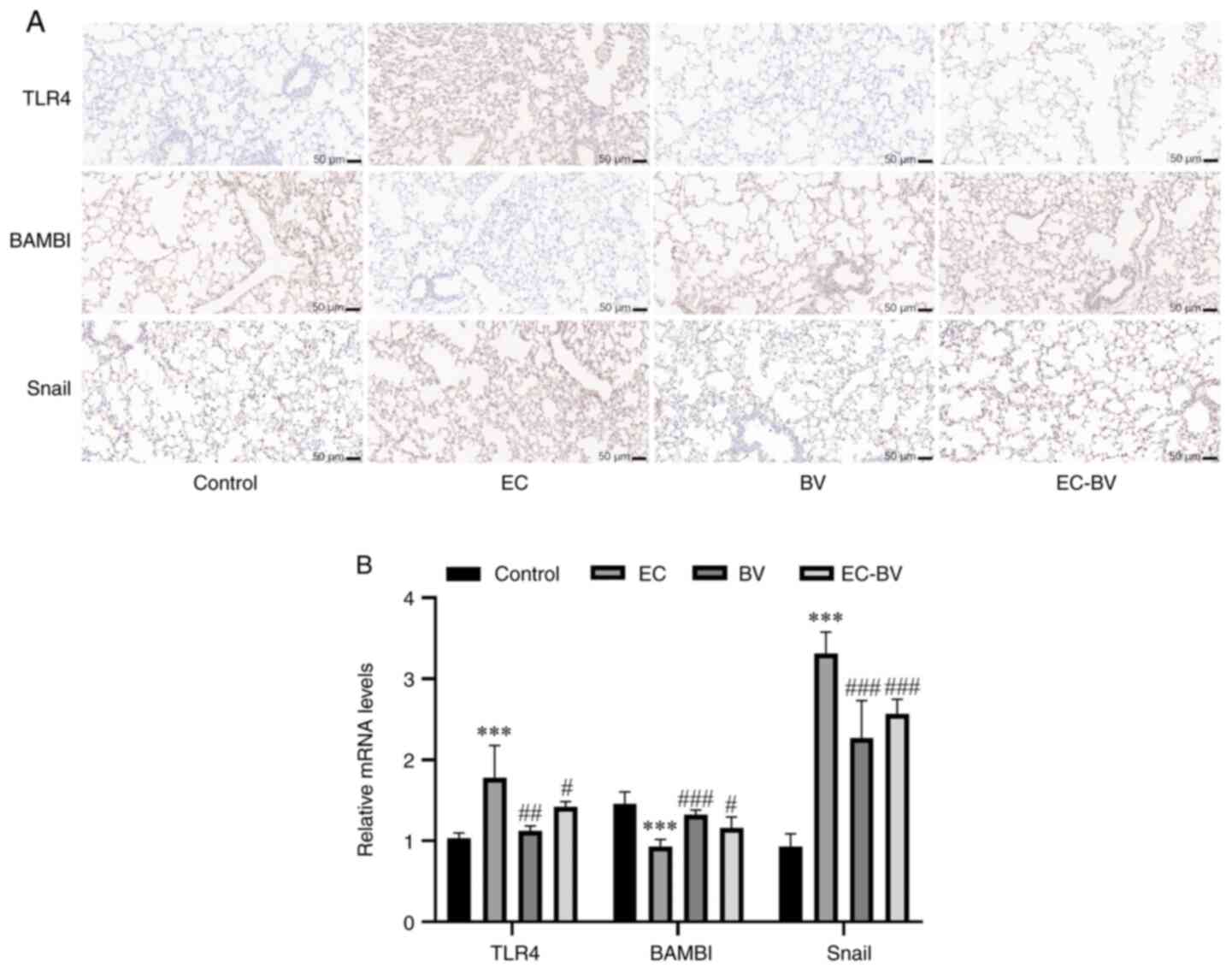
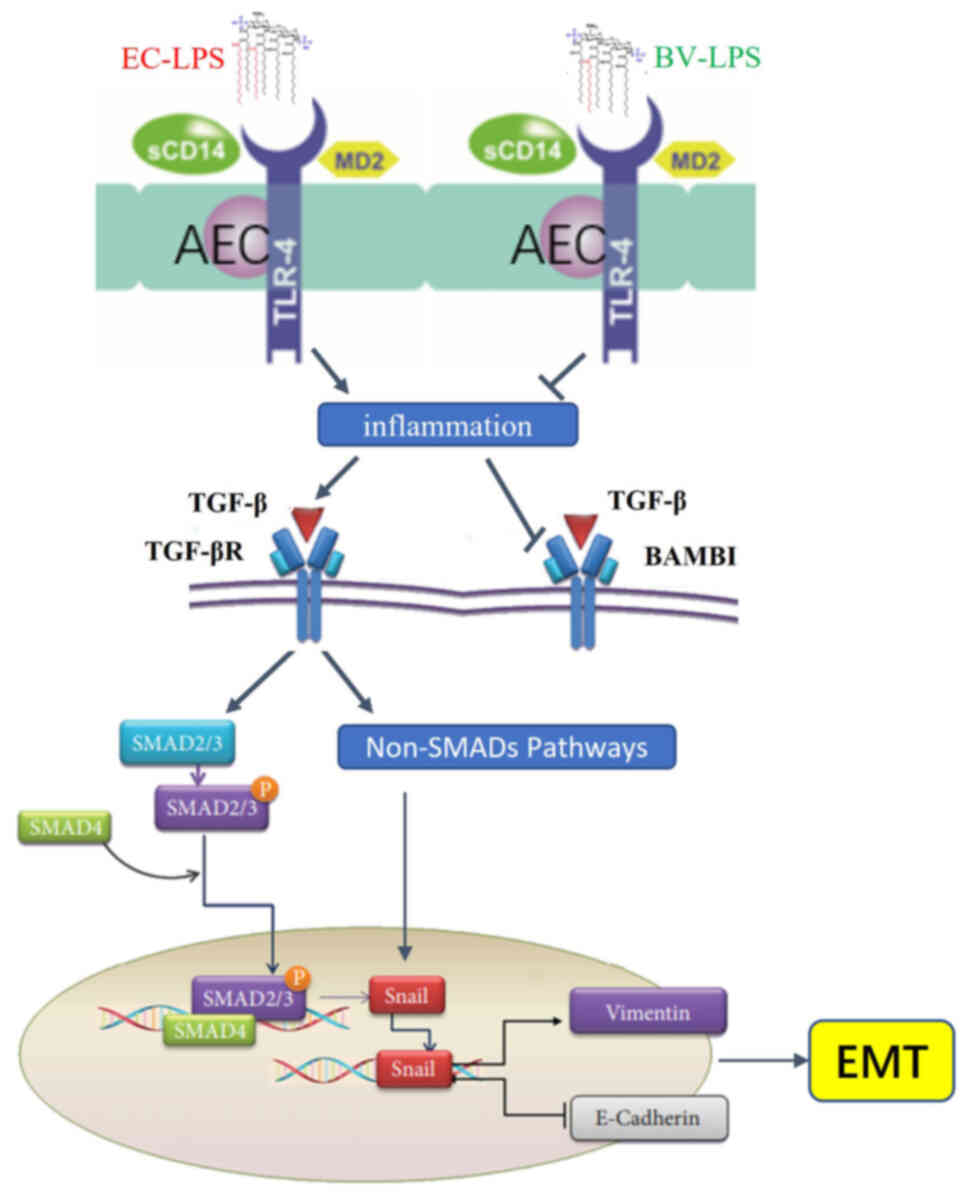
|
1
|
Rout-Pitt N, Farrow N, Parsons D and
Donnelley M: Epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT): A universal
process in lung diseases with implications for cystic fibrosis
pathophysiology. Respir Res. 19:1362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang Y, Hu L, Xia H, Chen L, Cui S, Wang
Y, Zhou T, Xiong W, Song L, Li S, et al: Resolvin D1 attenuates
mechanical stretch-induced pulmonary fibrosis via
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 316:L1013–L1024. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang ZC, Qu ZH, Yi MJ, Shan YC, Ran N, Xu
L and Liu XJ: MiR-448-5p inhibits TGF-β1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and pulmonary fibrosis by
targeting Six1 in asthma. J Cell Physiol. 234:8804–8814. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nieto MA, Huang RY, Jackson RA and Thiery
JP: EMT: 2016. Cell. 166:21–45. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
López-Novoa JM and Nieto MA: Inflammation
and EMT: An alliance towards organ fibrosis and cancer progression.
