101. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mak TW, Shahinian A, Yoshinaga SK, Wakeham
A, Boucher LM, Pintilie M, Duncan G, Gajewska BU, Gronski M,
Eriksson U, et al: Costimulation through the inducible costimulator
ligand is essential for both T helper and B cell functions in T
cell-dependent B cell responses. Nat Immunol. 4:765–772. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McAdam AJ, Greenwald RJ, Levin MA,
Chernova T, Malenkovich N, Ling V, Freeman GJ and Sharpe AH: ICOS
is critical for CD40-mediated antibody class switching. Nature.
409:102–105. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li DY and Xiong XZ: ICOS+
Tregs: A functional subset of tregs in immune diseases. Front
Immunol. 11:21042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu Y, Zou L and Liu YC: T follicular
helper cells, T follicular regulatory cells and autoimmunity. Int
Immunol. 28:173–179. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gang C, Jiahui Y, Huaizhou W, Qing C,
Dongbao Z and Qian S: Defects of mitogen-activated protein kinase
in ICOS signaling pathway lead to CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cell
dysfunction in patients with active SLE. Cell Immunol. 258:83–89.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou H, Li B, Li J, Wu T, Jin X, Yuan R,
Shi P, Zhou Y, Li L and Yu F: Dysregulated T cell activation and
aberrant cytokine expression profile in systemic lupus
erythematosus. Mediators Inflamm. 2019:84509472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Luo J, Liao X, Zhang L, Xu X, Ying S, Yu
M, Zhu L, Lin S and Wang X: Transcriptome sequencing reveals
potential roles of ICOS in primary Sjögren's syndrome. Front Cell
Dev Biol. 8:5924902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
García-Espinoza JA, Muñoz-Valle JF,
García-Chagollán M, Hernández-Bello J, Palafox-Sánchez CA,
López-Villalobos EF, Sánchez-Zuno GA, Martínez-Bonilla GE,
Cerpa-Cruz S, Carrillo-Ballesteros FJ and Oregon-Romero E: ICOS
gene polymorphisms (IVS1 + 173 T/C and c. 1624 C/T) in Primary
Sjögren's syndrome patients: Analysis of ICOS expression. Curr
Issues Mol Biol. 44:764–776. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gigoux M, Shang J, Pak Y, Xu M, Choe J,
Mak TW and Suh WK: Inducible costimulator promotes helper T-cell
differentiation through phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 106:20371–20376. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gigoux M, Lovato A, Leconte J, Leung J,
Sonenberg N and Suh WK: Inducible costimulator facilitates
T-dependent B cell activation by augmenting IL-4 translation. Mol
Immunol. 59:46–54. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bonifazi P, D'Angelo C, Zagarella S,
Zelante T, Bozza S, De Luca A, Giovannini G, Moretti S, Iannitti
RG, Fallarino F, et al: Intranasally delivered siRNA targeting
PI3K/Akt/mTOR inflammatory pathways protects from aspergillosis.
Mucosal Immunol. 3:193–205. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
King LS and Agre P: Pathophysiology of the
aquaporin water channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 58:619–648. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Farzan N, Vijverberg SJ, Arets HG,
Raaijmakers JA and Maitland-van der Zee AH: Pharmacogenomics of
inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene modifiers: A systematic
review. Clin Exp Allergy. 47:271–293. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene
Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Furumichi M
and Tanabe M: KEGG for integration and interpretation of
large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:(Database
issue). D109–D114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Kir J, Liu D,
Bryant D, Guo Y, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki RA:
DAVID Bioinformatics Resources: Expanded annotation database and
novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists.
Nucleic Acids Res. 35:(Web Server issue). W169–W175. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A,
Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork
P, et al: STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with
increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide
experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 47((D1)): D607–D613.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Gorodkin J and
Jensen LJ: Cytoscape StringApp: Network analysis and visualization
of proteomics data. J Proteome Res. 18:623–632. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Jonsson R,
Moutsopoulos HM, Alexander EL, Carsons SE, Daniels TE, Fox PC, Fox
RI, Kassan SS, et al: Classification criteria for Sjögren's
syndrome: A revised version of the European criteria proposed by
the American-European Consensus Group. Ann Rheum Dis. 61:554–558.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nocturne G: Sjögren's syndrome update:
Clinical and therapeutic aspects. Rev Med Interne. 40:433–439.
