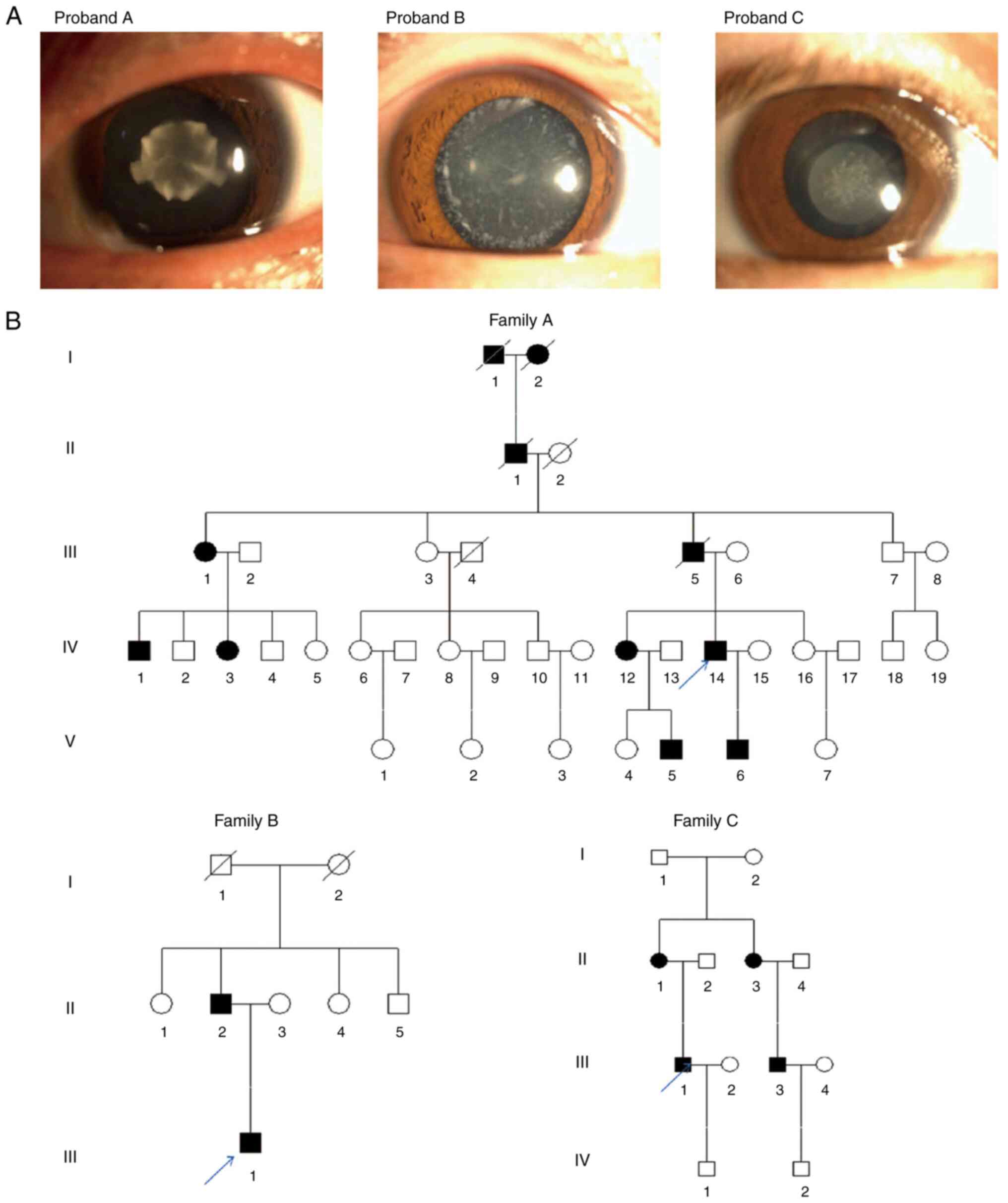
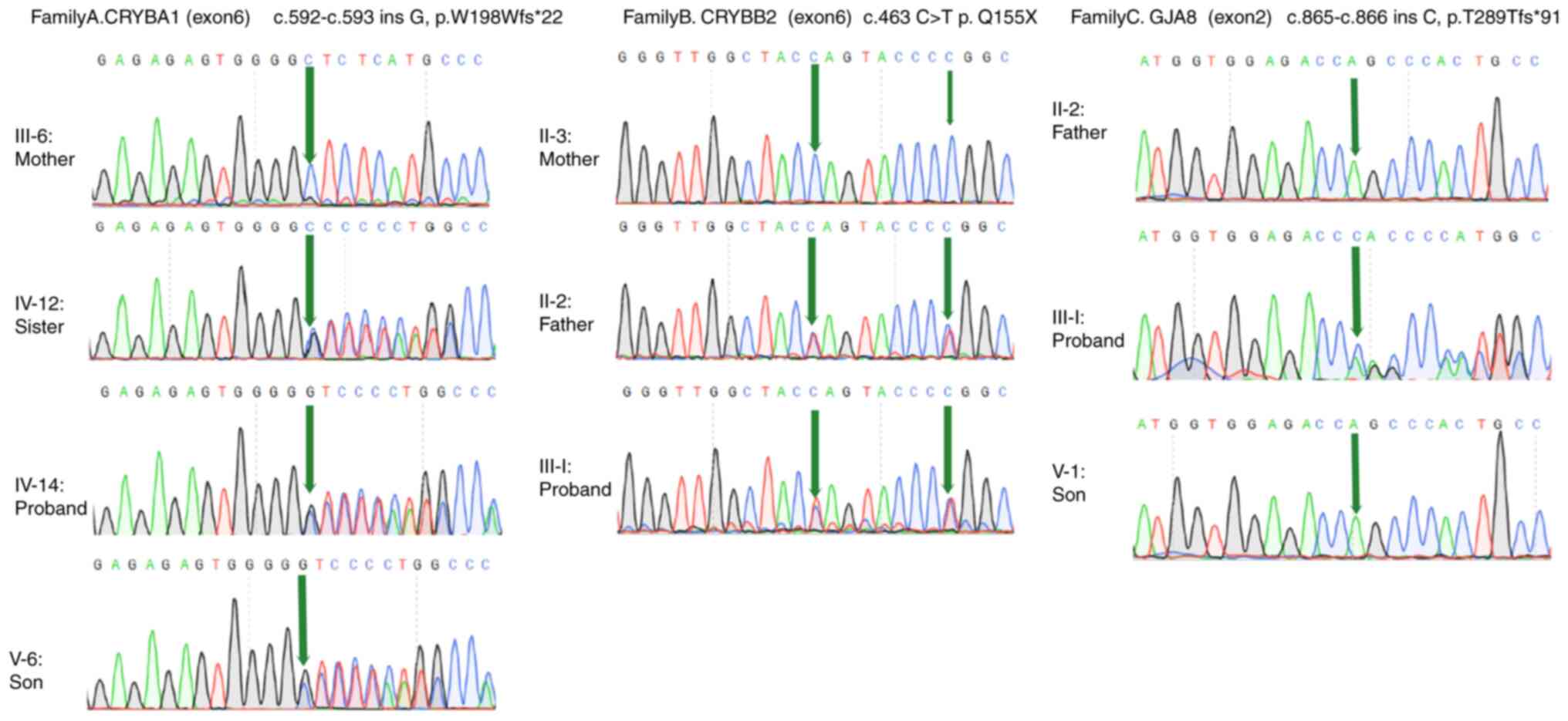
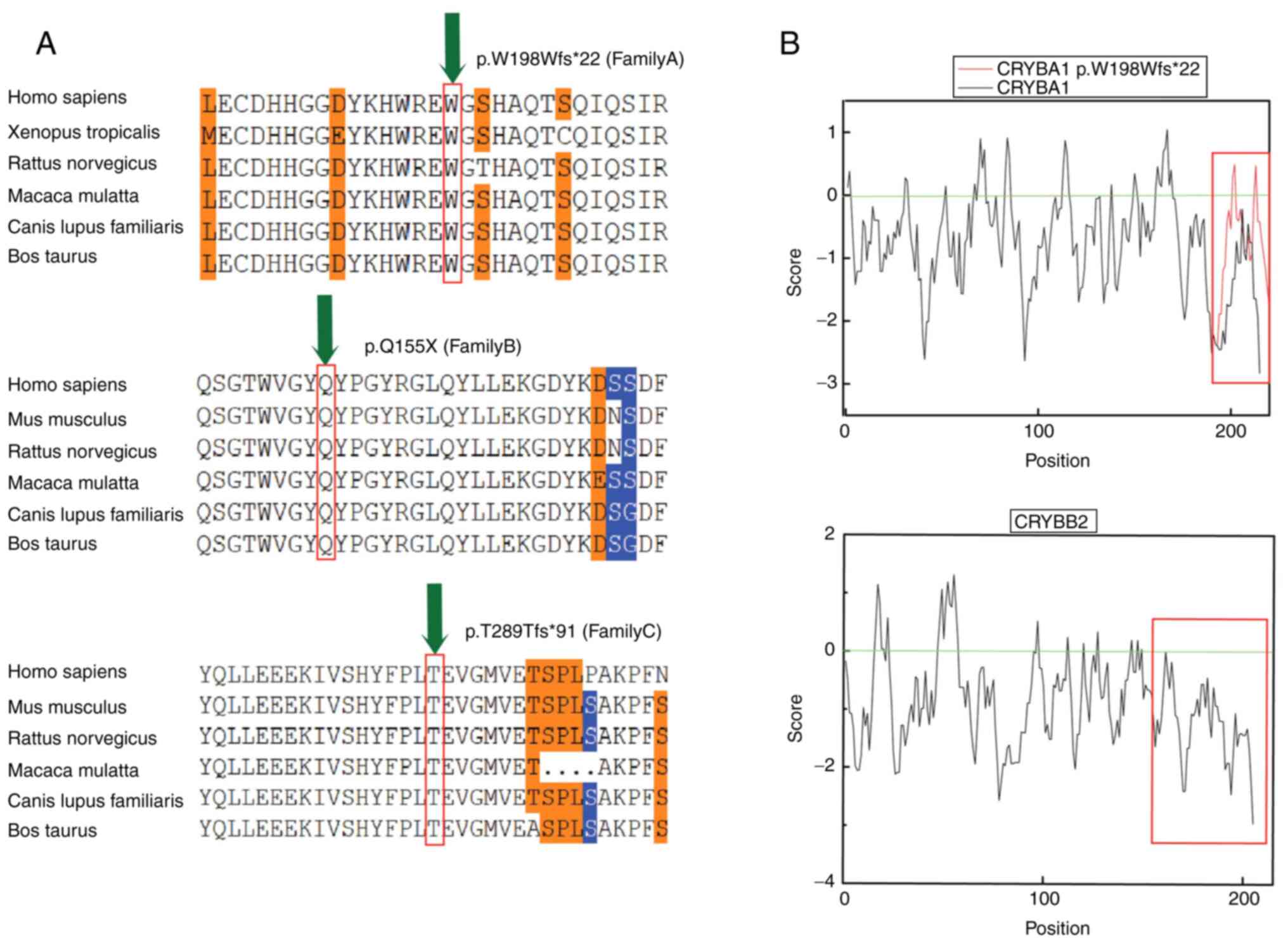
|
1
|
Sun W, Xiao X, Li S, Guo X and Zhang Q:
Exome sequencing of 18 Chinese families with congenital cataracts:
A new sight of the NHS gene. PLoS One. 9:e1004552014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li J, Chen X, Yan Y and Yao K: Molecular
genetics of congenital cataracts. Exp Eye Res. 191:1078722020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jiao X, Khan SY, Irum B, Khan AO, Wang Q,
Kabir F, Khan AA, Husnain T, Akram J, Riazuddin S, et al:
Correction: missense mutations in CRYAB are liable for recessive
congenital cataracts. PLoS One. 12:e01714032017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kumar M, Agarwal T, Kaur P, Kumar M,
Khokhar S and Dada R: Molecular and structural analysis of genetic
variations in congenital cataract. Mol Vision. 19:2436–2450.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Khan I, Chandani S and Balasubramanian D:
Structural study of the G57W mutant of human gamma-S-crystallin,