EMBO Mol Med. 1:303–314. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fedele G, Nasso M, Spensieri F, Palazzo R,
Frasca L, Watanabe M and Ausiello CM: Lipopolysaccharides from
Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis differently
modulate human dendritic cell functions resulting in divergent
prevalence of Th17-polarized responses. J Immunol. 181:208–216.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Park BS, Song DH, Kim HM, Choi BS, Lee H
and Lee JO: The structural basis of lipopolysaccharide recognition
by the TLR4-MD-2 complex. Nature. 458:1191–1195. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin TL, Shu CC, Chen YM, Lu JJ, Wu TS, Lai
WF, Tzeng CM, Lai HC and Lu CC: Like Cures Like: Pharmacological
activity of anti-inflammatory lipopolysaccharides from gut
microbiome. Front Pharmacol. 11:5542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cardinelli CS, Sala PC, Alves CC,
Torrinhas RS and Waitzberg DL: Influence of intestinal microbiota
on body weight gain: A narrative review of the literature. Obes
Surg. 25:346–353. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brown GC: The endotoxin hypothesis of
neurodegeneration. J Neuroinflammation. 16:1802019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He Z, Zhu Y and Jiang H: Inhibiting
toll-like receptor 4 signaling ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis
during acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide: An
experimental study. Respir Res. 10:1262009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hirschfeld M, Ma Y, Weis JH, Vogel SN and
Weis JJ: Cutting edge: Repurification of lipopolysaccharide
eliminates signaling through both human and murine toll-like
receptor 2. J Immunol. 165:618–622. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
d'Hennezel E, Abubucker S, Murphy LO and
Cullen TW: Total lipopolysaccharide from the human gut microbiome
silences toll-like receptor signaling. mSystems. 2:e00046–17.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ding Z, Wu X, Wang Y, Ji S, Zhang W, Kang
J, Li J and Fei G: Melatonin prevents LPS-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human alveolar epithelial
cells via the GSK-3β/Nrf2 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
132:1108272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen D, Qiu YB, Gao ZQ, Wu YX, Wan BB, Liu
G, Chen JL, Zhou Q, Yu RQ and Pang QF: Sodium propionate attenuates
the lipopolysaccharide-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem.
68:6554–6563. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang YQ, Liu YJ, Mao YF, Dong WW, Zhu XY
and Jiang L: Resveratrol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced
epithelial mesenchymal transition and pulmonary fibrosis through
suppression of oxidative stress and transforming growth factor-β1
signaling. Clin Nutr. 34:752–760. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tang S, Jiang X, Wu L, Chen S, Chen L,
Jiang J, Yan P, Wang F, Tu K, Wang D, et al: Toll-like receptor 4
shRNA attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells in rats. Biomed
Pharmacother. 107:1210–1217. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta DeltaC(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu W, Sun T and Wang Y: Integrin αvβ6
mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human bronchial
epithelial cells induced by lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas
aeruginosa via TGF-β1-Smad2/3 signaling pathway. Folia Microbiol
(Praha). 65:329–338. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gong JH, Cho IH, Shin D, Han SY, Park SH
and Kang YH: Inhibition of airway epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition and fibrosis by kaempferol in endotoxin-induced
epithelial cells and ovalbumin-sensitized mice. Lab Invest.
94:297–308. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li H, Li J, Zhang G, Da Q, Chen L, Yu S,
Zhou Q, Weng Z, Xin Z, Shi L, et al: HMGB1-Induced p62
overexpression promotes snail-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in glioblastoma cells via the degradation of GSK-3β.
Theranostics. 9:1909–1922. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lim KH and Staudt LM: Toll-like receptor
signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5:a0112472013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He Y, Ou Z, Chen X, Zu X, Liu L, Li Y, Cao
Z, Chen M, Chen Z, Chen H, et al: LPS/TLR4 signaling enhances TGF-β
response through downregulating BAMBI during prostatic hyperplasia.