2019.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rosas J, Sánchez-Piedra C,
Fernández-Castro M, Andreu JL, Martínez-Taboada V and Olivé A;
SJÖGRENSER Group and part of the Spanish Society of Rheumatology
Systemic Autoimmune Diseases Study Group (EASSER), : ESSDAI
activity index of the SJÖGRENSER cohort: Analysis and comparison
with other European cohorts. Rheumatol Int. 39:991–999. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen X, Aqrawi LA, Utheim TP, Tashbayev B,
Utheim ØA, Reppe S, Hove LH, Herlofson BB, Singh PB, Palm Ø, et al:
Elevated cytokine levels in tears and saliva of patients with
primary Sjögren's syndrome correlate with clinical ocular and oral
manifestations. Sci Rep. 9:73192019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Greenspan JS, Daniels TE, Talal N and
Sylvester RA: The histopathology of Sjögren's syndrome in labial
salivary gland biopsies. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol.
37:217–229. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vitali C, Moutsopoulos HM and Bombardieri
S: The European Community Study Group on diagnostic criteria for
Sjögren's syndrome. Sensitivity and specificity of tests for ocular
and oral involvement in Sjögren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis.
53:637–647. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Moutsopoulos HM,
Balestrieri G, Bencivelli W, Bernstein RM, Bjerrum KB, Braga S,
Coll J, de Vita S, et al: Preliminary criteria for the
classification of Sjögren's syndrome. Results of a prospective
concerted action supported by the European Community. Arthritis
Rheum. 36:340–347. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Moutsopoulos HM,
Coll J, Gerli R, Hatron PY, Kater L, Konttinen YT, Manthorpe R,
Meyer O, et al: Assessment of the European classification criteria
for Sjögren's syndrome in a series of clinically defined cases:
Results of a prospective multicentre study. The European Study
Group on Diagnostic Criteria for Sjögren's Syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis.
55:116–121. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Daniels TE and Whitcher JP: Association of
patterns of labial salivary gland inflammation with
keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Analysis of 618 patients with suspected
Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 37:869–877. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Panneton V, Bagherzadeh Yazdchi S, Witalis
M, Chang J and Suh WK: ICOS signaling controls induction and
maintenance of collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol.
200:3067–3076. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Daniels TE, Silverman S Jr, Michalski JP,
Greenspan JS, Sylvester RA and Talal N: The oral component of
Sjögren's syndrome. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 39:875–885.
1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Baudet-Pommel M, Albuisson E, Kemeny JL,
Falvard F, Ristori JM, Fraysse MP and Sauvezie B: Early dental loss
in Sjögren's syndrome. Histologic correlates. European Community
Study Group on Diagnostic Criteria for Sjögren's Syndrome (EEC
COMAC). Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 78:181–186. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Daniels TE and Fox PC: Salivary and oral
components of Sjögren's syndrome. Rheum Dis Clin North Am.
18:571–589. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Greenspan D: Xerostomia: Diagnosis and
management. Oncology (Williston Park). 10 (3 Suppl):S7–S11.
1996.
|
|
49
|
Lilly JP and Fotos PG: Sjögren's syndrome:
Diagnosis and management of oral complications. Gen Dent.
44:404–408; quiz. 419–420. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ravald N and List T: Caries and
periodontal conditions in patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome.
Swed Dent J. 22:97–103. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Soto-Rojas AE, Villa AR, Sifuentes-Osornio
J, Alarcón-Segovia D and Kraus A: Oral manifestations in patients
with Sjögren's syndrome. J Rheumatol. 25:906–910. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hernandez YL and Daniels TE: Oral
candidiasis in Sjögren's syndrome: Prevalence, clinical
correlations, and treatment. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol.