associated with congenital cataract. Mol Vis. 22:771–782.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yue B, Haddad BG, Khan U, Chen H, Atalla
M, Zhang Z, Zuckerman DM, Reichow SL and Bai D: Connexin 46 and
connexin 50 gap junction channel properties are shaped by
structural and dynamic features of their N-terminal domains. J
Physiol. 599:3313–3335. 2021. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Valiunas V, Brink PR and White TW: Lens
connexin channels have differential permeability to the second
messenger cAMP. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 60:3821–3829. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brink PR, Valiunas V and White TW: Lens
connexin channels show differential permeability to signaling
molecules. Int J Mol Sci. 21:69432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Berry V, Ionides A, Pontikos N, Georgiou
M, Yu J, Ocaka LA, Moore AT, Quinlan RA and Michaelides M: The
genetic landscape of crystallins in congenital cataract. Orphanet J
Rare Dis. 15:3332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mothobi ME, Guo S, Liu Y, Chen Q, Yussuf
AS, Zhu X and Fang Z: Mutation analysis of congenital cataract in a
Basotho family identified a new missense allele in CRYBB2. Mol Vis.
15:1470–1475. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pauli S, Söker T, Klopp N, Illig T, Engel
W and Graw J: Mutation analysis in a German family identified a new
cataract-causing allele in the CRYBB2 gene. Mol Vis. 13:962–967.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Micheal S, Niewold ITG, Siddiqui SN, Zafar
SN, Khan MI and Bergen AAB: Delineation of novel autosomal
recessive mutation in GJA3 and autosomal dominant mutations in GJA8
in Pakistani congenital cataract families. Genes (Basel).
9:1122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li H and Homer N: A survey of sequence
alignment algorithms for next-generation sequencing. Brief
Bioinform. 11:473–483. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li H and Durbin R: Fast and accurate short
read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics.
