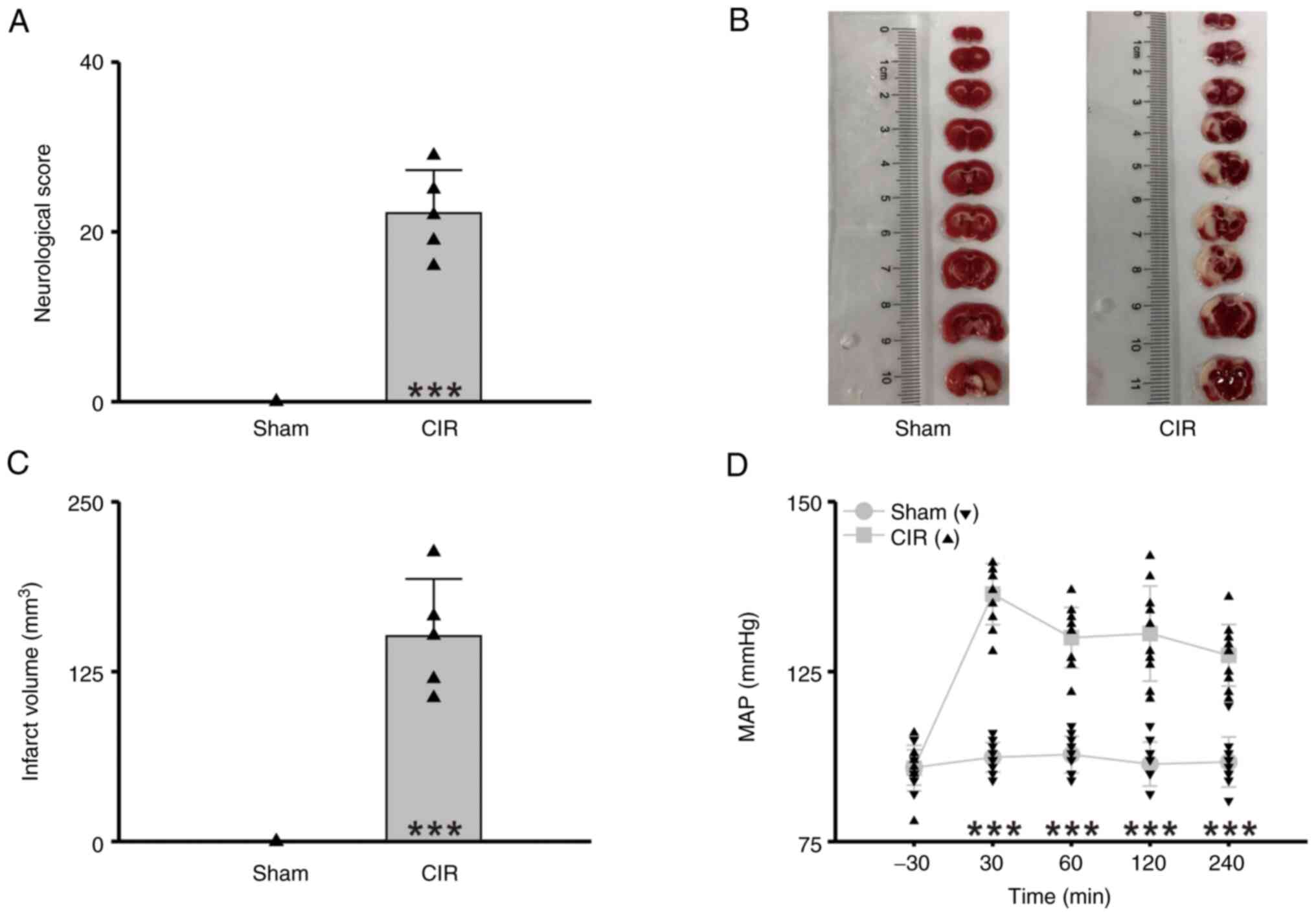
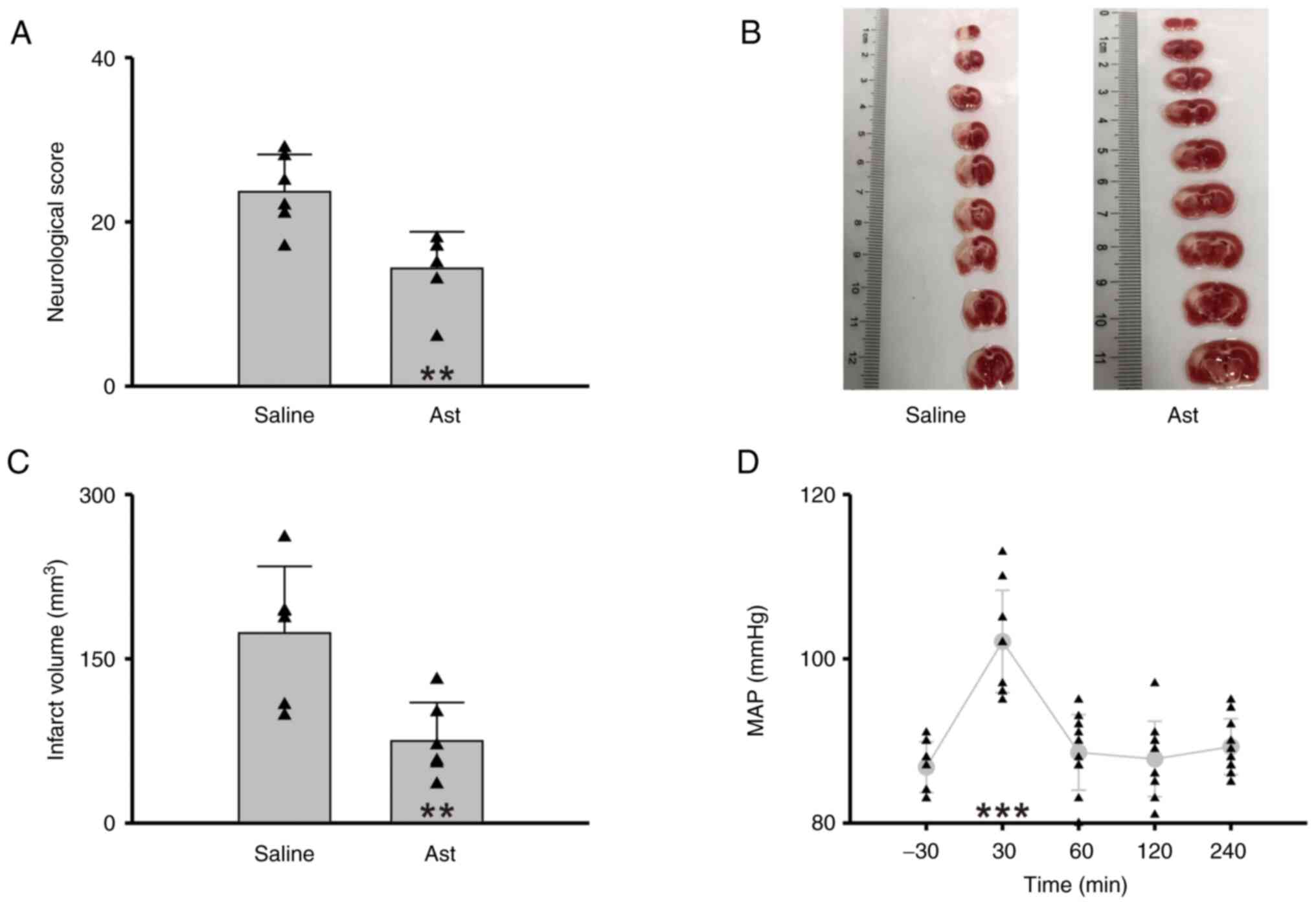
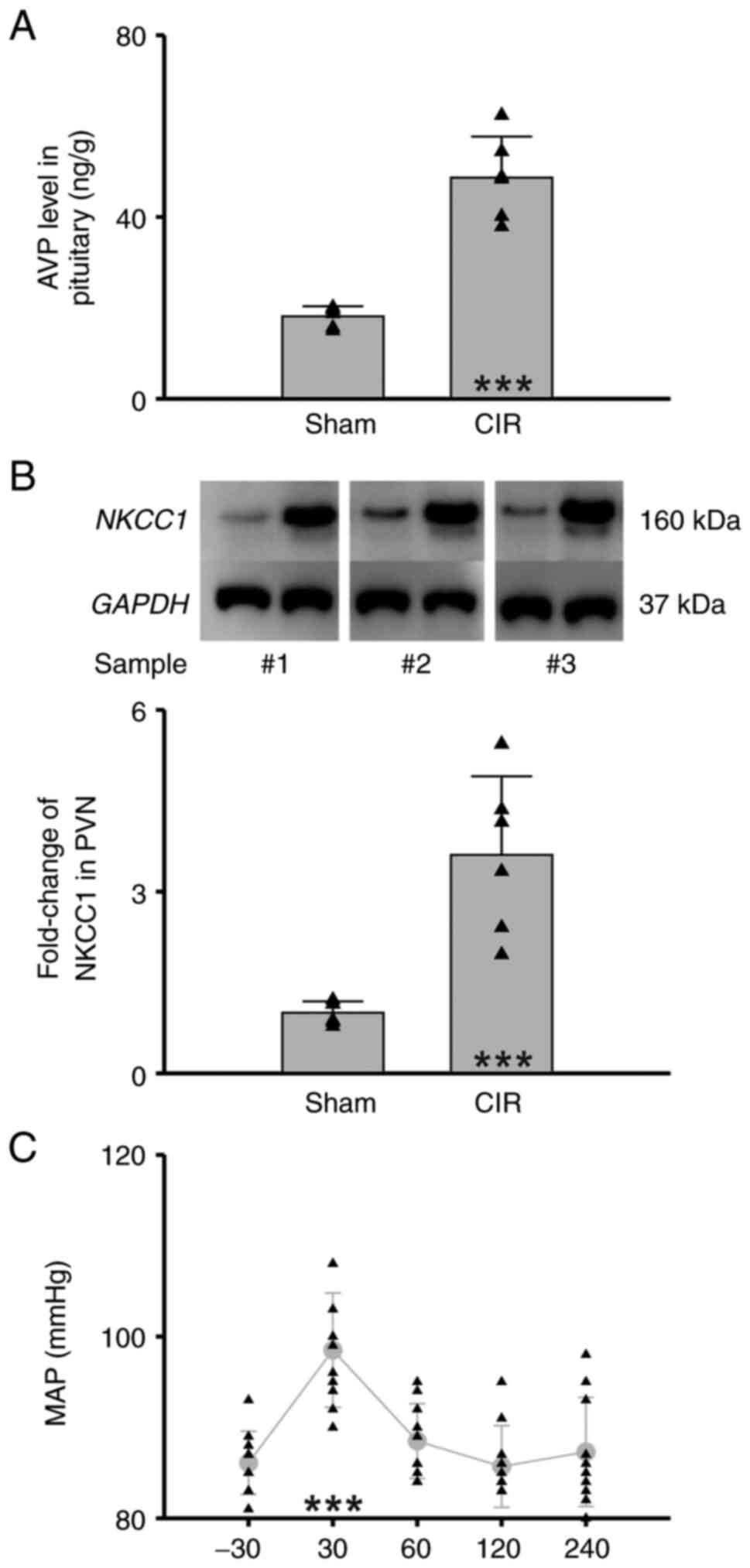
|
1
|
Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A,
Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR,
Cheng S, Das SR, et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019
update: A report from the American heart association. Circulation.
139:e56–e528. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stubblefield JJ and Lechleiter JD: Time to
target stroke: Examining the circadian system in stroke. Yale J
Biol Med. 92:349–357. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Puig B, Brenna S and Magnus T: Molecular
communication of a dying neuron in stroke. Int J Mol Sci.
19:28342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Feske SK: Ischemic stroke. Am J Med.
134:1457–1464. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu MY, Yiang GT, Liao WT, Tsai AP, Cheng