68:324–329. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Rhodus NL, Colby S, Moller K and Bereuter
J: Quantitative assessment of dysphagia in patients with primary
and secondary Sjögren's syndrome. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol
Oral Radiol Endod. 79:305–310. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Pedersen AM, Reibel J and Nauntofte B:
Primary Sjögren's syndrome (pSS): Subjective symptoms and salivary
findings. J Oral Pathol Med. 28:303–311. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Odegard JM, DiPlacido LD, Greenwald L,
Kashgarian M, Kono DH, Dong C, Flavell RA and Craft J: ICOS
controls effector function but not trafficking receptor expression
of kidney-infiltrating effector T cells in murine lupus. J Immunol.
182:4076–4084. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Deepa T and Thirrunavukkarasu N: Saliva as
a potential diagnostic tool. Indian J Med Sci. 64:293–306. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Katsiougiannis S and Wong DT: The
Proteomics of Saliva in Sjögren's Syndrome. Rheum Dis Clin North
Am. 42:449–456. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Giusti L, Baldini C, Bazzichi L,
Bombardieri S and Lucacchini A: Proteomic diagnosis of Sjögren's
syndrome. Expert Rev Proteomics. 4:757–767. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hu S, Wang J, Meijer J, Ieong S, Xie Y, Yu
T, Zhou H, Henry S, Vissink A, Pijpe J, et al: Salivary proteomic
and genomic biomarkers for primary Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis
Rheum. 56:3588–3600. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Verkman AS: Aquaporins at a glance. J Cell
Sci. 124((Pt 13)): 2107–2112. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Hoffert JD, Chou CL and Knepper MA:
Aquaporin-2 in the ‘-omics’ era. J Biol Chem. 284:14683–14687.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yoshimura S, Nakamura H, Horai Y, Nakajima
H, Shiraishi H, Hayashi T, Takahashi T and Kawakami A: Abnormal
distribution of AQP5 in labial salivary glands is associated with
poor saliva secretion in patients with Sjögren's syndrome including
neuromyelitis optica complicated patients. Mod Rheumatol.
26:384–390. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Brennan FM and McInnes IB: Evidence that
cytokines play a role in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest.
118:3537–3545. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Williams RO, Feldmann M and Maini RN:
Anti-tumor necrosis factor ameliorates joint disease in murine
collagen-induced arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:9784–9788.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Liu C, Guan Z, Zhao L, Song Y and Wang H:
Elevated level of circulating
CD4+Helios+FoxP3+ cells in primary
Sjogren's syndrome patients. Mod Rheumatol. 27:630–637. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Szodoray P, Papp G, Horvath IF, Barath S,
Sipka S, Nakken B and Zeher M: Cells with regulatory function of
the innate and adaptive immune system in primary Sjögren's
syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 157:343–349. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Roescher N, Tak PP and Illei GG: Cytokines
in Sjogren's syndrome: Potential therapeutic targets. Ann Rheum
Dis. 69:945–948. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Baturone R, Soto MJ, Márquez M, Macías I,
de Oca MM, Medina F, Chozas N, García-Pérez S and Girón-González
JA: Health-related quality of life in patients with primary
Sjögren's syndrome: Relationship with serum levels of
proinflammatory cytokines. Scand J Rheumatol. 38:386–389. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Szodoray P, Alex P, Brun JG, Centola M and
Jonsson R: Circulating cytokines in primary Sjögren's syndrome
determined by a multiplex cytokine array system. Scand J Immunol.
59:592–599. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Garcíc-Carrasco M, Font J, Filella X,
Cervera R, Ramos-Casals M, Sisó A, Aymamí A, Ballesta AM and
Ingelmo M: Circulating levels of Th1/Th2 cytokines in patients with
primary Sjögren's syndrome: Correlation with clinical and
immunological features. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 19:411–415.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Fox RI, Kang HI, Ando D, Abrams J and Pisa
E: Cytokine mRNA expression in salivary gland biopsies of Sjögren's
syndrome. J Immunol. 152:5532–5539. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Xu H, Li J, Zhao Y and Liu D: TNFα-induced
downregulation of microRNA-186 contributes to apoptosis in rat
primary cardiomyocytes. Immunobiology. 222:778–784. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|