25:1754–1760. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ghoneim DH, Myers JR, Tuttle E and
Paciorkowski AR: Comparison of insertion/deletion calling
algorithms on human next-generation sequencing data. BMC Res Notes.
7:8642014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bateman JB, von-Bischhoffshaunsen FR,
Richter L, Flodman P, Burch D and Spence MA: Gene conversion
mutation in crystallin, beta-B2 (CRYBB2) in a Chilean family with
autosomal dominant cataract. Ophthalmology. 114:425–432. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hegde S, Kesterson RA and Srivastava OP:
CRYβA3/A1-crystallin knockout develops nuclear cataract and causes
impaired lysosomal cargo clearance and calpain activation. PLoS
One. 11:e01490272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hejtmancik JF: Congenital cataracts and
their molecular genetics. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 19:134–149. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang Z, Li Q, Ma Z, Guo Y, Zhu S and Ma X:
A G→T splice site mutation of CRYBA1/A3 associated with autosomal
dominant suture cataracts in a Chinese family. Mol Vis.
17:2065–2071. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ni SH, Zhang JM and Zhao J: A novel
missense mutation of CRYBA1 in a northern Chinese family with
inherited coronary cataract with blue punctate opacities. Eur J
Ophthalmol. 32:193–199. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Weisschuh N, Aisenbrey S, Wissinger B and
Riess A: Identification of a novel CRYBB2 missense mutation causing
congenital autosomal dominant cataract. Mol Vis. 18:174–180.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Litt M, Carrero-Valenzuela R, LaMorticella
DM, Schultz DW, Mitchell TN, Kramer P and Maumenee IH: Autosomal
dominant cerulean cataract is associated with a chain termination
mutation in the human β-crystallin gene CRYBB2. Hum Mol Genet.
6:665–668. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gill D, Klose R, Munier FL, McFadden M,
Priston M, Billingsley G, Ducrey N, Schorderet DF and Héon E:
Genetic heterogeneity of the Coppock-like cataract: A mutation in
CRYBB2 on chromosome 22q11.2. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
41:159–165. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vanita, Sarhadi V, Reis A, Jung M, Singh
D, Sperling K, Singh JR and Bürger J: A unique form of autosomal
dominant cataract explained by gene conversion between
beta-crystallin B2 and its pseudogene. J Med Genet. 38:392–396.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Valiunas V and White TW: Connexin43 and
connexin50 channels exhibit different permeability to the second
messenger inositol triphosphate. Sci Rep. 10:87442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xin L and Bai D: Functional roles of the
amino terminal domain in determining biophysical properties of Cx50
gap junction channels. Front Physiol. 4:3732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Meşe G, Richard G and White TW: Gap
junctions: Basic structure and function. J Invest Dermatol.
127:2516–2524. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zheng JQ, Ma ZW and Sun HM: A heterozygous
transversion of connexin 50 in a family with congenital nuclear
cataract in the northeast of China. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za
Zhi. 22:76–78. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Berry V, Mackay D, Khaliq S, Francis PJ,
Hameed A, Anwar K, Mehdi SQ, Newbold RJ, Ionides A, Shiels A, et
al: Connexin 50 mutation in a family with congenital ‘zonular
nuclear’ pulverulent cataract of Pakistani origin. Hum Genet.
105:168–170. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Berry V, Ionides A, Pontikos N, Moghul I,
Moore AT, Quinlan RA and Michaelides M: Whole exome sequencing
reveals novel and recurrent disease-causing variants in lens
specific gap junctional protein encoding genes causing congenital
cataract. Genes. 11:5122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li L, Fan DB, Zhao YT, Li Y, Yang ZB and
Zheng GY: GJA8 missense mutation disrupts hemichannels and induces
cell apoptosis in human lens epithelial cells. Sci Rep.
9:191572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ponnam SP, Ramesha K, Tejwani S,
Ramamurthy B and Kannabiran C: Mutation of the gap junction protein
alpha 8 (GJA8) gene causes autosomal recessive cataract. J Med
Genet. 44:e852007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hadrami M, Bonnet C, Veten F, Zeitz C,
Condroyer C, Wang P, Biya M, Sidi Ahmed MA, Zhang Q, Cheikh S, et
al: A novel missense mutation of GJA8 causes congenital cataract in
a large Mauritanian family. Eur J Ophthalmol. 29:621–628. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ceroni F, Aguilera-Garcia D, Chassaing N,
Bax DA, Blanco-Kelly F, Ramos P, Tarilonte M, Villaverde C, da
Silva LRJ, Ballesta-Martínez MJ, et al: New GJA8 variants and
phenotypes highlight its critical role in a broad spectrum of eye
anomalies. Hum Genet. 138:1027–1042. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Devi RR and Vijayalakshmi P: Novel
mutations in GJA8 associated with autosomal dominant congenital
cataract and microcornea. Mol Vis. 12:190–195. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|