Sci Rep. 6:270512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kaufhold S and Bonavida B: Central role of
Snail1 in the regulation of EMT and resistance in cancer: A target
for therapeutic intervention. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:622014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yoshida N, Emoto T, Yamashita T, Watanabe
H, Hayashi T, Tabata T, Hoshi N, Hatano N, Ozawa G, Sasaki N, et
al: Bacteroides vulgatus and Bacteroides dorei Reduce gut microbial
lipopolysaccharide production and inhibit atherosclerosis.
Circulation. 138:2486–2498. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Steimle A, Michaelis L, Di Lorenzo F,
Kliem T, Münzner T, Maerz JK, Schäfer A, Lange A, Parusel R,
Gronbach K, et al: Weak agonistic LPS restores intestinal immune
homeostasis. Mol Ther. 27:1974–1991. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao L, Yang R, Cheng L, Wang M, Jiang Y
and Wang S: LPS-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of
intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells. J Surg Res. 171:819–825.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pulskens WP, Rampanelli E, Teske GJ,
Butter LM, Claessen N, Luirink IK, van der Poll T, Florquin S and
Leemans JC: TLR4 promotes fibrosis but attenuates tubular damage in
progressive renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 21:1299–1308. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bhattacharyya S, Kelley K, Melichian DS,
Tamaki Z, Fang F, Su Y, Feng G, Pope RM, Budinger GR, Mutlu GM, et
al: Toll-like receptor 4 signaling augments transforming growth
factor-β responses: A novel mechanism for maintaining and
amplifying fibrosis in scleroderma. Am J Pathol. 182:192–205. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Seki E, De Minicis S, Osterreicher CH,
Kluwe J, Osawa Y, Brenner DA and Schwabe RF: TLR4 enhances TGF-beta
signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med. 13:1324–1332. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lutz M and Knaus P: Integration of the
TGF-beta pathway into the cellular signalling network. Cell Signal.
14:977–988. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen J, Bush JO, Ovitt CE, Lan Y and Jiang
R: The TGF-beta pseudoreceptor gene Bambi is dispensable for mouse
embryonic development and postnatal survival. Genesis. 45:482–486.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang YE: Non-Smad pathways in TGF-beta
signaling. Cell Res. 19:128–139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sisto M, Lorusso L, Ingravallo G, Ribatti
D and Lisi S: TGFβ1-Smad canonical and -Erk noncanonical pathways
participate in interleukin-17-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in Sjögren's syndrome. Lab Invest. 100:824–836. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fabregat I, Moreno-Càceres J, Sánchez A,
Dooley S, Dewidar B, Giannelli G and Ten Dijke P; IT-LIVER
Consortium, : TGF-β signalling and liver disease. FEBS J.
283:2219–2232. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Willis BC and Borok Z: TGF-beta-induced
EMT: Mechanisms and implications for fibrotic lung disease. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L525–L534. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Prud'homme GJ: Pathobiology of
transforming growth factor beta in cancer, fibrosis and immunologic
disease and therapeutic considerations. Lab Invest. 87:1077–1091.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Heldin CH and Moustakas A: Signaling
receptors for TGF-β family members. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
8:a0220532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wrighton KH, Lin X and Feng XH:
Phospho-control of TGF-beta superfamily signaling. Cell Res.
19:8–20. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hill CS: Transcriptional control by the
SMADs. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 8:a0220792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Brandl M, Seidler B, Haller F, Adamski J,
Schmid RM, Saur D and Schneider G: IKK(α) controls canonical
TGF(ß)-SMAD signaling to regulate genes expressing SNAIL and SLUG
during EMT in panc1 cells. J Cell Sci. 123((Pt 24)): 4231–4239.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sisto M, Lorusso L, Ingravallo G, Tamma R,
Ribatti D and Lisi S: The TGF-1 signaling pathway as an attractive
target in the fibrosis pathogenesis of Sjögren's Syndrome.
Mediators Inflamm. 2018:19659352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen XF, Zhang HJ, Wang HB, Zhu J, Zhou
WY, Zhang H, Zhao MC, Su JM, Gao W, Zhang L, et al: Transforming
growth factor-β1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
human lung cancer cells via PI3K/Akt and MEK/Erk1/2 signaling
pathways. Mol Biol Rep. 39:3549–3556. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|