YL, Cheng PW, Li CY and Li CJ: Current mechanistic concepts in
ischemia and reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol Biochem.
46:1650–1667. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liang D, Bhatta S, Gerzanich V and Simard
JM: Cytotoxic edema: Mechanisms of pathological cell swelling.
Neurosurg Focus. 22:E22007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stokum JA, Gerzanich V and Simard JM:
Molecular pathophysiology of cerebral edema. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 36:513–538. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mestre H, Du T, Sweeney AM, Liu G, Samson
AJ, Peng W, Mortensen KN, Stæger FF, Bork PAR, Bashford L, et al:
Cerebrospinal fluid influx drives acute ischemic tissue swelling.
Science. 367:eaax71712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Han D, Sun M, He PP, Wen LL, Zhang H and
Feng J: Ischemic postconditioning alleviates brain edema after
focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats through down-regulation
of aquaporin-4. J Mol Neurosci. 56:722–729. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Simao F, Ustunkaya T, Clermont AC and
Feener EP: Plasma kallikrein mediates brain hemorrhage and edema
caused by tissue plasminogen activator therapy in mice after
stroke. Blood. 129:2280–2290. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zonneveld TP, Richard E, Vergouwen MD,
Nederkoorn PJ, de Haan R, Roos YB and Kruyt ND: Blood
pressure-lowering treatment for preventing recurrent stroke, major
vascular events, and dementia in patients with a history of stroke
or transient ischaemic attack. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
7:CD0078582018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Elewa HF, Kozak A, Johnson MH, Ergul A and
Fagan SC: Blood pressure lowering after experimental cerebral
ischemia provides neurovascular protection. J Hypertens.
25:855–859. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang HL, Zhou QH, Xu MB, Zhou XL and Zheng
GQ: Astragaloside IV for experimental focal cerebral ischemia:
Preclinical evidence and possible mechanisms. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017:84243262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang P, Ma D, Wang X, Wang Y, Bi Y, Yang
J, Wang X and Li X: Astragaloside IV prevents obesity-associated
hypertension by improving pro-inflammatory reaction and leptin
resistance. Mol Cells. 41:244–255. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang X, Chen J, Xu P and Tian X:
Protective effects of Astragaloside IV against hypoxic pulmonary
hypertension. Medchemcomm. 9:1715–1721. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Su Z, Miao B, Xu MQ, Yang MJ, Fei SJ and
Zhang JF: Protective effect of microinjection of glutamate into
hypothalamus paraventricular nucleus on chronic visceral
hypersensitivity in rats. Brain Res. 1747:1470482020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Savić B, Murphy D and Japundžić-Žigon N:
The Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus in Control of Blood
Pressure and Blood Pressure Variability. Front Physiol.
13:8589412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim YB, Kim YS, Kim WB, Shen FY, Lee SW,
Chung HJ, Kim JS, Han HC, Colwell CS and Kim YI: GABAergic
excitation of vasopressin neurons: Possible mechanism underlying
sodium-dependent hypertension. Circ Res. 113:1296–1307. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kaila K, Price TJ, Payne JA, Puskarjov M
and Voipio J: Cation-chloride cotransporters in neuronal
development, plasticity and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 15:637–654.
2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Virtanen MA, Uvarov P, Hubner CA and Kaila
K: NKCC1, an elusive molecular target in brain development: Making
sense of the existing data. Cells. 9:26072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gorelick PB and Ruland S: Cerebral
vascular disease. Dis Mon. 56:39–100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Spengos K, Tsivgoulis G and Zakopoulos N:
Blood pressure management in acute stroke: A long-standing debate.
Eur Neurol. 55:123–135. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Willmot M, Leonardi-Bee J and Bath PM:
High blood pressure in acute stroke and subsequent outcome: A
systematic review. Hypertension. 43:18–24. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gorelick PB and Aiyagari V: The management
of hypertension for an acute stroke: What is the blood pressure
goal? Curr Cardiol Rep. 15:3662013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Aoyagi T, Koshimizu TA and Tanoue A:
Vasopressin regulation of blood pressure and volume: Findings from
V1a receptor-deficient mice. Kidney Int. 76:1035–1039. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bankir L, Bichet DG and Morgenthaler NG:
Vasopressin: Physiology, assessment and osmosensation. J Intern
Med. 282:284–297. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Barreca T, Gandolfo C, Corsini G, Del
Sette M, Cataldi A, Rolandi E and Franceschini R: Evaluation of the
secretory pattern of plasma arginine vasopressin in stroke
patients. Cerebrovasc Dis. 11:113–118. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu X, Jin Y, Zheng H, Chen G, Tan B and
Wu B: Arginine vasopressin gene expression in supraoptic nucleus
and paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamous following cerebral
ischemia and reperfusion. Chin Med Sci J. 15:157–161.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vakili A, Kataoka H and Plesnila N: Role
of arginine vasopressin V1 and V2 receptors for brain damage after
transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
25:1012–1019. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shahzad M, Shabbir A, Wojcikowski K,
Wohlmuth H and Gobe GC: The antioxidant effects of Radix Astragali
(Astragalus membranaceus and related species) in protecting tissues
from injury and disease. Curr Drug Targets. 17:1331–1340. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li L, Hou X, Xu R, Liu C and Tu M:
Research review on the pharmacological effects of Astragaloside IV.
Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 31:17–36. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang J, Wu C, Gao L, Du G and Qin X:
Astragaloside IV derived from Astragalus membranaceus: A research
review on the pharmacological effects. Adv Pharmacol. 87:89–112.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kang X, Su S, Hong W, Geng W and Tang H:
Research progress on the ability of Astragaloside IV to protect the
brain against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Neurosci.
15:7559022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tan YQ, Chen HW and Li J: Astragaloside
IV: An effective drug for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 14:3731–3746. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jin H, Jiao Y, Guo L, Ma Y, Zhao R, Li X,
Shen L, Zhou Z, Kim SC and Liu J: Astragaloside IV blocks
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension by improving
inflammation and pulmonary artery remodeling. Int J Mol Med.
47:595–606. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jing H, Xie R, Bai Y, Duan Y, Sun C, Wang
Y, Cao R, Ling Z and Qu X: The mechanism actions of Astragaloside
IV prevents the progression of hypertensive heart disease based on
network pharmacology and experimental pharmacology. Front
Pharmacol. 12:7556532021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Candelario-Jalil E, Dijkhuizen RM and
Magnus T: Neuro-inflammation, stroke, blood-brain barrier
dysfunction, and imaging modalities. Stroke. 53:1473–1486. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang C, Hawkins KE, Doré S and
Candelario-Jalil E: Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of blood-brain
barrier damage in ischemic stroke. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
316:C135–C153. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|